Abstract
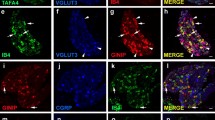
Recent studies demonstrated the expression of the insulin receptor (InsR) and its functional interaction with the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 receptor (TRPV1) in primary sensory neurons (PSNs). The present study was undertaken to reveal the target-specific expression of the InsR and its co-localization with the TRPV1 in rat PSNs. We assessed the localization of the InsR and its co-localization with the TRPV1 in PSNs retrogradely labelled with biotin-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin injected into the dorsal hind paw skin, the gastrocnemius muscle, the pancreas and the urinary bladder wall. The largest proportions of retrogradely labelled InsR-immunoreactive neurons were identified among PSNs serving the pancreas (~ 54%) and the urinary bladder (~ 53%). The proportions of retrogradely labelled InsR-immunoreactive neurons innervating the dorsal hind paw skin and the gastrocnemius muscle amounted to ~ 22 and ~ 21%. TRPV1-immunoreactive neurons amounted to ~ 63, ~ 62, ~ 67 and ~ 65% of retrogradely labelled cutaneous, muscle, pancreatic and urinary bladder PSNs, respectively. Co-localization of the TRPV1 with the InsR was observed in ~ 16, ~ 15, ~ 29 and ~ 30% of retrogradely labelled cutaneous, muscle, pancreatic and urinary bladder PSNs. These quantitative immunohistochemical data demonstrate a preponderance of InsR-immunoreactivity among PSNs, which innervate visceral targets. The present findings suggest that visceral spinal PSNs are more likely to be exposed to the modulatory effects of insulin on sensory functions, including neurotrophic, nociceptive and inflammatory processes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baiou D, Sántha P, Avelino A, Charrua A, Bacskai T, Matesz K, Cruz F, Nagy I (2007) Neurochemical characterization of insulin receptor-expressing primary sensory neurons in wild-type and vanilloid type 1 transient receptor potential receptor knockout mice. J Comp Neurol 503:334–347
Barber AJ, Nakamura M, Wolpert EB, Reiter CE, Seigel GM, Antonetti DA, Gardner TW (2001) Insulin rescues retinal neurons from apoptosis by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-mediated mechanism that reduces the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem 276:32814–32821
Buck SH, Burks TF (1986) The neuropharmacology of capsaicin: review of some recent observations. Pharmacol Rev 38:179–226
Caterina MJ, Julius D (2001) The vanilloid receptor: a molecular gateway to the pain pathway. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:487–517
Cesare P, Dekker LV, Sardini A, Parker PJ, McNaughton PA (1999) Specific involvement of PKC-epsilon in sensitization of the neuronal response to painful heat. Neuron 23:617–624
Chuang HH, Prescott ED, Kong H, Shields S, Jordt SE, Basbaum AI, Chao MV, Julius D (2001) Bradykinin and nerve growth factor release the capsaicin receptor from PtdIns(4,5)P2-mediated inhibition. Nature 411:957–962
Dux M, Rosta J, Pintér S, Sántha P, Jancsó G (2007) Loss of capsaicin-induced meningeal neurogenic sensory vasodilatation in diabetic rats. Neuroscience 150:194–201
Fernyhough P, Willars GB, Lindsay RM, Tomlinson DR (1993) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I enhance regeneration in cultured adult rat sensory neurones. Brain Res 607:117–124
Figlewicz DP (2016) Expression of receptors for insulin and leptin in the ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra (VTA/SN) of the rat: historical perspective. Brain Res 1645:68–70
Gamse R, Petsche U, Lembeck F, Jancsó G (1982) Capsaicin applied to peripheral nerve inhibits axoplasmic transport of substance P and somatostatin. Brain Res 239:447–462
Gamse R, Posch M, Saria A, Jancsó G (1987) Several mediators appear to interact in neurogenic inflammation. Acta Physiol Hung 69:343–354
