Abstract
Hox genes, with their similar roles in animals as evolutionarily distant as humans and flies, have fascinated biologists since their discovery nearly 30 years ago. During the last two decades, reports on Hox genes from a still growing number of eumetazoan species have increased our knowledge on the Hox gene contents of a wide range of animal groups. In this review, we summarize the current Hox inventory among deuterostomes, not only in the well-known teleosts and tetrapods, but also in the earlier vertebrate and invertebrate groups. We draw an updated picture of the ancestral repertoires of the different lineages, a sort of “genome Hox bar-code” for most clades. This scenario allows us to infer differential gene or cluster losses and gains that occurred during deuterostome evolution, which might be causally linked to the morphological changes that led to these widely diverse animal taxa. Finally, we focus on the challenging family of posterior Hox genes, which probably originated through independent tandem duplication events at the origin of each of the ambulacrarian, cephalochordate and vertebrate/urochordate lineages.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hox genes comprise a wide subfamily of homeobox-containing transcription factors. In most eumetazoans studied so far, Hox genes are clustered in the same genomic region and are transcribed in the same orientation, although there are cases where the cluster has been split, as in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, or has been completely disintegrated, as in the tunicate larvacean Oikopleura dioica. Usually, invertebrates possess a single Hox cluster, whereas vertebrates possess multiple clusters as a result of several rounds of whole-genome duplications (WGD). Namely, two rounds (2R) of WGD occurred in early vertebrate evolution ([1, 2]; see [3] for a review), resulting in the four Hox clusters of jawed vertebrates (the so-called HoxA, B, C and D clusters) [4, 5]. Teleost fishes experienced an additional third round (3R) of WGD [6–8] resulting in up to seven or eight Hox clusters [4, 5]. Therefore, the single cluster of invertebrates is thought to be reminiscent of the pre-duplicative state [2]. Within vertebrates, each Hox gene can be assigned by sequence comparison to one of 14 different cognate or paralogous groups (PGs) and each cluster retains a subset of these paralogues [9].
The expression patterns of Hox genes reflect their position in the cluster: genes at the 3′ end are expressed in and pattern the most anterior part of the embryo, while the genes at the 5′ end pattern more posterior body parts. This phenomenon is known as spatial colinearity. In some animals, like amphioxus (a cephalochordate) and vertebrates, the position in the cluster also determines the onset of expression, with the 3′ genes expressed earlier than the 5′ ones. This phenomenon is called temporal colinearity. As a result of spatial and temporal colinearity, the Hox genes are eventually expressed in a nested manner along the main anterior–posterior axis of the animal body, resulting in a Hox code that bestows differential structural identity [10].
It is thought that changes in the Hox code might be causative for evolutionary novelties, such as the fin-to-limb transition [11, 12], the number of vertebrae [13, 14], the snake body plan [15] or the presence or absence of ribs in the trunk [16], to mention some examples. To fully understand the nature of the changes in the Hox code leading to morphological evolution, it is essential to know the Hox content of a wide range of animals belonging to different phyla. Nonetheless, although the Hox genes and clusters are relatively well characterized in most groups of vertebrates (mainly in osteichthyans: the bony vertebrates), unfortunately few groups of invertebrates have received similar attention. Importantly, our knowledge of both the Hox content and regulation in invertebrate deuterostomes has grown significantly in recent years. In this review, we summarize old and new data and present a detailed picture of the current catalogue of Hox clusters in deuterostomes, inferring when possible the putative Hox repertoire of the last common ancestor (LCA) condition for different groups. We also discuss the implications of the different Hox gene/cluster repertoires within the frame of deuterostome evolution, giving special attention to the posterior genes, which might have originated by independent lineage-specific expansions in ambulacrarians, cephalochordates and vertebrates.
Hoxcontent in invertebrate deuterostomes
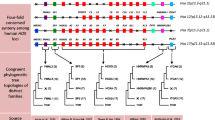
Deuterostomes and protostomes are the two major groups of bilaterian animals. Deuterostomes classically consist of two main groups: chordates and ambulacrarians (Figure 1), although recent phylogenetic studies also include the Xenoturbellida and/or Aceolomorpha as deuterostomes (see below). Chordates include cephalochordates (amphioxus), urochordates and vertebrates, the two latter forming the group called Olfactores [17] (Figure 1). The Ambulacraria encompasses a wide group of animals with different morphologies and consists basically of echinoderms (sea urchins, starfish, ophiurids, crinoids and sea cucumbers) and hemichordates (acorn worms and the class Pterobranchia) (Figure 1).
General phylogenetic tree of deuterostomes showing the Hox clusters of non-olfactores deuterostomes known to date. The Hox repertoire of a substantial number of groups within the invertebrate deuterostomes is still lacking (black question marks), and the origin of a 15 Hox gene cluster in cephalochordates, or when the Hox4 was lost in echinoderms are still a mystery (indicated by red question marks and arrows). Yellow, anterior Hox genes; orange, Hox3; blue, central Hox genes; green, posterior Hox genes.
Xenoturbellida and aceolomorpha: to be or not to be … deuterostomes
Xenoturbellids and acoelomorphs (acoels plus nemertodermatids) were classically classified as platyhelminthes. However, in the last decade and with the advance of molecular phylogenomics, their position has changed dramatically, depending on the methods and datasets used. Whereas acoelomorphs were classified as basal bilaterians [18–21] and Xenoturbellida formed a new phylum within deuterostomes [22, 23], the most recent analyses have grouped Xenoturbella and acoelomorphs in a monophyletic group, the so-called Xenacoelomorpha [24], either at the base of the Bilateria [25] or as a sister group of Ambulacraria within the deuterostomes [24]. Although the definite positions of xenoturbellids and acoelomorphs remain uncertain, here we will discuss the implications of the different possibilities.
Xenoturbellid Hox genes have been studied solely by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification survey in the species Xenoturbella bocki[26]. This study identified only an anterior Hox1, three central Hox genes (HoxM1, HoxM2 and HoxM3) and a posterior HoxP gene [26]. Acoels, on the other hand, have only three Hox genes: one anterior, one central and one posterior [27, 28]. Although acoel Hox genes are not clustered [28], they retain a spatially colinear expression pattern (we use the term colinearity with regards to PG order, regardless of gene clustering) [28, 29]. Regarding Nemertodermatida, only one study has been reported in which two central and one posterior Hox genes were identified by means of degenerate PCR [30].
Establishing a plausible evolutionary scenario for the Hox content of the LCA of Xenacoelomorpha remains difficult, because most of the sequences of the above-mentioned PCR surveys are very short and thus the datasets are poor. The simplest landscape is that of a single cluster consisting of one anterior, one central and one posterior Hox gene. If the Xenacoelomorpha is indeed confirmed as a group of the Deuterostomata, this would imply—compared with ambulacrarians and chordates—that the lineage suffered a massive loss of Hox genes and a complete disintegration of the cluster, at least in acoels. This would be in line with their simplified body plans from a more complex, Hox-rich, deuterostome ancestor. If eventually they are classified as the sister group of Nephrozoa (protostomes + deuterostomes), then their Hox content would nicely fit with that expected for their earlier bilaterian ancestor.
Ambulacrarian Hoxgenes
Within ambulacrarian groups, echinoderms are the most well studied, and several PCR surveys have been used to partially determine the Hox gene inventories of different species (see [31] and references therein), although the genomic organizations remain unknown in most cases (Figure 1). The exception within echinoderms is the well-known sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, whose draft genome has been published [32]. S. purpuratus possesses a single cluster of about 600 kb in length that contains 11 Hox genes (Figures 1 and 2). However, the order of the S. purpuratus Hox genes in the cluster is altered in comparison with other deuterostome Hox clusters, so that some anterior genes are near to posterior ones and have different transcriptional orientations (Figures 1 and 2; [33]).
