Abstract
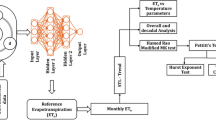
Reliable estimation of reference evapotranspiration (ETo), an essential component of optimal irrigation management, is challenging in many regions due to its complex dependence on meteorological factors. Alternative empirical models, often used to estimate ETo considering data limitations, provide highly unreliable estimates for Iraq. This study aimed to formulate simpler empirical models for accurate ETo estimation with fewer variables in different climate regions of Iraq. The metaheuristic Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) was used to finetune the coefficients of the nonlinear least square fitting regression (NLLSF) model during development. Two simpler models were developed based on (1) only mean air temperature (T) (NLLSF-T) and (2) solar radiation and T (NLLSF-R) as inputs. The performance of the models was validated using historical ground observations (2012–2021), and the ETo was estimated using the Penman–Monteith method from the reanalyzed (ERA5) datasets (1959–2021). The models' spatial, seasonal, and temporal performance in estimating daily ETo was rigorously evaluated using multiple statistical metrics and visual presentations. The Kling-Gupta Efficiency (KGE) and normalized root mean square error (NRMSE) of the NLLSF-T model were 0.95 and 0.30, respectively, compared to 0.75 and 0.40 for Kharrufa, the best-performing temperature-based models in Iraq. Similarly, NLLSF-R improved the KGE from 0.78 to 0.97 in KGE and NRMSE from 0.44 to 0.22 compared to Caprio, the best-performing radiation-based model in Iraq. The spatial assessment revealed both the models' excellent performance over most of Iraq, except in the far north, indicating their suitability in estimating ETo in arid and semi-arid regions.











Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
R software, R.3.4, and MATLAB were used for writing the code that can be provided upon request.
References
Abdollahzadeh B, SoleimanianGharehchopogh F, Mirjalili S (2021) Artificial gorilla troops optimizer: a new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Int J Intell Syst 36:5887–5958. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22535
Abdollahzadeh B, Gharehchopogh FS, Khodadadi N, Mirjalili S (2022) Mountain gazelle optimizer: a new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Adv Eng Softw 174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2022.103282
Abtew W (1996) Evapotranspiration measurements and modeling for three wetland systems in South Florida 1. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 32(3):465–473. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1996.tb04044.x
Agrawal Y, Kumar M, Ananthakrishnan S, Kumarapuram G (2022) Evapotranspiration modeling using different tree based ensembled machine learning algorithm. Water Resour Manage 36:1025–1042
Al-Ansari N (2013) Management of water resources in Iraq: perspectives and prognoses. Engineering 5:667–684
Al-Ansari N, Ali A and Knutsson S (2015) Iraq water resources planning: perspectives and prognoses. Int Confe Civil Constr Eng 26/01/2015–27/01/2015. URN: urn:nbn:se:ltu:diva-39590
Albrecht F (1950) Die methoden zur bestimmung der verdunstung der natürlichen erdoberfläche. Archiv für Meteorol, Geophysik und Bioklimatologie, Serie B 2:1–38
Al-Hasani AA (2021) Trend analysis and abrupt change detection of streamflow variations in the lower Tigris River Basin, Iraq. Int J River Basin Manag 19:523–534. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2020.1723603
Al-Hasani AAJ, Shahid S (2023) Assessment of 40 empirical models for estimating reference evapotranspiration under the three major climate zones of Iraq. J Irrig Drain Eng 149:04023025. https://doi.org/10.1061/JIDEDH.IRENG-10187
AL-Hasani AA J, Shahid S, (2022) Spatial distribution of the trends in potential evapotranspiration and its influencing climatic factors in Iraq. Theor Appl Climatol 150(1–2):677–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04184-4
Allen R, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998a) Chapter 1. Introduction to evapotranspiration. Crop evapotranspiration–Guidelines for computing crop water requirements [online]. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Irrigation and Drainage Paper, 56
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998b) Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Fao, Rome 300:D05109
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998c) FAO Irrigation and drainage paper No. 56. Rome: Food Agric Org Unit Nat 56:156
Baier W, Robertson GW (1965) Estimation of latent evaporation from simple weather observations. Can J Plant Sci 45:276–284
