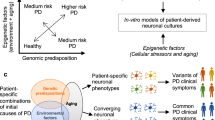
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease and its pathogenic mechanisms are poorly understood. The majority of PD cases are sporadic but a number of genes are associated with familial PD. Sporadic and familial PD have many molecular and cellular features in common, suggesting some shared pathogenic mechanisms. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have been derived from patients harboring a range of different mutations of PD-associated genes. PD patient-derived iPSCs have been differentiated into relevant cell types, in particular dopaminergic neurons and used as a model to study PD. In this review, we describe how iPSCs have been used to improve our understanding of the pathogenesis of PD. We describe what cellular and molecular phenotypes have been observed in neurons derived from iPSCs harboring known PD-associated mutations and what common pathways may be involved.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abud EM, Ramirez RN, Martinez ES, Healy LM, Nguyen CHH, Newman SA, Yeromin AV, Scarfone VM, Marsh SE, Fimbres C, Caraway CA, Fote GM, Madany AM, Agrawal A, Kayed R, Gylys KH, Cahalan MD, Cummings BJ, Antel JP, Mortazavi A, Carson MJ, Poon WW, Blurton-Jones M (2017) iPSC-derived human microglia-like cells to study neurological diseases. Neuron 94:278–293
Aflaki E, Borger DK, Moaven N, Stubblefield BK, Rogers SA, Patnaik S, Schoenen FJ, Westbroek W, Zheng W, Sullivan P, Fujiwara H, Sidhu R, Khaliq M, Lopez GJ, Goldstein DS, Ory DS, Marugan J, Sidransky E (2016) A new glucocerebrosidase chaperone reduces α-synuclein and glycolipid levels in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons from patients with gaucher disease and parkinsonism. J Neurosci 36:7441–7452
Alam ZI, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Marsden DC, Jenner P, Halliwell B (1997) A generalised increase in protein carbonyls in the brain in Parkinson’s but not incidental Lewy body disease. J Neurochem 69:1326–1329
Anglade P, Vyas S, Herrero MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC, Agid, Y. (1997) Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol Histopathol 12:25–31
Arrasate M, Finkbeiner S (2005) Automated microscope system for determining factors that predict neuronal fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:3840–3845
Arrasate M, Mitra S, Schweitzer ES, Segal MR, Finkbeiner S (2004) Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature 431:805–810
Banati RB, Daniel SE, Blunt SB (1998) Glial pathology but absence of apoptotic nigral neurons in long-standing Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 13:221–227
Beilina A, Rudenko IN, Kaganovich A, Civiero L, Chau H, Kalia SK, Kalia LV, Lobbestael E, Chia R, Ndukwe K, Ding J, Nalls MA, Olszewski M, Hauser DN, Kumaran R, Lozano AM, Baekelandt V, Greene LE, Taymans JM, Greggio E, Cookson MR (2014) Unbiased screen for interactors of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 supports a common pathway for sporadic and familial Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:2626–2631
Bellucci A, Mercuri NB, Venneri A, Faustini G, Longhena F, Pizzi M, Missale C, Spano P (2016) Parkinson’s disease: from synaptic loss to connectome dysfunction. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 42:77–94
Bezard E, Yue Z, Kirik D, Spillantini MG (2013) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: limits and relevance to neuroprotection studies. Mov Disord 28:61–70
Blesa J, Trigo-Damas I, Quiroga-Varela A, Jackson-Lewis VR (2015) Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease. Front Neuroanat 9:91
Borgs L, Peyre E, Alix P, Hanon K, Grobarczyk B, Godin JD, Purnelle A, Krusy N, Maquet P, Lefebvre P, Seutin V, Malgrange B, Nguyen L (2016) Dopaminergic neurons differentiating from LRRK2 G2019S induced pluripotent stem cells show early neuritic branching defects. Sci Rep 6:33377
Bové J, Perier C (2012) Neurotoxin-based models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 211:51–76
Burré J (2015) The synaptic function of α-synuclein. J Parkinsons Dis 5:699–713
Byers B, Cord B, Nguyen HN, Schüle B, Fenno L, Lee PC, Deisseroth K, Langston JW, Pera RR, Palmer TD (2011) SNCA triplication Parkinson’s patient’s iPSC-derived DA neurons accumulate α-synuclein and are susceptible to oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 6:e26159
Chambers SM, Fasano CA, Papapetrou EP, Tomishima M, Sadelain M, Studer L (2009) Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat Biotechnol 27:275–280
Chang KH, Lee-Chen GJ, Wu YR, Chen YJ, Lin JL, Li M, Chen IC, Lo YS, Wu HC, Chen CM (2016) Impairment of proteasome and anti-oxidative pathways in the induced pluripotent stem cell model for sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Park Relat Disord 24:81–88
Chu Y, Dodiya H, Aebischer P, Olanow CW, Kordower JH (2009) Alterations in lysosomal and proteasomal markers in Parkinson’s disease: relationship to alpha-synuclein inclusions. Neurobiol Dis 35:385–398