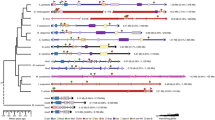
Reconstructed evolution of Hox gene families within deuterostomes. The Hox genes and clusters of those representative species with complete or almost complete Hox cluster sequences are shown, and gene losses (thin black squares) or other events (crossed red lines), such as Hox cluster duplication or loss are inferred. The ancestral conditions are reconstructed taking into account the information of species with non-complete Hox cluster sequences (see the main text). Pre-duplicative clusters are shown in turquoise; vertebrate Hox clusters are type-coloured: red, HoxA; blue, HoxB; green, HoxC; yellow, HoxD. For the sake of clarity, the phylogenetic relationships of tetrapods are shown in light blue and those of teleosts in orange. White squares indicate pseudogenes. Evx genes are shown when possible, with lighter colours. 2R, 3R and 4R indicate two, three teleost-specific and four salmonid-specific rounds of whole genome duplication, respectively. The phylogenetic relationships of teleosts here are based on [98].
Regarding the hemichordates, the presence of a single Hox cluster has been identified recently in two different enteropneust species: Saccoglossus kowalevskii and Ptychodera flava[34]. Their Hox clusters show identical organization, with 12 Hox genes arrayed in ~500 kb, all with the same transcriptional orientation except for the terminal pair of Ambulacrarian-specific posterior Hox genes AmbPb and AmbPc (previously named Hox11/13b and Hox11/13c, respectively [34]). Overall, the hemichordate Hox cluster reflects a more prototypical organization than its sea urchin counterpart and its comparison with that of S. purpuratus allowed Freeman and colleagues [34] to infer the changes accounting for the scrambled condition of the latter. For example, S. purpuratus lacks a Hox member of the PG4 when compared with hemichordates. Therefore, sea urchins would have lost Hox4 at some point in echinoderm evolution, probably arising from the genomic rearrangements that provoked first the inversion of Hox1–5 genes and then the translocation of Hox1–4 to the 5′ end of the cluster, eventually causing the loss of Hox4[34]. Besides, crinoids (Metacrinus rotundus) and asteroids (Asterina minor and Patiriella exigua) have a Hox4 gene [35–37]; thus, the loss of Hox4 must have occurred at least after the split of echinoids, holothuroids, and ophiuroids from the rest of the echinoderms (Figure 1). Nonetheless, the genomic sequences of more ambulacrarian lineages, mainly those within the group of echinoderms, must be investigated to depict a precise evolutionary scenario for the ancestral ambulacrarian Hox cluster.
Cephalochordates
Cephalochordates are the sister group of Olfactores and thus are in a key phylogenetic position to allow the ancestral condition of chordates to be understood. Given the divergent nature of tunicates (see the next section), cephalochordates are also a valuable out-group for evolutionary and comparative studies of vertebrates [38]. The Floridian amphioxus Branchiostoma floridae possesses the most prototypical Hox cluster identified so far in deuterostomes. It contains 15 Hox genes, the largest gene content for a Hox cluster hitherto reported, spanning a genomic stretch of ~470 kb and all in the same transcriptional orientation: thus it has not suffered any rearrangements since cephalochordates split from the LCA of chordates more than 500 million years ago (Mya) [39–41]. Similarly, 15 Hox genes, presumably in a single cluster, have been described in the European amphioxus Branchiostoma lanceolatum, thereby showing that a 15 gene Hox cluster is not a species oddity [42]. This discovery indicates that the amphioxus Hox cluster probably reflected the ancestral chordate condition, with counterparts for every PG of vertebrates, i.e., that it possessed a complete chordate Hox cluster. However, although this holds true for the anterior and medial PGs, it is still a matter of debate for the posterior genes, as phylogenetic trees do not show clear orthologous relationships between posterior genes from different deuterostome phyla. This phenomenon was thought to be the consequence of the higher evolutionary rate of the posterior part of the cluster, the so-called deuterostome posterior flexibility [43]. However, an alternative scenario is that some posterior genes originated independently in the different lineages by tandem duplication events, as claimed by recent reports [34, 44–46] that we will discuss below. Nonetheless, to further clarify this topic, genomic information for other cephalochordate genus, such as Asymmetron sp., an earlier branch of cephalochordates than Branchiostoma and Epigonichthys ([47]; Figure 1), might give more unambiguous insights into the ancestral cephalochordate Hox cluster condition and eventually into the ancestral chordate Hox cluster.
In addition to the doubtful nature of the posterior part of the Hox cluster, we recently reported the breaking of colinearity for some amphioxus Hox genes, where the most striking case was that of Hox14, found to be expressed in the cerebral vesicle [48]. Interestingly, the brains of other animals are characterized as Hox-negative regions, making the amphioxus case a surprising oddity and therefore bringing up the possibility that the amphioxus Hox cluster and its regulation are not as prototypical as previously thought.
Urochordates
The Hox complements of the urochordate genomes sequenced thus far provide little information of use in inferring the ancestral condition of the Olfactores (and thus the preduplicative state of vertebrates), because their genomes are very divergent as reflected in their body plans, with dramatic genome rearrangements and extensive gene losses.
Among the urochordates, the best-known model is the ascidian Ciona intestinalis, which possesses a rather disorganized set of Hox genes [49, 50]. The C. intestinalis Hox cluster has experienced a partial disintegration, although there are genomic stretches where several Hox genes are linked [49, 50]. These groupings are Hox1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 in chromosome 1 and Hox12 and 13 in chromosome 7 [51]. On the other hand, Hox7, 8, 9 and 11 are absent in all ascidians sequenced so far [50, 52]. Moreover, two independent translocation events disrupted the order of Hox genes in chromosome 1: Hox10 is located between the Hox4 and Hox5 genes, and the Hox-related gene EvxA sits between Hox1 and Hox2. In fact, some authors consider that sensu stricto, Hox1–10 genes are not linked because they span ~5 Mb [50], indicating that the ascidian Hox repertoire has a partially disintegrated nature. Surprisingly, even with such a disrupted organization, most ascidian Hox genes are expressed in a colinear fashion in the central nervous system (CNS) [50]. Another urochordate, the larvacean O. dioica, shows a dramatic disintegration of the cluster with all the Hox genes scattered along the genome. Only two genes—Hox9a and Hox9b—are linked, probably as a result of a species-specific tandem duplication event [53]. Moreover larvaceans seems to have lost Hox3, 5, 6, 7 and 8[53]. Additionally, it has been proposed that the previously named Hox11 gene of O. dioica is in fact Hox12, something that is consistent between phylogenetic trees and non-phylogenetic tree-based methods. Thus, O. dioica Hox11 and 12 should be renamed as Hox12a and Hox12b (Figure 2[46]), which implies that also Hox11 was lost in O. dioica, as in other ascidians. Strikingly, as in C. intestinalis, O. dioica Hox genes were expressed with partial spatial colinearity in the CNS [53].
Vertebrates
The increased number of Hox clusters in vertebrates compared with their invertebrate counterparts illustrates clearly the history of genome duplications. Following the 2R-WGD at the base of the vertebrates, tetrapods retained four clusters, whereas teleost fishes expanded to seven or eight clusters arising from a teleost-specific 3R-WGD [5] and salmonids up to 13 clusters after an additional salmonid-specific 4R-WGD [54, 55] (Figure 2). In all WGD events, the duplication of the Hox cluster was followed by differential Hox gene losses, eventually resulting in a unique combination of Hox genes in every group, like a bar code (a “genomic Hox-bar code”). Accordingly, it would be possible to determine to which group a genome of unknown source would belong, just by observing the Hox gene/cluster content.
In the following sections, we collate what is known about the Hox gene families in different vertebrate groups regarding their genomic configuration and plausible evolutionary origins and modifications.
