Abstract
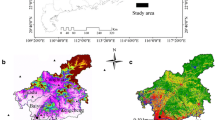
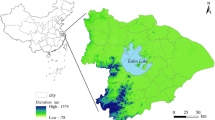
Rapid urbanization has produced many metropolitan areas in China, resulting in regional human-land-ecological environment contradiction phenomenon. In recent years, Chinese government has launched a series of new national ecological civilization construction and ecological protection projects. Monitoring the changes in land-use/land cove (LULC) and exploring its impact on net primary productivity (NPP) is a key hot issue to support sustainable development. This study took Wuhan metropolitan area as the research area to monitor the distribution and relationship between LULC and vegetation NPP changes is helpful to strengthen carbon balance and improve the quality of human settlements. The results showed that, from 2000 to 2020, land use types in the study area changed dramatically, mainly cultivated land, urban land, and other construction land. The vegetation NPP showed a continuous growth trend in time and space, with growth rate of 114.48%. With the passage of time, LULC spatial distribution had significant effects on NPP and chaotic urban sprawl has seriously affected NPP losses, while the ecological forest and grassland in remote areas can significantly increase NPP yield. This study also revealed the correlation between LULC and NPP, and opened up research approaches for land-use optimization and vegetation NPP based on different scenarios in the future. Our analysis not only contributes urban land-use planners, but also provides important insights into improving the competitiveness of green development among urban agglomeration systems.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in [figshare] at (https://figshare.com/s/867a8d018ead0147e3fd).
References
Aksoy H, Kaptan S, Varol T, Cetin M, Ozel HB (2022a) Exploring land use/land cover change by using density analysis method in yenice. Int J Environ Sci Tech 19(10):10257–10274
Aksoy T, Dabanli A, Cetin M, Kurkcuoglu MAS, Cengiz AE, Cabuk SN, Agacsapan B, Cabuk A (2022b) Evaluation of comparing urban area land use change with urban atlas and CORINE data. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(19):28995–29015
Bajocco S, Ceccarelli T, Smiraglia D, Salvati L, Ricotta C (2016) Modeling the ecological niche of long-term land use changes: the role of biophysical factors. Ecol Indic 60:231–236
Buonocore C, Pascual JJG, Cayeiro MLP, Salinas RM, Mejias MB (2021) Modelling the impacts of climate and land use changes on water quality in the Guadiana basin and the adjacent coastal area. Sci Total Environ 776:146034
Celleri C, Pratolongo P, Arena M (2022) Spatial and temporal patterns of soil salinization in shallow groundwater environments of the Bahia Blanca estuary: Influence of topography and land use. Land Degrad Dev 33(3):470–483
Cetin M (2015a) Using GIS analysis to assess urban green space in terms of accessibility: case study in Kutahya. Int J Sust Dev World 22(5):420–424
Cetin M (2015b) Evaluation of the sustainable tourism potential of a protected area for landscape planning: a case study of the ancient city of Pompeipolis in Kastamonu. Int J Sust Dev World 22(6):490–495
Cetin M (2016) Sustainability of urban coastal area management: a case study on Cide. J Sustain Forest 35(7):527–541
Cetin M (2019) The effect of urban planning on urban formations determining bioclimatic comfort area’s effect using satellitia imagines on air quality: a case study of bursa city. Air Qual Atmos Hlth 12(7):1237–1249
Cetin M (2020a) Climate comfort depending on different altitudes and land use in the urban areas in Kahramanmaras city. Air Qual Atmos Health 13(8):991–999
Cetin M (2020b) The changing of important factors in the landscape planning occur due to global climate change in temperature, rain and climate types: a case study of Mersin city. Turk Sci Tech Publ 8(12):2695–2701
Cetin M, Onac AK, Sevik H, Canturk U, Akpinar H (2018) Chronicles and geoheritage of the ancient roman city of pompeiopolis: a landscape plan. Arab J Geosci 11(24):798
Cetin M, Aksoy T, Cabuk SN, Senyel Kurkcuoglu MA, Cabuk A (2021) Employing remote sensing technique to monitor the influence of newly established universities in creating an urban development process on the respective cities. Land Use Pol 109:105705
Chen YZ, Lu HW, Li J, Xia J (2020) Effects of land use cover change on carbon emissions and ecosystem services in Chengyu urban agglomeration, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 34(8):1197–1215