Chung CY, Khurana V, Auluck PK, Tardiff, Daniel F, Mazzulli JR, Soldner F, Baru V, Lou Y, Freyzon Y, Cho S, Mungenast AE, Muffat J, Mitalipova M, Pluth MD, Jui NT, Schüle B, Lippard SJ, Tsai L, Krainc D, Buchwald SL, Jaenisch R, Lindquist S (2013) Identification and rescue of α-synuclein toxicity in Parkinson patient-derived neurons. Science 342:983–987
Chung SY, Kishinevsky S, Mazzulli JR, Graziotto J, Mrejeru A, Mosharov EV, Puspita L, Valiulahi P, Sulzer D, Milner TA, Taldone T, Krainc D, Studer L, Shim J (2016) Parkin and PINK1 patient iPSC-derived midbrain dopamine neurons exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction and α-synuclein accumulation. Stem Cell Reports 7:664–677
Cookson MR (2009) α-Synuclein and neuronal cell death. Mol Neurodegener 4:9
Cookson MR (2010) The role of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:791–797
Cooper O, Seo H, Andrabi S, Guardia-Laguarta C, Graziotto J, Sundberg M, McLean JR, Carrillo-Reid L, Xie Z, Osborn T, Hargus G, Deleidi M, Lawson T, Bogetofte H, Perez-Torres E, Clark L, Moskowitz C, Mazzulli J, Chen L, Volpicelli-Daley L, Romero N, Jiang H, Uitti RJ, Huang Z, Opala G, Scarffe LA, Dawson VL, Klein C, Feng J, Ross OA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Marder K, Surmeier DJ, Wszolek ZK, Przedborski S, Krainc D, Dawson TM, Isacson O. (2012) Pharmacological rescue of mitochondrial deficits in iPSC-derived neural cells from patients with familial Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med 4:141ra90
Cornacchia D, Studer L (2017) Back and forth in time: directing age in iPSC-derived lineages. Brain Res 1656:14–26
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2010) The role of parkin in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25:S32–S39
Dawson TM, Ko HS, Dawson VL (2010) Genetic animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 66:646–661
Deas E, Cremades N, Angelova PR, Ludtmann MHR, Yao Z, Chen S, Horrocks MH, Banushi B, Little D, Devine MJ, Gissen P, Klenerman D, Dobson CM, Wood NW, Gandhi S, Abramov AY (2016) Alpha-Synuclein oligomers interact with metal ions to induce oxidative stress and neuronal death in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 24:376–391
Dehay B, Bove J, Rodríguez-muela N, Perier C, Recasens A, Boya P, Vila M (2010) Pathogenic lysosomal depletion in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 30:12535–12544
Dettmer U, Newman AJ, Soldner F, Luth ES, Kim NC, von Saucken VE, Sanderson JB, Jaenisch R, Bartels T, Selkoe D (2015) Parkinson-causing α-synuclein missense mutations shift native tetramers to monomers as a mechanism for disease initiation. Nat Commun 6:7314
Dexter DT, Holley AE, Flitter WD, Slater TF, Wells FR, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1994) Increased levels of lipid hydroperoxides in the parkinsonian substantia nigra: an HPLC and ESR study. Mov Disord 9:92–97
Do CB, Tung JY, Dorfman E, Kiefer AK, Drabant EM, Francke U, Mountain JL, Goldman SM, Tanner CM, Langston JW, Wojcicki A, Eriksson N (2011) Web-based genome-wide association study identifies two novel loci and a substantial genetic component for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS Genet 7:e1002141
Douvaras P, Sun B, Wang M, Kruglikov I, Lallos G, Zimmer M, Terrenoire C, Zhang B, Gandy S, Schadt E, Freytes DO, Noggle S, Fossati V (2017) Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to microglia. Stem Cell Rep 8:1516–1524
Duke DC, Moran LB, Pearce RKB, Graeber MB (2007) The medial and lateral substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease: mRNA profiles associated with higher brain tissue vulnerability. Neurogenetics 8:83–94
Durcan TM, Fon EA (2015) The three “P”s of mitophagy: PARKIN, PINK1, and post-translational modifications. Genes Dev 29:989–999
Emamzadeh FN (2016) Alpha-synuclein structure, functions, and interactions. J Res Med Sci 21:29
Esteves AR, Cardoso SM (2017) LRRK2 at the crossroad between autophagy and microtubule trafficking: insights into Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858415616558
Farrer MJ (2006) Genetics of Parkinson disease: paradigm shifts and future prospects. Nat Rev Genet 7:306–318
Fernandes HJR, Hartfield EM, Christian HC, Emmanoulidou E, Zheng Y, Booth H, Bogetofte H, Lang C, Ryan BJ, Sardi SP, Badger J, Vowles J, Evetts S, Tofaris GK, Vekrellis K, Talbot K, Hu MT, James W, Cowley SA, Wade-Martins R (2016) ER stress and autophagic perturbations lead to elevated extracellular α-synuclein in GBA-N370S Parkinson’s iPSC-derived dopamine neurons. Stem Cell Rep 6:342–356
Finkbeiner S, Frumkin M, Kassner PD (2015) Cell-based screening: extracting meaning from complex data. Neuron 86:160–174
Frobel J, Hemeda H, Lenz M, Abagnale G, Joussen S, Denecke B, Šarić T, Zenke M, Wagner W (2014) Epigenetic rejuvenation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rep 3:414–422
Futerman AH, Hardy J (2016) Perspective: finding common ground. Nature 537:S160–S161