Geetha T, Rege SD, Mathews SE, Meakin SO, White MF, Babu JR (2013) Nerve growth factor receptor TrkA, a new receptor in insulin signaling pathway in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 288:23807–23813
Gram DX, Ahrén B, Nagy I, Olsen UB, Brand CL, Sundler F, Tabanera R, Svendsen O, Carr RD, Sántha P, Wierup N, Hansen AJ (2007) Capsaicin-sensitive sensory fibers in the islets of Langerhans contribute to defective insulin secretion in Zucker diabetic rat, an animal model for some aspects of human type 2 diabetes. Eur J Neurosci 25:213–223
Heidenreich KA, Toledo SP, Brunton LL, Watson MJ, Daniel-Issakani S, Strulovici B (1990) Insulin stimulates the activity of a novel protein kinase C, PKC-epsilon, in cultured fetal chick neurons. J Biol Chem 265:15076–15082
Holzer P (1991) Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanisms of action, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons. Pharmacol Rev 43:143–201
Iwasaki Y, Shimomura K, Kohno D, Dezaki K, Ayush EA, Nakabayashi H, Kubota N, Kadowaki T, Kakei M, Nakata M, Yada T (2013) Insulin activates vagal afferent neurons including those innervating pancreas via insulin cascade and Ca2+ influx: its dysfunction in IRS2-KO mice with hyperphagic obesity. PLoS One 8:e67198
Jancsó G, Maggi CA (1987) Distribution of capsaicin-sensitive urinary bladder afferents in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res 418:371–376
Jancsó N, Jancsó-Gábor A, Szolcsányi J (1967) Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 31:138–151
Jancsó G, Kiraly E, Jancsó-Gábor A (1977) Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurones. Nature 270:741–743
Kebapci N, Yenilmez A, Efe B, Entok E, Demirustu C (2007) Bladder dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients. Neurourol Urodyn 26:814–819
Lázár BA, Jancsó G, Oszlács O, Nagy I, Sántha P (2018) The insulin receptor is colocalized with the TRPV1 nociceptive ion channel and neuropeptides in pancreatic spinal and vagal primary sensory neurons. Pancreas 47:110–115
Maggi CA, Meli A (1988) The sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol 19:1–43
Maggi CA, Lecci A, Santicioli P, Del Bianco E, Giuliani S (1993) Cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in rats: involvement of capsaicin-sensitive primary afferents. Agents Actions 38 Spec No:C28–C30
Michael GJ, Priestley JV (1999) Differential expression of the mRNA for the vanilloid receptor subtype 1 in cells of the adult rat dorsal root and nodose ganglia and its downregulation by axotomy. J Neurosci 19:1844–1854
Nagy I, Sántha P, Jancsó G, Urbán L (2004) The role of the vanilloid (capsaicin) receptor (TRPV1) in physiology and pathology. Eur J Pharmacol 500:351–369
Nathan JD, AA P, McVey DC, Thomas JE, Prpic V, Vigna SR, RA L (2001) Capsaicin vanilloid receptor-1 mediates substance P release in experimental pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G1322–G1328
Peyronnard JM, Charron LF, Lavoie J, Messier JP (1986) Motor, sympathetic and sensory innervation of rat skeletal muscles. Brain Res 373:288–302
Razavi R, Chan Y, Afifiyan FN, Liu XJ, Wan X, Yantha J, Tsui H, Tang L, Tsai S, Santamaria P, Driver JP, Serreze D, Salter MW, Dosch HM (2006) TRPV1+ sensory neurons control β cell stress and islet inflammation in autoimmune diabetes. Cell 127:1123–1135
Recio-Pinto E, Ishii DN (1988) Insulin and related growth factors: effects on the nervous system and mechanism for neurite growth and regeneration. Neurochem Int 12:397–414
Recio-Pinto E, Lang FF, Ishii DN (1984) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II permit nerve growth factor binding and the neurite formation response in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81:2562–2566
Recio-Pinto E, Rechler MM, Ishii DN (1986) Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II, and nerve growth factor on neurite formation and survival in cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. J Neurosci 6:1211–1219
