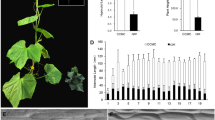
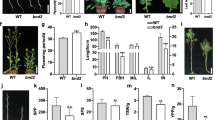
Abstract
Dwarfing is the development trend of pepper breeding. It is of great practical and scientific value to generate new dwarf germplasms, and identify new genes or alleles conferring dwarf traits in pepper. In our previous study, a weakly BR-insensitive dwarf mutant, E29, was obtained by EMS mutagenesis of the pepper inbred line 6421. It can be used as a good parent material for breeding new dwarf varieties. Here, we found that this dwarf phenotype was controlled by a single recessive gene. Whole-genome resequencing, dCAPs analysis, and VIGs validation revealed that this mutation was caused by a nonsynonymous single-nucleotide mutation (C to T) in CaBRI1. An enzyme activity assay, transcriptome sequencing, and BL content determination further revealed that an amino-acid change (Pro1157Ser) in the serine/threonine protein kinase and catalytic (S_TKc) domain of CaBRI1 impaired its kinase activity and caused the transcript levels of two important genes (CaDWF4 and CaROT3) participating in BR biosynthesis to increase dramatically in the E29 mutant, accompanied by significantly increased accumulation of brassinolide (BL). Therefore, we concluded that the novel single-base mutation in CaBRI1 conferred the dwarf phenotype and resulted in brassinosteroid (BR) accumulation in pepper. This study provides a new allelic variant of the height-regulating gene CaBRI1 that has theoretical and practical values for the breeding of the plants suitable for the facility cultivation and mechanized harvesting of pepper varieties.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The transcriptome sequencing data have been deposited into sequence read archive (SRA) database under Accession Number PRJNA540896.
References
Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Natsume S, Takagi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Mitsuoka C, Tamiru M, Innan H, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2012) Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat Biotechnol 30:174–178. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2095
Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W (2015) HTSeq-a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31:166–169. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638
Chen Z, Yan W, Wang N (2014) Cloning of a rice male sterility gene by a modified MutMap method. Hereditas 36:85–93. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1005.2014.00085
Choe S, Dilkes BP, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Sakurai A, Feldmann KA (1998) The DWF4 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a cytochrome P450 that mediates multiple 22ɑ-hydroxylation steps in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 10:231–243. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.10.2.231
Chono M, Honda I, Zeniya H, Yoneyama K, Saisho D, Takeda K, Takatsuto S, Hoshino T, Watanabe Y (2003) A semidwarf phenotype of barley uzu results from a nucleotide substitution in the gene encoding a putative brassinosteroid receptor. Plant Physiol 133:1209–1219. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.026195
Clouse SD, Langford M, McMorris TC (1996) A brassinosteroid-insensitive mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibits multiple defects in growth and development. Plant Physiol 111:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.3.671
Evans LT (1998) Feeding the ten billion: plants and population growth. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Friedrichsen DM, Joazeiro CAP, Li J, Hunter T, Chory J (2000) Brassinosteroid-insensitive-1 is a ubiquitously expressed leucine-rich repeat receptor serine/threonine kinase. Plant Physiol 123:1247–1256. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.123.4.1247
Hao J, Yin Y, Fei SZ (2013) Brassinosteroid signaling network: implications on yield and stress tolerance. Plant Cell Rep 32:1017–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1438-x
He JX, Gendron JM, Sun Y, Gampala SSL, Gendron N, Sun CQ, Wang ZY (2005) BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 307:1634–1638. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1107580
Hong Z, Jin H, Tzfira T, Li J (2008) Multiple mechanism-mediated retention of a defective brassinosteroid receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:3418–3429. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.061879
Kim GT, Fujioka S, Kozuka T, Tax FE, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tsukaya H (2005) CYP90C1 and CYP90D1 are involved in different steps in the brassinosteroid biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 41:710–721. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.061879
