Abstract
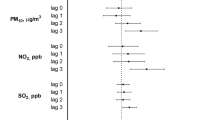
We present results on a time-series study that analyzed the acute effects of six criteria air pollutants on hospital outpatient with chronic pharyngitis (CP) in Xinxiang, China. Data on the concentration of air pollutants and CP outpatient records were collected daily in Xinxiang, China, from January 1, 2015 to December 31, 2018. This study identified 62,823 outpatients with CP. The annual average concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 are 75.7, 132.1, 33.2, 48.4, 1377, and 59.4 μg/m3, respectively. Further, a 10 μg/m3 increment in the concentration of PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO corresponds to an increase of 0.28% (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.03–0.53%), 1.10% (95% CI: 0.09–2.11%), 1.82% (95% CI: 0.84–2.80%), and 0.03% (95% CI: 0.01–0.06%) in daily CP hospital outpatients, respectively. Furthermore, results indicated that outpatients under the age of 15 are more susceptible to the air pollutants, excluding O3. Meanwhile, males might be more susceptible, and effect estimates appear slightly stronger in the cool season. Therefore, we should implement effective measures to manage air pollutants and reinforce protection of the high-risk population.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariana Zeka Antonella Z, Joel S (2006) Individual-level modifiers of the effects of particulate matter on daily mortality. Am J Epidemiol 163:849–859
Bhaskaran K, Gasparrini A, Hajat S, Smeeth L, Armstrong B (2013) Time series regression studies in environmental epidemiology. Int J Epidemiol 42:1187–1195
Chang Q, Zhang H, Zhao Y (2020) Ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for respiratory system-related diseases in a heavy polluted city in Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Chen C, Liu C, Chen R, Wang W, Li W, Kan H, Fu C (2018) Ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for mental disorders in Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 613-614:324–330
Ciencewicki J, Jaspers I (2007) Air pollution and respiratory viral infection. Inhal Toxicol 19:1135–1146
Falcon-Rodriguez CI, Osornio-Vargas AR, Sada-Ovalle I, Segura-Medina P (2016) Aeroparticles, composition, and lung diseases. Front Immunol 7:3
Goldizen FC, Sly PD, Knibbs LD (2016) Respiratory effects of air pollution on children. Pediatr Pulmonol 51:94–108
Huang L, Zhou L, Chen J, Chen K, Liu Y, Chen X, Tang F (2016) Acute effects of air pollution on influenza-like illness in Nanjing, China: a population-based study. Chemosphere 147:180–187
Janssen NA, Fischer P, Marra M, Ameling C, Cassee FR (2013) Short-term effects of PM2.5, PM10 and PM2.5-10 on daily mortality in the Netherlands. Sci Total Environ 463-464:20–26
Kan H, Chen B, Hong C (2009) Health impact of outdoor air pollution in China: current knowledge and future research needs. Environ Health Perspect 117:A187
Li F (2016) Physical activity and health in the presence of China's economic growth: meeting the public health challenges of the aging population. J Sport Health Sci 5:258–269
Li H, Chen R, Meng X, Zhao Z, Cai J, Wang C, Yang C, Kan H (2015) Short-term exposure to ambient air pollution and coronary heart disease mortality in 8 Chinese cities. Int J Cardiol 197:265–270
Li D, Wang JB, Zhang ZY, Shen P, Zheng PW, Jin MJ, Lu HC, Lin HB, Chen K (2018) Effects of air pollution on hospital visits for pneumonia in children: a two-year analysis from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:10049–10057
Liu P, Wang X, Fan J, Xiao W, Wang Y (2016) Effects of air pollution on hospital emergency room visits for respiratory diseases: urban-suburban differences in Eastern China. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 13
Luo L, Zhang Y, Jiang J, Luan H, Yu C, Nan P, Luo B, You M (2018) Short-term effects of ambient air pollution on hospitalization for respiratory disease in Taiyuan, China: a time-series analysis. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 15
Ma Y, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Zhou J, Yang S, Zheng X, Wang S (2017a) Short-term effects of air pollution on daily hospital admissions for cardiovascular diseases in western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:14071–14079
Ma Y, Zhao Y, Yang S, Zhou J, Xin J, Wang S, Yang D (2017b) Short-term effects of ambient air pollution on emergency room admissions due to cardiovascular causes in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex: 1987) 230:974–980
Mokoena KK, Ethan CJ, Yu Y, Shale K, Fan Y, Liu F, Rong J (2019a) The effect of ambient air pollution on circulatory mortality: a short-term exposure assessment in Xi'an, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:22512–22521
Mokoena KK, Ethan CJ, Yu Y, Shale K, Liu F (2019b) Ambient air pollution and respiratory mortality in Xi'’an, China: a time-series analysis. Respir Res 20:139
Murray RC, Chennupati SK (2012) Chronic streptococcal and non-streptococcal pharyngitis. Infect Disord Drug Targets 12:281–285