Salem N, Dunbar JC (2002) The insulin-mediated vascular and blood pressure responses are suppressed in CGRP-deficient normal and diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 18:238–244
Sántha P, Nagy I (2006) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I induce thermo-sensitive ionic currents in capsaicin-sensitive primary sensory neuron. FENS Forum Abstr 3
Santicioli P, Gamse R, Maggi CA, Meli A (1987) Cystometric changes in the early phase of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats: evidence for sensory changes not correlated to diabetic neuropathy. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 335:580–587
Sathianathan V, Avelino A, Charrua A, Sántha P, Matesz K, Cruz F, Nagy I (2003) Insulin induces cobalt uptake in a subpopulation of rat cultured primary sensory neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18:2477–2486
Schwartz ES, La J-H, Scheff NN, Davis BM, Albers KM, Gebhart GF (2013) TRPV1 and TRPA1 antagonists prevent the transition of acute to chronic inflammation and pain in chronic pancreatitis. J Neurosci 33:5603–5611
Singh B, Xu Y, McLaughlin T, Singh V, Martinez JA, Krishnan A, Zochodne DW (2012) Resistance to trophic neurite outgrowth of sensory neurons exposed to insulin. J Neurochem 121:263–276
Snider WD, McMahon SB (1998) Tackling pain at the source: new ideas about nociceptors. Neuron 20:629–632
Stella SLJ, Bryson EJ, Thoreson WB (2001) Insulin inhibits voltage-dependent calcium influx into rod photoreceptors. Neuroreport 12:947–951
Sugimoto K, Murakawa Y, Zhang W, Xu G, Sima AA (2000) Insulin receptor in rat peripheral nerve: its localization and alternatively spliced isoforms. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 16:354–363
Sugimoto K, Murakawa Y, Sima AAF (2002) Expression and localization of insulin receptor in rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord. J Peripher Nerv Syst 7:44–53
Swett JE, Torigoe Y, Elie VR, Bourassa CM, Miller PG (1991) Sensory neurons of the rat sciatic nerve. Exp Neurol 114:82–103
Takamido S, Kataoka Y, Tanano A, Cui Y, Ikeura T, Shimatani M, Kubota Y, Okazaki K, Yamada H (2006) Intrapancreatic axonal hyperbranching of dorsal root ganglia neurons in chronic pancreatitis model rats and its relation to pancreatic pain. Pancreas 33:268–279
Tsui H, Razavi R, Chan Y, Yantha J, Dosch HM (2007) “Sensing” autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. Trends Mol Med 13:405–413
Wan Q, Xiong ZG, Man HY, Ackerley CA, Braunton J, Lu WY, Becker LE, MacDonald JF, Wang YT (1997) Recruitment of functional GABA(A) receptors to postsynaptic domains by insulin. Nature 388:686–690
Wick EC, Hoge SG, Grahn SW, Kim E, Divino LA, Grady EF, Bunnett NW, Kirkwood KS (2006) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and substance P mediate nociception in acute pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G959–G969
Won MH, Park HS, Jeong YG, Park HJ (1998) Afferent innervation of the rat pancreas: retrograde tracing and immunohistochemistry in the dorsal root ganglia. Pancreas 16:80–87
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office (GINOP-2.3.2-15.2016-00034). B.A. Lázár was supported by the UNKP-17-3 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities and the TÁMOP 4.2.4.A/2-11/1-2012-0001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which studies were conducted (Ethics Committee for Animal Care at the University of Szeged—Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes and the Guidelines of the Committee for Research.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lázár, B.A., Jancsó, G., Nagy, I. et al. The insulin receptor is differentially expressed in somatic and visceral primary sensory neurons. Cell Tissue Res 374, 243–249 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2868-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2868-0