Gerhard A, Pavese N, Hotton G, Turkheimer F, Es M, Hammers A, Eggert K, Oertel W, Banati RB, Brooks DJ (2006) In vivo imaging of microglial activation with [11C](R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 21:404–412
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IVJ, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective α-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 290:985–989
Gillardon F (2009) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 phosphorylates brain tubulin-beta isoforms and modulates microtubule stability - a point of convergence in parkinsonian neurodegeneration? J Neurochem 110:1514–1522
Gómez-Suaga P, Fdez E, Fernández B, Martínez-Salvador M, Blanca Ramírez M, Madero-Pérez J, Rivero-Ríos P, Fuentes JM, Hilfiker S (2014) Novel insights into the neurobiology underlying LRRK2-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 85:45–56
González F, Stéphanie B, Izpisúa Belmonte JC (2011) Methods for making induced pluripotent stem cells: reprogramming à la carte. Nat Rev Genet 12:231–242
Good PF, Hsu A, Werner P, Perl DP, Olanow W (1998) Protein nitration in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:338–342
Haggarty SJ, Perlis RH (2014) Translation: screening for novel therapeutics with disease-relevant cell types derived from human stem cell models. Biol Psychiatry 75:952–960
Haston KM, Finkbeiner S (2016) Clinical trials in a dish: the potential of pluripotent stem cells to develop therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 56:489–510
Hatano Y, Li Y, Sato K, Asakawa S, Yamamura Y, Tomiyama H, Yoshino H, Asahina M, Kobayashi S, Hassin-Baer S, Lu CS, Ng AR, Rosales RL, Shimizu N, Toda T, Mizuno Y, Hattori N (2004) Novel PINK1 mutations in early-onset parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 56:424–427
Hattori N, Tanaka M, Ozawa T, Mizuno Y (1991) Immunohistochemical studies on complexes I, II, III, and IV of mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 30:563–571
Hendriks WT, Warren CR, Cowan CA (2016) Genome editing in human pluripotent stem cells: approaches, pitfalls, and solutions. Cell Stem Cell 18:53–65
Horvath S (2013) DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol 14:R115
Houlden H, Singleton AB (2012) The genetics and neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 124:325–338
Hsieh CH, Shaltouki A, Gonzalez AE, Bettencourt da Cruz A, Burbulla LF, St. Lawrence E, Schüle B, Krainc D, Palmer TD, Wang X (2016) Functional impairment in Miro degradation and mitophagy is a shared feature in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Cell Stem Cell 19:709–724
Hunot S, Dugas N, Faucheux B, Hartmann A, Tardieu M, Debre P, Agid Y, Dugas B, Hirsch EC (1999) Fcepsilon RII/CD23 is expressed in Parkinson’s disease and induces, in vitro, production of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in glial cells. J Neurosci 19:3440–3447
Imaizumi Y, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Koike M, Kuzumaki N, Hayakawa H, Nihira T, Kobayashi T, Ohyama M, Sato S, Takanashi M, Funayama M, Hirayama A, Soga T, Hishiki T, Suematsu M, Yagi T, Ito D, Kosakai A, Hayashi K, Shouji M, Nakanishi A, Suzuki N, Mizuno Y, Mizushima N, Amagai M, Uchiyama Y, Mochizuki H, Hattori N, Okano H (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with increased oxidative stress and α-synuclein accumulation in PARK2 iPSC-derived neurons and postmortem brain tissue. Mol Brain 5:35
Ischiropoulos H, Beckman JS (2003) Oxidative stress and nitration in neurodegeneration: cause, effect, or association? J Clin Invest 111:163–169
Jiang H, Jiang Q, Feng J (2004) Parkin increases dopamine uptake by enhancing the cell surface expression of dopamine transporter. J Biol Chem 279:54380–54386
Jiang H, Ren Y, Yuen EY, Zhong P, Ghaedi M, Hu Z, Azabdaftari G, Nakaso K, Yan Z, Feng J (2012) Parkin controls dopamine utilization in human midbrain dopaminergic neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Commun 3:668
Jung H-J, Coffinier C, Choe Y, Beigneux AP, Davies BSJ, Yang SH, Barnes RH, Hong J, Sun T, Pleasure SJ, Young SG, Fong LG (2012) Regulation of prelamin a but not lamin C by miR-9, a brain-specific microRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E423–E431
Kawakami F, Yabata T, Ohta E, Maekawa T, Shimada N, Maruyama H, Ichikawa T, Obata F (2012) LRRK2 phosphorylates tubulin-associated tau but not the free molecule : LRRK2-mediated regulation of the tau-tubulin association and neurite outgrowth. PLoS ONE 7:e30834
Kim B, Yang MS, Choi D, Kim JH, Kim HS, Seol W, Choi S, Jou I, Kim EY, Joe E (2012) Impaired inflammatory responses in murine Lrrk2-knockdown brain microglia. PLoS ONE 7:e34693
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Ko HC, Gelb BD (2014) Concise review: drug discovery in the age of the induced pluripotent stem cell. Stem Cells Transl Med 3:500–509
Kouroupi G, Taoufik E, Vlachos IS, Tsioras K, Antoniou N, Papastefanaki F, Chroni-Tzartou D, Wrasidlo W, Bohl D, Stellas D, Politis PK, Vekrellis K, Papadimitriou D, Stefanis L, Bregestovski P, Hatzigeorgiou AG, Masliah E, Matsas R (2017) Defective synaptic connectivity and axonal neuropathology in a human iPSC-based model of familial Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E3679–E3688
