Abstract
Introduction
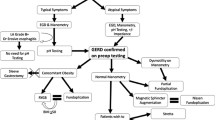
Zenker’s diverticulum (ZD) is a false pulsion diverticulum of the cervical esophagus. It is typically found in older adults and manifests with dysphagia. The purpose of this study is to describe our experience with Per-oral endoscopic myotomy for Zenker’s (Z-POEM) and intraoperative impedance planimetry (FLIP).
Methods
We performed a single institution retrospective review of patients undergoing Z-POEM in a prospective database between 2014 and 2022. Upper esophageal sphincter (UES) distensibility index (DI, mm2/mmHg) was measured by FLIP before and after myotomy. The primary outcome was clinical success. Secondary outcomes included technical failure, adverse events, and quality of life as assessed by the gastroesophageal health-related quality of life (GERD-HRQL), reflux severity index (RSI), and dysphagia score. A statistical analysis of DI was done with the paired t-test (p < 0.05).
Results
Fifty-four patients underwent Z-POEM, with FLIP measurements available in 30 cases. We achieved technical success and clinical success in 54/54 (100%) patients and 46/54 patients (85%), respectively. Three patients (6%) experienced contained leaks. Three patients were readmitted: one for aforementioned contained leak, one for dysphagia, and one post-operative pneumonia. Three patients with residual dysphagia underwent additional endoscopic procedures, all of whom had diverticula > 4 cm. Following myotomy, mean DI increased by 2.0 ± 1.7 mm2/mmHg (p < 0.001). In those with good clinical success, change in DI averaged + 1.6 ± 1.1 mm2/mmHg. Significant improvement was found in RSI and GERD-HRQL scores, but not dysphagia score.
Conclusion
Z-POEM is a safe and feasible for treatment of ZD. We saw zero cases of intraoperative abandonment. We propose that large diverticula (> 4 cm) are a risk factor for poor outcomes and may require additional endoscopic procedures. An improvement in DI is expected after myotomy, however, the ideal range is still not known.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang J, Novak S, Ujiki M, Hernandez O, Desai P, Benias P, Lee D, Chang K, Brieau B, Barret M, Kumta N, Zeng X, Hu B, Delis K, Khashab MA (2020) An international study on the use of peroral endoscopic myotomy in the management of Zenker’s diverticulum. Gastrointest Endosc 91:163–168
Law R, Katzka DA, Baron TH (2014) Zenker’s diverticulum. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:1773–1782
Sondhi AR, Watts LS, Baker JR, Law R (2019) Functional luminal imaging probe technology to assess response after flexible endoscopic Zenker diverticulotomy. VideoGIE 4:551–553
Calderon LF, Kline M, Hersh M, Shah KP, Kundu S, Tkaczuk A, McColloch N, Jain A (2022) The upper esophageal sphincter distensibility index measured using functional lumen imaging probe identifies defective barrier function of the upper esophageal sphincter. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 28:463–473
Zhang LY, Wu PI, Szczesniak M, Cook IJ, Craig PI (2021) Clinical utility of cricopharyngeal distensibility measurements during endoscopic myotomy for Zenker’s diverticulum. Gastrointest Endosc 93:390–397
Sondhi AR, Watts LS, Law R (2021) Changes in impedance planimetry metrics predict clinical response to flexible endoscopy in Zenker’s diverticulotomy. Endosc Int Open 9:E31–E34
Su B, Callahan ZM, Kuchta K, Linn JG, Haggerty SP, Denham W, Ujiki MB (2020) Use of impedance planimetry (EndoFLIP) in foregut surgery practice: experience of more than 400 cases. J Am Coll Surg 231:160–171
Zhang H, Huang S, Xia H, Shi L, Zeng X, Jiang J, Ren W, Peng Y, Lu M, Tang X (2022) The role of peroral endoscopic myotomy for Zenker’s diverticulum: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 36:2749–2759
Facciorusso A, Ramai D, Ichkhanian Y, Yadlapati R, Annese V, Wani S, Khashab MA (2022) Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of esophageal diverticula: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol 56:853–862
Ishaq S, Hassan C, Antonello A, Tanner K, Bellisario C, Battaglia G, Anderloni A, Correale L, Sharma P, Baron TH, Repici A (2016) Flexible endoscopic treatment for Zenker’s diverticulum: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 83(1076–1089):e1075
Crawley B, Dehom S, Tamares S, Marghalani A, Ongkasuwan J, Reder L, Ivey C, Amin M, Fritz M, Pitman M, Tulunay-Ugur O, Weissbrod P (2019) Adverse events after rigid and flexible endoscopic repair of zenker’s diverticula: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 161:388–400
Kahrilas PJ (2022) Retrograde upper esophageal sphincter function… and dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 34:14328
Regan J, Walshe M, Rommel N, Tack J, McMahon BP (2013) New measures of upper esophageal sphincter distensibility and opening patterns during swallowing in healthy subjects using EndoFLIP(R). Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:e25-e34
Kothari T, Stone J, Haber G (2013) Kothari Haber scoring system: Zenker’s diverticulum myotomy assessed with the help of new scoring system: 30. Off J Am Coll Gastroenterol 108:S11–S12
Funding
There was no funding or financial support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Michael B. Ujiki is a scientific advisory board member for Boston Scientific and Apollo, a consultant and speaker for WL Gore and Associates, and a speaker for Medtronic. Simon YW Che, Stephanie Joseph, Kristine Kuchta, Julia R. Amundson,Vanessa N. VanDruff, Shun Ishii, Christopher J. Zimmermann, Herbert M. Hedberg, Michael B. Ujiki have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This manuscript was accepted for an oral quick shot presentation at the 2023 Society or American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) Conference on March 30, 2023 in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Che, S.Y.W., Joseph, S., Kuchta, K. et al. Outcomes after per-oral endoscopic myotomy for Zenker’s diverticula (Z-POEM) and correlation with impedance planimetry (FLIP). Surg Endosc 38, 957–963 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10512-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10512-0