Kim TW, Guan S, Sun Y, Deng Z, Tang W, Shang JX, Sun Y, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2009) Brassinosteroid signal transduction from cell-surface receptor kinases to nuclear transcription factors. Nat Cell Biol 11:1254–1260. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1970
Li J, Chory J (1997) A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell 90:929–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80357-8
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Liu Y, Huang X, Li M, He P, Zhang Y (2016) Loss-of-function of Arabidopsis receptor-like kinase BIR1 activates cell death and defense responses mediated by BAK1 and SOBIR1. New Phytol 212:637–645. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14072
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Malinowski R, Higgins R, Luo Y, Piper L, Nazir A, Bajwa VS, Clouse SD, Thompson PR, Stratmann JW (2009) The tomato brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 increases binding of systemin to tobacco plasma membranes, but is not involved in systemin signaling. Plant Mol Biol 70:603–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9494-x
Mayer K, Schüller C, Wambutt R, Murphy G, Volckaert G, Pohl T, Düsterhöft A, Stiekema W, Entian KD, Terryn N, Harris B, Ansorge W, Brandt P, Grivell L, Rieger M, Weichselgartner M, de Simone V, Obermaier B, Mache R, Müller M, Kreis M, Delseny M, Puigdomenech P, Watson M, Schmidtheini T, Reichert B, Portatelle D, Perez-Alonso M, Boutry M, Bancroft I, Vos P, Hoheisel J, Zimmermann W, Wedler H, Ridley P, Langham SA, McCullagh B, Bilham L, Robben J, Van der Schueren J, Grymonprez B, Chuang YJ, Vandenbussche F, Braeken M, Weltjens I, Voet M, Bastiaens I, Aert R, Defoor E, Weitzenegger T, Bothe G, Ramsperger U, Hilbert H, Braun M, Holzer E, Brandt A, Peters S, van Staveren M, Dirkse W, Mooijman P, Lankhorst RK, Rose M, Hauf J, Kötter P, Berneiser S, Hempel S, Feldpausch M, Lamberth S, Van den Daele H, De Keyser A, Buysshaert C, Gielen J, Villarroel R, De Clercq R, Van Montagu M, Rogers J, Cronin A, Quail M, Bray-Allen S, Clark L, Doggett J, Hall S, Kay M, Lennard N, McLay K, Mayes R, Pettett A, Rajandream MA, Lyne M, Benes V, Rechmann S, Borkova D, Blöcker H, Scharfe M, Grimm M, Löhnert TH, Dose S, de Haan M, Maarse A, Schäfer M, Müller-Auer S, Gabel C, Fuchs M, Fartmann B, Granderath K, Dauner D, Herzl A, Neumann S, Argiriou A, Vitale D, Liguori R, Piravandi E, Massenet O, Quigley F, Clabauld G, Mündlein A, Felber R, Schnabl S, Hiller R, Schmidt W, Lecharny A, Aubourg S, Chefdor F, Cooke R, Berger C, Montfort A, Casacuberta E, Gibbons T, Weber N, Vandenbol M, Bargues M, Terol J, Torres A, Perez-Perez A, Purnelle B, Bent E, Johnson S, Tacon D, Jesse T, Heijnen L, Schwarz S, Scholler P, Heber S, Francs P, Bielke C, Frishman D, Haase D, Lemcke K, Mewes HW, Stocker S, Zaccaria P, Bevan M, Wilson RK, de la Bastide M, Habermann K, Parnell L, Dedhia N, Gnoj L, Schutz K, Huang E, Spiegel L, Sehkon M, Murray J, Sheet P, Cordes M, Abu-Threideh J, Stoneking T, Kalicki J, Graves T, Harmon G, Edwards J, Latreille P, Courtney L, Cloud J, Abbott A, Scott K, Johnson D, Minx P, Bentley D, Fulton B, Miller N, Greco T, Kemp K, Kramer J, Fulton L, Mardis E, Dante M, Pepin K, Hillier L, Nelson J, Spieth J, Ryan E, Andrews S, Geisel C, Layman D, Du H, Ali J, Berghoff A, Jones K, Drone K, Cotton M, Joshu C, Antonoiu B, Zidanic M, Strong C, Sun H, Lamar B, Yordan C, Ma P, Zhong J, Preston R, Vil D, Shekher M, Matero A, Shah R, Swaby I’K, Shaughnessy AO’, Rodriguez M, Hoffman J, Till S, Granat S, Shohdy N, Hasegawa A, Hameed A, Lodhi M, Johnson A, Chen E, Marra M, Martienssen R, McCombie WR (1999) Sequence and analysis of chromosome 4 of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 402:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1038/47134
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.107524.110
Montoya T, Nomura T, Farrar K, Kaneta T, Yokota T, Bishop GJ (2002) Cloning the tomato curl3 gene highlights the putative dual role of the leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase tBRI1/SR160 in plant steroid hormone and peptide hormone signaling. Plant Cell 14:3163–3176. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.006379
Morinaka Y, Sakamoto T, Inukai Y, Agetsuma M, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2006) Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol 141:924–931. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.077081
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1226
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Nakamura A, Fujioka S, Sunohara H, Kamiya N, Hong Z, Inukai Y, Miura K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Hasegawa Y, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2006) The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol 140:580–590. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.072330
