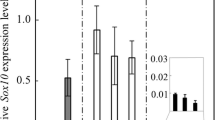
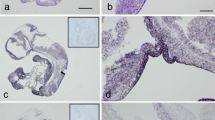
Abstract
The pituitary gland, an indispensable endocrine organ that synthesizes and secretes pituitary hormones, develops with the support of many factors. Among them, neuronatin (NNAT), which was discovered in the neonatal mouse brain as a factor involved in neural development, has subsequently been revealed to be coded by an abundantly expressing gene in the pituitary gland but its role remains elusive. We analyze the expression profile of Nnat and the localization of its product during rat pituitary development. The level of Nnat expression was high during the embryonic period but remarkably decreased after birth. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated that NNAT appeared in the SOX2-positive stem/progenitor cells in the developing pituitary primordium on rat embryonic day 11.5 (E11.5) and later in the majority of SOX2/PROP1 double-positive cells on E13.5. Thereafter, during pituitary embryonic development, Nnat expression was observed in some stem/progenitor cells, proliferating cells and terminally differentiating cells. In postnatal pituitaries, NNAT-positive cells decreased in number, with most coexpressing Sox2 or Pit1, suggesting a similar role for NNAT to that during the embryonic period. NNAT was widely localized in mitochondria, peroxisomes and lysosomes, in addition to the endoplasmic reticulum but not in the Golgi. The present study thus demonstrated the variability in expression of NNAT-positive cells in rat embryonic and postnatal pituitaries and the intracellular localization of NNAT. Further investigations to obtain functional evidence for NNAT are a prerequisite.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- DAPI:
-
4′ 6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- EYFP:
-
Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- FSHβ:
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GH:
-
Growth hormone
- LHβ:
-
Luteinizing hormone
- MCL:
-
Marginal cell layer
- NNAT:
-
Neuronatin
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PDI:
-
Protein disulfide isomerase
- PIT1:
-
Pituitary-specific transcription factor 1
- PRL:
-
Prolactin
- PROP1:
-
Prophet of PIT1
- PRRX1:
-
Paired-related homeobox 1
- PRRX2:
-
Paired-related homeobox 2
- SERCA2:
-
Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase isoform 2
- SOX2:
-
Sex-determining region Y-box 2
- TBP:
-
TATA-box-binding protein
- TSHβ:
-
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
References
Aikawa S, Kato T, Elsaeesser F, Kato Y (2003) Molecular cloning of porcine neuronatin and analysis of its expression during pituitary ontogeny. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 111:1–5
Arroyo A, Pernasetti F, Vasilyev VV, Amato P, Yen SS, Mellon PL (2002) A unique case of combined pituitary hormone deficiency caused by a PROP1 gene mutation (R120C) associated with normal height and absent puberty. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 57:283–291
Chen M, Kato T, Higuchi M, Yoshida S, Yako H, Kanno N, Kato Y (2013) Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor-positive cells compose the putative stem/progenitor cell niches in the marginal cell layer and parenchyma of the rat anterior pituitary. Cell Tissue Res 354:823–836
Chu K, Tsai M-J (2005) Neuronatin, a downstream target of BETA2/NeuroD1 in the pancreas, is involved in glucose-mediated insulin secretion. Diabetes 54:1064–1073
Cushman LJ, Watkins-Chow DE, Brinkmeier ML, Raetzman LT, Radak AL, Lloyd RV, Camper SA (2001) Persistent Prop1 expression delays gonadotrope differentiation and enhances pituitary tumor susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet 10:1141–1153
