Abstract
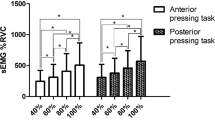
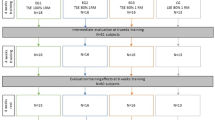
The activities of the suprahyoid muscles have been reported to be induced by tongue muscle contraction. The purpose of this research was to investigate whether tongue-strengthening exercises using a device cause hypertrophy of the geniohyoid muscle in healthy adults. Seven healthy young adults (3 men and 4 women, 21.0 ± 1.3 years old) received 8-week tongue muscle training with the JMS Tongue Pressure Measuring Device. The participants were instructed to press the anterior tongue against the hard palate 30 times in each session, three sessions a day, and 3 days a week. The exercise intensity was set to 60% of maximum tongue pressure in the first week, and to 80% of maximum tongue pressure for the remaining period. The training effect was evaluated by measuring (1) maximum tongue pressure value with the JMS Tongue Pressure Measuring Device, and (2) the area at rest, shortening amount, and contraction ratio of the geniohyoid muscle using ultrasonic imaging. After the 8-week training program, the maximum tongue pressure increased significantly from 44.9 to 61.6 kPa. The area of the geniohyoid muscle at rest also increased significantly from 2.3 to 2.6 cm2 after the program. There were no significant differences in the shortening amounts and the contraction ratios of the geniohyoid muscle between the values before and after the program. The tongue-strengthening exercise was useful to increase the muscle power of the geniohyoid, as well as the tongue muscles, in healthy young adults.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Hyoid movement during swallowing in older patients with dysphagia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127:1224–9.
Steele CM, Bailey GL, Chau T, Molfenter SM, Oshalla M, Waito AA, Zoratto DC. The relationship between hyoid and laryngeal displacement and swallowing impairment. Clin Otolaryngol. 2011;36:30–6.
Dodds WJ. Physiology of swallowing. Dysphagia. 1989;3:171–8.
Palmer JB. Bolus aggregation in the oropharynx does not depend on gravity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79:691–6.
Hori K, Srinivasan M, Barbezat C, Tamine K, Ono T, Müller F. Effect of lingual plates on generating intra-oral pressure during swallowing: an experimental study in healthy subjects. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-10-64.
McCormack J, Casey V, Conway R, Saunders J, Perry A. OroPress a new wireless tool for measuring oro-lingual pressures: a pilot study in healthy adults. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-015-0024-6.
McConnel FM. Analysis of pressure generation and bolus transit during pharyngeal swallowing. Laryngoscope. 1988;98:71–8.
Cerenko D, McConnel FM, Jackson RT. Quantitative assessment of pharyngeal bolus driving forces. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989;100:57–63.
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA, Kahrilas PJ, Smith CH. Temporal and biomechanical characteristics of oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older men. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43:1264–74.
Youmans SR, Youmans GL, Stierwalt JA. Differences in tongue strength across age and gender: is there a diminished strength reserve? Dysphagia. 2009;24:57–65.
Hara K, Tohara H, Kobayashi K, Yamaguchi K, Yoshimi K, Nakane A, Minakuchi S. Age-related declines in the swallowing muscle strength of men and women aged 20-89 years: a cross-sectional study on tongue pressure and jaw-opening force in 980 subjects. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2018;78:64–70.
Jahnke V. Dysphagia in the elderly. HNO. 1991;39:442–4.
Humbert IA, Robbins J. Dysphagia in the elderly. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2008;19:853–66.
Ney DM, Weiss JM, Kind AJ, Robbins J. Senescent swallowing: impact, strategies, and interventions. Nutr Clin Pract. 2009;24:395–413.
Feng X, Todd T, Lintzenich CR, Ding J, Carr JJ, Ge Y, Browne JD, Kritchevsky SB, Butler SG. Aging-related geniohyoid muscle atrophy is related to aspiration status in healthy older adults. J Gerontol A. 2013;68:853–60.
Maeda K, Akagi J. Sarcopenia is an independent risk factor of dysphagia in hospitalized older people. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016;16:515–21.
Maeda K, Takaki M, Akagi J. Decreased skeletal muscle mass and risk factors of sarcopenic dysphagia: a prospective observational cohort study. J Gerontol A. 2017;72:1290–4.
Fujishima I, Fujiu-Kurachi M, Arai H, Hyodo M, Kagaya H, Maeda K, Mori T, Nishioka S, Oshima F, Ogawa S, Ueda K, Umezaki T, Wakabayashi H, Yamawaki M, Yoshimura Y. Sarcopenia and dysphagia: position paper by four professional organizations. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2019;19:91–7.
Wakabayashi H. Presbyphagia and sarcopenic dysphagia: association between aging, sarcopenia, and deglutition disorders. J Frailty Aging. 2014;3:97–103.
Steele CM, Bayley MT, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Nagy A, Namasivayam AM, Stokely SL, Wolkin T. A randomized trial comparing two tongue-pressure resistance training protocols for post-stroke dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2016;31:452–61.
