Abstract
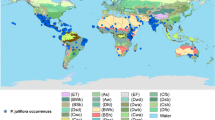
Procambarus clarkii is a notorious invasive species that has led to ecological concerns owing to its high viability and rapid reproduction. South Korea, a country exposed to a high risk of introduction of invasive species due to active international trade, has suffered from recent massive invasions by invasive species, necessitating the evaluation of potential areas requiring intensive monitoring. In this study, we developed two different types of species distribution models, CLIMEX and random forest, for P. clarkii using occurrence records from the United States. The potential distribution in the United States was predicted along coastal lines and inland regions located below 40°N latitude The model was then applied to evaluate the potential distribution in South Korea, and an ensemble map was constructed to identify the most vulnerable domestic regions. According to both models, the domestic potential distribution was highest in most areas located at low altitudes. In the ensemble model, most of the low-altitude western regions, the eastern coast, and some southern inland regions were predicted to be suitable for the distribution of P. clarkii, and a similar distribution pattern was predicted when the model was projected into the future climate. Through this study, it is possible to secure basic data that can be used for the early monitoring of the introduction and subsequent distribution of P. clarkii.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acharya BK, Chen W, Ruan Z, Pant GP, Yang Y, Shah LP, Cao C, Xu Z, Dhimal M, Lin H (2019) Mapping environmental suitability of scrub typhus in Nepal using MaxEnt and random forest models. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:4845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16234845
Al-Chokhachy R, Wenger SJ, Isaak DJ, Kershner JL (2013) Characterizing the thermal suitability of instream habitat for salmonids: a cautionary example from the Rocky Mountains. Trans Am Fish Soc 142:793–801. https://doi.org/10.1080/00028487.2013.778900
Allouche O, Tsoar A, Kadmon R (2006) Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). J Appl Ecol 43:1223–1232. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2006.01214.x
Araújo MB, New M (2007) Ensemble forecasting of species distributions. Trends Ecol Evol 22:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2007.06.010
Archer KJ, Kimes RV (2008) Empirical characterization of random forest variable importance measures. Comput Stat Data Anal 52:2249–2260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2008.04.015
Baines O, Chung A, Raval R (2020) Random forest classification algorithm. Leic Undergrad Math J 2.
Baltensperger AP, Huettmann F (2015) Predicted shifts in small mammal distributions and biodiversity in the altered future environment of Alaska: an open access data and machine learning perspective. PLoS ONE 10:e0132054. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132054
Barbet-Massin M, Rome Q, Villemant C, Courchamp F (2018) Can species distribution models really predict the expansion of invasive species? PLoS ONE 13:e0193085. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193085
Blank GS, Figler MH (1996) Interspecific shelter competition between the sympatric crayfish species Procambarus clarkii (Girard) and Procambarus zonangulus (Hobbs and Hobbs). J Crustac Biol 16:300–309. https://doi.org/10.1163/193724096X00108
Boria RA, Olson LE, Goodman SM, Anderson RP (2014) Spatial filtering to reduce sampling bias can improve the performance of ecological niche models. Ecol Modell 275:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.12.012
Brown JL (2014) SDM toolbox: a python-based GIS toolkit for landscape genetic, biogeographic and species distribution model analyses. Methods Ecol Evol 5:694–700. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210x.12200
Byeon DH, Kim SH, Jung JM, Jung S, Kim KH, Lee WH (2021) Climate-based ensemble modelling to evaluate the global distribution of Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky). Agric for Entomol 23:569–583. https://doi.org/10.1111/afe.12462
CABI (Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International) (2021) Procambarus clarkii. In: Invasive Species Compendium. Wallingford: CAB International. https://www.cabi.org/isc. Accessed 12 Mar 2021
Capinha C, Anastacio P, Tenedorio JA (2012) Predicting the impact of climate change on the invasive decapods of the Iberian inland waters: an assessment of reliability. Biol Invasions 14:1737–1751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0187-z
Castillo-Escriva A, Mestre A, Monrós JS, Mesquita-Joanes F (2013) Population dynamics of an epibiont Ostracoda on the invasive red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii in a western Mediterranean wetland. Hydrobiologia 714:217–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1542-5
Chen S, Wu J, Malone RF (1995) Effects of temperature on mean molt interval, molting and mortality of red swamp crawfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquaculture 131:205–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(94)00327-K