Neff MM, Neff JD, Chory J, Pepper AE (1998) dCAPS, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: experimental applications in Arabidopsis thaliana genetics. Plant J 14:387–392. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00124.x
Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Choe S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yuan H, Feldmann KA, Tax FE (1999) Brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf mutants of Arabidopsis accumulate brassinosteroids. Plant Physiol 121:743–752. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.121.3.743
Nomura T, Nakayam M, Reid JB, Takeuchi Y, Yokota T (1997) Blockage of brassinosteroid biosynthesis and sensitivity causes dwarfism in garden pea. Plant Physiol 113:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.1.31
Nomura T, Kitasaka Y, Takatsuto S, Reid JB, Fukami M, Yokota T (1999) Brassinosteroid/Sterol synthesis and plant growth as affected by lka and lkb mutations of pea. Plant Physiol 119:1517–1526. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.119.4.1517
Ohnishi T, Szatmari AM, Watanabe B, Fujita S, Bancos S, Koncz C, Lafos M, Shibata K, Yokota T, Sakata K, Szekeres M, Mizutani M (2006) C-23 hydroxylation by Arabidopsis CYP90C1 and CYP90D1 reveals a novel shortcut in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 18:3275–3288. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.045443
Peng JR, Richards DE, Hartley NM, Murphy GP, Devos KM, Flintham JE, Beales J, Fish LJ, Worland AJ, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape JW, Gale MD, Harberd NP (1999) ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 400:256–261. https://doi.org/10.1038/22307
Perez MBM, Zhao J, Yin Y, Hu J, Fernandez MGS (2014) Association mapping of brassinosteroid candidate genes and plant architecture in a diverse panel of Sorghum bicolor. Theor Appl Genet 127:2645–2662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2405-9
Qin C, Yu C, Shen Y, Fang X, Chen L, Min J, Cheng J, Zhao S, Xu M, Luo Y, Yang Y, Wu Z, Mao L, Wu H, Hu-Ling C, Zhou H, Lin H, González-Morales S, Trejo-Saavedra DL, Tian H, Tang X, Zhao M, Huang Z, Zhou A, Yao X, Cui J, Li W, Chen Z, Feng Y, Niu Z, Bi S, Yang X, Li W, Cai H, Luo X, Montes-Hernández S, Leyva-González MA, Xiong ZQ, He X, Bai L, Tan S, Tang X, Liu D, Liu J, Zhang S, Chen M, Zhang L, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Liao W, Zhang Y, Wang M, Lv X, Wen B, Liu H, Luan H, Zhang Y, Yang S, Wang X, Xu J, Li X, Li S, Wang J, Palloix A, Bosland PW, Li Y, Krogh A, Rivera-Bustamante RF, Herrera-Estrella L, Yin Y, Yu J, Hu K, Zhang Z (2014) Whole-genome sequencing of cultivated and wild peppers provides insights into Capsicum domestication and specialization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:5135–5140. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1400975111
Rouse D, Mackay P, Stirnberg P, Estelle M, Leyser O (1998) Changes in auxin response from mutations in an AUX/IAA gene. Science 279:1371–1373. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.279.5355.1371
Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush GS, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2002) Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 416:701. https://doi.org/10.1038/416701a
Scheer JM, Ryan CA Jr (2002) The systemin receptor SR160 from Lycopersicon peruvianum is a member of the LRR receptor kinase family. P Natl Acad Sci 99:9585–9590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.279.5355.1371
Silverstone AL, Sun TP (2000) Gibberellins and the green revolution. Trends Plant Sci 5:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(99)01516-2
Suh HS (1978) The segregation mode of plant height in the cross of rice varieties. II. Linkage analysis of the semi-dwarfness of rice variety “Tongil”. Korean J Breeding 10:1–6
Sun C, Li J (2017) Biosynthesis, catabolism, and signal transduction of brassinosteroids. Plant Physiol J 53:291–307. https://doi.org/10.13592/cnki/ppj.2017.1002
Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano LM, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013) QTL-seq: rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J 74:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12105
Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Yoshida K, Uemura A, Yaegashi H, Obara T, Oikawa K, Utsushi H, Kanzaki E, Mitsuoka C, Natsume S, Kosugi S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Urasaki N, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2015) MutMap accelerates breeding of a salt-tolerant rice cultivar. Nat Biotechnol 33:445–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3188
Tang M, Zeng H, Ren J, Zhang N, Li Y (2017) Research progress on dwarf character of cucurbit plants. J Changjiang Veg 2:41–44. https://doi.org/10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2017.02.016
