Abstract
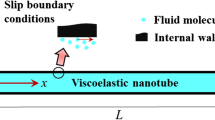
In this paper, the pulsatile coupled vibrations of a viscoelastic microtube conveying pulsatile fluid is examined for the first time. The problem is grouped into the class of parametrically excited, internally damped, gyroscopic where both Coriolis and parametric forces are present in the presence of viscosity. The Kelvin–Voigt approach of the viscosity, the Euler–Bernoulli for the deformation, the modified couple stress theory for the small size, and Hamilton’s principle for deriving differential equations are used. Parametric frequency–response curves are obtained in the vicinity of the parametric resonance near the critical speed for both subcritical and supercritical regimes. The effect of the flow pulsation on the oscillations is investigated.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasnejad B, Shabani R, Rezazadeh G (2015) Stability analysis of a piezoelectrically actuated micro-pipe conveying fluid. Microfluid Nanofluid 19:577–584
Abouelregal AE (2018) Response of thermoelastic microbeams to a periodic external transverse excitation based on MCS theory. Microsyst Technol 24:1925–1933
Ahangar S, Rezazadeh G, Shabani R et al (2011) On the stability of a microbeam conveying fluid considering modified couple stress theory. Int J Mech Mater Des 7:327
Ahmed MS, Ghommem M and Abdelkefi A (2018) Nonlinear analysis and characteristics of electrically-coupled microbeams under mechanical shock. Microsyst Technol
Chen X, Li Y (2018) Size-dependent post-buckling behaviors of geometrically imperfect microbeams. Mech Res Commun 88:25–33
Chen X, Lu Y, Li Y (2019a) Free vibration, buckling and dynamic stability of bi-directional FG microbeam with a variable length scale parameter embedded in elastic medium. Appl Math Model 67:430–448
Chen X, Zhang X, Lu Y et al (2019b) Static and dynamic analysis of the postbuckling of bi-directional functionally graded material microbeams. Int J Mech Sci 151:424–443
Dai H, Wang L, Ni Q (2015) Dynamics and pull-in instability of electrostatically actuated microbeams conveying fluid. Microfluid Nanofluid 18:49–55
Dehrouyeh-Semnani AM, Nikkhah-Bahrami M, Yazdi MRH (2017) On nonlinear stability of fluid-conveying imperfect micropipes. Int J Eng Sci 120:254–271
Deng J, Liu Y, Liu W (2017) Size-dependent vibration analysis of multi-span functionally graded material micropipes conveying fluid using a hybrid method. Microfluid Nanofluid 21:133
Duan K, Li Y, Li L et al (2018a) Diamond nanothread based resonators: ultrahigh sensitivity and low dissipation. Nanoscale 10:8058–8065
Duan K, Li Y, Li L et al (2018b) High intrinsic dissipation of graphyne nanotubes. EPL (Europhysics Letters) 122:46001
Elwenspoek M, Jansen HV (2004) Silicon micromachining. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Farajpour A, Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2019) Chaotic motion analysis of fluid-conveying viscoelastic nanotubes. Euro J Mechanics-A/Solids 74:281–296
Farajpour A, Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH, Hussain Sh (2018a) Nonlinear mechanics of nanotubes conveying fluid. Int J Eng Sci 133:132–143
Farajpour A, Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H (2018b) A review on the mechanics of nanostructures. Int J Eng Sci 133:231–263
Farajpour MR, Shahidi AR, Tabataba’i-Nasab F, Farajpour A (2018c) Vibration of initially stressed carbon nanotubes under magneto-thermal environment for nanoparticle delivery via higher-order nonlocal strain gradient theory. European Phys J Plus 133(6):219
Farajpour A, Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H (2019) Large-amplitude coupled scale-dependent behaviour of geometrically imperfect NSGT nanotubes. Int J Mech Sci 150:510–525
Farajpour A, Rastgoo A, Farajpour MR (2017) Nonlinear buckling analysis of magneto-electro-elastic CNT-MT hybrid nanoshells based on the nonlocal continuum mechanics. Compos Struct 180:179–191
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2017) Nonlinear thermo-mechanical behaviour of MEMS resonators. Microsyst Technol 23:5303–5315
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2018) Nonlinear mechanical behaviour of microshells. Int J Eng Sci 127:127–144
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH, Amabili M (2013) Nonlinear dynamics of a geometrically imperfect microbeam based on the modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 68:11–23
