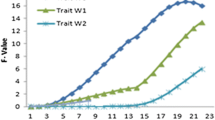
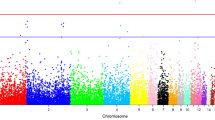
Abstract
This study aimed to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for growth-related traits by constructing a genetic linkage map based on single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers in Japanese quail. A QTL mapping population of 277 F2 birds was obtained from an intercross between a male of a large-sized strain and three females of a normal-sized strain. Body weight (BW) was measured weekly from hatching to 16 weeks of age. Non-linear regression growth models of Weibull, Logistic, Gompertz, Richards, and Brody were analyzed, and growth curve parameters of Richards was selected as the best model to describe the quail growth curve of the F2 birds. Restriction-site associated DNA sequencing developed 125 SNP markers that were informative between their parental strains. The SNP markers were distributed on 16 linkage groups that spanned 795.9 centiMorgan (cM) with an average marker interval of 7.3 cM. QTL analysis of phenotypic traits revealed four main-effect QTLs. Detected QTLs were located on chromosomes 1 and 3 and were associated with BW from 4 to 16 weeks of age and asymptotic weight of Richards model at genome-wide significant at 1% or 5% level. No QTL was detected for BW from 0 to 3 weeks of age. This is the first report identified QTLs for asymptotic weight of the Richards parameter in Japanese quail. These results highlight that the combination of QTL studies and the RAD-seq method will aid future breeding programs identify genes underlying the QTL and the application of marker-assisted selection in the poultry industry, particularly the Japanese quail.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 19(6):716–723. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705
Ambo M, Moura ASAMT, Ledur MC, Pinto LFB, Baron EE, Ruy DC et al (2009) Quantitative trait loci for performance traits in a broiler x layer cross. Anim Genet 40(2):200–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2008.01824.x
Aslam ML, Bastiaansen JWM, Crooijmans RPMA, Vereijken A, Groenen MAM (2011) Whole genome QTL mapping for growth, meat quality and breast meat yield traits in turkey. BMC Genet 12:61. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-12-61
Baird NA, Etter PD, Atwood TS, Currey MC, Shiver AL, Lewis ZA et al (2008) Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS ONE 3(10):e3376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003376
Beaumont C, Roussot O, Feve K, Vignoles F, Leroux S, Pitel F et al (2005) A genome scan with AFLPTM markers to detect fearfulness-related QTLs in Japanese quail. Anim Genet 36(5):401–407. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2005.01336.x
Beiki H, Pakdel A, Moradi-Shahrbabak M, Mehrban H (2013) Evaluation of growth functions on Japanese quail lines. J Poult Sci 50(1):20–27. https://doi.org/10.2141/jpsa.0110142
Beuzen ND, Stear MJ, Chang KC (2000) Molecular markers and their use in animal breeding. Vet J 160(1):42–52. https://doi.org/10.1053/tvjl.2000.0468
Broman KW, Wu H, Sen S, Churchill GA (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19(7):889–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg112
Broman KW, Sen S, Owens SE, Manichaikul A, Southard-Smith EM, Churchill GA (2006) The X chromosome in quantitative trait locus mapping. Genetics 174(4):2151–2158. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.106.061176
Broman KW, Sen S (2009) A guide to QTL mapping with R/qtl. Springer, New York
Cain JR, Cawley WO (1974) Japanese quail (Coturnix): Care, management, propagation. http://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/92988. Accessed 19 February 2020. College Station, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, TX. pp. 5–14. Available electronically
Carlborg Ö, Kerje S, Schütz K, Jacobsson L, Jensen P, Andersson L (2003) A global search reveals epistatic interaction between QTL for early growth in the chicken. Genome Res 13(3):413–421. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.528003
Charati H, Koshkoiyeh AE, Ori RJ, Moradian H, Mehrgardi AA (2014) Detection of quantitative trait loci affecting carcass traits and internal organs on chromosome 3 in an F2 intercross of Japanese quail. Anim Sci Pap Rep 32(4):369–383
Chicken QTL Database. https://www.animalgenome.org/cgi-bin/QTLdb/GG/index Accessed Feb 23 2020
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA et al (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27(15):2156–2158. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330
Darvasi A, Soller M (1997) A simple method to calculate resolving power and confidence interval of QTL map location. Behav Genet 27(2):125–132. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025685324830