Hoxgenes of cyclostomes: the main vertebrate gap
Cyclostomes (the only extant group of agnathans or jawless vertebrates) are the sister group of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates) and are much less known than the latter, also in terms of Hox gene content. Cyclostomes are composed of two different groups: lampreys and hagfishes. In the case of the hagfish, the most recent report is that of Stadler et al. [56], who obtained up to 33 Hox genes using degenerate PCR, a lower number than that of a general gnathostome, but still compatible with multiple clusters. The authors [56] concluded from their analyses that cyclostomes had split at least after the first WGD and that subsequent independent gene/cluster duplications expanded their Hox inventory. However, their analysis was based on very short sequences, so their conclusions remained very speculative. A conclusive repertoire of Hox genes and clusters of the hagfish is far from definitive, since the genomic organization of the hagfish Hox genes still remains a mystery. New advances in hagfish research [57, 58] together with the new and powerful sequencing techniques available will surely help to fill this gap in the future.
Regarding lampreys, several PCR surveys have been done using different lamprey species: Petromyzon marinus[59–63], Lampetra planeri[64] and the Japanese lamprey Lethenteron japonicum[44, 65, 66]. Moreover, the draft genome of the sea lamprey (P. marinus) has been published recently [67] and the Hox genes were investigated. A total of 25 Hox genes were found but only two Hox clusters were recognizable: clusters Pm1Hox (with Hox2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 11) and Pm2Hox (Hox1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11). Besides these clusters, eight additional genes were found lacking genomic information, except for two of them that are linked, indicating the presence of a putative third cluster [67].
Because the information from the above-mentioned studies is rather scattered and incomplete in terms of a definitive lamprey Hox repertoire, we have compiled all the information of genes and clusters reported thus far for lampreys in Table 1. Taking into account that there are genes identified exclusively in some individual studies, a total of 44 distinct lamprey Hox genes are recognizable (this number can vary, depending on whether some are just allelic variations; see Table 1). These 44 Hox genes would represent the ancestral condition of lampreys, and some of them might not be present in all species. Also, we propose a shift and normalization of the nomenclature of lamprey Hox genes, using the Greek alphabet (as in [44]) to indicate the absence of a clear homologous relationship to the gnathostome HoxA, B, C and D clusters. Assignments of some lamprey central Hox genes to PG5–7 remain doubtful (Table 1). Interestingly, no Hox gene belonging to PG12 has been found in any of these studies (Table 1), suggesting the possible loss of all Hox12 genes in the LCA of lampreys.
The number of Hox clusters of the lamprey can be estimated to be four or five: there are four cognates for at least PG1, 8 and 10 (see Table 1); strikingly, there are five distinct genes for PG4, 9 and 11 and although there are four Hox1 genes, the cluster Pm1Hox does not seem to have a Hox1 member [67]. Conversely, there might be fewer clusters, depending on allelic polymorphisms or independent tandem duplication events within a cluster [63]. Nonetheless, none of the above-mentioned scenarios is conclusive and further investigation is needed. At present, it is not clear whether lampreys hold representatives of the four gnathostome Hox clusters or whether some originated by independent duplication events (for example, if five clusters are confirmed) [68]. Finally, phylogenetic analysis of dozens of gene families [69] and the recent analysis of the P. marinus genome [67] pointed to a post 2R-WGD origin of cyclostomes, indicating that the LCA of vertebrates most probably possessed four Hox clusters. Accordingly, the synteny of non-Hox genes linked to the Hox clusters has been generally conserved between cyclostomes and gnathostomes, although with a differential retention of paralogues [67].
Condrichthyans: a Hoxcluster loss
The gnathostomes consist of two main groups: condrichthyans (cartilaginous fishes) and osteichthyans (bony vertebrates); and all of them possess members of the four Hox clusters (A, B, C and D), indicating that they diverged after the 2R-WGDs [70]. The condrichthyans are divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, skates and rays) and Holocephali (chimaeras).
Apart from some partial reports on the horn shark Heterodontus francisci (elasmobranch) [71–73], the first complete condrichthyan Hox repertoire was reported in a chimaera, the elephant shark Callorhinchus milii (holocephalian). C. milii possesses a total of 45 Hox genes, retaining the HoxD14 gene, plus two Hox14 pseudogenes (A and B, see Figure 2). The C. milii Hox repertoire substantially increased the putative Hox contents of the gnathostome ancestor [74]. Surprisingly, elasmobranchs seem to have lost the HoxC cluster completely. Studies with both the lesser-spotted cat shark Scyliorhinus canicula and the little skate Leucoraja erinacea did not find any of the HoxC cluster members, including sequences encoding Hox cluster-associated microRNAs [75, 76]. These are the first reports on the loss of a complete Hox cluster type (A, B, C or D) within jawed vertebrates, a loss that dates back to 250 Mya [77].
Osteichthyans
The Hox clusters of osteichthyans are the most well-known within vertebrates and deuterostomes. Here we include recent reports on newly investigated species that have changed the overall scenario of the previously inferred ancestral conditions [5].
Osteichthyans comprise two major groups: sarcopterygians (coelacanths, lungfish and tetrapods) and actinopterygians (ray-finned fishes, including teleosts). Within the former, the complete repertoire of many tetrapods (chicken, mouse and human genomes among others) is known [5, 78]. Comparison of the Hox inventories of different tetrapods allows to infer a tetrapod ancestral condition of up to 41 genes [78], one more than previously thought [5], and an amniote ancestral condition of 40 Hox genes (after the loss of HoxC1; Figure 2), of which only the green anole (Anolis carolinensis) retains all of them [78, 79], while mammals and the chicken have lost the HoxC3 gene independently. Liang et al. [78] also did not identify HoxC3 in crocodiles and turtles by degenerate PCR and it is absent from turtle genomes [80, 81]. Therefore, HoxC3 was probably lost before the evolutionary split of archosaurians and turtles. Amphibian repertoires vary: Xenopus tropicalis has 38 Hox genes, three fewer than in the ancestral tetrapod. One of these lost genes is HoxC1, also lost from amniotes. Because HoxC1 is still present in the amphibian caecilian Ichthyophis bannanicus[78], it means that it was lost independently in amniotes and X. tropicalis (Figure 2). Taking into account data from I. bannanicus and the salamander Batrachuperus tibetanus[78], the amphibian ancestor probably had 40 genes, after losing HoxD12 from its tetrapod ancestor (Figure 2).
The Hox clusters of the coelacanths Latimeria menadoensis[82] and Latimeria chalumnae[83], the closest living relative to the sarcopterygian ancestor [83], include a HoxA14 gene that was later lost in tetrapods. Moreover, a PCR survey of the lungfish Protopterus annectens also found a HoxA14 gene ([78]; data from the lungfish are not included in Figure 2 because they lack clustering information, but they were taken into account to infer the ancestral condition). This enabled Liang and colleagues [78] to reconstruct a more complete ancestral sarcopterygian Hox inventory, with a total of 43 Hox genes (Figure 2).
The case of actinopterygians is rather more complicated, because after the teleost-specific 3R-WGD, more genes—and in some cases a complete cluster—were lost differentially (Figure 2). Teleosts are the most numerous group of vertebrates with more than 27,000 extant species [84]. It has been already 15 years since more than four Hox clusters were found in the cyprinid zebrafish Danio rerio[60, 85], which instead has seven Hox clusters: HoxAa, HoxAb, HoxBa, HoxBb, HoxCa, HoxCb and HoxDa. The cluster HoxDb has been reduced to only the Hox-related microRNA miR-10d[86]. Another cyprinid, Megalobrama amblycephala, might also lack the HoxDb cluster [87], implying that it was probably lost in the cyprinid ancestor. Other teleosts with known Hox complement include pufferfishes, cichlids, medakas, sticklebacks, salmonids and some early lineages such as the eel and the bichir (although data are not complete for the last species). The Hox complement of several pufferfishes has been already reported: Spheroides nephelus[88], Takifugu rubripes[88, 89] and Tetraodon nigroviridis[90] showing differential species-specific losses (see Figure 2). The case of T. rubripes is curious. Amores and colleagues described a possible duplication of the HoxAa cluster in T. rubripes, which they called HoxAc[88]. This cluster duplication was considered doubtful by other authors [4, 5]. Later it was found that the sequence of this HoxAc cluster, present in version 2.0 of the genome of T. rubripes, corresponded to a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone of the Nile tilapia and was not present in later versions of the T. rubripes genome [91]. Comparisons of the Hox complement of the above-mentioned pufferfishes with those of the medaka Oryzia latipes[92], cichlids such as the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus[93] (not present in Figure 2 because the clusters are largely not sequenced), of Astatotilapia burtoni[94, 95] and the three-spine stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus[94], show a common loss of the HoxCb cluster in their LCA (the ancestral Neoteleosteii; see Figure 2). Moreover, independent losses of Hox genes are not rare: for example HoxBa7 and HoxCa1[94, 95] have been lost several times (Figure 2). HoxBa7 is present in O. niloticus and thus was independently lost in the medaka and A. burtoni.