Thole JM, Strader LC (2015) Next-generation sequencing as a tool to quickly identify causative EMS-generated mutations. Plant Signal Behav 10:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2014.1000167
Thyssen GN, Fang DD, Turley RB, Florane CB, Li P, Mattison CP, Naoumkina M (2017) A Gly65Val substitution in an actin, GhACT_LI1, disrupts cell polarity and F-actin organization resulting in dwarf, lintless cotton plants. Plant J 90:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13477
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflink. Nat Protoc 7:562–578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.016
Tribhuvan KU, Kumar K, Sevanthi AM, Gaikwad K (2018) MutMap: a versatile tool for identification of mutant loci and mapping of genes. Indian J Plant Physiol 23:612–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0417-1
Tsuchiya Y, McCourt P (2009) Strigolactones: a new hormone with a past. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:556–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.07.018
Van Schie CCN, Ament K, Schmidt A, Lange T, Haring MA, Schuurink RC (2007) Geranyl diphosphate synthase is required for biosynthesis of gibberellins. Plant J 52:752–762. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03273.x
Vert G, Chory J (2006) Downstream nuclear events in brassinosteroid signalling. Nature 441:96–100. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04681
Vert G, Nemhauser JL, Geldner N, Hong F, Chory J (2005) Molecular mechanisms of steroid hormone signaling in plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:177–201. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.090704.151241
Wang X, Li X, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J (2005) Autoregulation and homodimerization are involved in the activation of the plant steroid receptor BRI1. Dev Cell 8:855–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.05.001
Wang X, Kota U, He K, Blackbum K, Li J, Goshe MB, Huber SC, Clouse SD (2008) Sequential transphosphorylation of the BRI1/BAK1 receptor kinase complex impacts early events in brassinosteroid signaling. Dev Cell 15:220–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2008.06.011
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2010) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38:e164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq603
Wang ZY, Bai MY, Oh E, Zhu JY (2012) Brassinosteroid signaling network and regulation of photomorphogenesis. Annu Rev Genet 46:701–724. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163450
Xu Z, Li J (2006) Plant hormones research in China: past, present and future. Chinese Bull Bot 23:433–442
Xu W, Huang J, Li B, Li J, Wang Y (2008) Is kinase activity essential for biological functions of BRI1? Cell Res 18:472–478. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.36
Xu M, Wang S, Zhang S, Cui Q, Gao D, Chen H, Huang S (2015) A new gene conferring the glabrous trait in cucumber identified using MutMap. Hortic Plant J 1:29–34. https://doi.org/10.16420/j.issn.2095-9885.2015-0003
Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2000) Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 12:1591–1605. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.9.1591
Yang CJ, Zhang C, Lu YN, Jin JQ, Wang XL (2011) The mechanisms of brassinosteroids’ action: from signal transduction to plant development. Mol Plant 4:588–600. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr020
Yang BZ, Zhou SD, Yang LL, Ma YQ, Zou XX (2017) Phenotypic characteristic of a dwarf mutant in pepper and its response to exogenous hormones. J Hunan Agric Univ 43:518–523. https://doi.org/10.13331/j.cnki.jhau.2017.05.009
Yin Y, Vafeados D, Tao Y, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J (2005) A new class of transcription factors mediates brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Cell 120:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.044
Zhao J, Wu C, Yuan S, Yin L, Sun W, Zhao Q, Zhao B, Li X (2013) Kinase activity of OsBRI1 is essential for brassinosteroids to regulate rice growth and development. Plant Sci 199:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.10.011
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31601757).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BZY and SDZ performed the experiments and wrote this manuscript. LJO and FL helped data analysis. LYY, JYZ, WCC, ZQZ, and SY assisted in the experiments. YQM and XXZ supervised the study. All authors read, commented, and approved the submitted and final versions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Zhou, S., Ou, L. et al. A novel single-base mutation in CaBRI1 confers dwarf phenotype and brassinosteroid accumulation in pepper. Mol Genet Genomics 295, 343–356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01626-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01626-z