Abstract
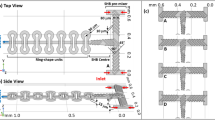
Oscillatory/pulsatile flow is an important approach for mixing enhancement at micro scales. Here we report a micromixer that consists of a microfluidic oscillator and divergent chambers. The oscillator autonomously produces an oscillatory flow, which further causes efficient stretching and folding of the fluids to improve the mixing. Testing results show that the design works well at relatively high flow rates and high viscosities. At around 40 ml/min, the mixing index can reach 0.97 at 8 mPa s, and 0.89 at 12 mPa s, respectively. Efficient mixing can also be achieved at viscosity ratios of up to 10 (20 mPa s:2 mPa s). Application of the micromixer for preparation of nano sized RDX (cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine) is investigated. Using the anti-solvent crystallization method, nano-RDX particles with the size ranging from 150 to 900 nm are obtained. Its thermal decomposition characteristics are tested and compared with the raw RDX.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
The pre-exponential factor (–)
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- E a :
-
The apparent activation energy (kJ/mol)
- f :
-
Frequency of the oscillatory flow (Hz)
- \(I_{i}\) :
-
Pixel intensity (–)
- \(I_{mix}\) :
-
Pixel intensity after complete mixing (–)
- \(I_{unmix}\) :
-
Pixel intensity before mixing (–)
- L :
-
Characteristic length of fluid channel (mm)
- P o :
-
Operating pressure of the microfluidic oscillator (bar)
- Q :
-
Flow rate (m3/s)
- \(\bar{Q}_{1}\) :
-
Time-averaged flow rate of the oscillatory flow applied at inlet 1 (ml/min)
- Q 2 :
-
Flow rate at inlet 2 (ml/min)
- R :
-
Gas constant (J/(K mol))
- Re :
-
Reynolds number (–)
- T :
-
Oscillation period (s)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- T m :
-
The temperature of molten endothermic peak (°C)
- T p :
-
The temperature of thermal decomposition exothermic peak (°C)
- U :
-
Fluid velocity (m/s)
- β :
-
Heating rate (°C/min)
- μ :
-
Fluid viscosity (Pa s)
- ν :
-
Fluid kinematic viscosity (m2/s)
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Mixing index (–)
- τ :
-
Normalized mixing time, τ = t/T (–)
- χ:
-
Viscosity ratio (–)
References
Afzal A, Kim KY (2015a) Convergent-divergent micromixer coupled with pulsatile flow. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 211:198–205
Afzal A, Kim KY (2015b) Optimization of pulsatile flow and geometry of a convergent-divergent micromixer. Chem Eng J 281:134–143
Alam A, Kim KY (2013) Mixing performance of a planar micromixer with circular chambers and crossing constriction channels. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 176:639–652
Bottausci F, Cardonne C, Meinhart C, Mezić I (2007) An ultrashort mixing length micromixer: The shear superposition micromixer. Lab Chip 7(3):396–398
Chen XY, Li TC, Hu ZL (2017) A novel research on serpentine microchannels of passive micromixers. Microsyst Technol 23(7):2649–2656
Cho CC, Chen CL, Chen CK (2012) Mixing enhancement in crisscross micromixer using aperiodic electrokinetic perturbing flows. Int J Heat Mass Tran 55(11–12):2926–2933
Glasgow I, Aubry N (2003) Enhancement of microfluidic mixing using time pulsing. Lab Chip 3(2):114–120
Glasgow I, Lieber S, Aubry N (2004) Parameters influencing pulsed flow mixing in microchannels. Anal Chem 76(16):4825–4832
Hessel V, Löwe H, Schönfeld F (2005) Micromixers—a review on passive and active mixing principles. Chem Eng Sci 60(8–9):2479–2501
Hirata Y, Ohkawa K (2016) Development of channel mixers utilising 180° fluid rotation combined with split and recombination. Chem Eng Res Des 108:118–125
Hossain S, Kim KY (2015) Mixing analysis in a three-dimensional serpentine split-and-recombine micromixer. Chem Eng Res Des 100:95–103
Jung W, Park J, Lee W, Lee J, Koo K, Oh M (2016) Scale-up of a crystallizer for production of nano-sized energetic materials. Chem Eng Technol 39(7):1309–1316
Kuo JN, Jiang LR (2014) Design optimization of micromixer with square-wave microchannel on compact disk microfluidic platform. Microsyst Technol 20(1):91–99
Lee CY, Chang CL, Wang YN, Fu LM (2011) Microfluidic mixing: a review. Int J Mol Sci 12(5):3263–3287