Strikingly, the Atlantic salmon Salmo salar and the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss contain 13 Hox clusters [55, 96, 97], arising from a salmonid-specific 4R-WGD [54], the former with a total of 118 Hox genes plus eight pseudogenes: the largest Hox repertoire to date [55]. S. salar lost the HoxDb cluster before the 4R-WGD (as did zebrafish independently). S. salar still retains HoxD1a copies (α and β) within the HoxDa cluster. Therefore, HoxD1a was indeed present in the teleost ancestor, in contrast to previous ideas [5]. The complete repertoire of Hox clusters of the European eel Anguilla anguilla, representing the earliest branch of teleosts [98], helped in reconstructing a more reliable teleost ancestral inventory [99]. A. anguilla also retains HoxD1a, like S. salar, meaning that it was independently lost later in zebrafish and neoteleosts (e.g., medakas, pufferfishes, cichlids and sticklebacks; Figure 2). A. anguilla is the best representative of the teleost ancestor, having lost only four Hox genes (three of them are pseudogenes) and retaining all eight Hox clusters after the 3R-WGD ([99]; Figure 2). The osteoglossomorph Hiodon alosoides (the goldeye), a representative of a basal branch diverging after the eels [98], also seems to have retained the original eight clusters [100]. In summary, the teleost ancestor probably had at least 74 Hox genes, with eight Hox clusters (after the 3R-WGD), quickly followed by differential gene and cluster losses in the different lineages ([99]; Figure 2).
There are few reports on Hox genes of fishes outside the teleosts. Several studies report either few Hox genes or partial information about Hox clusters for the Senegal bichir Polypterus senegalus. The bichir is a representative of the earliest branch of actinopterygians that diverged prior to the 3R-WGD. Only the HoxA cluster sequence out of a total of four clusters has been reported thus far [101, 102]. There is also a report of cDNA screening in another bichir species, Polypterus palmas[103]. Although again, while the data presented are fragmented and not complete, these studies allow to infer the presence of HoxD2 in the LCA of osteichthyans (and actinopterygians), a gene that was lost in all the osteichthyans species studied so far except in the bichir ([102]; Figure 2). In another gnathostome species, the catshark S. canicula, HoxD2 is expressed in very important tissues such as the pharyngeal arches and the rhombencephalon [104]. However, we predict that the loss of this gene may have little importance in the general patterning of such tissues, because the expression of Hox genes is quite redundant; once a gene is lost, other Hox genes patterning the pharynx and the hindbrain could compensate for its function. The information for other early branches of actinopterygians (the paddlefish, sturgeon, gar and Amia calva), diverging after the bichir, is also scattered and partial [6, 105], although it is important to note that some of them, for instance sturgeon and paddlefish, probably have more than four Hox clusters caused by lineage-specific WGDs [105]. In fact, the American paddlefish Polyodon spathula has at least two HoxA and two HoxD clusters (each termed α and β, to denote their different duplicative origins from the teleost 3R-WGD). Surprisingly, P. spathula retains a HoxD14β paralogue [105], indicating that, unlike as previously inferred, HoxD14 was present in the LCA of actinopterygians (and thus in the osteichthyan LCA) and was secondarily lost in the rest of the lineages of the group (shown in Figure 2).
The unsolved origin of the deuterostome posterior Hoxgenes
More than a decade ago, the discovery and analysis of the posterior Hox genes in amphioxus reflected the problematic issue of their one-to-one orthology assignments with their vertebrate counterparts [43]. This phenomenon, also present in posterior ambulacrarian Hox genes (the posterior AmbP genes, namely Hox11/13a, b and c, form an independent clade [34]), was explained by a possibly higher rate of evolution of the posterior Hox genes, eventually precluding their grouping in phylogenetic trees. This process was called deuterostome posterior flexibility [43]. The discovery of the PG14 in vertebrates [73], disallowed alternative explanations because it equated the number of vertebrate PGs to the number of amphioxus Hox genes known by that time and because of the amount of tandem duplications and losses implicated in an origin by independent duplications. Therefore, the notion of deuterostome posterior flexibility was commonly accepted. However, in the last few years, new results based on different methods have turned the tables. We will try here to integrate the information from both phylogenetic trees performed previously by several studies [34, 41, 44, 46] and from two methods not based on phylogenetic trees [45, 46] and summarize them into the most parsimonious scenario.
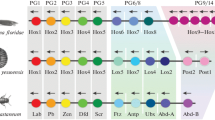
It is remarkable that amphioxus Hox9–12 genes seldom group in a one-to-one relationship with their vertebrate cognates, but they tend to group together in a single clade. The same occurs with amphioxus Hox13–15[34, 41, 46]. Interestingly, the amphioxus Hox9–12 and Hox13–15 clades usually group with vertebrate Hox9–10 and Hox11–14, respectively, suggesting an independent origin for these genes from at least two ancestral posterior Hox genes, as proposed in one of the evolutionary scenarios put forward by Freeman et al. [34]. However, how vertebrates and amphioxus obtained their final set of posterior Hox genes is trickier, so we have pictured a likely evolutionary scenario (represented in Figure 3), based on several lines of evidence. First, the recently discovered amphioxus Hox15 gene groups with vertebrate PG13 in a well-supported clade [34, 41] and both of them group with vertebrate PG14. In addition, a weight matrix-based method also assigned amphioxus Hox15 to PG13 [46]. This would imply the presence of at least one ancestral PG13/14 gene in chordates from which the amphioxus Hox15 and vertebrate PG13 and PG14 genes originated (Figure 3; green boxes). Alternatively, amphioxus may have lost the PG14 cognate secondarily if there were both PG13 and PG14 genes ancestrally. Second, amphioxus Hox13 and Hox14 generally group together, suggesting an origin by tandem duplication in the cephalochordate lineage. In addition, the amphioxus Hox13/14 clade tends to fall in a bigger clade with vertebrate PG11–12, implying a common origin (an ancestral PG11/12 gene: Figure 3; orange boxes). Third, as mentioned above, amphioxus Hox9–12 genes tend to group together in an independent clade [41], suggesting their independent origin in this taxon by a tandem duplication event. Moreover, amphioxus Hox9–12 genes tend to fall within the vertebrate PG9–10 clade, symptomatic of the existence of an ancestral PG9/10 gene in chordates (Figure 3; red boxes). Therefore, the last common ancestor of chordates had at least three posterior Hox genes (see Figure 3): one PG9/10, one PG11/12, from which amphioxus Hox13–14 originated and one PG13/14, from which amphioxus Hox15 originated. The two latter probably come from a PG11/14 ancestral gene, because all chordate Hox11–15 genes form a monophyletic clade [34], implying a first condition of two ancestral genes, that quickly expanded into a three-gene condition arising from a duplication in tandem (Figure 3).
