Abstract
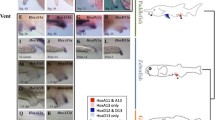
The Hox and ParaHox genes of bilateria share a similar expression pattern along the body axis and are known to be associated with anterior-posterior patterning. In vertebrates, the Hox genes are also expressed in presomitic mesoderm and gut endoderm and the ParaHox genes show a restricted expression pattern in the gut-related derivatives. Regional expression patterns in the embryonic central nervous system of the basal chordates amphioxus and ascidian have been reported; however, little is known about their endodermal expression in the alimentary canal. We focus on the Hox and ParaHox genes in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis and investigate the gene expression patterns in the juvenile, which shows morphological regionality in the alimentary canal. Gene expression analyses by using whole-mount in situ hybridization reveal that all Hox genes have a regional expression pattern along the alimentary canal. Expression of Hox1 to Hox4 is restricted to the posterior region of pharyngeal derivatives. Hox5 to Hox13 show an ordered expression pattern correlated with each Hox gene number along the postpharyngeal digestive tract. This expression pattern along the anterior-posterior axis has also been observed in Ciona ParaHox genes. Our observations suggest that ascidian Hox and ParaHox clusters are dispersed; however, the ordered expression patterns along the alimentary canal appear to be conserved among chordates.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arenas-Mena C, Cameron AR, Davidson EH (2000) Spatial expression of Hox cluster genes in the ontogeny of a sea urchin. Development 127:4631–4643
Aronowicz J, Lowe CJ (2006) Hox gene expression in the hemichordate Saccoglossus kowalevskii and the evolution of deuterostome nervous systems. Integr Comp Biol 46:890–901
Beck F, Tata F, Chawengsaksophak K (2000) Homeobox genes and gut development. Bioessays 22:431–441
Brooke NM, Garcia-Fernàndez J, Holland PW (1998) The ParaHox gene cluster is an evolutionary sister of the Hox gene cluster. Nature 392:920–922
Brusca RC, Brusca GJ (1990) Invertebrates. Sinauer, Sunderland
Cameron RA, Rowen L, Nesbitt R, Bloom S, Rast JP, Berney K, Arenas-Mena C, Martinez P, Lucas S, Richardson PM, Davidson EH, Peterson KJ, Hood L (2006) Unusual gene order and organization of the sea urchin Hox cluster. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 306:45–58
Charité J, Graaff W de, Consten D, Reijnen MJ, Korving J, Deschamps J (1998) Transducing positional information to the Hox genes: critical interaction of cdx gene products with position-sensitive regulatory elements. Development 125:4349–4358
Chawengsaksophak K, James R, Hammond VE, Köntgen F, Beck F (1997) Homeosis and intestinal tumours in Cdx2 mutant mice. Nature 386:84–87
Cole AG, Rizzo F, Martinez P, Fernandez-Serra M, Arnone MI (2009) Two ParaHox genes, SpLox and SpCdx, interact to partition the posterior endoderm in the formation of a functional gut. Development 136:541–549
Corrado M, Aniello F, Fucci L, Branno M (2001) Ci-IPF1, the pancreatic homeodomain transcription factor, is expressed in neural cells of Ciona intestinalis larva. Mech Dev 102:271–274
Davis AP, Witte DP, Hsieh-Li HM, Potter SS, Capecchi MR (1995) Absence of radius and ulna in mice lacking Hoxa-11 and Hoxd-11. Nature 375:791–795
Duboule D, Dollé P (1989) The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J 8:1497–1505
Duprey P, Chowdhury K, Dressler GR, Balling R, Simon D, Guenet JL, Gruss P (1988) A mouse gene homologous to the Drosophila gene caudal is expressed in epithelial cells from the embryonic intestine. Genes Dev 2:1647–1654
Ferrier DE, Holland PW (2002) Ciona intestinalis ParaHox genes: evolution of Hox/ParaHox cluster integrity, developmental mode, and temporal colinearity. Mol Phylogenet Evol 24:412–417
Garcia-Fernàndez J (2005) The genesis and evolution of homeobox gene clusters. Nat Rev Genet 6:881–892
Gee H (1996) Before the backbone. Views on the origin of the vertebrates. Chapman & Hall, London
Grapin-Botton A, Melton DA (2000) Endoderm development: from patterning to organogenesis. Trends Genet 16:124–130
Hinman VF, Becker E, Degnan BM (2000) Neuroectodermal and endodermal expression of the ascidian Cdx gene is separated by metamorphosis. Dev Genes Evol 210:212–216