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH, Gholipour A et al (2018) Resonant responses of three-layered shear-deformable microbeams. Microsyst Technol 24:2123–2136
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH, Hussain Sh (2016) Large-amplitude dynamical behaviour of microcantilevers. Int J Eng Sci 106:29–41
Gaafar E, Zarog M (2017) A low-stress and low temperature gradient microgripper for biomedical applications. Microsyst Technol 23:5415–5422
Ghayesh MH (2018a) Functionally graded microbeams: simultaneous presence of imperfection and viscoelasticity. Int J Mech Sci 140:339–350
Ghayesh MH (2018b) Dynamics of functionally graded viscoelastic microbeams. Int J Eng Sci 124:115–131
Ghayesh MH (2018c) Nonlinear vibration analysis of axially functionally graded shear-deformable tapered beams. Appl Math Model 59:583–596
Ghayesh MH (2019) Viscoelastic dynamics of axially FG microbeams. Int J Eng Sci 135:75–85
Ghayesh MH, Farajpour A (2018a) Nonlinear coupled mechanics of nanotubes incorporating both nonlocal and strain gradient effects. Mech Adv Mater Struct. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2018.1473537
Ghayesh MH, Farajpour A (2018b) Nonlinear mechanics of nanoscale tubes via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Int J Eng Sci 129:84–95
Ghayesh MH, Farajpour A (2018c) Vibrations of shear deformable FG viscoelastic microbeams. Microsyst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4184-8
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H (2015a) Chaotic motion of a parametrically excited microbeam. Int J Eng Sci 96:34–45
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H (2015b) Nonlinear dynamics of microplates. Int J Eng Sci 86:60–73
Ghayesh MH, Amabili M, Farokhi H (2013a) Three-dimensional nonlinear size-dependent behaviour of Timoshenko microbeams. Int J Eng Sci 71:1–14
Ghayesh MH, Amabili M, Farokhi H (2013b) Coupled global dynamics of an axially moving viscoelastic beam. Int J Non-linear Mech 51:54–74
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Amabili M (2013c) Nonlinear dynamics of a microscale beam based on the modified couple stress theory. Compos Part B: Eng 50:318–324
Ghayesh MH, Païdoussis MP, Amabili M (2013d) Nonlinear dynamics of cantilevered extensible pipes conveying fluid. J Sound Vib 332:6405–6418
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Amabili M (2014) In-plane and out-of-plane motion characteristics of microbeams with modal interactions. Compos Part B: Eng 60:423–439
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Alici G (2016) Size-dependent performance of microgyroscopes. Int J Eng Sci 100:99–111
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Farajpour A (2019) Global dynamics of fluid conveying nanotubes. Int J Eng Sci 135:37–57
Gholipour A, Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2015) In-plane and out-of-plane nonlinear size-dependent dynamics of microplates. Nonlinear Dyn 79:1771–1785
Gholipour A, Ghayesh MH, Zander A (2018a) Nonlinear biomechanics of bifurcated atherosclerotic coronary arteries. Int J Eng Sci 133:60–83
Gholipour A, Ghayesh MH, Zander A, Mahajan R (2018b) Three-dimensional biomechanics of coronary arteries. Int J Eng Sci 130:93–114
Hamzah MH, Karim J, Ralib AAM, et al (2017) Design and analysis of a boosted pierce oscillator using MEMS SAW resonators. Microsyst Technol, 1–8
Hari K, Verma SK, Praveen Krishna IR et al (2017) Out-of-plane dual flexure MEMS piezoresistive accelerometer with low cross axis sensitivity. Microsyst Technol, 1–8
Hosseini M, Bahaadini R (2016) Size dependent stability analysis of cantilever micro-pipes conveying fluid based on modified strain gradient theory. Int J Eng Sci 101:1–13
Hu K, Dai H, Wang L, et al (2017) Dynamics and stability of pinned-free micropipes conveying fluid. J Mech 1–7
Ke L-L, Wang Y-S, Yang J et al (2012) Free vibration of size-dependent Mindlin microplates based on the modified couple stress theory. J Sound Vib 331:94–106
Kural S, Özkaya E (2017) Size-dependent vibrations of a micro beam conveying fluid and resting on an elastic foundation. J Vib Control 23:1106–1114
Li L, Hu Y, Li X et al (2016) Size-dependent effects on critical flow velocity of fluid-conveying microtubes via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Microfluid Nanofluid 20(5):76