Possible evolutionary scenario for the origin of posterior Hox genes in amphioxus, ambulacrarians and vertebrates. The presence of the second intron splitting the homeobox into two exons is shown in those genes where it is present, and inferred in ancestral conditions. The red asterisk indicates that the amphioxus Hox12 gene intron is in a different position and thus was acquired secondarily. The green asterisk indicates that Hox13β of the lamprey L. japonicum has retained the ancestral intron, but that intron has been lost in all other vertebrate Hox13 genes. The black question marks indicate the unclear evolutionary origin of AmbP and PG11/14 ancestral genes: they could have been originated independently, or were present in the last common ancestor of deuterostomes. The existence of more Hox genes in the ancestral states cannot be excluded at this time.
When including the available data from ambulacrarians to this hypothesis, it becomes still more complicated. On one side, the ambulacrarian Hox9/10 genes group with their chordate cognates PG9 and PG10, also proved by non-phylogenetic tree-based methods [45, 46], suggesting that the LCA of deuterostomes likely had the PG9/10 ancestral gene. On the other hand, the phylogenetic relationships between ambulacrarian AmbP genes and the chordate PG11–14 genes are not consistent between different studies and several scenarios are possible (see [34]). Thomas-Chollier et al. [46] assigned AmbP genes to the vertebrate PG9, suggesting an independent origin of these genes from the ancestral PG9/10 gene in the ambulacrarian lineage (Figure 3), but, because there are no other studies suggesting this, the origin of AmbP remains unsolved.
This entire evolutionary scenario gets even more complicated when considering the presence of introns within the homeobox. Hox genes have generally only one intron, splitting the gene into two exons, the second one containing the homeobox. However, some posterior Hox genes possess a second intron splitting the homeobox into two exons. These are the vertebrate Hox14 genes, lamprey Hox13β and amphioxus Hox11, Hox12 and Hox14. This second intron is in the same position for all of them (except for amphioxus Hox12) and equal to the second intron position of the dipteran posterior Abdominal-B genes [44, 73]. Common introns suggest an ancestral origin, because it seems more probable to gain an intron once and then lose it secondarily, than to gain it in the same position independently [106]. Therefore, and within the evolutionary frame suggested above, ambulacrarian posterior Hox genes lost this intron in the LCA of ambulacrarians, while in vertebrates, the two or three ancestral posterior Hox genes contained this intron, which subsequently was lost in different genes independently in the amphioxus and vertebrate lineages; finally amphioxus Hox12 gained secondarily a different second intron (Figure 3).
Review and conclusion
In summary, the posterior Hox genes are thus more flexible than central and anterior Hox genes, at least in terms of non-stasis: thus, while the number of posterior Hox genes seems to have changed independently in the different deuterostome lineages (Figure 3), the numbers of anterior and central Hox genes have been kept fixed since the deuterostome LCA (PG1–8) [34]. These more recent changes in the posterior part of the cluster may also explain why the non-coding regions of this part of the cluster are less conserved than those of more anterior parts [42, 74, 107]. This new cis-deuterostome posterior flexibility implies a lack of regulatory constraints for the PG9–14 cognates that eventually allowed posterior genes to be uncoupled from the stricter Hox code of more anterior genes [44, 48, 108] or to be co-opted to pattern novel morphological structures, such as the limbs and genital tracts of vertebrates.
Future perspectives
We have presented here a catalogue and a current view on the evolution of Hox gene families in deuterostomes, showing that we are still far from picturing a conclusive scenario for the ancestral conditions. In fact, many early branches within vertebrates remain to be examined, as do more invertebrate deuterostomes (for example, more ambulacrarians); hence we cannot exclude the existence of more Hox genes in the ancestral states until the number of sequenced genomes from non-model animals has increased considerably. With the new genome projects being carried out currently in a wide range of animals, mainly in vertebrates (e.g., the 10 K Genome Project [109]), this landscape will change in the very near future. On the other hand, the problematic origin of the posterior Hox genes will not be solved just by reporting more Hox genes, but also will require improved methods, both phylogenetic and non-phylogenetic.
References
Ohno S: Evolution by Gene Duplication. 1970, New York: Springer-Verlag
Putnam NH, Butts T, Ferrier DE, Furlong RF, Hellsten U, Kawashima T, Robinson-Rechavi M, Shoguchi E, Terry A, Yu JK, et al: The amphioxus genome and the evolution of the chordate karyotype. Nature. 2008, 453 (7198): 1064-1071. 10.1038/nature06967.
Kasahara M: The 2R hypothesis: an update. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007, 19 (5): 547-552. 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.009.
Hoegg S, Meyer A: Hox clusters as models for vertebrate genome evolution. Trends Genet. 2005, 21 (8): 421-424. 10.1016/j.tig.2005.06.004.
Kuraku S, Meyer A: The evolution and maintenance of Hox gene clusters in vertebrates and the teleost-specific genome duplication. Int J Dev Biol. 2009, 53 (5–6): 765-773.
Crow KD, Stadler PF, Lynch VJ, Amemiya C, Wagner GP: The "fish-specific" Hox cluster duplication is coincident with the origin of teleosts. Mol Biol Evol. 2006, 23 (1): 121-136.
Hoegg S, Brinkmann H, Taylor JS, Meyer A: Phylogenetic timing of the fish-specific genome duplication correlates with the diversification of teleost fish. J Mol Evol. 2004, 59 (2): 190-203. 10.1007/s00239-004-2613-z.
Taylor JS, Van de Peer Y, Braasch I, Meyer A: Comparative genomics provides evidence for an ancient genome duplication event in fish. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001, 356 (1414): 1661-1679. 10.1098/rstb.2001.0975.
Scott MP: Vertebrate homeobox gene nomenclature. Cell. 1992, 71 (4): 551-553. 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90588-4.
Pearson JC, Lemons D, McGinnis W: Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning. Nat Rev Genet. 2005, 6 (12): 893-904. 10.1038/nrg1726.
Ahn D, Ho RK: Tri-phasic expression of posterior Hox genes during development of pectoral fins in zebrafish: implications for the evolution of vertebrate paired appendages. Dev Biol. 2008, 322 (1): 220-233. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.06.032.
Freitas R, Gómez-Marín C, Wilson JM, Casares F, Gómez-Skarmeta JL: Hoxd13 contribution to the evolution of vertebrate appendages. Dev Cell. 2012, 23 (6): 1219-1229. 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.10.015.
Burke AC, Nelson CE, Morgan BA, Tabin C: Hox genes and the evolution of vertebrate axial morphology. Development. 1995, 121 (2): 333-346.
Gaunt SJ: Conservation in the Hox code during morphological evolution. Int J Dev Biol. 1994, 38 (3): 549-552.
Di-Poï N, Montoya-Burgos JI, Miller H, Pourquié O, Milinkovitch MC, Duboule D: Changes in Hox genes' structure and function during the evolution of the squamate body plan. Nature. 2010, 464 (7285): 99-103. 10.1038/nature08789.
Wellik DM, Capecchi MR: Hox10 and Hox11 genes are required to globally pattern the mammalian skeleton. Science. 2003, 301 (5631): 363-367. 10.1126/science.1085672.
Delsuc F, Brinkmann H, Chourrout D, Philippe H: Tunicates and not cephalochordates are the closest living relatives of vertebrates. Nature. 2006, 439 (7079): 965-968. 10.1038/nature04336.
Ruiz-Trillo I, Riutort M, Littlewood DT, Herniou EA, Baguñà J: Acoel flatworms: earliest extant bilaterian metazoans, not members of platyhelminthes. Science. 1999, 283 (5409): 1919-1923. 10.1126/science.283.5409.1919.
Ruiz-Trillo I, Paps J, Loukota M, Ribera C, Jondelius U, Baguñà J, Riutort M: A phylogenetic analysis of myosin heavy chain type II sequences corroborates that acoela and nemertodermatida are basal bilaterians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002, 99 (17): 11246-11251. 10.1073/pnas.172390199.