Bates D (1988) Nonlinear regression analysis and its applications. Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics. New York google schola, vol 2, pp 379–416
Bell B, Hersbach H, Simmons A, Berrisford P, Dahlgren P, Horányi A, Muñoz-Sabater J, Nicolas J, Radu R, Schepers D (2021) The ERA5 global reanalysis: Preliminary extension to 1950. Q J R Meteorol Soc 147:4186–4227
Brockamp B, Wenner H (1963) Verdunstungsmessungen auf den Steiner see bei münster. Dt Gewässerkundl Mitt 7:149–154
Caprio JM (1974) The solar thermal unit concept in problems related to plant development and potential evapotranspiration. Phenology and seasonality modeling. Springer, Berlin, pp 353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-51863-8_29
Chia MY, Huang YF, Koo CH (2020) Support vector machine enhanced empirical reference evapotranspiration estimation with limited meteorological parameters. Comput Electron Agric 175:105577
Chia MY, Huang YF, Koo CH (2021) Swarm-based optimization as stochastic training strategy for estimation of reference evapotranspiration using extreme learning machine. Agric Water Manag 243:106447
Dalton J (1802) Experimental Essays, on the Constitution of Mixed Gases: On the Force of Steam Or Vapour from Water and Other Liquids in Different Temperatures, Both in a Torricellian Vacuum and in Air; on Evaporation; and on the Expansion of Elastic Fluids by Heat, RW Dean & Company Market-street-lane
Diop L, Samadianfard S, Bodian A, Yaseen ZM, Ghorbani MA, Salimi H (2020) Annual rainfall forecasting using hybrid artificial intelligence model: integration of multilayer perceptron with whale optimization algorithm. Water Resour Manage 34:733–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02473-8
Doorenbos J, Pruitt W (1977) Crop water requirements. FAO irrigation and drainage paper 24. Land and Water Development Division, FAO, Rome, 144. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Dorigo M, Birattari M, Stutzle T (2006) Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 1:28–39
Droogers P, Allen RG (2002) Estimating reference evapotranspiration under inaccurate data conditions. Irrig Drain Syst 16:33–45
Ehteram M, Singh VP, Ferdowsi A, Mousavi SF, Farzin S, Karami H, Mohd NS, Afan HA, Lai SH, Kisi O (2019) An improved model based on the support vector machine and cuckoo algorithm for simulating reference evapotranspiration. PLoS ONE 14:e0217499
Ellenburg WL, Cruise J, Singh VP (2018) The role of evapotranspiration in streamflow modeling–An analysis using entropy. J Hydrol 567:290–304
Fathian F, Mehdizadeh S, Sales AK, Safari MJS (2019) Hybrid models to improve the monthly river flow prediction: Integrating artificial intelligence and non-linear time series models. J Hydrol 575:1200–1213
Fox J, Weisberg S (2002) Nonlinear regression and nonlinear least squares. Citeseer. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=a2f2ab9edf3fe6e970c651ac3a43dc0aff79acbc
Gangopadhyaya M, Urwaev V, Omar M, Nordenson T, Harbeck G (1966) Measurement and estimation of evaporation and evapotranspiration. Tech, Note
Ghahreman R, Rahimzadegan M (2022) Calculating net radiation of freshwater reservoir to estimate spatial distribution of evaporation using satellite images. J Hydrol 605:127392
Gharehchopogh FS, Nadimi-Shahraki MH, Barshandeh S, Abdollahzadeh B, Zamani H (2023) Cqffa: A chaotic quasi-oppositional farmland fertility algorithm for solving engineering optimization problems. J Bionic Eng 20:158–183
Gleixner S, Demissie T, Diro GT (2020) Did ERA5 improve temperature and precipitation reanalysis over East Africa? Atmosphere 11:996
Goyal S, Bhushan S, Kumar Y, Rana AUHS, Bhutta MR, Ijaz MF, Son Y (2021) An optimized framework for energy-resource allocation in a cloud environment based on the whale optimization algorithm. Sensors 21:1583
Goyal P, Kumar S, Sharda R (2023) A review of the Artificial Intelligence (AI) based techniques for estimating reference evapotranspiration: Current trends and future perspectives. Comput Electron Agric 209:107836
Granata F (2019) Evapotranspiration evaluation models based on machine learning algorithms—A comparative study. Agric Water Manag 217:303–315
Gupta HV, Kling H, Yilmaz KK, Martinez GF (2009) Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J Hydrol 377:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.003
Hamon WR (1963) Computation of direct runoff amounts from storm rainfall. Int Assoc Sci Hydrol Publ 63:52–62
Hansen PC, Pereyra V, Scherer G (2013) Least squares data fitting with applications, JHU Press. https://books.google.iq/books?hl=en&lr=&id=8IrZe3QX0LQC&oi=fnd&pg=PP2&dq=+HANSEN,+P.+C.,+PEREYRA,+V.+%26+SCHERER,+G.+2013