Cheng FY, Liu SL, Zhang YQ, Yin YJ, Hou XY (2017) Effects of land-use change on net primary productivity in Beijing based on the MODIS series. Acta Ecol Sin 37(18):5924–5934
Cramer W, Kicklighter DW, Bondeau A, Moore B, Churkina G, Nemry B, Ruimy A, Schloss AL (1999) Comparing global models of terrestrial net primary productivity (NPP): overview and key results. Glob Change Biol 5:1–15
DeFries RS, Field CB, Fung I, Collatz GJ, Bounoua L (1999) Combining satellite data and biogeocbemical models to estimate global effects of human—induced land cover change on carbon emissions and primary productivity. Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 13(3):803–815
deSouza P, Malhi Y (2018) Land use change in India (1700–2000) as examined through the lens of human appropriation of net primary productivity. J Ind Ecol 22(5):1202–1212
Dharumarajan S, Lalitha M, Natarajan A, Naidu LGK, Balasubramanian R, Hegde R, Vasundhara R, Kumar KSA, Singh SK (2017) Biophysical and socio-economic causes for increasing fallow land in Tamil Nadu. Soil Use Manage 33(3):487–498
Dong GT, Yang ST, Gao YF, Bai J, Wang XL, Zheng DH (2014) Spatial evaluation of phosphorus retention in riparian zones using remote sensing data. Environ Earth Sci 72(5):1643–1657
Donmez C, Berberoglu S, Curran PJ (2011) Modelling the current and future spatial distribution of NPP in a Mediterranean watershed. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 13(3):336–345
Duveneck MJ, Thompson JR (2017) Climate change imposes phenological trade-offs on forest net primary productivity. Climate change imposes phenological trade-offs on forest net primary productivity. J Geophys Res: Biosci 122(9):2298–2313
Fan QD, Liang LK, Li W (2020) Development of ecological civilization in China. Fresen Environ Bull 29(7):5570–5575
Fetzel T, Niedertscheider M, Haberl H, Krausmann F, Erb KH (2016) Patterns and changes of land use and land-use efficiency in Africa 1980–2005: an analysis based on the human appropriation of net primary production framework. Reg Environ Change 16(5):1507–1520
Gao LA, Tao F, Liu RR, Wang ZL, Leng HJ, Zhou T (2022) Multi-scenario simulation and ecological risk analysis of land use based on the PLUS model: a case study of Nanjing. Sustain Cities Soc 85:104055
Gu L, Gong ZW, Du YX (2021) Evolution characteristics and simulation prediction of forest and grass landscape fragmentation based on the “Grain for Green” projects on the. Ecol Indic 131:108240
Hazarika MK, Yasuoka Y, Ito A, Dye D (2005) Estimation of net primary productivity by integrating remote sensing data with an ecosystem model. Remote Sens Environ 94(3):298–310
He LJ, Wang LC, Huang B, Wei J, Zhou ZG, Zhong Y (2020) Anthropogenic and meteorological drivers of 1980–2016 trend in aerosol optical and radiative properties over the Yangtze River Basin. Atmos Environ 223:117188
HPDRC (Hubei Provincial Development and Reform Commission) (2019) The national development and reform commission approved the "Wuhan metropolitan regional development Plan" (2019–2035), 011043110, pp 2019–59976. https://fgw.hubei.gov.cn/
Huang N, Wang ZM, Liu DW, Niu Z (2010) Selecting sites for converting farmlands to Wetlands in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China, Based on Remote Sensing and GIS. Environ Manage 46(6):790–800
Hurlimann A, Cobbinah PB, Bush J, March A (2021) Is climate change in the curriculum? An analysis of Australian urban planning degrees. Environ Educ Res 27(7):970–991
Imhoff ML, Bounoua L, DeFiles R, Lawrence WT, Stutzer D, Tucker CJ, Ricketts T (2004) The consequences of urban land transformation on net primary productivity in the United States. Remote Sens Environ 89(4):434–443
Jia XX, Shao MG, Wei XR, Horton R, Li XZ (2011) Estimating total net primary productivity of managed grasslands by a state-space modeling approach in a small catchment on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 160(281–291):281–291
Kamwi JM, Chirwa PWC, Manda SOM, Graz PF, Katsch C (2015) Livelihoods, land use and land cover change in the Zambezi Region. Namibia Popul Env 37(2):207–230
Kaya E, Agca M, Adiguzel F, Cetin M (2019) Spatial data analysis with R programming for environment. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(6):1521–1530
Kilicoglu C, Cetin M, Aricak B, Sevik H (2020) Site selection by using the multi-criteria technique-a case study of Bafra. Turkey Environ Monit Assess 192(9):608
Kochaphum C, Gheewala SH, Vinitnantharat S (2015) Does palm biodiesel driven land use change worsen greenhouse gas emissions? An environmental and socio-economic assessment. Energy Sustain Dev 29:100–111