Telford MJ, Lockyer AE, Cartwright-Finch C, Littlewood DT: Combined large and small subunit ribosomal RNA phylogenies support a basal position of the acoelomorph flatworms. Proc Biol Sci. 2003, 270 (1519): 1077-1083. 10.1098/rspb.2003.2342.
Sempere LF, Cole CN, McPeek MA, Peterson KJ: The phylogenetic distribution of metazoan microRNAs: insights into evolutionary complexity and constraint. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2006, 306 (6): 575-588.
Bourlat SJ, Nielsen C, Lockyer AE, Littlewood DT, Telford MJ: Xenoturbella is a deuterostome that eats molluscs. Nature. 2003, 424 (6951): 925-928. 10.1038/nature01851.
Bourlat SJ, Juliusdottir T, Lowe CJ, Freeman R, Aronowicz J, Kirschner M, Lander ES, Thorndyke M, Nakano H, Kohn AB, et al: Deuterostome phylogeny reveals monophyletic chordates and the new phylum xenoturbellida. Nature. 2006, 444 (7115): 85-88. 10.1038/nature05241.
Philippe H, Brinkmann H, Copley RR, Moroz LL, Nakano H, Poustka AJ, Wallberg A, Peterson KJ, Telford MJ: Acoelomorph flatworms are deuterostomes related to xenoturbella. Nature. 2011, 470 (7333): 255-258. 10.1038/nature09676.
Hejnol A, Obst M, Stamatakis A, Ott M, Rouse GW, Edgecombe GD, Martinez P, Baguñà J, Bailly X, Jondelius U, et al: Assessing the root of bilaterian animals with scalable phylogenomic methods. Proc Biol Sci. 2009, 276 (1677): 4261-4270. 10.1098/rspb.2009.0896.
Fritzsch G, Böhme MU, Thorndyke M, Nakano H, Israelsson O, Stach T, Schlegel M, Hankeln T, Stadler PF: PCR survey of xenoturbella bocki hox genes. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2008, 310 (3): 278-284.
Cook CE, Jiménez E, Akam M, Saló E: The hox gene complement of acoel flatworms, a basal bilaterian clade. Evol Dev. 2004, 6 (3): 154-163. 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2004.04020.x.
Moreno E, Nadal M, Baguñà J, Martínez P: Tracking the origins of the bilaterian Hox patterning system: insights from the acoel flatworm. Symsagittifera roscoffensis. Evol Dev. 2009, 11 (5): 574-581. 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2009.00363.x.
Hejnol A, Martindale MQ: Coordinated spatial and temporal expression of Hox genes during embryogenesis in the acoel Convolutriloba longifissura. BMC Biol. 2009, 7: 65-10.1186/1741-7007-7-65.
Jiménez-Guri E, Paps J, Garcia-Fernàndez J, Saló E: Hox and ParaHox genes in nemertodermatida, a basal bilaterian clade. Int J Dev Biol. 2006, 50 (8): 675-679. 10.1387/ijdb.062167ej.
Kondo M, Akasaka K: Current status of echinoderm genome analysis - what do we know?. Curr Genomics. 2012, 13 (2): 134-143. 10.2174/138920212799860643.
Sodergren E, Weinstock GM, Davidson EH, Cameron RA, Gibbs RA, Angerer RC, Angerer LM, Arnone MI, Burgess DR, Burke RD, et al: The genome of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Science. 2006, 314 (5801): 941-952.
Cameron RA, Rowen L, Nesbitt R, Bloom S, Rast JP, Berney K, Arenas-Mena C, Martínez P, Lucas S, Richardson PM, et al: Unusual gene order and organization of the sea urchin Hox cluster. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2006, 306 (1): 45-58.
Freeman R, Ikuta T, Wu M, Koyanagi R, Kawashima T, Tagawa K, Humphreys T, Fang GC, Fujiyama A, Saiga H, et al: Identical genomic organization of two hemichordate Hox clusters. Curr Biol. 2012, 22 (21): 2053-2058. 10.1016/j.cub.2012.08.052.
Hara Y, Yamaguchi M, Akasaka K, Nakano H, Nonaka M, Amemiya S: Expression patterns of Hox genes in larvae of the sea lily Metacrinus rotundus. Dev Genes Evol. 2006, 216 (12): 797-809. 10.1007/s00427-006-0108-1.
Mito T, Endo K: A PCR survey of Hox genes in the sea star. Asterina minor. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1997, 8 (2): 218-224. 10.1006/mpev.1997.0417.
Long S, Martinez P, Chen WC, Thorndyke M, Byrne M: Evolution of echinoderms may not have required modification of the ancestral deuterostome HOX gene cluster: first report of PG4 and PG5 Hox orthologues in echinoderms. Dev Genes Evol. 2003, 213 (11): 573-576. 10.1007/s00427-003-0355-3.
Bertrand S, Escriva H: Evolutionary crossroads in developmental biology: amphioxus. Development. 2011, 138 (22): 4819-4830. 10.1242/dev.066720.
Garcia-Fernàndez J, Holland PWH: Archetypal organization of the amphioxus Hox gene cluster. Nature. 1994, 370 (6490): 563-566. 10.1038/370563a0.
Amemiya CT, Prohaska SJ, Hill-Force A, Cook A, Wasserscheid J, Ferrier DE, Pascual-Anaya J, Garcia-Fernàndez J, Dewar K, Stadler PF: The amphioxus Hox cluster: characterization, comparative genomics, and evolution. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2008, 310 (5): 465-477.
Holland LZ, Albalat R, Azumi K, Benito-Gutiérrez E, Blow MJ, Bronner-Fraser M, Brunet F, Butts T, Candiani S, Dishaw LJ, et al: The amphioxus genome illuminates vertebrate origins and cephalochordate biology. Genome Res. 2008, 18 (7): 1100-1111. 10.1101/gr.073676.107.
Pascual-Anaya J, D'Aniello S, Garcia-Fernàndez J: Unexpectedly large number of conserved noncoding regions within the ancestral chordate Hox cluster. Dev Genes Evol. 2008, 218 (11–12): 591-597.
Ferrier DE, Minguillón C, Holland PWH, Garcia-Fernàndez J: The amphioxus Hox cluster: deuterostome posterior flexibility and Hox14. Evol Dev. 2000, 2 (5): 284-293. 10.1046/j.1525-142x.2000.00070.x.
Kuraku S, Takio Y, Tamura K, Aono H, Meyer A, Kuratani S: Noncanonical role of Hox14 revealed by its expression patterns in lamprey and shark. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008, 105 (18): 6679-6683. 10.1073/pnas.0710947105.
Hueber SD, Weiller GF, Djordjevic MA, Frickey T: Improving Hox protein classification across the major model organisms. PLoS One. 2010, 5 (5): e10820-10.1371/journal.pone.0010820.
Thomas-Chollier M, Ledent V, Leyns L, Vervoort M: A non-tree-based comprehensive study of metazoan Hox and ParaHox genes prompts new insights into their origin and evolution. BMC Evol Biol. 2010, 10: 73-10.1186/1471-2148-10-73.
Kon T, Nohara M, Yamanoue Y, Fujiwara Y, Nishida M, Nishikawa T: Phylogenetic position of a whale-fall lancelet (Cephalochordata) inferred from whole mitochondrial genome sequences. BMC Evol Biol. 2007, 7: 127-10.1186/1471-2148-7-127.
Pascual-Anaya J, Adachi N, Alvarez S, Kuratani S, D'Aniello S, Garcia-Fernàndez J: Broken colinearity of the amphioxus Hox cluster. EvoDevo. 2012, 3 (1): 28-10.1186/2041-9139-3-28.
Spagnuolo A, Ristoratore F, Di Gregorio A, Aniello F, Branno M, Di Lauro R: Unusual number and genomic organization of Hox genes in the tunicate Ciona intestinalis. Gene. 2003, 309 (2): 71-79. 10.1016/S0378-1119(03)00488-8.