Holland PW, Holland LZ, Williams NA, Holland ND (1992) An amphioxus homeobox gene: sequence conservation, spatial expression during development and insights into vertebrate evolution. Development 116:653–661
Hudson C, Lemaire P (2001) Induction of anterior neural fates in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Mech Dev 100:189–203
Hunt P, Gulisano M, Cook M, Sham MH, Faiella A, Wilkinson D, Boncinelli E, Krumlauf R (1991) A distinct Hox code for the branchial region of the vertebrate head. Nature 353:861–864
Ikuta T (2011) Evolution of invertebrate deuterostomes and Hox/ParaHox genes. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform 9:77–96
Ikuta T, Yoshida N, Satoh N, Saiga H (2004) Ciona intestinalis Hox gene cluster: its dispersed structure and residual colinear expression in development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15118–15123
Ikuta T, Chen YC, Annunziata R, Ting HC, Tung CH, Koyanagi R, Tagawa K, Humphreys T, Fujiyama A, Saiga H, Satoh N, Yu JK, Arnone MI, Su YH (2013) Identification of an intact ParaHox cluster with temporal colinearity but altered spatial colinearity in the hemichordate Ptychodera flava. BMC Evol Biol 13:129
Izpisúa-Belmonte JC, Falkenstein H, Dollé P, Renucci A, Duboule D (1991) Murine genes related to the Drosophila AbdB homeotic genes are sequentially expressed during development of the posterior part of the body. EMBO J 10:2279–2289
Jonsson J, Carlsson L, Edlund T, Edlund H (1994) Insulin-promoter-factor 1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature 371:606–609
Kaufman TC, Lewis R, Wakimoto B (1980) Cytogenetic analysis of chromosome 3 in Drosophila melanogaster: the homoeotic gene complex in polytene chromosome interval 84a-B. Genetics 94:115–133
Kawai N, Ogura Y, Ikuta T, Saiga H, Hamada M, Sakuma T, Yamamoto T, Satoh N, Sasakura Y (2015) Hox10-regulated endodermal cell migration is essential for development of the ascidian intestine. Dev Biol 403:43–56
Kawazoe Y, Sekimoto T, Araki M, Takagi K, Araki K, Yamamura K (2002) Region-specific gastrointestinal Hox code during murine embryonal gut development. Dev Growth Differ 44:77–84
Kuraku S, Meyer A (2009) The evolution and maintenance of Hox gene clusters in vertebrates and the teleost-specific genome duplication. Int J Dev Biol 53:765–773
Lemons D, McGinnis W (2006) Genomic evolution of Hox gene clusters. Science 313:1918–1922
Lewis EB (1978) A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature 276:565–570
McGinnis W, Garber RL, Wirz J, Kuroiwa A, Gehring WJ (1984a) A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell 37:403–408
McGinnis W, Levine MS, Hafen E, Kuroiwa A, Gehring WJ (1984b) A conserved DNA sequence in homoeotic genes of the Drosophila antennapedia and bithorax complexes. Nature 308:428–433
Nakazawa K, Yamazawa T, Moriyama Y, Ogura Y, Kawai N, Sasakura Y, Saiga H (2013) Formation of the digestive tract in Ciona intestinalis includes two distinct morphogenic processes between its anterior and posterior parts. Dev Dyn 242:1172–1183
Nielsen C (1995) Animal evolution. Interrelationships of the living phyla. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Offield MF, Jetton TL, Labosky PA, Ray M, Stein RW, Magnuson MA, Hogan BL, Wright CV (1996) PDX-1 is required for pancreatic outgrowth and differentiation of the rostral duodenum. Development 122:983–995
Ogasawara M (2000) Overlapping expression of amphioxus homologs of the thyroid transcription factor-1 gene and thyroid peroxidase gene in the endostyle: insight into evolution of the thyroid gland. Dev Genes Evol 210:231–242
Ogasawara M, Satoh N (1998) Isolation and characterization of endostyle-specific genes in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Biol Bull 195:60–69
Ogasawara M, Wada H, Peters H, Satoh N (1999) Developmental expression of Pax1/9 genes in urochordate and hemichordate gills: insight into function and evolution of the pharyngeal epithelium. Development 126:2539–2550
Ogasawara M, Minokawa T, Sasakura Y, Nishida H, Makabe KW (2001) A large-scale whole-mount in situ hybridization system: rapid one-tube preparation of DIG-labeled RNA probes and high throughput hybridization using 96-well silent screen plates. Zool Sci 18:187–193