Nhung NTT, Schindler C, Dien TM, Probst-Hensch N, Perez L, Kunzli N (2018) Corrigendum to “Acute effects of ambient air pollution on lower respiratory infections in Hanoi children: an eight-year time series study” [Environ. Int. 110 (2018) 139-148]. Environ Int 119:240
Orellano P, Quaranta N, Reynoso J, Balbi B, Vasquez J (2017) Effect of outdoor air pollution on asthma exacerbations in children and adults: systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis. PLoS One 12:e0174050
Pun VC, Tian L, Yu IT, Kioumourtzoglou MA, Qiu H (2015) Differential distributed lag patterns of source-specific particulate matter on respiratory emergency hospitalizations. Environ Sci Technol 49:3830–3838
Ren M, Li N, Wang Z, Liu Y, Chen X, Chu Y, Li X, Zhu Z, Tian L, Xiang H (2017) The short-term effects of air pollutants on respiratory disease mortality in Wuhan, China: comparison of time-series and case-crossover analyses. Sci Rep 7:40482
Rey-Ares L, Irazola V, Althabe F, Sobrino E, Mazzoni A, Seron P, Lanas F, Calandreli M, Rubinstein A (2016) Lower tract respiratory infection in children younger than 5 years of age and adverse pregnancy outcomes related to household air pollution in Bariloche (Argentina) and Temuco (Chile). Indoor Air 26:964–975
Song J, Lu M, Zheng L, Liu Y, Xu P, Li Y, Xu D, Wu W (2018) Acute effects of ambient air pollution on outpatient children with respiratory diseases in Shijiazhuang, China. BMC Pulm Med 18:150
Su W, Wu X, Geng X, Zhao X, Liu Q, Liu T (2019) The short-term effects of air pollutants on influenza-like illness in Jinan, China. BMC Public Health 19:1319
Sun Y, Zang Z, Xu X, Zhang Z, Zhong L, Zan W, Zhao Y, Sun L (2011) Experimental investigation of the immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of the traditional Chinese medicine “Li-Yan Zhi-Ke granule” for relieving chronic pharyngitis in rats. Mol Biol Rep 38:199–203
Tong L, Li K, Zhou Q (2016) Season, sex and age as modifiers in the association of psychosis morbidity with air pollutants: a rising problem in a Chinese metropolis. Sci Total Environ 541:928–933
Valacchi G, Porada E, Rowe BH (2015) Ambient ozone and bacterium Streptococcus: a link between cellulitis and pharyngitis. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 28:771–774
Wang Y, Zu Y, Huang L, Zhang H, Wang C, Hu J (2018) Associations between daily outpatient visits for respiratory diseases and ambient fine particulate matter and ozone levels in Shanghai, China. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex: 1987) 240:754–763
Wang M, Luo X, Xu S, Liu W, Ding F, Zhang X, Wang L, Liu J, Hu J, Wang W (2019) Trends in smoking prevalence and implication for chronic diseases in China: serial national cross-sectional surveys from 2003 to 2013. Lancet Respir Med 7:35–45
Wang J, Lu M, An Z, Jiang J, Li J, Wang Y, Du S, Zhang X, Zhou H, Cui J, Wu W, Liu Y, Song J (2020): Associations between air pollution and outpatient visits for allergic rhinitis in Xinxiang, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Wu J, Liu L, Wang G, Lu J (2016) One health in China. Infection ecology & epidemiology 6:33843
Yang C, Chen A, Chen R, Qi Y, Ye J, Li S, Li W, Liang Z, Liang Q, Guo D, Kan H, Chen X (2014) Acute effect of ambient air pollution on heart failure in Guangzhou, China. Int J Cardiol 177:436–441
Yuming G (2017) Hourly associations between heat and ambulance calls. Environ Pollut
Zeger SL, Thomas D, Dominici F, Samet JM, Schwartz J, Dockery D, Cohen A (2000) Exposure measurement error in time-series studies of air pollution: concepts and consequences. Environ Health Perspect 108:419–426
Zhang H, Zhang J (2012) Review of the diseases which be misdiagnosed as chronic pharyngitis. China Modern Doctor 2012:2
Zhang Y, Peng M, Yu C, Zhang L (2017) Burden of mortality and years of life lost due to ambient PM10 pollution in Wuhan, China. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987) 230:1073–1080
Zhang Y, Ding Z, Xiang Q, Wang W, Huang L, Mao F (2020a) Short-term effects of ambient PM1 and PM2.5 air pollution on hospital admission for respiratory diseases: case-crossover evidence from Shenzhen, China. Int J Hyg Environ Health 224:113418
Zhang Y, Fang J, Mao F, Ding Z, Xiang Q, Wang W (2020b) Age- and season-specific effects of ambient particles (PM1, PM2.5, and PM10) on daily emergency department visits among two Chinese metropolitan populations. Chemosphere 246:125723
Zhou M, He G, Liu Y, Yin P, Li Y, Kan H, Fan M, Xue A, Fan M (2015) The associations between ambient air pollution and adult respiratory mortality in 32 major Chinese cities, 2006-2010. Environ Res 137:278–286
Funding
The study was supported by the PhD Research Project of Xinxiang Medical University (XYBSKYZZ201804), Key Scientific Research Projects in Universities of Henan (19B330004), and Peak Subject Project of Public Health in Xinxiang Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 75 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Lu, M., An, Z. et al. Acute effects of ambient air pollution on hospital outpatients with chronic pharyngitis in Xinxiang, China. Int J Biometeorol 64, 1923–1931 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01980-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01980-3