Ikuta T, Yoshida N, Satoh N, Saiga H: Ciona intestinalis Hox gene cluster: Its dispersed structure and residual colinear expression in development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004, 101 (42): 15118-15123. 10.1073/pnas.0401389101.
Shoguchi E, Hamaguchi M, Satoh N: Genome-wide network of regulatory genes for construction of a chordate embryo. Dev Biol. 2008, 316 (2): 498-509. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.01.009.
Dehal P, Satou Y, Campbell RK, Chapman J, Degnan B, De Tomaso A, Davidson B, Di Gregorio A, Gelpke M, Goodstein DM, et al: The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science. 2002, 298 (5601): 2157-2167. 10.1126/science.1080049.
Seo HC, Edvardsen RB, Maeland AD, Bjordal M, Jensen MF, Hansen A, Flaat M, Weissenbach J, Lehrach H, Wincker P, et al: Hox cluster disintegration with persistent anteroposterior order of expression in Oikopleura dioica. Nature. 2004, 431 (7004): 67-71. 10.1038/nature02709.
Allendorf FW, Thorgaard GH: Tetraploidy and the evolution of salmonid fish. Evolutionary genetics of fish. Edited by: Turner JB. 1984, New York: Plenum Press, 1-53.
Mungpakdee S, Seo HC, Angotzi AR, Dong X, Akalin A, Chourrout D: Differential evolution of the 13 atlantic salmon Hox clusters. Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25 (7): 1333-1343. 10.1093/molbev/msn097.
Stadler PF, Fried C, Prohaska SJ, Bailey WJ, Misof BY, Ruddle FH, Wagner GP: Evidence for independent Hox gene duplications in the hagfish lineage: a PCR-based gene inventory of Eptatretus stoutii. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2004, 32 (3): 686-694. 10.1016/j.ympev.2004.03.015.
Oisi Y, Ota KG, Kuraku S, Fujimoto S, Kuratani S: Craniofacial development of hagfishes and the evolution of vertebrates. Nature. 2013, 493 (7431): 175-180.
Ota KG, Kuraku S, Kuratani S: Hagfish embryology with reference to the evolution of the neural crest. Nature. 2007, 446 (7136): 672-675. 10.1038/nature05633.
Pendleton JW, Nagai BK, Murtha MT, Ruddle FH: Expansion of the Hox gene family and the evolution of chordates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993, 90 (13): 6300-6304. 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6300.
Amores A, Force A, Yan YL, Joly L, Amemiya C, Fritz A, Ho RK, Langeland J, Prince V, Wang YL, et al: Zebrafish Hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science. 1998, 282 (5394): 1711-1714.
Carr JL, Shashikant CS, Bailey WJ, Ruddle FH: Molecular evolution of Hox gene regulation: cloning and transgenic analysis of the lamprey HoxQ8 gene. J Exp Zool. 1998, 280 (1): 73-85. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19980101)280:1<73::AID-JEZ9>3.0.CO;2-E.
Force A, Amores A, Postlethwait JH: Hox cluster organization in the jawless vertebrate Petromyzon marinus. J Exp Zool. 2002, 294 (1): 30-46. 10.1002/jez.10091.
Irvine SQ, Carr JL, Bailey WJ, Kawasaki K, Shimizu N, Amemiya CT, Ruddle FH: Genomic analysis of Hox clusters in the sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus. J Exp Zool. 2002, 294 (1): 47-62. 10.1002/jez.10090.
Sharman AC, Holland PW: Estimation of Hox gene cluster number in lampreys. Int J Dev Biol. 1998, 42 (4): 617-620.
Takio Y, Kuraku S, Murakami Y, Pasqualetti M, Rijli FM, Narita Y, Kuratani S, Kusakabe R: Hox gene expression patterns in lethenteron japonicum embryos–insights into the evolution of the vertebrate Hox code. Dev Biol. 2007, 308 (2): 606-620. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.009.
Takio Y, Pasqualetti M, Kuraku S, Hirano S, Rijli FM, Kuratani S: Evolutionary biology: lamprey Hox genes and the evolution of jaws. Nature. 2004, 429 (6989): 1-262.
Smith JJ, Kuraku S, Holt C, Sauka-Spengler T, Jiang N, Campbell MS, Yandell MD, Manousaki T, Meyer A, Bloom OE, et al: Sequencing of the sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) genome provides insights into vertebrate evolution. Nat Genet. 2013, 45 (4): 415-421. 10.1038/ng.2568.
Fried C, Prohaska SJ, Stadler PF: Independent Hox-cluster duplications in lampreys. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2003, 299 (1): 18-25.
Kuraku S, Meyer A, Kuratani S: Timing of genome duplications relative to the origin of the vertebrates: did cyclostomes diverge before or after?. Mol Biol Evol. 2009, 26 (1): 47-59.
Kuraku S: Hox gene clusters of early vertebrates: do they serve as reliable markers for genome evolution?. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2011, 9 (3): 97-103. 10.1016/S1672-0229(11)60012-0.
Kim CB, Amemiya C, Bailey W, Kawasaki K, Mezey J, Miller W, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Wagner G, Ruddle F: Hox cluster genomics in the horn shark, Heterodontus francisci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000, 97 (4): 1655-1660. 10.1073/pnas.030539697.
Chiu CH, Amemiya C, Dewar K, Kim CB, Ruddle FH, Wagner GP: Molecular evolution of the HoxA cluster in the three major gnathostome lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002, 99 (8): 5492-5497. 10.1073/pnas.052709899.
Powers TP, Amemiya CT: Evidence for a Hox14 paralog group in vertebrates. Curr Biol. 2004, 14 (5): R183-R184. 10.1016/j.cub.2004.02.015.
Ravi V, Lam K, Tay BH, Tay A, Brenner S, Venkatesh B: Elephant shark (Callorhinchus milii) provides insights into the evolution of Hox gene clusters in gnathostomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009, 106 (38): 16327-16332. 10.1073/pnas.0907914106.
Oulion S, Debiais-Thibaud M, d'Aubenton-Carafa Y, Thermes C, Da Silva C, Bernard-Samain S, Gavory F, Wincker P, Mazan S, Casane D: Evolution of Hox gene clusters in gnathostomes: insights from a survey of a shark (Scyliorhinus canicula) transcriptome. Mol Biol Evol. 2010, 27 (12): 2829-2838. 10.1093/molbev/msq172.
King BL, Gillis JA, Carlisle HR, Dahn RD: A natural deletion of the HoxC cluster in elasmobranch fishes. Science. 2011, 334 (6062): 1517-10.1126/science.1210912.
Inoue JG, Miya M, Lam K, Tay BH, Danks JA, Bell J, Walker TI, Venkatesh B: Evolutionary origin and phylogeny of the modern holocephalans (chondrichthyes: chimaeriformes): a mitogenomic perspective. Mol Biol Evol. 2010, 27 (11): 2576-2586. 10.1093/molbev/msq147.
Liang D, Wu R, Geng J, Wang C, Zhang P: A general scenario of Hox gene inventory variation among major sarcopterygian lineages. BMC Evol Biol. 2011, 11: 25-10.1186/1471-2148-11-25.
Di-Poï N, Montoya-Burgos JI, Duboule D: Atypical relaxation of structural constraints in Hox gene clusters of the green anole lizard. Genome Res. 2009, 19 (4): 602-610. 10.1101/gr.087932.108.
Wang Z, Pascual-Anaya J, Zadissa A, Li W, Niimura Y, Huang Z, Li C, White S, Xiong Z, Fang D, et al: The draft genomes of soft-shell turtle and green sea turtle yield insights into the development and evolution of the turtle-specific body plan. Nat Genet. 2013, 45 (6): 701-706. 10.1038/ng.2615.