Ogasawara M, Sasaki A, Metoki H, Shin-i T, Kohara Y, Satoh N, Satou Y (2002) Gene expression profiles in young adult Ciona intestinalis. Dev Genes Evol 212:173–185
Ogasawara M, Satoh N, Shimada Y, Wang Z, Tanaka T, Noji S (2006) Rapid and stable buffer exchange system using InSitu Chip suitable for multi-color and large-scale whole-mount analyses. Dev Genes Evol 216:100–104
Pascual-Anaya J, D’Aniello S, Kuratani S, Garcia-Fernàndez J (2013) Evolution of Hox gene clusters in deuterostomes. BMC Dev Biol 13:26
Pitera JE, Smith VV, Thorogood P, Milla PJ (1999) Coordinated expression of 3′ Hox genes during murine embryonal gut development: an enteric Hox code. Gastroenterology 117:1339–1351
Sakiyama J, Yokouchi Y, Kuroiwa A (2001) HoxA and HoxB cluster genes subdivide the digestive tract into morphological domains during chick development. Mech Dev 101:233–236
Sasakura Y, Kanda M, Ikeda T, Horie T, Kawai N, Ogura Y, Yoshida R, Hozumi A, Satoh N, Fujiwara S (2012) Retinoic acid-driven Hox1 is required in the epidermis for forming the otic/atrial placodes during ascidian metamorphosis. Development 139:2156–2160
Satoh N, Satou Y, Davidson B, Levine M (2003) Ciona intestinalis: an emerging model for whole-genome analyses. Trends Genet 19:376–381
Sekimoto T, Yoshinobu K, Yoshida M, Kuratani S, Fujimoto S, Araki M, Tajima N, Araki K, Yamamura K (1998) Region-specific expression of murine Hox genes implies the Hox code-mediated patterning of the digestive tract. Genes Cells 3:51–64
Seo HC, Edvardsen RB, Maeland AD, Bjordal M, Jensen MF, Hansen A, Flaat M, Weissenbach J, Lehrach H, Wincker P, Reinhardt R, Chourrout D (2004) Hox cluster disintegration with persistent anteroposterior order of expression in Oikopleura dioica. Nature 431:67–71
Swalla BJ (2006) Building divergent body plans with similar genetic pathways. Heredity 97:235–243
Willmer P (1990) Invertebrate relationships. Patterns in animal evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Yokouchi Y, Sakiyama J, Kuroiwa A (1995) Coordinated expression of Abd-B subfamily genes of the HoxA cluster in the developing digestive tract of chick embryo. Dev Biol 169:76–89
Yoshida R, Sasakura Y (2012) Establishment of enhancer detection lines expressing GFP in the gut of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Zool Sci 29:11–20
Zorn AM, Wells JM (2009) Vertebrate endoderm development and organ formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:221–251
Acknowledgments
We thank Professors Nori Satoh and Kazuko Hirayama for providing the Ciona cDNA clones and juvenile specimens. We also thank Takatsugu Takiguchi and Takuya Nomura for their help in the in situ hybridizations of the Ciona juveniles and larvae.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Expression of larval CNS-positive Hox genes in the neural complex of the Ciona juvenile. a Expression of Hox1 is observed in the middle to posterior part of the cerebral ganglion. b Expression of Hox3 is also observed in the middle to posterior part of the cerebral ganglion, extending posterior to the neuron. c–e Strict expression patterns of Hox5 (c), Hox10 (d) and Hox12 (e) are not observed in the juvenile neural complex (cf ciliated funnel, cg cerebral ganglion, ng neural gland). Bar 20 μm. (GIF 210 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Expression of larval CNS-positive Hox genes in the trunk region of Ciona larvae. The expression of Hox1 is observed in the visceral ganglion, anterior nerve cord and posterior pharyngeal endoderm (a, c). Expression of Hox3 is mainly observed in the visceral ganglion; however strict expression is observed in the posterior pharyngeal endoderm (b, d). The dashed line indicates the edge of the posterior pharyngeal endoderm. The dotted line indicates the region of the prospective stomach (n notochord, nc nerve cord, pe pharyngeal endoderm, ps prospective stomach, vg visceral ganglion). Bar 50 μm (a, b), 20 μm (c, d). (GIF 190 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakayama, S., Satou, K., Orito, W. et al. Ordered expression pattern of Hox and ParaHox genes along the alimentary canal in the ascidian juvenile. Cell Tissue Res 365, 65–75 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2360-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2360-7