Davey JW, Blaxter ML (2010) RADseq: Next-generation population genetics. Brief Funct Genomics 9(5–6):416–423. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elq031
Davey JW, Hohenlohe PA, Etter PD, Boone JQ, Catchen JM, Blaxter ML (2011) Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 12(7):499–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3012
De Donato M, Peters SO, Mitchell SE, Hussain T, Imumorin IG (2013) Genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS): a novel, efficient and cost-effective genotyping method for cattle using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 8(5):e62137. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062137
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, Mitchell SE (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019379
Ernst RA (1978) Raising and propagating Japanese quails. Extension Poultry Specialist of the University of California Davis, Davis, CA, pp 1–8
Essa BH, Suzuki S, Nagano AJ, Elkholya SZ, Ishikawa A (2021) QTL analysis for early growth in an intercross between native Japanese Nagoya and White Plymouth Rock chicken breeds using RAD sequencing-based SNP markers. Anim Genet 52(2):232–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/age.13039
Faraji-Arough H, Rokouei M, Maghsoudi A, Ghazaghi M (2018) Comparative study of growth patterns in seven strains of Japanese quail using nonlinear regression modeling. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 42(5):441–451. https://doi.org/10.3906/vet-1801-13
Frésard L, Leroux S, Dehais P, Servin B, Gilbert H, Bouchez O et al (2012) Fine mapping of complex traits in non-model species: using next generation sequencing and advanced intercross lines in Japanese quail. BMC Genom 13(1):551. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-551
Gao Y, Hu XX, Du ZQ, Deng XM, Huang YH, Fei J et al (2006) A genome scan for quantitative trait loci associated with body weight at different developmental stages in chickens. Anim Genet 37(3):276–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2006.01428.x
Gateway to poultry production and products. http://www.fao.org/poultry-production-products/en/. Accessed Feb 23, 2020 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Goto T, Ishikawa A, Onitsuka S, Goto N, Fujikawa Y, Umino T, Nishibori M, Tsudzuki M (2011a) Mapping quantitative trait loci for egg production traits in an F2 intercross of Oh-Shamo and White Leghorn chickens. Anim Genet 42(6):634–641. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2011.02190.x
Goto N, Ishikawa A, Tsudzuki M (2011b) Growth curve analysis for a QTL resource family F2 intercross of the Oh-Shamo and White leghorn breeds of chickens. J Anim Vet Adv 10(24):3207–3211. https://doi.org/10.3923/javaa.2011.3207.3211
Goto T, Ishikawa A, Goto N, Nishibori M, Umino T, Tsudzuki M (2014a) Mapping of main-effect and epistatic quantitative trait loci for internal egg traits in an F2 resource population of chickens. J Poult Sci 51(4):375–386. https://doi.org/10.2141/jpsa.0140030
Goto T, Ishikawa A, Yoshida M, Goto N, Umino T, Nishibori M, Tsudzuki M (2014b) Quantitative trait loci mapping for external egg traits in F2 chickens. J Poult Sci 51(2):118–129. https://doi.org/10.2141/jpsa.0130100
Goto T, Fernandes AFA, Tsudzuki M, Rosa GJM (2019) Causal phenotypic networks for egg traits in an F2 chicken population. Mol Genet Genom 294(6):1455–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01588-2
Haley CS, Knott SA (1992) A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69(4):315–324
Haqani MI, Nomura S, Nakano M, Goto T, Nagano AJ, Takenouchi A, Nakamura Y, Ishikawa A, Tsudzuki M (2021a) Mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling egg-quality and-production traits in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) using restriction-site associated DNA sequencing. Genes 12(5):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050735
Haqani MI, Kawamura K, Takenouchi A, Kabir MH, Nakamura Y, Ishikawa A, Tsudzuki M (2021b) Growth performance and nonlinear growth curve functions of Large- and Normal-sized Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). J Poult Sci 58(2):88–96. https://doi.org/10.2141/jpsa.0200020
Hohenlohe PA, Bassham S, Etter PD, Stiffler N, Johnson EA, Cresko WA (2010) Population genomics of parallel adaptation in threespine stickleback using sequenced RAD tags. PLOS Genet 6(2):e1000862. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000862
