Abstract
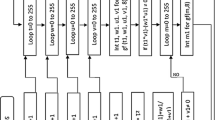
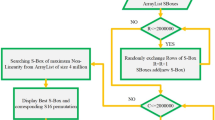
The strength of cryptosystems heavily relies on the substitution boxes. Cryptosystems with weak substitution boxes cannot resist algebraic attacks, linear and differential cryptanalysis. In this paper, first, we propose a strong algebraic structure for the construction of substitution boxes. The proposed substitution boxes have good algebraic properties and are able to resist against algebraic attacks. Second, we propose a new method for creating multiple substitution boxes with the same algebraic properties using permutation of symmetric group on a set of size 8 and bitwise XOR operation. Third, the proposed substitution boxes with the same algebraic properties are then applied to images and it is observed that the statistical properties of substituted images are different from each other. The simulation results and statistical and security analysis for the proposed substitution boxes are very competitive. Also, it is shown in this work that the proposed substitution boxes can resist differential and linear cryptanalysis and sustain algebraic attacks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen J, Han F, Qian W, Yao Y-D, Zhu Z- (2018) Cryptanalysis and improvement in an image encryption scheme using combination of the 1D chaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn 93(4):2399–2413
Ahmed F, Anees A (2015) Hash-based authentication of digital images in noisy channels. In: Živić N (ed) Robust image authentication in the presence of noise. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13156-6_1
Anees A, Khan WA, Gondal MA, Hussain I (2013) Application of mean of absolute deviation method for the selection of best nonlinear component based on video encryption. Z Naturforsch A 68(a):479–482
Liu X, Dong M, Ota K, Yang LT, Liu A (2018) Trace malicious source to guarantee cyber security for mass monitor critical infrastructure. J Comput Syst Sci 98:1–26
Anees A, Gondal MA (2015) Construction of nonlinear component for block cipher based on one-dimensional chaotic map. 3D Res 6(2):17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13319-015-0049-4
Anees A, Siddiqui AM (2013) A technique for digital watermarking in combined spatial and transform domains using chaotic maps. In: IEEE 2nd national conference on information assurance (NCIA), pp 119–124. https://doi.org/10.1109/ncia.2013.6725335
Jung Y, Festijo E (2014) One-time packet key exchange scheme for secure real-time multimedia applications. J Comput Syst Sci 80(8):1584–1596
Anees A, Siddiqui AM, Ahmed J, Hussain I (2014) A technique for digital steganography using chaotic maps. Nonlinear Dyn 75(4):807–816
Anees A (2015) An image encryption scheme based on Lorenz system for low profile applications. 3D Res 6(3):1–10
Potlapally NR, Ravi S, Raghunathan A, Jha NK (2006) A study of the energy consumption characteristics of cryptographic algorithms and security protocols. IEEE Trans Mobile Comput 5(2):128–143
Anees A, Siddiqui AM, Ahmed F (2014) Chaotic substitution for highly autocorrelated data in encryption algorithm. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 19(9):3106–3118
Daemen J, Rijmen V (2002) The design of Rijndael: AES—the advanced encryption standard. Springer, Berlin
Chen G (2008) A novel heuristic method for obtaining S-boxes. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 36(4):1028–1036
Özkaynaka F, Özer AB (2010) A method for designing strong S-boxes based on chaotic Lorenz system. Phys Lett A 374(36):3733–3738
Hussain I, Shah T, Mahmood H, Gondal MA (2013) A projective general linear group based algorithm for the construction of substitution box for block ciphers. Neural Comput Appl 22(6):1085–1093
Hussain I, Shah T, Gondal MA, Khan WA, Mahmood H (2013) A group theoretic approach to construct cryptographically strong substitution boxes. Neural Comput Appl 23(1):97–104
Zhang W, Pasalic E (2014) Highly nonlinear balanced S-boxes with good differential properties. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 60(12):7970–7979
Jithendra KB, Shahana TK (2016) High-security pipelined elastic substitution box with embedded permutation facility. In: Saini H, Sayal R, Rawat S (eds) Innovations in computer science and engineering, vol 413. Springer, Singapore, pp 79–86
Picek A, Batina L, Jakobović D, Ege B, Golub M (2014) S-box, SET, match: a toolbox for S-box analysis. In: Information security theory and practice. Securing the internet of things, vol 8501. Springer, Berlin, pp 140–149
Lorenz EN (1963) Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J Atmos Sci 20:130–141
Anees A, Hussain I (2019) A novel method to identify initial values of chaotic maps in cybersecurity. Symmetry 11(2):1–21
