Abstract
Introduction
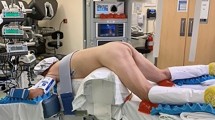
This study describes the experience with robot-assisted transanal minimally invasive surgery (rTAMIS) at a single institution. TAMIS has become a popular minimally invasive technique for local excision of well-selected rectal lesions. rTAMIS has been proposed as another option as it improves the ergonomics of conventional laparoscopic techniques.
Methods
Retrospective case series of patients with rectal lesions who underwent rTAMIS. Patient demographics, final pathology, surgical and admission details, and clinical outcomes were recorded. Successful procedures were defined as having negative margins on final pathology.
Results
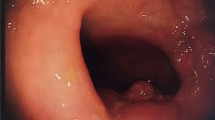
A total of 16 patients underwent rTAMIS by a single surgeon between April 2018 and December 2019. Mean age of patients was 63 years. Final pathologies were negative for tumor (n = 4), tubulovillous adenoma (n = 4), tubulovillous adenoma with high-grade dysplasia (n = 4), and invasive rectal adenocarcinoma (n = 4). 43% were located in the middle rectum and 56% were located in the distal rectum. Mean maximum diameter was 4.1 cm (IQR 2–3.1 cm). Negative margins were seen in 100% of the excision cases, and 100% were intact. Mean operative time was 87 min (IQR 54.8–97.3 min), and median length of stay was 0 days (IQR 0–1 days). Postoperative complications included incontinence (n = 1) and abscess formation (n = 2). rTAMIS provided curative treatment for 12/16 patients, and the remaining 4 patients received the appropriate standard of care for their respective pathologies.
Conclusions
Robot-assisted TAMIS is a safe alternative to laparoscopic TAMIS for resection of appropriate rectal polyps and early rectal cancers. rTAMIS may provide a modality for resecting larger or more proximal rectal lesions due to the wristed instruments and superior visualization with the robotic camera. Future studies should focus on comparing outcomes between robotic and laparoscopic TAMIS, and whether rTAMIS allows for the removal of larger, more complex lesions, which may save patients from a more morbid radical proctectomy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monson JRT, Weiser MR, Buie WD, Chang GJ, Rafferty JF (2013) Practice Parameters for the Management of Rectal Cancer (Revised). Dis Colon & Rectum 56(6):535–550
Buess G, Theiss R, Hutterer F, Pichlamaier H, Pelz C, Holfeld T, Isselhard W (1983) Transanal endoscopic surgery of the rectum - testing a new method in animal experiments [in German]. Leber Magen Darm 13(2):73–77
Buess G, Kipfmüller K, Ibald R et al (1988) Clinical results of transanal endoscopic microsurgery. Surg Endosc 2(4):245–250
Attalah S, Albert M, Larach S (2010) Transanal minimally invasive surgery: a giant leap forward. Surg Endosc 24:2200–2205
deBeche-Adams T, Nassif G (2015) Transanal Minimally Invasive Surgery. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 28:176–180
Lim SB, Seo SI, Lee JL, Kwak JY, Jang TY, Kim CW, Yoon YS, Yu CS, Kim JC (2012) Feasibility of Transanal Minimally Invasive Surgery for Mid-Rectal Lesions. Surg Endosc 26(11):3127–3132
Barendse RM, Doornebosch PG, Bemelman WA, Fockens P, Dekker E, de Graaf EJ (2012) Transanal employment of single access ports is feasible for rectal surgery. Ann Surg 256(6):1030–1033
Thompson EV, Bleier JIS (2017) Transanal Minimally Invasive Surgery. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 30:112–119
Attalah SB, Albert MR, DeBeche-Adams TH, Larach SW (2011) Robotic TransAnal Minimally Invasive Surgery in a cadaveric model. Tech Coloproctol 15(4):461–464
Hompes R, Rauh SM, Ris F, Tuynman JB, Mortensen NJ (2014) Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery for local excision of rectal neoplasms. Br J Surg 101(5):578–581
Tomassi MJ, Janos T, Yuhan R, Ruan JH, Klaristenfeld DD (2019) Robotic transanam minimally invasive surgery for the excision of rectal neoplasia: Clinical experience with 58 consecutive patients. Dis Colon Rectum 62:279–285
Keller DS, Tahilramani RN, Flores-Gonzalez JR, Mahmood A, Haas EM (2016) Transanal minimally invasive surgery: Review of indications and outcomes from 75 consecutive patients. J Am Coll 222(5):814–822
Martin-Perez B, Andrade-Ribeiro GD, Hunter L, Atallah, (2014) A systematic review of Transanal Minimally Invasive Surgery (TAMIS) from 2010–2013. Tech Coloproctol 18(9):775–788
McLemore EC, Weston LA, Coker AM, Jacobsen GR, Talamini MA, Horgan S, Ramamoorth SL (2014) Transanal Minimally Invasive Surgery for benign and malignant rectal neoplasia. Am J Surg 208(3):372–381
Rimonda R, Arezzo A, Arolfo S, Salvai A, Morino M (2013) TransAnal Minimally Invasive Surgery (TAMIS) with SILS Port versus Transanal Endoscopic Microsurgery (TEM): a comparative experimental study. Surg Endosc 27:3762–3786
Albert MR, Atallah SB, deBeche-Adams TC, Izfar S, Larach SW (2013) Transanal minimally invasive surgery (TAMIS) for local excision of benign neoplasms and early-stage rectal cancer: Efficacy and outcomes in the first 50 patients. Dis Colon Rectum 56(3):301–306
Lee L, Burke JP, DeBeche-Adams T, Nassif G, Martin-Perez B, Monson JRT, Albert MR, Attalah SB (2018) Transanal minimally invasive surgery for local excision of benign and malignant rectal neoplasia: outcomes from 200 consecutive cases with midterm follow up. Ann Surg 267(5):910–916
Huang YJ, Huan YM, Wang WL, Tong YS, Hsu W, Wei PL (2020) Surgical outcomes of robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery for selected rectal neoplasms: A single-hospital experience. Asian J Surg 43(1):290–296
Baik SH, Kwon HY, Kim JS, Hur H, Sohn SK, Cho HC, Kim H (2009) Robotic versus laparoscopic low anterior resection of rectal cancer: Short-term outcome of a prospective comparative study. Ann Surg Oncol 16:1480–1487
Van der Schatte Oliver RH, Van’t Hullenaar CD, Ruurda JP, Broeders IA, (2009) Ergonomics, user comfort, and performance in standard and robot-assissted laparoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 23:1365–1371
Tarr ME, Brancato SJ, Cunkelman JA, Polcari A, Nutter B, Kenton K (2015) Comparison of postural ergonomics between laparoscopic and robotic sacrocolpopexy: a pilot study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol 22:234–238
Lee SG, Russ AJ, Casillas MA Jr (2019) Laparsocopic transanal minimally invasive surgery (L-TAMIS) versus robotic TAMIS (R-TAMIS): short-term outcomes and costs of a comparative study. Surg Endosc 33:1981–1987
Lee GI, Lee MR, Clanton T, Sutton E, Park AE, Marohn MR (2013) Comparative assessment of physical and cognitive ergonomics associated with robotic and traditional laparscopic surgeries. Surg Endosc 28:456–465
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Karina W Lo, MD, David N Blitzer, MD, Sami Shoucair, MD, and David M Lisle, MD have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, K.W., Blitzer, D.N., Shoucair, S. et al. Robotic transanal minimally invasive surgery: a case series. Surg Endosc 36, 793–799 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-08257-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-08257-1