Agrawal D, Kern M, Edeani F, Balasubramanian G, Hyngstrom A, Sanvanson P, Shaker R. Swallow strength training exercise for elderly: a health maintenance need. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;30:e13382. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13382.
Wakabayashi H, Matsushima M, Momosaki R, Yoshida S, Mutai R, Yodoshi T, Murayama S, Hayashi T, Horiguchi R, Ichikawa H. The effects of resistance training of swallowing muscles on dysphagia in older people: a cluster, randomized, controlled trial. Nutrition. 2018;48:111–6.
Shaker R, Kern M, Bardan E, Taylor A, Stewart ET, Hoffmann RG, Arndorfer RC, Hofmann C, Bonnevier J. Augmentation of deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter opening in the elderly by exercise. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:G1518–22.
Shaker R, Easterling C, Kern M, Nitschke T, Massey B, Daniels S, Grande B, Kazandjian M, Dikeman K. Rehabilitation of swallowing by exercise in tube-fed patients with pharyngeal dysphagia secondary to abnormal UES opening. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1314–22.
Robbins J, Gangnon RE, Theis SM, Kays SA, Hewitt AL, Hind JA. The effects of lingual exercise on swallowing in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:1483–9.
Robbins J, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, Taylor AJ. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88:150–8.
Steele CM, Bailey GL, Polacco RE, Hori SF, Molfenter SM, Oshalla M, Yeates EM. Outcomes of tongue-pressure strength and accuracy training for dysphagia following acquired brain injury. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013;15:492–502.
Rofes L, Arreola V, Romea M, Palomera E, Almirall J, Cabré M, Serra-Prat M, Clavé P. Pathophysiology of oropharyngeal dysphagia in the frail elderly. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;22:851–8.
Machida N, Tohara H, Hara K, Kumakura A, Wakasugi Y, Nakane A, Minakuchi S. Effects of aging and sarcopenia on tongue pressure and jaw-opening force. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17:295–301.
Easterling C, Grande B, Kern M, Sears K, Shaker R. Attaining and maintaining isometric and isokinetic goals of the Shaker exercise. Dysphagia. 2005;20:133–8.
Palmer PM, Luschei ES, Jaffe D, McCulloch TM. Contributions of individual muscles to the submental surface electromyogram during swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1999;42:1378–91.
Yoshida M, Groher ME, Crary MA, Mann GC, Akagawa Y. Comparison of surface electromyographic (sEMG) activity of submental muscles between the head lift and tongue press exercises as a therapeutic exercise for pharyngeal dysphagia. Gerodontology. 2007;24:111–6.
Palmer PM, Jaffe DM, McCulloch TM, Finnegan EM, Van Daele DJ, Luschei ES. Quantitative contributions of the muscles of the tongue, floor-of-mouth, jaw, and velum to tongue-to-palate pressure generation. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2008;51:828–35.
Yano J, Yamamoto-Shimizu S, Yokoyama T, Kumakura I, Hanayama K, Tsubahara A. Effects of anterior tongue strengthening exercises on posterior tongue strength in healthy young adults. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;98:238–42.
Shimizu S, Hanayama K, Metani H, Sugiyama T, Abe H, Seki S, Hiraoka T, Tsubahara A. Retest reliability of ultrasonic geniohyoid muscle measurement. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci. 2016;7:55–60.
Kim Y, McCullough GH. Maximum hyoid displacement in normal swallowing. Dysphagia. 2008;23:274–9.
Sia I, Carvajal P, Carnaby-Mann GD, Crary MA. Measurement of hyoid and laryngeal displacement in video fluoroscopic swallowing studies: variability, reliability, and measurement error. Dysphagia. 2012;27:192–7.
Inamoto Y, Saitoh E, Okada S, Kagaya H, Shibata S, Ota K, Baba M, Fujii N, Katada K, Wattanapan P, Palmer JB. The effect of bolus viscosity on laryngeal closure in swallowing: kinematic analysis using 320-row area detector CT. Dysphagia. 2013;28:33–42.
Hsiao MY, Chang YC, Chen WS, Chang HY, Wang TG. Application of ultrasonography in assessing oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38:1522–8.
Macrae PR, Doeltgen SH, Jones RD, Huckabee ML. Intra- and inter-rater reliability for analysis of hyoid displacement measured with sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012;40:74–8.
Kraemer WJ, Fleck SJ, Evans WJ. Strength and power training: physiological mechanisms of adaptation. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1996;24:363–97.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of A. Matsushima, M. Tohda, M. Hara, and M. Tsuji.
Funding
This study was supported by the Kawasaki Foundation for Medical Science & Medical Welfare and the Kawasaki University of Medical Welfare Scientific Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JY contributed in conceiving study concept, analyzing data, and drafting manuscript. SYS and TY helped in conceiving the study concept, data collection, and interpretation. IK, KH, and AT conceived the study and supervised the whole project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Kawasaki University of Medical Welfare (No. 16-045), and all participants provided written, informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yano, J., Yamamoto-Shimizu, S., Yokoyama, T. et al. Effects of Tongue-Strengthening Exercise on the Geniohyoid Muscle in Young Healthy Adults. Dysphagia 35, 110–116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10011-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10011-2