Kriks S, Shim J-W, Piao J, Ganat YM, Wakeman DR, Xie Z, Carrillo-Reid L, Auyeung G, Antonacci C, Buch A, Yang L, Beal MF, Surmeier DJ, Kordower JH, Tabar V, Studer L (2011) Dopamine neurons derived from human ES cells efficiently engraft in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 480:547–551
Lashuel HA, Overk CR, Oueslati A, Masliah E (2013) The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Neurosci:38–48
Le W, Sayana P, Jankovic J (2014) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: a gateway to therapeutics? Neurotherapeutics 11:92–110
Levy OA, Malagelada C, Greene LA (2009) Cell death pathways in Parkinson’s disease: proximal triggers, distal effectors, and final steps. Apoptosis 14:478–500
Lewis SJG, Foltynie T, Blackwell AD, Robbins TW, Owen AM, Barker RA (2005) Heterogeneity of Parkinson’s disease in the early clinical stages using a data driven approach. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:343–348
Lin MT, Cantuti-castelvetri I, Zheng K, Jackson KE, Tan YB, Arzberger T, Lees AJ, Betensky RA, Beal MF, Simon DK (2012) Somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in early Parkinson and incidental Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol 71:850–854
Lin L, Gö J, Cukuroglu E, Dranias MR, Vandongen AMJ, Stanton LW (2016) Molecular features underlying neurodegeneration identified through in vitro modeling of genetically diverse Parkinson’s disease patients. Cell Rep 15:2411–2426
Lindvall O (2016) Clinical translation of stem cell transplantation in Parkinson’s disease. J Intern Med 279:30–40
Liu Y, Qiang M, Wei Y, He R (2011) A novel molecular mechanism for nitrated α-synuclein-induced cell death. J Mol Cell Biol 3:239–249
Liu G-H, Qu J, Suzuki K, Nivet E, Li M, Montserrat N, Yi F, Xu X, Ruiz S, Zhang W, Wagner U, Kim A, Ren B, Li Y, Goebl A, Kim J, Soligalla RD, Dubova I, Thompson J, Yates Iii J, Rodriguez Esteban C, Sancho-Martinez I, Izpisua Belmonte JC (2012) Progressive degeneration of human neural stem cells caused by pathogenic LRRK2. Nature 491:603–607
López de Maturana R, Lang V, Zubiarrain A, Sousa A, Vázquez N, Gorostidi A, Águila J, López de Munain A, Rodríguez M, Sánchez-Pernaute R (2016) Mutations in LRRK2 impair NF-κB pathway in iPSC-derived neurons. J Neuroinflammation 13:295
MacLeod D, Dowman J, Hammond R, Leete T, Inoue K, Abeliovich A (2006) The familial parkinsonism gene LRRK2 regulates neurite process morphology. Neuron 52:587–593
MacLeod DA, Rhinn H, Kuwahara T, Zolin A, Di Paolo G, MacCabe BD, Marder KS, Honig LS, Clark LN, Small SA, Abeliovich A (2013) RAB7L1 interacts with LRRK2 to modify intraneuronal protein sorting and Parkinson’s disease risk. Neuron 77:425–439
Madero-Pérez J, Fdez E, Fernández B, Lara Ordóñez AJ, Blanca Ramírez M, Romo Lozano M, Rivero-Ríos P, Hilfiker S (2017) Cellular effects mediated by pathogenic LRRK2: homing in on Rab-mediated processes. Biochem Soc Trans 45:147–154
Malik N, Rao MS (2013) A review of the methods for human iPSC derivation. Methods Mol Biol 997:23–33
Marion RM, Strati K, Li H, Tejera A, Schoeftner S, Ortega S, Serrano M, Blasco MA (2009) Telomeres acquire embryonic stem cell characteristics in induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 4:141–154
Martin I, Kim JW, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2014) LRRK2 pathobiology in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 131:554–565
Mazzulli JR, Xu YH, Sun Y, Knight AL, McLean PJ, Caldwell GA, Sidransky E, Grabowski GA, Krainc D (2011) Gaucher disease glucocerebrosidase and α-synuclein form a bidirectional pathogenic loop in synucleinopathies. Cell 146:37–52
Mazzulli JR, Zunke F, Isacson O, Studer L, Krainc D (2016a) α-Synuclein–induced lysosomal dysfunction occurs through disruptions in protein trafficking in human midbrain synucleinopathy models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:1931–1936
Mazzulli JR, Zunke F, Tsunemi T, Toker NJ, Jeon S, Burbulla LF, Patnaik S, Sidransky E, Marugan JJ, Sue CM, Krainc D (2016b) Activation of β-Glucocerebrosidase reduces pathological α-synuclein and restores lysosomal function in Parkinson’s patient midbrain neurons. J Neurosci 36:7693–7706
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1285
Mertens J, Paquola ACM, Ku M, Hatch E, Böhnke L, Ladjevardi S, McGrath S, Campbell B, Lee H, Herdy JR, Gonçalves JT, Toda T, Kim Y, Winkler J, Yao J, Hetzer MW, Gage FH (2015) Directly reprogrammed human neurons retain aging-associated transcriptomic signatures and reveal age-related nucleocytoplasmic defects. Cell Stem Cell 17:705–718
Migdalska-Richards A, Schapira AHV (2016) The relationship between glucocerebrosidase mutations and Parkinson disease. J Neurochem 139:77–90
Miller JD, Ganat YM, Kishinevsky S, Bowman RL, Liu B, Tu EY, Mandal PK, Vera E, Shim JW, Kriks S, Taldone T, Fusaki N, Tomishima MJ, Krainc D, Milner TA, Rossi DJ, Studer L (2013) Human iPSC-based modeling of late-onset disease via progerin-induced aging. Cell Stem Cell 13:691–705