Davis SW, Castinetti F, Carvalho LR, Ellsworth BS, Potok MA, Lyons RH, Brinkmeier ML, Raetzman LT, Carninci P, Mortensen AH, Hayashizaki Y, Arnhold IJ, Mendonca BB, Brue T, Camper SA (2010) Molecular mechanisms of pituitary organogenesis: in search of novel regulatory genes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 323:4–19
de Jong R, Meijlink F (1993) The homeobox gene S8: mesoderm-specific expression in presomite embryos and in cells cultured in vitro and modulation in differentiating pluripotent cells. Dev Biol 157:133–146
de Moraes DC, Vaisman M, Conceicao FL, Ortiga-Carvalho TM (2012) Pituitary development: a complex, temporal regulated process dependent on specific transcriptional factors. J Endocrinol 215:239–345
Dou D, Joseph R (1996) Cloning of human neuronatin gene and its localization to chromosome-20q 11.2-12: the deduced protein is a novel “proteolipid”. Brain Res 723:8-22
Dugu L, Nakahara T, Wu Z, Uchi H, Liu M, Hirano K, Yokomizo T, Furue M (2014) Neuronatin is related to keratinocyte differentiation by up-regulating involucrin. J Dermatol Sci 73:225–231
Fluck C, Deladoey J, Rutishauser K, Eble A, Marti U, Wu W, Mullis PE (1998) Phenotypic variability in familial combined pituitary hormone deficiency caused by a PROP1 gene mutation resulting in the substitution of Arg→Cys at codon 120 (R120C). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:3727–3734
Higuchi M, Kato T, Chen M, Yako H, Yoshida S, Kanno N, Kato Y (2013) Temporospatial gene expression of Prx1 and Prx2 is involved in morphogenesis of cranial placode-derived tissues through epithelio-mesenchymal interaction during rat embryogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 353:27–40
Higuchi M, Yoshida S, Ueharu H, Chen M, Kato T, Kato Y (2014) PRRX1 and PRRX2 distinctively participate in pituitary organogenesis and cell supply system. Cell Tissue Res 357:323–335
Joe MK, Lee HJ, Suh YH, Han KL, Lim JH, Song J, Seong JK, Jung MH (2008) Crucial roles of neuronatin in insulin secretion and high glucose-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Signal 20:907–915
Joseph R, Dou D, Tsang W (1994) Molecular cloning of a novel mRNA (neuronatin) that is highly expressed in neonatal mammalian brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 201:1227–1234
Joseph R, Dou D, Tsang W (1995) Neuronatin mRNA: alternatively spliced forms of a novel brain-specific mammalian developmental gene. Biomed Res 690:92–98
Lin HH, Bell E, Uwanogho D, Perfect LW, Noristani H, Bates TJ, Snetkov V, Price J, Sun YM (2010) Neuronatin promotes neural lineage in ESCs via Ca(2+) signaling. Stem Cells 28:1950–1960
Nishida Y, Yoshioka M, St-Amand J (2005) The top 10 most abundant transcripts are sufficient to characterize the organs functional specificity: evidences from the cortex, hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Gene 344:133–141
Opstelten DJ, Vogels R, Robert B, Kalkhoven E, Zwartkruis F, de Laaf L, Destree OH, Deschamps J, Lawson KA, Meijlink F (1991) The mouse homeobox gene, S8, is expressed during embryogenesis predominantly in mesenchyme. Mech Dev 34:29–41
Oyang EL, Davidson BC, Lee W, Poon MM (2011) Functional characterization of the dendritically localized mRNA neuronatin in hippocampal neurons. PLoS One 6:e24879
Sato T, Kitahara K, Susa T, Kato T, Kato Y (2006) Pituitary transcription factor Prop-1 stimulates porcine pituitary glycoprotein hormone α gene expression. J Mol Endocrinol 37:341–352
Sornson MW, Wu W, Dasen JS, Flynn SE, Norman DJ, O’Connell SM, Gukovsky I, Carriere C, Ryan AK, Miller AP, Zuo L, Gleiberman AS, Andersen B, Beamer WG, Rosenfeld MG (1996) Pituitary lineage determination by the Prophet of Pit-1 homeodomain factor defective in Ames dwarfism. Nature 384:327–333