Kumar P, Dasgupta R, Johnson BA, Saraswat C, Basu M, Kefi M, Mishra BK (2019) Effect of land use changes on water quality in an ephemeral coastal plain: Khambhat City, Gujarat. India Water 11(4):724
Lambin EF, Meyfroidt P (2010) Land use transitions: socio-ecological feedback versus socio-economic change. Land Use Pol 27(2):108–118
Lavigne MB, Foster RJ, Goodine G, Bernier PY, Ung CH (2005) Alternative method for estimating aboveground net primary productivity applied to balsam fir stands in eastern Canada. Can J for Res 35(5):1193–1201
Liang X, Liu X, Li D, Zhao H, Chen G (2018) Urban growth simulation by incorporating planning policies into a CA-based future land-use simulation mode. Int J Geogr Inf 32(11):2294–2316
Liang X, Guan QF, Clarke KC, Liu SS, Wang BY, Yao Y (2021a) Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: a case study in Wuhan, China. Comput Environ Urban 85:101569
Liang X, Guan QF, Clarke KC, Chen GZ, Guo S, Yao Y (2021b) Mixed-cell cellular automata: a new approach for simulating the spatio-temporal dynamics of mixed land use structures. Landsc Urban Plan 205:103960
Liu JY, Liu ML, Deng XZ, Zhuang DF, Zhang ZX, Luo D (2002) The land use and land cover change database and its relative studies in China. J Geog Sci 12(3):275–282
Liu JY, Zhang ZX, Xu XL, Kuang WH, Zhou WC, Zhang SW, Li RD, Yan CZ, Yu DS, Wu SX, Nan J (2010) Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China during the early 21st century. J Geog Sci 20(4):483–494
Liu JY, Liu JY, Kuang WH, Zhang ZX, Xu XL, Qin YW, Ning J, Zhou WC, Zhang SW, Li RD, Yan CZ, Wu SX, Shi XZ, Jiang N, Yu DS, Pan XZ, Chi WF (2014) Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in china since the late 1980s. J Geog Sci 24(2):195–210
Liu YL, Wang HM, Jiao LM, Liu YF, He JH, Ai TH (2015) Road centrality and landscape spatial patterns in Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. Chin Geogr Sci 25(4):511–522
Liu JY, Ning J, Kuang WH, Xu XL, Zhang SW, Yan CZ, Li RD, Wu SX, Hu YF, Du GM, Chi WF, Pan T, Jing N (2018) Spatio-temporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010–2015. Acta Geogr Sin 73(5):789–802
Liu PJ, Hu YC, Jia WT (2021) Land use optimization research based on FLUS model and ecosystem services-setting Jinan City as an example. Urban Clim 40:100984
Ma SH, Wen ZZ (2021) Optimization of land use structure to balance economic benefits and ecosystem services under uncertainties: a case study in Wuhan, China. J Clean Prod 311:127537
Martinez YM, Coll DG, Aguayo M, Casas-Ledon Y (2019) Effects of landcover changes on net primary production (NPP)-based exergy in south-central of Chile. Appl Geogr 113:102101
Masayi NN, Omondi P, Tsingalia M (2021) Assessment of land use and land cover changes in Kenya’s Mt. Elgon forest ecosystem. Afr J Ecol 59(4):988–1003
Meng FX, Guo JL, Guo ZQ, Lee JCK, Liu GY, Wang N (2021) Urban ecological transition: the practice of ecological civilization construction in China. Sci Total Environ 755:142633
Milesi C, Elvidge CD, Nemani RR, Running SW (2003) Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the southeastern United States. Remote Sens Environ 86(3):401–410
Mohammady M (2021) Land use change optimization using a new ensemble model in Ramian county. Iran Environ Earth Sci 80(23):780
Noel LMLJ, Griffin JN, Thompson RC, Hawkins SJ, Burrows MT, Crowe TP, Jenkins SR (2010) Assessment of a field incubation method estimating primary productivity in rockpool communities. Estuar Coast Shelf S 88(1):153–159
O’Sullivan D, Evans T, Manson S, Metcalf S, Ligmann-Zielinska A, Bone C (2016) Strategic directions for agent-based modeling: avoiding the YAAWN syndrome. J Land Use Sci 11(2):177–187
Onac AK, Cetin M, Sevik H, Orman P, Sutcuoglu GG (2021) Rethinking the campus transportation network in the scope of ecological design principles: case study of Izmir Katip Elebi University Ili Campus. Environ Sci Pollut R 28(36):50847–50866
Ortakavak Z, Cabuk SN, Cetin M, Senyel Kurkcuoglu MA, Cabuk A (2020) Determination of the nighttime light imagery for urban city population using DMSP-OLS methods in Istanbul. Environ Monit Assess 192(12):790
Pachavo G, Murwira A (2014) Remote sensing net primary productivity (NPP) estimation with the aid of GIS modelled shortwave radiation (SWR) in a Southern African Savanna. Int J Appl Earth Obs 30:217–226
Park JH, Gan JB, Park C (2021) Discrepancies between global forest net primary productivity estimates derived from MODIS and forest inventory data and underlying factors. Remote Sens 13(8):1441