Moretto A, Colosio C (2013) The role of pesticide exposure in the genesis of Parkinson’s disease: epidemiological studies and experimental data. Toxicology 307:24–34
Muffat J, Li Y, Yuan B, Mitalipova M, Omer A, Corcoran S, Bakiasi G, Tsai L, Aubourg P, Ransohoff RM, Jaenisch R (2016) Efficient derivation of microglia-like cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Med 22:1358–1367
Mullane K, Williams M (2013) Alzheimer’s therapeutics: continued clinical failures question the validity of the amyloid hypothesis - but what lies beyond? Biochem Pharmacol 85:289–305
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183:795–803
Narendra DP, Jin SM, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Gautier CA, Shen J, Cookson MR, Youle RJ (2010) PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol 8:e1000298
Neudorfer O, Giladi N, Elstein D, Abrahamov A, Turezkite T, Aghai E, Reches A, Bembi B, Zimran A (1996) Occurrence of Parkinson’s syndrome in type I Gaucher disease. Q J Med 89:691–694
Nguyen HN, Byers B, Cord B, Shcheglovitov A, Byrne J, Gujar P, Kee K, Schüle B, Dolmetsch RE, Langston W, Palmer TD, Pera RR (2011) LRRK2 mutant iPSC-derived da neurons demonstrate increased susceptibility to oxidative stress. Cell Stem Cell 8:267–280
Nissan X, Blondel S, Navarro C, Maury Y, Denis C, Girard M, Martinat C, De Sandre-Giovannoli A, Levy N, Peschanski M (2012) Unique preservation of neural cells in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is due to the expression of the neural-specific miR-9 microRNA. Cell Rep 2:1–9
Nuytemans K, Theuns J, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C (2010) Genetic etiology of Parkinson disease associated with mutations in the SNCA, PARK2, PINK1, PARK7, and LRRK2 genes: a mutation update. Hum Mutat 31:763–780
Ohta E, Nihira T, Uchino A, Imaizumi Y, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Takahashi K, Hayakawa H, Nagai M, Ohyama M, Ryo M, Ogino M, Murayama S, Takashima A, Nishiyama K, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H, Obata F, Okano H (2015) I2020T mutant LRRK2 iPSC-derived neurons in the Sagamihara family exhibit increased tau phosphorylation through the AKT/GSK-3 β signaling pathway. Hum Mol Genet 24:4879–4900
Orenstein SJ, Kuo S-H, Tasset I, Arias E, Koga H, Fernandez-Carasa I, Cortes E, Honig LS, Dauer W, Consiglio A, Raya A, Sulzer D, Cuervo AM (2013) Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Neurosci 16:394–406
Pandya H, Shen MJ, Ichikawa DM, Sedlock AB, Choi Y, Johnson KR, Kim G, Brown MA, Elkahloun AG, Maric D, Sweeney CL, Gossa S, Malech HL, McGavern DB, Park K (2017) Differentiation of human and murine induced pluripotent stem cells to microglia-like cells. Nat Neurosci 20:753–759
Parisiadou L, Xie C, Cho HJ, Lin X, Gu X, Long C, Lobbestael E, Baekelandt V, Taymans J, Sun L, Cai H (2009) Phosphorylation of ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins by LRRK2 promotes the rearrangement of actin cytoskeleton in neuronal morphogenesis. J Neurosci 29:13971–13980
Perrier AL, Tabar V, Barberi T, Rubio ME, Bruses J, Topf N, Harrison NL, Studer L (2004) Derivation of midbrain dopamine neurons from human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:12543–12548
Perrin S (2014) Preclinical research: make mouse studies work. Nature 507:423–425
Plowey ED, Cherra SJ, Liu YJ, Chu CT (2008) Role of autophagy in G2019S-LRRK2-associated neurite shortening in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 105:1048–1056
Pramstaller PP, Schlossmacher MG, Jacques TS, Scaravilli F, Eskelson C, Pepivani I, Hedrich K, Adel S, Gonzales-McNeal M, Hilker R, Kramer PL, Klein C (2005) Lewy body Parkinson’s disease in a large pedigree with 77 Parkin mutation carriers. Ann Neurol 58:411–422
Prigione A, Fauler B, Lurz R, Lehrach H, Adjaye J (2010) The senescence-related mitochondrial/oxidative stress pathway is repressed in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 28:721–733
Rakovic A, Grünewald A, Seibler P, Ramirez A, Kock N, Orolicki S, Lohmann K, Klein C (2010) Effect of endogenous mutant and wild-type PINK1 on Parkin in fibroblasts from Parkinson disease patients. Hum Mol Genet 19:3124–3137
Rakovic A, Shurkewitsch K, Seibler P, Grünewald A, Zanon A, Hagenah J, Krainc D, Klein C (2013) Phosphatase and Tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1)-dependent ubiquitination of endogenous Parkin attenuates mitophagy. J Biol Chem 288:2223–2237
Ramonet D, Daher JPL, Lin BM, Stafa K, Kim J, Banerjee R, Westerlund M, Pletnikova O, Glauser L, Yang L, Liu Y, Swing DA, Beal MF, Troncoso JC, McCaffery JM, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Galter D, Thomas B, Lee MK, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Moore DJ (2011) Dopaminergic neuronal loss, reduced neurite complexity and autophagic abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing G2019S mutant LRRK2. PLoS ONE 6:e18568