Shaffer B, Minx P, Warren DE, Shedlock AM, Thomson RC, Valenzuela N, Abramyan J, Amemiya CT, Badenhorst D, Biggar KK, et al: The western painted turtle genome, a model for the evolution of extreme physiological adaptations in a slowly evolving lineage. Genome biology. 2013, 14 (3): R28-10.1186/gb-2013-14-3-r28.
Amemiya CT, Powers TP, Prohaska SJ, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Dickson M, Miyake T, Schoenborn MA, Myers RM, Ruddle FH, et al: Complete HOX cluster characterization of the coelacanth provides further evidence for slow evolution of its genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010, 107 (8): 3622-3627. 10.1073/pnas.0914312107.
Amemiya CT, Alföldi J, Lee AP, Fan S, Philippe H, Maccallum I, Braasch I, Manousaki T, Schneider I, Rohner N, et al: The African coelacanth genome provides insights into tetrapod evolution. Nature. 2013, 496 (7445): 311-316. 10.1038/nature12027.
Nelson JS: Fishes of the world. 2006, New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc
Prince VE, Joly L, Ekker M, Ho RK: Zebrafish hox genes: genomic organization and modified colinear expression patterns in the trunk. Development. 1998, 125 (3): 407-420.
Woltering JM, Durston AJ: The zebrafish hoxDb cluster has been reduced to a single microRNA. Nat Genet. 2006, 38 (6): 601-602. 10.1038/ng0606-601.
Zou SM, Jiang XY, He ZZ, Yuan J, Yuan XN, Li SF: Hox gene clusters in blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala and comparison with those of zebrafish, fugu and medaka genomes. Gene. 2007, 400 (1–2): 60-70.
Amores A, Suzuki T, Yan YL, Pomeroy J, Singer A, Amemiya C, Postlethwait JH: Developmental roles of pufferfish Hox clusters and genome evolution in ray-fin fish. Genome Res. 2004, 14 (1): 1-10.
Aparicio S, Chapman J, Stupka E, Putnam N, Chia JM, Dehal P, Christoffels A, Rash S, Hoon S, Smit A, et al: Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science. 2002, 297 (5585): 1301-1310. 10.1126/science.1072104.
Jaillon O, Aury JM, Brunet F, Petit JL, Stange-Thomann N, Mauceli E, Bouneau L, Fischer C, Ozouf-Costaz C, Bernot A, et al: Genome duplication in the teleost fish Tetraodon nigroviridis reveals the early vertebrate proto-karyotype. Nature. 2004, 431 (7011): 946-957. 10.1038/nature03025.
Lee AP, Koh EG, Tay A, Brenner S, Venkatesh B: Highly conserved syntenic blocks at the vertebrate Hox loci and conserved regulatory elements within and outside Hox gene clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006, 103 (18): 6994-6999. 10.1073/pnas.0601492103.
Kurosawa G, Takamatsu N, Takahashi M, Sumitomo M, Sanaka E, Yamada K, Nishii K, Matsuda M, Asakawa S, Ishiguro H, et al: Organization and structure of hox gene loci in medaka genome and comparison with those of pufferfish and zebrafish genomes. Gene. 2006, 370: 75-82.
Santini S, Bernardi G: Organization and base composition of tilapia Hox genes: implications for the evolution of Hox clusters in fish. Gene. 2005, 346: 51-61.
Hoegg S, Boore JL, Kuehl JV, Meyer A: Comparative phylogenomic analyses of teleost fish Hox gene clusters: lessons from the cichlid fish Astatotilapia burtoni. BMC Genomics. 2007, 8: 317-10.1186/1471-2164-8-317.
Thomas-Chollier M, Ledent V: Comparative phylogenomic analyses of teleost fish Hox gene clusters: lessons from the cichlid fish Astatotilapia burtoni: comment. BMC Genomics. 2008, 9: 35-10.1186/1471-2164-9-35.
Moghadam HK, Ferguson MM, Danzmann RG: Evolution of Hox clusters in salmonidae: a comparative analysis between atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Mol Evol. 2005, 61 (5): 636-649. 10.1007/s00239-004-0338-7.
Moghadam HK, Ferguson MM, Danzmann RG: Evidence for Hox gene duplication in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): a tetraploid model species. J Mol Evol. 2005, 61 (6): 804-818. 10.1007/s00239-004-0230-5.
Near TJ, Eytan RI, Dornburg A, Kuhn KL, Moore JA, Davis MP, Wainwright PC, Friedman M, Smith WL: Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109 (34): 13698-13703. 10.1073/pnas.1206625109.
Henkel CV, Dirks RP, de Wijze DL, Minegishi Y, Aoyama J, Jansen HJ, Turner B, Knudsen B, Bundgaard M, Hvam KL, et al: First draft genome sequence of the japanese eel. Anguilla japonica. Gene. 2012, 511 (2): 195-201.
Chambers KE, McDaniell R, Raincrow JD, Deshmukh M, Stadler PF, Chiu CH: Hox cluster duplication in the basal teleost Hiodon alosoides (Osteoglossomorpha). Theory Biosci. 2009, 128 (2): 109-120. 10.1007/s12064-009-0056-1.
Chiu CH, Dewar K, Wagner GP, Takahashi K, Ruddle F, Ledje C, Bartsch P, Scemama JL, Stellwag E, Fried C, et al: Bichir HoxA cluster sequence reveals surprising trends in ray-finned fish genomic evolution. Genome Res. 2004, 14 (1): 11-17.
Raincrow JD, Dewar K, Stocsits C, Prohaska SJ, Amemiya CT, Stadler PF, Chiu CH: Hox clusters of the bichir (Actinopterygii, Polypterus senegalus) highlight unique patterns of sequence evolution in gnathostome phylogeny. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2011, 316 (6): 451-464.
Ledje C, Kim CB, Ruddle FH: Characterization of Hoxgenes in the bichir Polypterus palmas. J Exp Zool. 2002, 294 (2): 107-111. 10.1002/jez.10152.
Oulion S, Borday-Birraux V, Debiais-Thibaud M, Mazan S, Laurenti P, Casane D: Evolution of repeated structures along the body axis of jawed vertebrates, insights from the Scyliorhinus canicula Hox code. Evol Dev. 2011, 13 (3): 247-259. 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2011.00477.x.
Crow KD, Smith CD, Cheng JF, Wagner GP, Amemiya CT: An independent genome duplication inferred from Hox paralogs in the american paddlefish–a representative basal ray-finned fish and important comparative reference. Genome Biol Evol. 2012, 4 (9): 937-953.
Roy SW, Irimia M: Mystery of intron gain: new data and new models. Trends Genet. 2009, 25 (2): 67-73. 10.1016/j.tig.2008.11.004.
Santini S, Boore JL, Meyer A: Evolutionary conservation of regulatory elements in vertebrate Hox gene clusters. Genome Res. 2003, 13 (6A): 1111-1122.
Feiner N, Ericsson R, Meyer A, Kuraku S: Revisiting the origin of the vertebrate Hox14 by including its relict sarcopterygian members. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2011, 316 (7): 515-525.
Genome 10K Community of Scientists: Genome 10K: a proposal to obtain whole-genome sequence for 10,000 vertebrate species. J Hered. 2009, 100 (6): 659-674.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank José M. Martín-Durán and Manuel Irimia for helpful discussions and suggestions. SDA is supported by a Marie Curie Career Integration Grant FP7-PEOPLE-2011-CIG (PCIG09-GA-2011-293871). JG-F is supported by grant BFU2011-23921 from the Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad (Spain) and the ICREA Academia Prize (Generalitat de Catalunya).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
JPA and JGF conceived of the study. JPA, SDA and JGF drafted the manuscript. SK critically revised and discussed the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Pascual-Anaya, J., D’Aniello, S., Kuratani, S. et al. Evolution of Hoxgene clusters in deuterostomes. BMC Dev Biol 13, 26 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-13-26
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-13-26