Hargreaves GH, Samani ZA (1985) Reference crop evapotranspiration from temperature. Appl Eng Agric 1:96–99
Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P, Dahlgren P, Horányi A, Munoz-Sebater J, Nicolas J, Radu R, Schepers D, Simmons A (2020) The ERA5 Global Reanalysis: achieving a detailed record of the climate and weather for the past 70 years. Eur Geophys Union Gen Assemb, 3–8
Irmak S, Allen R, Whitty E (2003) Daily grass and alfalfa-reference evapotranspiration estimates and alfalfa-to-grass evapotranspiration ratios in Florida. J Irrig Drain Eng 129:360–370
Irmak S, Irmak A, Allen R, Jones J (2003) Solar and net radiation-based equations to estimate reference evapotranspiration in humid climates. J Irrig Drain Eng 129:336–347
Jasim AI, Awchi TA (2020) Regional meteorological drought assessment in Iraq. Arab J Geosci 13:284
Jensen ME, Haise HR (1963) Estimating evapotranspiration from solar radiation. J Irrig Drain Div 89:15–41
Karaboga D (2005) An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization. Tech Rep-tr06, Erciyes Univ, Eng Facult, Comput
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. Proc of ICNN'95-Int Conf Neural Net, vol 4. IEEE, pp 1942–1948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Kharrufa N (1985) Simplified equation for evapotranspiration in arid regions. Beiträge zur Hydrol 5:39–47
Kumar M, Bandyopadhyay A, Raghuwanshi N, Singh R (2008) Comparative study of conventional and artificial neural network-based ETo estimation models. Irrig Sci 26:531–545
Kumar R, Jat M, Shankar V (2012) Methods to estimate irrigated reference crop evapotranspiration–a review. Water Sci Technol 66:525–535. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.191
Li M, Chu R, Islam ARMT, Shen S (2018) Reference evapotranspiration variation analysis and its approaches evaluation of 13 empirical models in sub-humid and humid regions: A case study of the Huai river basin, eastern China. Water 10:493
Li S, Wang G, Sun S, Hagan DFT, Chen T, Dolman H, Liu Y (2021) Long-term changes in evapotranspiration over China and attribution to climatic drivers during 1980–2010. J Hydrol 595:126037
Linacre ET (1977) A simple formula for estimating evaporation rates in various climates, using temperature data alone. Agric Meteorol 18:409–424
Liu Z (2022) Evaluation of remotely sensed global evapotranspiration data from inland river basins. Hydrol Process 36:e14774. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.14774
Mahringer W (1970) Verdunstungsstudien am neusiedler See. Archiv für Meteorol, Geophysik und Bioklimatol, Serie B 18:1–20
Makkink G (1957) Testing the Penman formula by means of lysimeters. J Inst Water Eng 11:277–288
Mcguinness JL, Bordne EF (1972) A comparison of lysimeter-derived potential evapotranspiration with computed values, US Department of Agriculture. https://books.google.iq/books?hl=en&lr=&id=oqYoAAAAYAAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&ots=xyw9xcW_g9&sig=JTiEE51KdzzN8fl7y8oPRCljXrE&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
Mehdizadeh S, Saadatnejadgharahassanlou H, Behmanesh J (2017) Calibration of Hargreaves-Samani and Priestley-Taylor equations in estimating reference evapotranspiration in the Northwest of Iran. Arch Agron Soil Sci 63:942–955
Mehdizadeh S, Mohammadi B, Pham QB, Duan Z (2021) Development of boosted machine learning models for estimating daily reference evapotranspiration and comparison with empirical approaches. Water 13:3489
Meyer A (1926) Über einige zusammenhänge zwischen klima und boden in Europa. ETH Zurich
Miarnaeimi F, Azizyan G, Rashki M (2021) Horse herd optimization algorithm: A nature-inspired algorithm for high-dimensional optimization problems. Knowl-Based Syst 213:106711
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Saremi S, Mirjalili S (2020) Whale optimization algorithm: theory, literature review, and application in designing photonic crystal filters. Nat-Ins Optimizers: Theor, Lit Rev Appl. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 811. Springer Verlag, pp 219–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12127-3_13
Mohammadi B, Mehdizadeh S (2020) Modeling daily reference evapotranspiration via a novel approach based on support vector regression coupled with whale optimization algorithm. Agric Water Manag 237:106145
Mohammadi A, Sheikholeslam F, Mirjalili S (2023) Nature-inspired metaheuristic search algorithms for optimizing benchmark problems: inclined planes system optimization to state-of-the-art methods. Arch Comput Methods Eng 30:331–389
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, van Liew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50:885–900