Peng J, Hu X, Qiu S, Hu Y, Meersmans J, Liu Y (2019) Multifunctional landscapes identification and associated development zoning in mountainous area. Sci Total Environ 660(10):765–775
Potter CS, Randerson JT, Field CB, Matson PA, Vitousek PM, Mooney HA (1993) Terrestrial ecosystem production: a process model based on global satellite and surface data. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 7(4):811–841
Qu YB, Jiang GH, Li ZT, Tian YY, Wei SW (2019) Understanding rural land use transition and regional consolidation implications in China. Land Use Pol 82:742–753
Renwick A, Dynes R, Johnstone P, King W, Holt L, Penelope J (2022) Balancing the push and pull factors of land-use change: a New Zealand case study. Reg Environ Change 22(1):17
Ruimy A, Kergoat L, Bondeau A (1999) Comparing global models of terrestrial net primary productivity (NPP): analysis of differences in light absorption and light-use efficiency. Glob Change Biol 5:56–64
Schlenger AJ, Libralato S, Ballance LT (2019) Temporal variability of primary production explains marine ecosystem structure and function. Ecosystems 22(2):331–345
Schloss AL, Kicklighter DW, Kaduk J, Wittenberg U (1999) Comparing global models of terrestrial net primary productivity (NPP): comparison of NPP to climate and the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI). Glob Change Biol 5:25–34
Schoeneberger PJ, Wysocki DA (2005) Hydrology of soils and deep regolith: a nexus between soil geography, ecosystems and land management. Geoderma 126(1–2):117–128
Simic A, Chen JM, Liu J, Csillag F (2004) Spatial scaling of net primary productivity using subpixel information. Remote Sens Environ 93(1–2):246–258
Smith A (2010) Image segmentation scale parameter optimization and land cover classification using the Random Forest algorithm. J Spat Sci 55(1):69–79
Sun ZG, Sun CM, Yang Q, Li JL (2012) Effects of land use and land cover change on net primary productivity in small and medium-sized cities. Chin Agr Sci Bull 28(15):291–296
Tian YS, Qian J, Wang L (2021) Village classification in metropolitan suburbs from the perspective of urban-rural integration and improvement strategies: a case study of Wuhan, central China. Land Use Pol 111:105748
Ustaoglu E, Williams B, Petrov LO (2017) Scenario Analysis of alternative land development patterns for the Leipzig-Halle region: implications for transport-land-use sustainability. J Urban Plan 2(1):108–129
van Vliet J, Bregt AK, Hagen-Zanker A (2011) Revisiting Kappa to account for change in the accuracy assessment of land-use change models. Ecol Model 222(8):1367–1375
Varga OG, Pontius RG, Singh SK, Szabo S (2019) Intensity analysis and the figure of Merit’s components for assessment of a cellular automata—Markov simulation model. Ecol Indic 101:933–942
Wang Q, Wang HJ (2022b) An integrated approach of logistic-MCE-CA-Markov to predict the land use structure and their micro-spatial characteristics analysis in Wuhan metropolitan area. Central China Environ Sci Pollut 29(20):30030–30053
Wang Q, Wang HJ (2022c) Spatiotemporal dynamics and evolution relationships between land-use/land cover change and landscape pattern in response to rapid urban sprawl process: a case study in Wuhan, China. Ecol Eng 182:106716
Wang J, Chen YQ, Shao XM, Zhang YY, Cao YG (2012) Land-use changes and policy dimension driving forces in China: present, trend and future. Land Use Pol 29(4):737–749
Wang PJ, Xie DH, Zhou YY, Youhao E, Zhu QJ (2014) Estimation of net primary productivity using a process-based model in Gansu Province. Northwest Chin Environ Earth Sci 71(2):647–658
Wang Q, Wang HJ, Chang RH, Zeng HR, Bai XP (2022) Dynamic simulation patterns and spatiotemporal analysis of land-use/land-cover changes in the Wuhan metropolitan area, China. Ecol Model 464:109850
Wang Q, Wang HJ (2022a) Evaluation for the spatiotemporal patterns of ecological vulnerability and habitat quality: implications for supporting habitat conservation and healthy sustainable development. Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01328-3
Wang XC, Wang SD, Zhang HB (2013) Temporal and spatial patterns of NPP in Henan Province based on MOD17A3. Chin J Ecol 32(10):2797–2805
Wei YX, Wang LW (2014) Simulating alpine vegetation net primary productivity by remote sensing in Qinghai province, China. J Mt Sci 11(4):967–978
Woo B, Jun HJ (2020) Globalization and slums: How do economic, political, and social globalization affect slum prevalence? Habitat Int 98:102152