Lee JE, Kim JW, Han SK, Chae JS, Lee KD, Koo KK (2014) Production of submicrometer-sized hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine by drowning-out. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(12):4739–4747
Lin Y (2015) Numerical characterization of simple three-dimensional chaotic micromixers. Chem Eng J 277:303–311
Lin CH, Tsai CH, Fu LM (2005) A rapid three-dimensional vortex micromixer utilizing self-rotation effects under low Reynolds number conditions. J Micromech Microeng 15(5):935–943
Liu RH, Lenigk R, Druyor-Sanchez RL, Yang JN, Grodzinski P (2003) Hybridization enhancement using cavitation microstreaming. Anal Chem 75(8):1911–1917
Nguyen NT (2011) Micromixers: fundamentals, design and fabrication. William Andrew Norwich, NewYork, p 2011
Nguyen NT, Huang XY (2005) Mixing in microchannels based on hydrodynamic focusing and time-interleaved segmentation: modelling and experiment. Lab Chip 5(11):1320–1326
Niu XZ, Lee YK (2003) Efficient spatial-temporal chaotic mixing in microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 13(3):454–462
Niu XZ, Liu LY, Wen WJ, Sheng P (2006) Active microfluidic mixer chip. Appl Phys Lett 88(15)
Squires TM, Quake SR (2005) Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev Mod Phys 77(3):977–1026
Stone HA, Stroock AD, Ajdari A (2004) Engineering flows in small devices: Microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:381–411
Stroock AD, Dertinger SKW, Ajdari A, Mezić I, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2002) Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295(5555):647–651
Tabeling P, Chabert M, Dodge A, Jullien C, Okkels F (2004) Chaotic mixing in cross-channel micromixers. Philos T Roy Soc A 362(1818):987–1000
Valencia PM, Pridgen EM, Rhee M, Langer R, Farokhzad OC, Karnik R (2013) Microfluidic platform for combinatorial synthesis and optimization of targeted nanoparticles for cancer therapy. ACS Nano 7(12):10671–10680
Wang BB, Liao X, Wang ZS, DeLuca LT, Liu ZT, Fu Y (2017a) Preparation and properties of a nRDX-based propellant. Propell Explos Pyrot 42(6):649–658
Wang JC, Zhang F, Wang YJ, Luo GS (2017b) Preparation of In(OH)(3) Nanorods and nanocubes and the effect on In2O3 particle size in the microreactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(23):6637–6644
Xia HM, Wang ZP, Fan W, Wijaya A, Wang W, Wang ZF (2012) Converting steady laminar flow to oscillatory flow through a hydroelasticity approach at microscales. Lab Chip 12(1):60–64
Xia HM, Seah YP, Liu YC, Wang W, Toh AGG, Wang ZP (2015) Anti-solvent precipitation of solid lipid nanoparticles using a microfluidic oscillator mixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 19(2):283–290
Xia HM, Wu JW, Wang ZP (2017) The negative-differential-resistance (NDR) mechanism of a hydroelastic microfluidic oscillator. J Micromech Microeng 27(7):075001
Xia HM, Wu JW, Wang ZP (2018) A comparative discussion of different designs of passive micromixers: specific sensitivities of mixing efficiency on Reynolds numbers and fluid properties. Microsyst Technol 24(2):1253–1263
Yang AS, Chuang FC, Chen CK, Lee MH, Chen SW, Su TL, Yang YC (2015) A high-performance micromixer using three-dimensional Tesla structures for bio-applications. Chem Eng J 263:444–451
Zhang K, Guo SS, Zhao LB, Zhao XZ, Chan HLW, Wang Y (2011) Realization of planar mixing by chaotic velocity in microfluidics. Microelectron Eng 88(6):959–963
Zhang WP, Wang X, Feng X, Yang C, Mao ZS (2016) Investigation of mixing performance in passive micromixers. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(38):10036–10043
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51575282), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (30915118803; 30916012101), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (AVI 7960 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J.W., Xia, H.M., Zhang, Y.Y. et al. An efficient micromixer combining oscillatory flow and divergent circular chambers. Microsyst Technol 25, 2741–2750 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4193-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-4193-7