Muhammad MKI, Nashwan MS, Shahid S, Ismail TB, Song YH, Chung E-S (2019) Evaluation of empirical reference evapotranspiration models using compromise programming: a case study of Peninsular Malaysia. Sustainability 11:4267
Muhammad MKI, Shahid S, Ismail T, Harun S, Kisi O, Yaseen ZM (2021) The development of evolutionary computing model for simulating reference evapotranspiration over Peninsular Malaysia. Theoret Appl Climatol 144:1419–1434
Muñoz-Sabater J, Dutra E, Agustí-Panareda A, Albergel C, Arduini G, Balsamo G, Boussetta S, Choulga M, Harrigan S, Hersbach H (2021) ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth System Sci Data 13:4349–4383
Muslih KD (2014) Identifying the climatic conditions in Iraq by tracking down cooling events in the North Atlantic Ocean in the period 3000–0 BC. Miscellanea Geographica, Regional Studies on Development, p 18
Nadimi-Shahraki MH, Zamani H, Asghari Varzaneh Z, Mirjalili S (2023) A Systematic Review of the Whale Optimization Algorithm: Theoretical Foundation, Improvements, and Hybridizations. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 1–47
Oudin L, Hervieu F, Michel C, Perrin C, Andréassian V, Anctil F, Loumagne C (2005) Which potential evapotranspiration input for a lumped rainfall–runoff model?: Part 2—Towards a simple and efficient potential evapotranspiration model for rainfall–runoff modelling. J Hydrol 303:290–306
Papadakis J (1965) Crop ecologic survey in relation to agricultural development of Western Pakistan. Draft report 100(3):225
Penman HL (1948) . Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Math Phys Sci 193:120–145
Pinos J (2022) Estimation methods to define reference evapotranspiration: a comparative perspective. Water Pract Technol 17:940–948
Pour SH, AbdWahab AK, Shahid S, Ismail ZB (2020) Changes in reference evapotranspiration and its driving factors in peninsular Malaysia. Atmos Res 246:105096
Priestley CHB, Taylor RJ (1972) On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon Weather Rev 100:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1972)1002.3.CO;2
Rahimpour M, Rahimzadegan M (2021) Assessment of surface energy balance algorithm for land and operational simplified surface energy balance algorithm over freshwater and saline water bodies in Urmia Lake Basin. Theoret Appl Climatol 143:1457–1472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03472-1
Rajabioun R (2011) Cuckoo optimization algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 11:5508–5518
Ravazzani G, Corbari C, Morella S, Gianoli P, Mancini M (2012) Modified Hargreaves-Samani equation for the assessment of reference evapotranspiration in Alpine river basins. J Irrig Drain Eng 138:592–599
Rohwer C (1931) Evaporation from free water surfaces, US Department of Agriculture. USDA, Washington, DC
Romanenko V (1961) Computation of the autumn soil moisture using a universal relationship for a large area. Proc Ukrainian Hydrometeorol Res Inst 3:12–25
Roy DK, Barzegar R, Quilty J, Adamowski J (2020) Using ensembles of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and optimization algorithms to predict reference evapotranspiration in subtropical climatic zones. J Hydrol 591:125509
Roy DK, Sarkar TK, Biswas SK, Datta B (2023) Generalized daily reference evapotranspiration models based on a hybrid optimization algorithm tuned fuzzy tree approach. Water Resour Manage 37:193–218
Salam R, Islam ARMT, Pham QB, Dehghani M, Al-Ansari N, Linh NTT (2020) The optimal alternative for quantifying reference evapotranspiration in climatic sub-regions of Bangladesh. Sci Rep 10:20171
Salem GSA, Kazama S, Shahid S, Dey NC (2018) Impacts of climate change on groundwater level and irrigation cost in a groundwater dependent irrigated region. Agric Water Manag 208:33–42
Salman SA, Shahid S, Ismail T, Chung E-S, Al-Abadi AM (2017) Long-term trends in daily temperature extremes in Iraq. Atmos Res 198:97–107
Salman SA, Shahid S, Ismail T, Rahman NBA, Wang X, Chung E-S (2018) Unidirectional trends in daily rainfall extremes of Iraq. Theoret Appl Climatol 134:1165–1177
Salman SA, Shahid S, Sharafati A, Ahmed Salem GS, Abu Bakar A, Farooque AA, Chung E-S, Ahmed YA, Mikhail B, Yaseen ZM (2021) Projection of Agricultural Water Stress for Climate Change Scenarios: A Regional Case Study of Iraq. Agriculture 11:1288
Sanikhani H, Kisi O, Maroufpoor E, Yaseen ZM (2019) Temperature-based modeling of reference evapotranspiration using several artificial intelligence models: application of different modeling scenarios. Theoret Appl Climatol 135:449–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2390-z