Hu Q, Chang C, Wang Q, Tian H, Qiao Z, Wang L et al (2019) Genome-wide RAD sequencing to identify a sex-specific marker in Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus. BMC Genomics 20(1):415. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5771-5
Ibáñez-Escriche N, Blasco A (2011) Modifying growth curve parameters by multitrait genomic selection. J Anim Sci 89(3):661–668. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2010-2984
Iranmanesh M, Esmailizadeh A, Mohammad Abadi MR, Zand E, Mokhtari MS, Wu DD (2016) A molecular genome scan to identify DNA segments associated with live weight in Japanese quail. Mol Biol Rep 43(11):1267–1272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4059-y
Ishikawa A, Sakaguchi M, Nagano AJ, Suzuki S (2020) Genetic architecture of innate fear behavior in chickens. Behav Genet 50(6):411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-020-10012-0
Jeke A, Phiri C, Chitindingu K, Taru P (2018) Ethnomedicinal use and pharmacological potential of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) birds` meat and eggs, and its potential implications on wild quail conservation in Zimbabwe: a review. Cogent Food Agric 4(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311932.2018.1507305
Kabir MH, Takenouchi A, Haqani MI, Nakamura Y, Takeuchi S, Tsudzuki M (2020) Discovery of a new nucleotide substitution in the MC1R gene and haplotype distribution in native and non-Japanese chicken breeds. Anim Genet 51(2):235–248. https://doi.org/10.1111/age.12906
Kaplan S, Gürcan EK (2018) Comparison of growth curves using non-linear regression function in Japanese quail. J Appl Anim Res 46(1):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.2016.1268965
Kawahara-Miki R, Sano S, Nunome M, Shimmura T, Kuwayama T, Takahashi S et al (2013) Next-generation sequencing reveals genomic features in the Japanese quail. Genomics 101(6):345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.03.006
Kayang BB, Inoue-Murayama M, Hoshi T, Matsuo K, Takahashi H, Minezawa M, Mizutani M, Ito S (2002) Microsatellite loci in Japanese quail and cross-species amplification in chicken and guinea fowl. Genet Sel Evol 34(2):233–253. https://doi.org/10.1051/gse:2002006
Kayang BB, Vignal A, Inoue-Murayama M, Miwa M, Monvoisin JL, Ito S, Minvielle F (2004) A first-generation microsatellite linkage map of the Japanese quail. Anim Genet 35(3):195–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2004.01135.x
Kirkwood JK, Hubrecht R (2010) The UFAW handbook on the care and management of laboratory and other research animals. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, NJ
Knaga S, Siwek M, Tavaniello S, Maiorano G, Witkowski A, Jezewska-Witkowska G, Bednarczyk M, Ziȩba G (2018) Identification of quantitative trait loci affecting production and biochemical traits in a unique Japanese quail resource population. Poult Sci 97(7):2267–2277. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey110
Koboldt DC, Zhang Q, Larson DE, Shen D, McLellan MD, Lin L et al (2012) VarScan 2: somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing. Genome Res 22(3):568–576. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.129684.111
Kosambi DD (1943) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kucukonder H, Demirarslan PC, Alkan S, Birgul ÖB (2019) Curve fitting with nonlinear regression and grey prediction model of broiler growth in chickens. Pak J Zool 52(1):347–354. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjz/2020.52.1.347.354
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9(4):357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Laoun A, Harkat S, Lafri M, Gaouar SBS, Belabdi I, Ciani E et al (2020) Inference of breed structure in farm animals: empirical comparison between SNP and microsatellite performance. Genes 11(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010057
Le Rouzic A, Álvarez-Castro JM, Carlborg Ö (2008) Dissection of the genetic architecture of body weight in chicken reveals the impact of epistasis on domestication traits. Genetics 179(3):1591–1599. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.108.089300
Lee BY, Kim MS, Choi BS, Nagano AJ, Au DWT, Wu RSS, Takehana Y, Lee JS (2019) Construction of high-resolution RAD-seq based linkage map, anchoring reference genome, and QTL mapping of the sex chromosome in the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. G3 Genes Genom Genet 9(11):3537–3545. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.119.400708
Li H (2011) A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 27(21):2987–2993. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr509