Hussain I, Anees A, Al-Maadeed TA, Mustafa MT (2019) Construction of S-Box based on chaotic map and algebraic structures. Symmetry 11(3):1–11
Hussain I, Shah T, Gondal MA, Mahmood H (2012) An efficient approach for the construction of LFT S-boxes using chaotic logistic map. Nonlinear Dyn 71(1–2):133–140
Li C, Feng B, Li S, Kurths J, Chen G (2019) Dynamic analysis of digital chaotic maps via state-mapping networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap Early Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2018.2888688
Li C, Lin D, Lü J, Hao F (2018) Cryptanalyzing an image encryption algorithm based on autoblocking and electrocardiography. IEEE Multimedia 25(4):46–56
Li C, Lin D, Feng B, Lü J, Hao F (2018) Cryptanalysis of a chaotic image encryption algorithm based on information entropy. IEEE Access 6:75834–75842
Ullah A, Jamal SS, Shah T (2017) A novel construction of substitution box using a combination of chaotic maps with improved chaotic range. Nonlinear Dyn 88(4):2757–2769
Ullah A, Jamal SS, Shah T (2018) A novel scheme for image encryption using substitution box and chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn 91(1):359–370
Aboytes-González JA, Murguía JS, Mejía-Carlos M, González-Aguilar H, Ramírez-Torres MT (2018) Design of a strong S-box based on a matrix approach. Nonlinear Dyn 94(3):2003–2012
Alamsyah, Bejo A, Adji TB (2018) The replacement of irreducible polynomial and affine mapping for the construction of a strong S-box. Nonlinear Dyn 93(4):2105–2118
Çavuşoğlu Ü, Zengin A, Pehlivan I, Kaçar S (2017) A novel approach for strong S-box generation algorithm design based on chaotic scaled Zhongtang system. Nonlinear Dyn 87(2):1081–1094
Farah T, Rhouma R, Belghith S (2017) A novel method for designing S-box based on chaotic map and teaching-learning-based optimization. Nonlinear Dyn 88(2):1059–1074
Lambić D (2017) A novel method of S-box design based on discrete chaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn 87(4):2407–2413
Li Y, Ge G, Xia D (2016) Chaotic hash function based on the dynamic S-box with variable parameters. Nonlinear Dyn 84(4):2387–2402
Ye T, Zhimao L (2018) Chaotic S-box: six-dimensional fractional Lorenz-Duffing chaotic system and O-shaped path scrambling. Nonlinear Dyn 94(3):2115–2126
Ahmed F, Anees A, Abbas VU, Siyal MY (2014) A noisy channel tolerant image encryption scheme. Wirel Pers Commun 77(4):2771–2791
Bogdanov A, Knudsen LR, Leander G, Paar C, Poschmann A, Robshaw MJB, Seurin Y, Vikkelsoe C (2007) PRESENT: an ultra-lightweight block cipher. In: Cryptographic hardware and embedded systems, vol 4727. Springer, pp 450–466
Shirai T, Shibutani K, Akishita T, Moriai S, Iwata T (2007) The 128-bit Blockcipher CLEFIA (Extended Abstract). In: Fast software encryption, vol 4593. Springer, pp 181–195
Shirai T, Shibutani K (2006) On Feistel structures using a diffusion switching mechanism. In: Fast software encryption, vol 4047. Springer, pp 41–56
Diffie W, Hellman ME (1977) Exhaustive cryptanalysis of the NBS data encryption standard. Computer 10(6):74–84
Zheng Y, Matsumoto T, Imai H (1989) On the construction of block ciphers provably secure and not relying on any unproved hypotheses. In: Advances in cryptology, vol 435. Springer, pp 461–480
Anees A, Ahmed Z (2015) A technique for designing substitution box based on Van der pol oscillator. Wirel Pers Commun 82(3):1497–1503
Khan M, Shah T, Batool SI (2016) Construction of S-box based on chaotic Boolean functions and its application in image encryption. Neural Comput Appl 27(3):677–685
Belazi A, Khan M, El-Latif AAA, Belghith S (2017) Efficient cryptosystem approaches: S-boxes and permutation-substitution-based encryption. Wirel Pers Commun 87(1):337–361
Skipjack and Kea (1998) Algorithm specifications version, vol 2, pp 1–23. http://csrc.nist.gov/CryptoToolkit/. Updated 10 Oct 2018
Jakimoski G, Kocarev L (2001) Chaos and cryptography: block encryption ciphers based on chaotic maps. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl 48(2):163–169
Chen G, Chen Y, Liao X (2017) An extended method for obtaining S-boxes based on three-dimensional chaotic Baker maps. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 31(3):571–579
Alkhaldi H, Hussain I, Gondal MA (2015) A novel design for the construction of safe S-boxes based on TDERC sequence. Alex Eng J 54(1):65–69
Cui L, Cao Y (2007) A new S-box structure named Affine-Power-Affine. Int J Innov Comput Inf Control 3(3):751–759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anees, A., Chen, YP.P. Designing secure substitution boxes based on permutation of symmetric group. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 7045–7056 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04207-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04207-8