Schendel U (1967) Vegetationswasserverbrauch und-wasserbedarf. Habil, Kiel 137:1–11
Shiru MS, Shahid S, Alias N, Chung E-S (2018) Trend analysis of droughts during crop growing seasons of Nigeria. Sustainability 10:871
Singer MB, Asfaw DT, Rosolem R, Cuthbert MO, Miralles DG, Macleod D, Quichimbo EA, Michaelides K (2021) Hourly potential evapotranspiration at 0.1° resolution for the global land surface from 1981-present. Scientific Data 8:1–13
Singh V, Xu CY (1997) Evaluation and generalization of 13 mass-transfer equations for determining free water evaporation. Hydrol Process 11:311–323. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(19970315)11:33.0.CO;2-Y
Sobh MT, Nashwan MS, Amer N (2022) High-resolution reference evapotranspiration for arid Egypt: Comparative analysis and evaluation of empirical and artificial intelligence models. Int J Climatol 42(16):10217–10237. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7894
Szász G (1973) A potenciális párolgás meghatározásának új módszere. Hidrol Közl 10:435–442
Tabari H, Kisi O, Ezani A, Talaee PH (2012) SVM, ANFIS, regression and climate based models for reference evapotranspiration modeling using limited climatic data in a semi-arid highland environment. J Hydrol 444:78–89
Tabari H, Grismer ME, Trajkovic S (2013) Comparative analysis of 31 reference evapotranspiration methods under humid conditions. Irrig Sci 31:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-011-0295-z
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geograph Rev 38:55–94. https://doi.org/10.2307/210739
Trabert W (1896) Neue beobachtungen über verdampfungsgeschwindigkeiten. Meteorol Z 13:261–263
Trajkovic S (2007) Hargreaves versus Penman-Monteith under humid conditions. J Irrig Drain Eng 133:38–42. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2007)133:1(38)
Trajkovic S (2009) Comparison of radial basis function networks and empirical equations for converting from pan evaporation to reference evapotranspiration. Hydrol Process: An Int J 23:874–880
Trajkovic S, Kolakovic S (2009) Wind-adjusted Turc equation for estimating reference evapotranspiration at humid European locations. Hydrol Res 40:45–52
Turc L (1961) Water requirements assessment of irrigation, potential evapotranspiration: simplified and updated climatic formula. Annales agronomiques, 1961. L’Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA) Paris, France, 13–49
Un-Escwa B (2013) United Nations economic and social commission for western Asia; Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe. Shared Tributaries of the Tigris River. Inventory of Shared Water Resources in Western Asia, Beirut
Wang L, Yang X, Liu Z, Zhang S, Kong J, Yang Y (2021) Estimation of evapotranspiration and its relationship with environmental factors in Jinghe River Basin. J Appl Remote Sens 15:034518–034518
Yaseen ZM, Naghshara S, Salih SQ, Kim S, Malik A, Ghorbani MA (2020) Lake water level modeling using newly developed hybrid data intelligence model. Theoret Appl Climatol 141:1285–1300
Ye L, Zahra MMA, Al-Bedyry NK, Yaseen ZM (2022) Daily scale evapotranspiration prediction over the coastal region of southwest Bangladesh: new development of artificial intelligence model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36:451–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02055-4
Yu H, Wen X, Li B, Yang Z, Wu M, Ma Y (2020) Uncertainty analysis of artificial intelligence modeling daily reference evapotranspiration in the northwest end of China. Comput Electron Agric 176:105653
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Iraqi Agrometeorological Centre (IAC) / Ministry of Agriculture and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) for providing the IAC and ERA5 climate datasets.
Funding
This research received no specific funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to the study’s conception and design. Alaa A. Jasim did data curation, conceptualization, wrote the original draft, review, editing, visualization, and software. Shamsuddin Shahid did conceptualization, programming code, writing, review, editing, and supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The article is established based on the ethics of the aimed journal.
Consent to publish
The research is technically consent to be published.
Competing of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Hasani, A.A.J., Shahid, S. Development of radiation and temperature-based empirical models for accurate daily reference evapotranspiration estimation in Iraq. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-024-02736-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-024-02736-w