Li C, Cordovilla F, Ocaña JL (2017) The design and analysis of a novel structural piezoresistive pressure sensor for low pressure measurement. Microsyst Technol 23:5677–5687
Liu F, Gao S, Niu S, et al (2017) Optimal design of high-g MEMS piezoresistive accelerometer based on Timoshenko beam theory. Microsyst Technol, 1–13
Lotfi M, Moghimi Zand M, Isaac Hosseini I et al (2017) Transient behavior and dynamic pull-in instability of electrostatically-actuated fluid-conveying microbeams. Microsyst Technol 23:6015–6023
Ma H, Gao X-L, Reddy J (2008) A microstructure-dependent Timoshenko beam model based on a modified couple stress theory. J Mech Phys Solids 56:3379–3391
Menon PK, Nayak J, Pratap R (2017) Sensitivity analysis of an in-plane MEMS vibratory gyroscope. Microsyst Technol, 1–15
Paidoussis MP (1998) Fluid-structure interactions: slender structures and axial flow. Academic Press, London
Pasharavesh A, Ahmadian MT, Zohoor H (2016) Coupled electromechanical analysis of MEMS-based energy harvesters integrated with nonlinear power extraction circuits. Microsyst Technol, 1–18
Rajaei A, Vahidi-Moghaddam A, Ayati M, et al (2018) Integral sliding mode control for nonlinear damped model of arch microbeams. Microsyst Technol, 1–12
Samaali H, Najar F (2017) Design of a capacitive MEMS double beam switch using dynamic pull-in actuation at very low voltage. Microsyst Technol 23:5317–5327
Saxena S, Sharma R, Pant BD (2017) Dynamic characterization of fabricated guided two beam and four beam cantilever type MEMS based piezoelectric energy harvester having pyramidal shape seismic mass. Microsyst Technol 23:5947–5958
Setoodeh A, Afrahim S (2014) Nonlinear dynamic analysis of FG micro-pipes conveying fluid based on strain gradient theory. Compos Struct 116:128–135
Tang M, Ni Q, Wang L et al (2014) Nonlinear modeling and size-dependent vibration analysis of curved microtubes conveying fluid based on modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 84:1–10
Teh KS, Lin L (1999) Time-dependent buckling phenomena of polysilicon micro beams. Microelectron J 30:1169–1172
Tuck K, Jungen A, Geisberger A et al (2005) A study of creep in polysilicon MEMS devices. J Eng Mater Technol 127:90–96
Wang L (2010) Size-dependent vibration characteristics of fluid-conveying microtubes. J Fluids Struct 26:675–684
Wang L, Zhang W, Liu YA et al (2017) Impact analysis of convected motion on the carrier frequency of a carrier-driven gyroscope signal. Microsyst Technol 23:5805–5813
Xi Z, Cao Y, Yu P et al (2016) The simulation and visual test contact process of a MEMS inertial switch with flexible electrodes. Microsyst Technol 22:2035–2042
Xia W, Wang L (2010) Microfluid-induced vibration and stability of structures modeled as microscale pipes conveying fluid based on non-classical Timoshenko beam theory. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:955–962
Yang T-Z, Ji S, Yang X-D et al (2014) Microfluid-induced nonlinear free vibration of microtubes. Int J Eng Sci 76:47–55
Yin L, Qian Q, Wang L (2011) Strain gradient beam model for dynamics of microscale pipes conveying fluid. Appl Math Model 35:2864–2873
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: Comparison study
Appendix: Comparison study
The critical fluid speeds are compared to those available in the literature employing the classical beam theory. A closed-form solution was obtained by Li et al. (2016) for the critical speed of fluid-conveying tubes at nanoscale levels. Ignoring nonlinear terms, couple-stress effects, flow pulsation and external loading, one obtains the following equation from Eqs. (11) and (12)
For this special case, the transverse deflection of the tube can be written as
Substituting the above relation into Eq. (19), one obtains
It is worth mentioning that the flow-profile-modification factor is neglected for comparison purposes. Equation (21) for the critical fluid speed perfectly matches that determined in the literature for macroscale tubes conveying fluid flow of a constant velocity (Li et al. 2016); size effects are ignored.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghayesh, M.H., Farokhi, H. & Farajpour, A. Pulsatile vibrations of viscoelastic microtubes conveying fluid. Microsyst Technol 25, 3609–3623 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04381-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04381-8