Wu LH, Wang SJ, Bai XY, Tian YC, Luo GJ, Wang JF, Li Q, Chen F, Deng YH, Yang YJ, Hu ZY (2020) Climate change weakens the positive effect of human activities on karst vegetation productivity restoration in southern China. Ecol Indic 115:106392
Yang Q, Zhang DJ (2021) The influence of agricultural industrial policy on non-grain production of cultivated land: a case study of the “one village, one product” strategy implemented in Guanzhong Plain of China. Land Use Pol 108:105579
Yang HF, Mu SJ, Li JL (2014) Effects of ecological restoration projects on land use and land cover change and its influences on territorial NPP in Xinjiang, China. CATENA 115:85–95
Yang H, Hu DD, Xu H, Zhong XN (2020) Assessing the spatiotemporal variation of NPP and its response to driving factors in Anhui province, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 27(13):14915–14932
Yang ZH, Shen NN, Qu YB, Zhang BL (2021) Association between rural land use transition and urban-rural integration development: from 2009 to 2018 based on county-level data in Shandong province, China. Land 10(11):1228
Ye SJ, Ren SY, Song CQ, Cheng CX, Shen S, Yang JY, Zhu DH (2022) Spatial patterns of county-level arable land productive-capacity and its coordination with land-use intensity in mainland China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 326:107757
Yeung HWC (2002) The limits to globalization theory: a geographic perspective on global economic change. Econ Geogr 78(3):285–305
Yu D, Shao HB, Shi PJ, Zhu WQ, Pan YZ (2009) How does the conversion of land cover to urban use affect net primary productivity? A case study in Shenzhen city, China. Agr Forest Meteorol 149(11):2054–2060
Zhang B, Wang HJ (2022a) Exploring the advantages of the maximum entropy model in calibrating cellular automata for urban growth simulation: a comparative study of four methods. Gisci Remote Sens 59(1):71–95
Zhang B, Wang HJ (2022b) A new type of dual-scale neighborhood based on vectorization for cellular automata models. Gisci Remote Sens 58(3):386–404
Zhang J, Wang TM, Ge JP (2015) Assessing vegetation cover dynamics induced by policy-driven ecological restoration and implication to soil erosion in Southern China. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0131352
Zhang R, Zhou Y, Luo HX, Wang FT, Wang SX (2017) Estimation and analysis of spatiotemporal dynamics of the net primary productivity integrating efficiency model with process model in Karst Area. Remote Sens 9(5):477
Zhang MX, Chen SL, Jiang H, Peng CH, Zhang JM, Zhou GM (2020a) The impact of intensive management on net ecosystem productivity and net primary productivity of a Lei bamboo forest. Ecol Model 439:109248
Zhang J, Zhang CH, Zhang AD, Fang MH, Wu MQ, Lin Z, Zhang YA (2020b) Song XL (2020) The relative effects of hydrothermal fluctuation and land cover change on NPP of vegetation in Northeast China. Acta Ecol Sin 40(21):7733–7744
Zhou Y, Li XH, Liu YS (2020) Land use change and driving factors in rural China during the period 1995–2015. Land Use Pol 99:105048
Zhou M, Yuan M, Huang YP, Lin KX (2021) Effects of institutions on spatial patterns of manufacturing industries and policy implications in metropolitan areas: a case study of Wuhan, China. Land 10(7):710
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42171411) and the Project Supported by the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Monitoring, Evaluation and Early Warning of Territorial Spatial Planning Implementation, Ministry of Natural Resources (LMEE-KF2021006).
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42171411) and the Project Supported by the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Monitoring, Evaluation and Early Warning of Territorial Spatial Planning Implementation, Ministry of Natural Resources (LMEE-KF2021006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Quan Wang contributed to conceptualization and methodology, software writing–original draft preparation. Haijun Wang contributed to formal analysis, review, editing, &validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Consent to publish
As a result of the research, we unanimously agree that this paper can be published in your journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, H. Spatiotemporal simulation of land-use/land cover scenarios and impacts on the dynamics of vegetation net primary productivity in the Wuhan metropolitan area, Central China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37, 1137–1162 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02328-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02328-6