Reinhardt P, Schmid B, Burbulla LF, Schöndorf DC, Wagner L, Glatza M, Höing S, Hargus G, Heck SA, Dhingra A, Wu G, Müller S, Brockmann K, Kluba T, Maisel M, Krüger R, Berg D, Tsytsyura Y, Thiel CS, Psathaki OE, Klingauf J, Kuhlmann T, Klewin M, Müller H, Gasser T, Schöler HR, Sterneckert J (2013) Genetic correction of a lrrk2 mutation in human iPSCs links parkinsonian neurodegeneration to ERK-dependent changes in gene expression. Cell Stem Cell 12:354–367
Ren Y, Jiang H, Hu Z, Fan K, Wang J, Janoschka S, Wang X, Ge S, Feng J (2015) Parkin mutations reduce the complexity of neuronal processes in iPSC-derived human neurons. Stem Cell Rev Rep 33:68–78
Ross CA, Poirier MA (2005) Opinion: what is the role of protein aggregation in neurodegeneration? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:891–898
Rudenko IN, Cookson MR (2014) Heterogeneity of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 mutations: genetics, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neurotherapeutics 11:738–750
Russo I, Berti G, Plotegher N, Bernardo G, Filograna R, Bubacco L, Greggio E (2015) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 positively regulates inflammation and down-regulates NF-κB p50 signaling in cultured microglia cells. J Neuroinflammation 12:230
Ryan SD, Dolatabadi N, Chan SF, Zhang X, Akhtar MW, Parker J, Soldner F, Sunico CR, Nagar S, Talantova M, Lee B, Lopez K, Nutter A, Shan B, Molokanova E, Zhang Y, Han X, Nakamura T, Masliah E, Yates JR, Nakanishi N, Andreyev AY, Okamoto SI, Jaenisch R, Ambasudhan R, Lipton SA (2013) Isogenic human iPSC Parkinson’s model shows nitrosative stress-induced dysfunction in MEF2-PGC1α transcription. Cell 155:1351–1364
Samaranch L, Lorenzo-Betancor O, Arbelo JM, Ferrer I, Lorenzo E, Irigoyen J, Pastor MA, Marrero C, Isla C, Herrera-Henriquez J, Pastor P (2010) PINK1-linked parkinsonism is associated with Lewy body pathology. Brain 133:1128–1142
Sánchez-Danés A, Richaud-Patin Y, Carballo-Carbajal I, Jiménez-Delgado S, Caig C, Mora S, Di Guglielmo C, Ezquerra M, Patel B, Giralt A, Canals JM, Memo M, Alberch J, López-Barneo J, Vila M, Cuervo AM, Tolosa E, Consiglio A, Raya A (2012) Disease-specific phenotypes in dopamine neurons from human iPS-based models of genetic and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 4:380–395
Sanchez-Guajardo V, Tentillier N, Romero-Ramos M (2015) The relation between α-synuclein and microglia in Parkinson’s disease: recent developments. Neuroscience 302:47–58
Sanders LH, Laganière J, Cooper O, Mak K, Vu BJ, Huang YA, Paschon DE, Vangipuram M, Sundararajan R, Urnov FD, Langston JW, Gregory PD, Zhang HS, Greenamyre JT, Isacson O, Schüle B (2014) LRRK2 mutations cause mitochondrial DNA damage in iPSC-derived neural cells from Parkinson’s disease patients: reversal by gene correction. Neurobiol Dis 62:381–386
Sandor C, Robertson P, Lang C, Heger A, Booth H, Vowles J, Witty L, Bowden R, Hu M, Cowley SA, Wade-Martins R, Webber C (2017) Transcriptomic profiling of purified patient-derived dopamine neurons identifies convergent perturbations and therapeutics for Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 26:552–566
Schapansky J, Nardozzi JD, Lavoie MJ (2015) The complex relationships between microglia, alpha-synuclein, and LRRK2 in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 302:74–88
Schapira AHV (2015) Glucocerebrosidase and Parkinson disease: recent advances. Mol Cell Neurosci 66:37–42
Schapira AHV, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Clark JB, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 54:823–827
Schlossmacher MG, Frosch MP, Gai WP, Medina M, Sharma N, Forno L, Ochiishi T, Shimura H, Sharon R, Hattori N, Langston JW, Mizuno Y, Hyman BT, Selkoe DJ, Kosik KS (2002) Parkin localizes to the Lewy bodies of Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am J Pathol 160:1655–1667
Schöndorf DC, Aureli M, McAllister FE, Hindley CJ, Mayer F, Schmid B, Sardi SP, Valsecchi M, Hoffmann S, Schwarz LK, Hedrich U, Berg D, Shihabuddin LS, Hu J, Pruszak J, Gygi SP, Sonnino S, Gasser T, Deleidi M (2014) iPSC-derived neurons from GBA1-associated Parkinson’s disease patients show autophagic defects and impaired calcium homeostasis. Nat Commun 5:4028
Schüle B, Pera RAR, Langston JW (2009) Can cellular models revolutionize drug discovery in Parkinson’s disease? Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:1043–1051
Schulte C, Gasser T (2011) Genetic basis of Parkinson’s disease: inheritance, penetrance, and expression. Appl Clin Genet 4:67–80
Schwab AJ, Ebert AD (2015) Neurite aggregation and calcium dysfunction in iPSC-derived sensory neurons with Parkinson’s disease-related LRRK2 G2019S mutation. Stem Cell Rep 5:1039–1052
Segura-Aguilar J, Paris I, Muñoz P, Ferrari E, Zecca L, Zucca FA (2014) Protective and toxic roles of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 129:898–915
Seibler P, Graziotto J, Jeong H, Simunovic F, Klein C, Krainc D (2011) Mitochondrial Parkin recruitment is impaired in neurons derived from mutant PINK1 induced pluripotent stem cells. J Neurosci 31:5970–5976