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N et al (2009) The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25(16):2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li Y, Wu R (2010) Functional mapping of growth and development. Biol Rev 85(2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2009.00096.x
Liu C, Chen H, Ren Z, Zhang C, Yang X (2019) Population genetic analysis of the domestic Bactrian camel in China by RAD-seq. Ecol Evol 9(19):11232–11242. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5624
Loureiro LO, Engstrom MD, Lim BK (2020) Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) provide unprecedented resolution of species boundaries, phylogenetic relationships, and genetic diversity in the mastiff bats (Molossus). Mol Phylogenet Evol 143:106690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106690
Mackay TFC, Stone EA, Ayroles JF (2009) The genetics of quantitative traits: challenges and prospects. Nat Rev Genet 10(8):565–577. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2612
Manly KF, Cudmore RH, Meer JM (2001) Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genom 12(12):930–932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-001-1016-3
Mannen H, Murata K, Kikuchi S, Fujima D, Sasazaki S, Fujiwara A, Tsuji S (2005) Development and mapping of microsatellite markers derived from cDNA in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). J Poult Sci 42(3):263–271
Masoudi A, Azarfar A (2017) Comparison of nonlinear models describing growth curves of broiler chickens fed on different levels of corn bran. IJAWB 2(2):34–39. https://doi.org/10.15406/ijawb.2017.02.00012
Minvielle F (2004) The future of Japanese quail for research and production. Worlds Poult Sci J 60(4):500–507. https://doi.org/10.1079/wps200433
Minvielle F, Kayang BB, Inoue-Murayama M, Miwa M, Vignal A, Gourichon D et al (2005) Microsatellite mapping of QTL affecting growth, feed consumption, egg production, tonic immobility and body temperature of Japanese quail. BMC Genom 6(87):87. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-6-87
Minvielle F, Kayang BB, Inoue-Murayama M, Miwa M, Vignal A, Gourichon D et al (2006) Search for QTL affecting the shape of the egg laying curve of the Japanese quail. BMC Genet 7(26):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-7-26
Moradian H, Esmailizadeh AK, Sohrabi SS, Nasirifar E, Askari N, Mohammadabadi MR, Baghizadeh A (2014) Genetic analysis of an F2 intercross between two strains of Japanese quail provided evidence for quantitative trait loci affecting carcass composition and internal organs. Mol Biol Rep 41(7):4455–4462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3316-1
Morenikeji OB, Capria AL, Ojurongbe O, Thomas BN (2020) SNP diversity in CD14 gene promoter suggests adaptation footprints in trypanosome tolerant N’Dama (Bos taurus) but not in susceptible white Fulani (Bos indicus) Cattle. Genes 11(1):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010112
Morris KM, Hindle MM, Boitard S, Burt DW, Danner AF, Eory L et al (2020) The quail genome: Insights into social behaviour, seasonal biology and infectious disease response. BMC Biol 18(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-020-0743-4
Nasirifar E, Talebi M, Esmailizadeh A, Moradian H, Sohrabi SS, Askari N (2016) A chromosome-wide QTL mapping on chromosome 2 to identify loci affecting live weight and carcass traits in F2 population of Japanese quail. Czech J Anim Sci 61(6):290–297. https://doi.org/10.17221/113/2014-CJAS
Nishibori M, Hayashi T, Tsudzuki M, Yamamoto Y, Yasue H (2001) Complete sequence of the Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) mitochondrial genome and its genetic relationship with related species. Anim Genet 32(6):380–385. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2052.2001.00795.x
Norris D, Ngambi JW, Benyi K, Makgahlela ML, Shimelis HA, Nesamvuni EA (2007) Analysis of growth curves of indigenous male Venda and Naked Neck chickens. SA J Anim Sci 37(1):21–26. https://doi.org/10.4314/sajas.v37i1.4021
Ohara K, Takayama M, Goto T, Osman SAM, Tsudzuki M (2013) Comparison of growth in three varieties of the Japanese extremely long-tailed chicken breed (Tosa-no-Onagadori). Int J Poult Sci 12(9):517–522. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijps.2013.517.522
Ono T, Kouguchi T, Ishikawa A, Nagano AJ, Takenouchi A, Igawa T, Tsudzuki M (2019a) Quantitative trait loci mapping for the shear force value in breast muscle of F2 chickens. Poult Sci 98(3):1096–1101. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey493
Ono T, Ohara K, Ishikawa A, Kouguchi T, Nagano AJ, Takenouchi A, Igawa T, Tsudzuki M (2019b) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for growth and carcass-related traits in chickens using a restriction-site associated DNA sequencing method. J Poult Sci 56(3):166–176. https://doi.org/10.2141/jpsa.0180066