Choi JY, Kim SK, Kim JC, Yun JH (2021) Invasion and dispersion of the exotic species Procambarus clarkii (Decapoda Cambaridae) in Yeongsan River Basin, South Korea. Animals 11:3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123489
Chucholl C (2011) Population ecology of an alien “warm water” crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in a new cold habitat. Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosyst 401:29. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2011053
Croll SL, Watts SA (2004) The effect of temperature on feed consumption and nutrient absorption in Procambarus clarkii and Procambarus zonangulus. J World Aquac Soc 35:478–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2004.tb00113.x
Cruz MJ, Rebelo R (2007) Colonization of freshwater habitats by an introduced crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, in Southwest Iberian Peninsula. Hydrobiologia 575:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0376-9
Daniels WH, D’Abramo LR, Graves KF (1994) Ovarian development of female red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) as influenced by temperature and photoperiod. J Crust Biol 14:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1163/193724094x00100
Dong C, Bai S, Du L (2015) Temperature regulates circadian rhythms of immune responses in red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45:641–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.05.025
Egly RM, Larson ER (2018) Distribution, habitat associations, and conservation status updates for the pilose crayfish Pacifastacus gambelii (Girard, 1852) and Snake River pilose crayfish Pacifastacus connectens (Faxon, 1914) of the western United States. PeerJ 6:e5668. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5668
Ejigu D, Tassie N (2020) Present and future suitability of the Lake Tana Biosphere Reserve in Ethiopia for the Nile monitor (Varanus niloticus) using the MaxEnt model. Environ Syst Res 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-020-00197-y
Espina S, Herrera FD (1993) Preferred and avoided temperatures in the crawfish Procambarus clarkii (Decapoda, Cambaridae). J Therm Biol 18:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4565(93)90039-V
Evans JS, Murphy MA, Holden ZA, Cushman SA (2011) Modeling species distribution and change using random forest. In: Drew CS, Wiersma YF, Huettmann F (eds) Predictive species and habitat modeling in landscape ecology. Springer, New York, pp 139–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-7390-0_8
Fick SE, Hijmans RJ (2017) WorldClim 2: new 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 37:4302–4315. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5086
Finch DM, Butler JL, Runyon JB, Fettig CJ, Kilkenny FF, Jose S, Frankel SJ, Cushman SA, Cobb RC, Dukes JS, Hicke JA, Amelon SK (2021) Effects of climate change on invasive species. In: Poland TM, Patel-Weynand T, Finch DM, Miniat CF, Hayes DC, Lopez VM (eds) Invasive species in forests and rangelands of the United States. Springer, Berlin, pp 57–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45367-1
GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2021) GBIF Occurrence Download. https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.pkzfxa
Gherardi F (2006) Crayfish invading Europe: the case study of Procambarus clarkii. Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 39:175–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/10236240600869702
Gherardi F, Tricarico E, Ilhéu M (2002) Movement patterns of an invasive crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, in a temporary stream of southern Portugal. Ethol Ecol Evol 14:183–197. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2002.9522739
Gil-Sanchez JM, Alba-Tercedor J (2002) Ecology of the native and introduced crayfishes Austropotamobius pallipes and Procambarus clarkii in southern Spain and implications for conservation of the native species. Biol Conserv 105:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3207(01)00205-1
Grenouillet G, Buisson L, Casajus N, Lek S (2011) Ensemble modelling of species distribution: the effects of geographical and environmental ranges. Ecography 34:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2010.06152.x
Haubrock PJ, Inghilesi AF, Mazza G, Bendoni M, Solari L, Tricarico E (2019) Burrowing activity of Procambarus clarkii on levees: analysing behaviour and burrow structure. Wetl Ecol Manag 27:497–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-019-09674-3
Hellmann JJ, Byers JE, Bierwagen BG, Dukes JS (2008) Five potential consequences of climate change for invasive species. Conserv Biol 22:534–543. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2008.00951.x
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol J Rl Meteorol Soc 25:1965–1978. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1276