Shaltouki A, Sivapatham R, Pei Y, Gerencser AA, Momčilović O, Rao MS, Zeng X (2015) Mitochondrial alterations by PARKIN in dopaminergic neurons using PARK2 patient-specific and PARK2 knockout isogenic iPSC lines. Stem Cell Rep 4:847–859
Shi M, Shi C, Xu Y (2017) Rab GTPases: the key players in the molecular pathway of Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 11:81
Shimura H, Schlossmacher MG, Hattori N, Frosch MP, Trockenbacher A, Schneider R, Mizuno Y, Kosik KS, Selkoe DJ (2001) Ubiquitination of a new form of α-synuclein by parkin from human brain: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Science 293:263–269
Sidransky E, Lopez G (2012) The link between the GBA gene and parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol 11:986–998
Skibinski G, Hwang V, Ando DM, Daub A, Lee AK, Ravisankar A, Modan S, Finucan MM, Shaby BA, Finkbeiner S (2016) Nrf2 mitigates LRRK2- and α-synuclein–induced neurodegeneration by modulating proteostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:1165–1170
Skibinski G, Nakamura K, Cookson MR, Finkbeiner S (2014) Mutant LRRK2 toxicity in neurons depends on LRRK2 levels and synuclein but not kinase activity or inclusion bodies. J Neurosci 34:418–433
Soldner F, Laganière J, Cheng AW, Hockemeyer D, Gao Q, Alagappan R, Khurana V, Golbe LI, Myers RH, Lindquist S, Zhang L, Guschin D, Fong LK, Vu BJ, Meng X, Urnov FD, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Zhang HS, Jaenisch R (2011) Generation of isogenic pluripotent stem cells differing exclusively at two early onset parkinson point mutations. Cell 146:318–331
Soldner F, Stelzer Y, Shivalila CS, Abraham BJ, Latourelle JC, Barrasa MI, Goldmann J, Myers RH, Young RA, Jaenisch R (2016) Parkinson-associated risk variant in distal enhancer of α-synuclein modulates target gene expression. Nature 533:95–99
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) α-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Steele JC, Guella I, Szu-Tu C, Lin MK, Thompson C, Evans DM, Sherman HE, Vilariño-Güell C, Gwinn K, Morris H, Dickson DW, Farrer MJ (2015) Defining neurodegeneration on Guam by targeted genomic sequencing. Ann Neurol 77:458–468
Steger M, Tonelli F, Ito G, Davies P, Trost M, Vetter M, Wachter S, Lorentzen E, Duddy G, Wilson S, Baptista MA, Fiske BK, Fell MJ, Morrow JA, Reith AD, Alessi DR, Mann M (2016) Phosphoproteomics reveals that Parkinson’s disease kinase LRRK2 regulates a subset of Rab GTPases. elife 5:e12813
Studer L (2012) Derivation of dopaminergic neurons from pluripotent stem cells In: Progress in Brain Research, vol 200. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 243–263
Su YC, Qi X (2013) Inhibition of excessive mitochondrial fission reduced aberrant autophagy and neuronal damage caused by LRRK2 G2019S mutation. Hum Mol Genet 22:4545–4561
Subramaniam SR, Chesselet M-F (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 106–107:17–32
Suhr ST, Chang EA, Rodriguez RM, Wang K, Ross PJ, Beyhan Z, Murthy S, Cibelli JB (2009) Telomere dynamics in human cells reprogrammed to pluripotency. PLoS ONE 4:e8124
Suhr ST, Chang EA, Tjong J, Alcasid N, Perkins GA, Goissis MD, Ellisman MH, Perez GI, Cibell JB (2010) Mitochondrial rejuvenation after induced pluripotency. PLoS ONE 5:e14095
Sun Y, Grabowski GA (2010) Impaired autophagosomes and lysosomes in neuronopathic Gaucher disease. Autophagy 6:648–649
Suzuki S, Akamatsu W, Kisa F, Sone T, Ishikawa KI, Kuzumaki N, Katayama H, Miyawaki A, Hattori N, Okano H (2017) Efficient induction of dopaminergic neuron differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells reveals impaired mitophagy in PARK2 neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483:88–93
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126:663–676
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131:861–872
Takanashi M, Li Y, Hattori N (2016) Absence of Lewy pathology associated with PINK1 homozygous mutation. Neurology 86:2212–2213
Tansey MG, McCoy MK, Frank-Cannon TC (2007) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: potential environmental triggers, pathways, and targets for early therapeutic intervention. Exp Neurol 208:1–25
Tayebi N, Callahan M, Madike V, Stubblefield BK, Orvisky E, Krasnewich D, Fillano JJ, Sidransky E (2001) Gaucher disease and parkinsonism: a phenotypic and genotypic characterization. Mol Genet Metab 73:313–321
Theillet F-X, Binolfi A, Bekei B, Martorana A, Rose HM, Stuiver M, Verzini S, Lorenz D, van Rossum M, Goldfarb D, Selenko P (2016) Structural disorder of monomeric α-synuclein persists in mammalian cells. Nature 530:45–50
Tofaris GK, Tae H, Hourez R, Jung J, Pyo K, Goldberg AL (2011) Ubiquitin ligase Nedd4 promotes α-synuclein degradation by the endosomal – lysosomal pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:17004–17009