Ori RJ, Esmailizadeh AK, Charati H, Mohammadabadi MR, Sohrabi SS (2014) Identification of QTL for live weight and growth rate using DNA markers on chromosome 3 in an F2 population of Japanese quail. Mol Biol Rep 41(2):1049–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2950-3
Pacific Biosciences (2012) Extracting DNA using phenol-chloroform. https://www.pacb.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/SharedProtocol-Extracting-DNA-usinig-Phenol-Chloroform.pdf. Accessed Feb 23 2020
Padgett CA, Ivey WD (1959) Coturnix quail as a laboratory research animal. Science 129(3344):267–268. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.129.3344.267
Pértille F, Guerrero-Bosagna C, Silva VH, Boschiero C, Nunes Jde R, Ledur MC, Jensen P, Coutinho LL (2016) High-throughput and cost-effective chicken genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Sci Rep 6:26929. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26929
Podisi BK, Knott SA, Burt DW, Hocking PM (2013) Comparative analysis of quantitative trait loci for body weight, growth rate and growth curve parameters from 3 to 72 weeks of age in female chickens of a broiler-layer cross. BMC Genet 14(22):22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-14-22
R core team (2019) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed May 17 2019. R Foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria
Recoquillay J, Pitel F, Arnould C, Leroux S, Dehais P, Moréno C et al (2015) A medium density genetic map and QTL for behavioral and production traits in Japanese quail. BMC Genom 16(10):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-014-1210-9
Ren A, Du K, Jia X, Yang R, Wang J, Chen SY, Lai SJ (2019) Genetic diversity and population structure of four Chinese rabbit breeds. PLoS ONE 14(9):e0222503. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0222503
Rezvannejad E, Yaghoobi M, Rashki M (2014) Quantitative trait loci for body weight and carcass traits in Japanese quail. J Livest Sci Techno 2(1):49–55. https://doi.org/10.22103/JLST.2014.739
Robledo D, Palaiokostas C, Bargelloni L, Martínez P, Houston R (2018) Applications of genotyping by sequencing in aquaculture breeding and genetics. Rev Aquac 10(3):670–682. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12193
Roussot O, Feve K, Plisson-Petit F, Pitel F, Faure JM, Beaumont C, Vignal A (2003) AFLP linkage map of the Japanese quail Coturnix japonica. Genet Sel Evol 35:559–572. https://doi.org/10.1051/gse:2003039
Sakaguchi S, Sugino T, Tsumura Y, Ito M, Crisp MD, Bowman DMJS et al (2015) High-throughput linkage mapping of Australian white cypress pine (Callitris glaucophylla) and map transferability to related species. Tree Genet Genomes 11(6):121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0944-0
Santos HB, Vieira DA, Souza LP, Santos AL, Santos FR, Araujo Neto FR (2018) Application of non-linear mixed models for modelling the quail growth curve for meat and laying. J Agric Sci 156(10):1216–1221. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859619000169
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann Statist 6(2):461–464
Science Council of Japan (2006) Guidelines for proper conduct of animal experiments. http://www.scj.go.jp/ja/info/kohyo/pdf/kohyo-20-k16-2e.pdf. Accessed Feb 24 2020
Sewalem A, Morrice DM, Law A, Windsor D, Haley CS, Ikeobi CON et al (2002) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for body weight at three, six, and nine weeks of age in a broiler layer cross. Poult Sci 81(12):1775–1781. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/81.12.1775
Shibusawa M, Minai S, Nishida-Umehara C, Suzuki T, Mano T, Yamada K, Namikawa T, Matsuda Y (2001) A comparative cytogenetic study of chromosome homology between chicken and Japanese quail. Cytogenet Cell Genet 95(1–2):103–109. https://doi.org/10.1159/000057026
Shirasawa K, Hirakawa H, Isobe S (2016) Analytical workflow of double-digest restriction site-associated DNA sequencing based on empirical and in silico optimization in tomato. DNA Res 23(2):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsw004
Sohrabi SS, Esmailizadeh AK, Baghizadeh A, Moradian H, Mohammadabadi MR, Askari N, Nasirifar E (2012) Quantitative trait loci underlying hatching weight and growth traits in an F2 intercross between two strains of Japanese quail. Anim Prod Sci 52(11):1012–1018. https://doi.org/10.1071/AN12100
Sonah H, Bastien M, Iquira E, Tardivel A, Légaré G, Boyle B et al (2013) An improved genotyping by sequencing (GBS) approach offering increased versatility and efficiency of SNP discovery and genotyping. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54603. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054603