Suh YH, Kim WH, Moon C, Hong YH, Eun SY, Lim JH, Choi JS, Song J, Jung MH (2005) Ectopic expression of neuronatin potentiates adipogenesis through enhanced phosphorylation of cAMP-response element-binding protein in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337:481–489
Susa T, Kato T, Kato Y (2008) Reproducible transfection in the presence of carrier DNA using FuGENE6 and Lipofectamine 2000. Mol Biol Rep 35:313–319
Susa T, Ishikawa A, Kato T, Nakayama M, Kato Y (2009) Molecular cloning of paired related homeobox 2 (Prx2) as a novel pituitary transcription factor. J Reprod Dev 55:502–511
Susa T, Kato T, Yoshida S, Yako M, Higuchi M, Kato Y (2012) Paired-related homeodomain proteins Prx1 and Prx2 are expressed in embryonic pituitary stem/progenitor cells and may be involved in the early stage of pituitary differentiation. J Neuroendocrinol 24:1201–1212
Usui H, Ichikawa T, Miyazaki Y, Nagai S, Kumanishi T (1996) Isolation of cDNA clones of the rat mRNAs expressed preferentially in the prenatal stages of brain development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 97:185–193
Wang L, Li W, Yang Y, Hu Y, Gu Y, Shu Y, Sun Y, Wu X, Shen Y, Xu Q (2014) High expression of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase 2b blocks cell differentiation in human liposarcoma cells. Life Sci 99:37–43
Wijnholds J, Chowdhury K, Wehr R, Gruss P (1995) Segment-specific expression of the neuronatin gene during early hindbrain development. Dev Biol 171:73–84
Wu W, Cogan JD, Pfaffle RW, Dasen JS, Frisch H, O’Connell SM, Flynn SE, Brown MR, Mullis PE, Parks JS, Phillips JA 3rd, Rosenfeld MG (1998) Mutations in PROP1 cause familial combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Nat Genet 18:147–149
Yoshida S, Kato T, Susa T, Cai L-Y, Nakayama M, Kato Y (2009) PROP1 coexists with SOX2 and induces PIT1-commitment cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385:11–15
Yoshida S, Kato T, Yako H, Susa T, Cai L-Y, Osuna M, Inoue K, Kato Y (2011) Significant quantitative and qualitative transition in pituitary stem/progenitor cells occurs during the postnatal development of the rat anterior pituitary. J Neuroendocrinol 23:933–943
Yoshida S, Kato T, Higuchi M, Yako H, Chen M, Kanno N, Ueharu H, Kato Y (2013) Rapid transition of NESTIN-expressing dividing cells from PROP1-positive to PIT1-positive advances prenatal pituitary development. J Neuroendocrinol 25:779–791
Yoshida S, Kato T, Chen M, Higuchi M, Ueharu H, Nishimura N, Kato Y (2015) Localization of a juxtacrine factor ephrin-B2 in the pituitary stem/progenitor cell niches throughout life. Cell Tissue Res 359:755–766
Zhu X, Gleiberman AS, Rosenfeld MG (2007) Molecular physiology of pituitary development: signaling and transcriptional networks. Physiol Rev 87:933–963
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. A.F. Parlow and the NIDDK for antibodies against pituitary hormones, Dr. S. Tanaka at Shizuoka University for the antibody against human adrenocorticotropic hormone and GH, Dr. P. Mellon for providing us with LβT2 cells and Mr. K. Kawai for his excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grants, nos. 21380184 to Y.K. and 24580435 to T.K., by the MEXT-Supported Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities, 2014–2018 and by a research grant (A) to Y.K. from the Institute of Science and Technology, Meiji University. This study was also supported by the Meiji University International Institute for BioResource Research (MUIIR).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanno, N., Higuchi, M., Yoshida, S. et al. Expression studies of neuronatin in prenatal and postnatal rat pituitary. Cell Tissue Res 364, 273–288 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2325-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2325-2