Tóth G, Gardai SJ, Zago W, Bertoncini CW, Cremades N, Roy SL, Tambe MA, Rochet JC, Galvagnion C, Skibinski G, Finkbeiner S, Bova M, Regnstrom K, Chiou SS, Johnston J, Callaway K, Anderson JP, Jobling MF, Buell AK, Yednock TA, Knowles TPJ, Vendruscolo M, Christodoulou J, Dobson CM, Schenk D, McConlogue L (2014) Targeting the intrinsically disordered structural ensemble of α-Synuclein by small molecules as a potential therapeutic strategy for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 9:e87133
Trinh J, Farrer M (2013) Advances in the genetics of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 9:445–454
Uversky VN, Oldfield CJ, Dunker AK (2008) Intrinsically disordered proteins in human diseases: introducing the D 2 concept. Annu Rev Biophys 37:215–246
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MMK, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Turco DD, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG, Albanese A, Nussbaum R, Gonzalez-Maldonado R, Deller T, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW (2004) Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304:1158–1160
Várkonyi J, Rosenbaum H, Baumann N, MacKenzie JJ, Simon Z, Aharon-Peretz J, Walker JM, Tayebi N, Sidransky E (2003) Gaucher disease associated with parkinsonism: four further case reports. Am J Med Genet A 116A:348–351
Victor MB, Richner M, Hermanstyne TO, Ransdell JL, Sobieski C, Deng PY, Klyachko VA, Nerbonne JM, Yoo AS (2014) Generation of human striatal neurons by microRNA-dependent direct conversion of fibroblasts. Neuron 84:311–323
Vidailhet M (2003) Heterogeneity of Parkinson’s disease. Bull Acad Natl Med 187:256–259
Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Pang ZP, Kokubu Y, Südhof TC, Wernig M (2010) Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature 463:1035–1042
Vivekanantham S, Shah S, Dewji R, Dewji A, Khatri C, Ologunde R (2015) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: role in neurodegeneration and tissue repair. Int J Neurosci 125:717–725
Vives-Bauza C, Zhou C, Huang Y, Cui M, de Vries RLA, Kim J, May J, Tocilescu MA, Liu W, Ko HS, Magrane J, Moore DJ, Dawson VL, Grailhe R, Dawson TM, Li C, Tieu K, Przedborski S (2010) PINK1-dependent recruitment of Parkin to mitochondria in mitophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:378–383
Wang T, Hay JC (2015) Alpha-synuclein toxicity in the early secretory pathway: how it drives neurodegeneration in Parkinsons disease. Front Neurosci 9:433
Wang X, Winter D, Ashrafi G, Schlehe J, Wong YL, Selkoe D, Rice S, Steen J, Lavoie MJ, Schwarz TL (2011) PINK1 and Parkin target Miro for phosphorylation and degradation to arrest mitochondrial motility. Cell 147:893–906
Wang B, Abraham N, Gao G, Yang Q (2016) Dysregulation of autophagy and mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. Transl Neurodegener 5:19
Winner B, Melrose HL, Zhao C, Hinkle KM, Yue M, Kent C, Braithwaite AT, Ogholikhan S, Aigner R, Winkler J, Farrer MJ, Gage FH (2011) Adult neurogenesis and neurite outgrowth are impaired in LRRK2 G2019S mice. Neurobiol Dis 41:706–716
Woodard CM, Campos BA, Kuo S-H, Nirenberg MJ, Nestor MW, Zimmer M, Mosharov EV, Sulzer D, Zhou H, Paull D, Clark L, Schadt EE, Sardi SP, Rubin L, Eggan K, Brock M, Lipnick S, Rao M. (2014) iPSC-derived dopamine neurons reveal differences between monozygotic twins discordant for Parkinson’s disease.Cell Rep 9:1173–1182
Xilouri M, Brekk OR, Stefanis L (2013) Alpha-synuclein and protein degradation systems: a reciprocal relationship. Mol Neurobiol 47:537–551
Xu L, Pu J (2016) Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: From pathogenetic dysfunction to potential clinical application. Parkinsons Dis 1720621
Yoo AS, Sun AX, Li L, Shcheglovitov A, Portmann T, Li Y, Lee-Messer C, Dolmetsch RE, Tsien RW, Crabtree GR (2011) MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons. Nature 476:228–232
Yoritaka A, Hattori N, Uchida K, Tanaka M, Stadtman ER, Mizuno Y (1996) Immunohistochemical detection of 4-hydroxynonenal protein adducts in Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:2696–2701
Yu Z, Xu X, Xiang Z, Zhou J, Zhang Z, Hu C, He C (2010) Nitrated α-Synuclein induces the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of rats. PLoS ONE 5:e9956
Zhang XQ, Zhang SC (2010) Differentiation of neural precursors and dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol 584:355–366
Zhong P, Hu Z, Jiang H, Yan Z, Feng J (2017) Dopamine induces oscillatory activities in human midbrain neurons with parkin mutations. Cell Rep 19:1033–1044
Zuo L, Motherwell MS (2013) The impact of reactive oxygen species and genetic mitochondrial mutations in Parkinson’s disease. Gene 532:18–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This review is supported by the Michael J Fox Foundation, Gladstone Institutes, NIH U54 HG008105, R01 NS039074 and R01 NS083390
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobb, M.M., Ravisankar, A., Skibinski, G. et al. iPS cells in the study of PD molecular pathogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 373, 61–77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2749-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2749-y