Tavaniello S, Maiorano G, Siwek M, Knaga S, Witkowski A, Di Memmo D, Bednarczyk M (2014) Growth performance, meat quality traits, and genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci in 3 generations of Japanese quail populations (Coturnix japonica). Poult Sci 93(8):2129–2140. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2014-03920
Teleken JT, Galvão AC, Robazza WDS (2017) Comparing non-linear mathematical models to describe growth of different animals. Act Sci Anim Sci 39(1):73–81. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascianimsci.v39i1.31366
Terčič D, Holcman A, Dovč P, Morrice DR, Burt DW, Hocking PM, Horvat S (2009) Identification of chromosomal regions associated with growth and carcass traits in an F3 full sib intercross line originating from a cross of chicken lines divergently selected on body weight. Anim Genet 40(5):743–748. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2009.01917.x
Tsudzuki M (2008) Mutations of Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) and recent advances of molecular genetics for this species. J Poult Sci 45(3):159–179. https://doi.org/10.2141/jpsa.45.159
Tsudzuki M, Onitsuka S, Akiyama R, Iwamizu M, Goto N, Nishibori M, Takahashi H, Ishikawa A (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci affecting shank length, body weight and carcass weight from the Japanese cockfighting chicken breed, Oh-Shamo (Japanese Large Game). Cytogenet Genome Res 117(1–4):288–295. https://doi.org/10.1159/000103190
Vignal A, Milan D, Sancristobal M, Eggen A (2002) A review on SNP and other types of molecular markers and their use in animal genetics. Genet Sel Evol 34(3):275–305. https://doi.org/10.1051/gse:2002009
von Thaden VA, Nowak C, Tiesmeyer A, Reiners TE, Alves PC, Lyons LA et al (2020) Applying genomic data in wildlife monitoring: development guidelines for genotyping degraded samples with reduced single nucleotide polymorphism panels. Mol Ecol Resour 20(3):662–680. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13136
Wan SM, Liu H, Zhao BW, Nie CH, Wang WM, Gao ZX (2017) Construction of a high-density linkage map and fine mapping of QTLs for growth and gonad related traits in blunt snout bream. Sci Rep 7(March):46509. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46509
Wang L, Wang A, Huang X, Zhao Q, Dong G, Qian Q, Sang T, Han B (2011) Mapping 49 quantitative trait loci at high resolution through sequencing-based genotyping of rice recombinant inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 122(2):327–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1449-8
Woodard AE, Abplanalp H, Wilson WO, Vohra P (1973) Japanese quail husbandry in the laboratory (Coturnix coturnix japonica). University of California Davis, Davis, CA, p 22
Wu W, Zhou Y, Li W, Mao D, Chen Q (2002) Mapping of quantitative trait loci based on growth models. Theor Appl Genet 105(6–7):1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1052-8
Yin X, Goudriaan J, Lantinga EA, Vos J, Spiertz HJ (2003) A flexible sigmoid function of determinate growth. Ann Bot 91(3):361–371. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcg029
Yoshida M, Ishikawa A, Goto T, Goto N, Nishibori M, Tsudzuki M (2013) QTL mapping for meat color traits using the F2 intercross between the Oh-Shamo (Japanese Large Game) and White Leghorn chickens. J Poult Sci 50(3):198–205. https://doi.org/10.2141/jpsa.0120189
Zhai Z, Zhao W, He C, Yang K, Tang L, Liu S et al (2015) SNP discovery and genotyping using restriction-site-associated DNA sequencing in chickens. Anim Genet 46(2):216–219. https://doi.org/10.1111/age.12250
Acknowledgements
MIH would like to thank the Honjo International Scholarship Foundation for providing scholarships. We would like to thank Dr. L. Kawaguchi for assistance with the RAD-seq analysis, and the members of the Laboratory of Animal Breeding and Genetics at Hiroshima University for their collaboration and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards. The animals were cared according to the protocol described in the Guidelines for Proper Conduct of Animal Experiments, Science Council, Japan.
Informed consent
Informed consent was collected from all participants in this study.
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haqani, M.I., Nomura, S., Nakano, M. et al. Quantitative trait loci for growth-related traits in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) using restriction-site associated DNA sequencing. Mol Genet Genomics 296, 1147–1159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-021-01806-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-021-01806-w