Hill MP, Axford JK, Hoffmann AA (2014) Predicting the spread of Aedes albopictus in Australia under current and future climates: multiple approaches and datasets to incorporate potential evolutionary divergence. Aust Ecol 39:469–478. https://doi.org/10.1111/aec.12105
Holdich DM, Reynolds JD, Souty-Grosset C, Sibley PJ (2009) A review of the ever increasing threat to European crayfish from non-indigenous crayfish species. Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosyst 11:394–395. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2009025
Huner JV (2002) Procambarus. In: Holdich DM (ed) Biology of freshwater crayfish. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 541–584
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) (2010) Invasive species and climate change form a ‘deadly duo’, warn top scientists. https://www.iucn.org/content/invasive-species-and-climate-change-form-%E2%80%98deadly-duo%E2%80%99-warn-top-scientists. Accessed 6 Apr 2021
Kaiser BA, Burnett KM (2010) Spatial economic analysis of early detection and rapid response strategies for an invasive species. Resour Energy Econ 32:566–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reseneeco.2010.04.007
Kawai T, Kobayashi Y (2005) Origin and current distribution of the alien crayfish, Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) in Japan. Crustaceana 78:1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685400577536103
Kim JM, Kil JH, Kim WM, Seo JH, Shin HC, Kim WH, Ban JY, Kim UG, Lee JY, Go GS, Park SH, Oh HS (2006) A study of detailed survey on invasive alien species in Korea and designation of invasive alien species in foreign countries. National Institute of Environmental Research. Korea
Kim S, Baek HJ, Yang GB (2019) Report on settlement of alien species red swamp crawfish (Procambarus clarkii) in Korea. Korean J Ecol Environ 52:333–339. https://doi.org/10.11614/KSL.2019.52.4.333
Kim SH, Kim DE, Lee H, Jung S, Lee WH (2021) Ensemble evaluation of the potential risk areas of yellow-legged hornet distribution. Environ Monit Assess 193:601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09406-2
Kirschbaum D, Stanley T, Yatheendradas S (2016) Modeling landslide susceptibility over large regions with fuzzy overlay. Landslides 13:485–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0577-2
KNSDIP (Korea National Spatial Data Infrastructure Portal) (2021). https://www.nsdi.go.kr. Accessed 15 Feb 2021
Kramer-Schadt S, Niedballa J, Pilgrim JD, Schröder B, Lindenborn J, Reinfelder V, Stillfried M, Heckmann I, Scharf AK, Augeri DM, Cheyne SM, Hearn AJ, Ross J, Macdonald DW, Mathai J, Eaton J, Marshall AJ, Semiadi G, Rustam R, Bernard H, Alfred R, Samejima H, Duckworth JW, Breitenmoser-Wuersten C, Belant JL, Hofer H, Wilting A (2013) The importance of correcting for sampling bias in MaxEnt species distribution models. Divers Distrib 19:1366–1379. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12096
Kriticos DJ, Maywald GF, Yonow T, Zurcher EJ, Herrmann NI, Sutherst RW (2015) CLIMEX, Version 4. Exploring the effects of climate on plants, animals and diseases. CISRO, Canberra
Kumar S, Neven LG, Zhu H, Zhang R (2015) Assessing the global risk of establishment of Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) using CLIMEX and MaxEnt niche models. J Econ Entomol 108:1708–1719. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/tov166
Lee DS, Park YS (2019) Evaluation of potential distribution area of the red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkia) in South Korea. Korean J Ecol Environ 52:340–347. https://doi.org/10.11614/KSL.2019.52.4.340
Lee WH, Jung JM, Lee HS, Lee JH, Jung S (2021) Evaluating the invasion risk of longhorn crazy ants (Paratrechina longicornis) in South Korea using spatial distribution model. J Asia-Pac Entomol 24:279–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2021.01.007
Lobo JM, Jiménez-Valverde A, Real R (2008) AUC: a misleading measure of the performance of predictive distribution models. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 17:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2007.00358.x
Lo Parrino E, Falaschi M, Manenti R, Ficetola GF (2023) All that changes is not shift: methodological choices influence niche shift detection in freshwater invasive species. Ecography 2023:e06432. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.06432
Loureiro TG, Anastácio PM, Bueno SL, Araujo PB, Souty-Grosset C, Almerão MP (2015) Distribution, introduction pathway, and invasion risk analysis of the North American crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Decapoda: Cambaridae) in Southeast Brazil. J Crust Biol 35:88–96
Marini MÂ, Barbet-Massin M, Lopes LE, Jiguet F (2010) Predicting the occurrence of rare Brazilian birds with species distribution models. J Ornithol 151:857–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10336-010-0523-y
Mehta SV, Haight RG, Homans FR, Polasky S, Venette RC (2007) Optimal detection and control strategies for invasive species management. Ecol Econ 61:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.10.024
Miller J (2010) Species distribution modeling. Geogr Compass 4:490–509. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-8198.2010.00351.x
Norallahi M, Seyed Kaboli H (2021) Urban flood hazard mapping using machine learning models: GARP, RF, MaxEnt and NB. Nat Hazards 106:119–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04453-3
Nori J, Rojas-Soto O (2019) On the environmental background of aquatic organisms for ecological niche modeling: a call for caution. Aquatic Ecol 53:595–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-019-09711-6
Park CW, Kim JW, Cho YJ, Kim JG, Lee MJ, Kim SH (2020) Distribution of invasive alien species red swamp crawfish (Procambarus clarkii) in Korea. Korean Soc Limnol 53:331–335. https://doi.org/10.11614/KSL.2020.53.4.331
Parmesan C (2006) Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 37:637–669. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.37.091305.110100
Pattison RR, Mack RN (2008) Potential distribution of the invasive tree Triadica sebifera (Euphorbiaceae) in the United States: evaluating CLIMEX predictions with field trials. Glob Chang Biol 14:813–826. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01528.x
Pearce J, Ferrier S (2000) Evaluating the predictive performance of habitat models developed using logistic regression. Ecol Modell 133:225–245
Peiró DF, Almerão MP, Delaunay C, Jussila J, Makkonen J, Bouchon D, Araujo PB, Souty-Grosset C (2016) First detection of the crayfish plague pathogen Aphanomyces astaci in South America: a high potential risk to native crayfish. Hydrobiologia 781:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2841-4
Preau C, Trochet A, Bertrand R, Isselin-Nondereu F (2018) Modeling potential distributions of three European amphibian species comparing ENFA and Maxent. Herpetol Conserv Biol 13:91–104
Rahel FJ, Olden JD (2008) Assessing the effects of climate change on aquatic invasive species. Conserv Biol 22:521–533. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2008.00950.x
Reynolds JD (2002) Growth and reproduction. In: Holdich DM (ed) Biology of freshwater crayfish. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 541–584
Rodriguez-Galiano V, Sanchez-Castillo M, Chica-Olmo M, Chica-Rivas MJOGR (2015) Machine learning predictive models for mineral prospectivity: an evaluation of neural networks, random forest, regression trees and support vector machines. Ore Geol Rev 71:804–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.01.001
Shabani F, Kumar L, Ahmadi M (2016) A comparison of absolute performance of different correlative and mechanistic species distribution models in an independent area. Ecol Evol 6:5973–5986. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.2332
Song HR, Kim NY, Kim SH, Kim DE, Lee DH, Choi DR, Sim S (2018) Investigating ecological risk of alien species (V). National Institute of Ecology, Seocheon
Srivastava V, Lafond V, Griess VC (2019) Species distribution models (SDM): applications, benefits and challenges in invasive species management. CAB Rev 14:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1079/PAVSNNR201914020
Stein BA, Flack SR (1996) America’s least wanted: Alien Species Invasions of U.S. Ecosystems. The Nature Conservancy, Arlington, Virginia
Sutherst RW, Bottomley W, Yonow T, Maywald GF (2004) Use of CLIMEX in pest risk analysis for quarantine. CABI, Wallingford
Tebaldi C, Debeire K, Eyring V, Fischer E, Fyfe J, Friedlingstein P, Knutti R, Lowe J, O’Neill B, Sanderson B, van Vuuren D, Riahi K, Meinshausen M, Nicholls Z, Tokarska KB, Hurtt G, Kriegler E, Lamarque JF, Meehl G, Moss R (2021) Climate model projections from the scenario model intercomparison project (ScenarioMIP) of cmip6. Earth Syst Dyn 12:253–293. https://doi.org/10.5194/esd-12-253-2021
Zhang Z, Capinha C, Usio N, Weterings R, Liu X, Li Y, Landeria J, Zhou Q, Yokota M (2020) Impacts of climate change on the global potential distribution of two notorious invasive crayfishes. Freshw Biol 65:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13429
Zhang Y, Tang J, Ren G, Zhao K, Wang X (2021) Global potential distribution prediction of Xanthium italicum based on Maxent model. Sci Rep 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96041-
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) through Exotic Invasive Species Management Program, funded by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (2018002270005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DB and WHL conceived the ideas and designed the manuscript. DB conducted the analysis and wrote the manuscript. WHL gave conceptual advices and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed critically to the drafts and gave final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Donald DeAngelis .
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Byeon, Dh., Lee, WH. Ensemble evaluation of potential distribution of Procambarus clarkii using multiple species distribution models. Oecologia 204, 589–601 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-024-05516-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-024-05516-z