Abstract
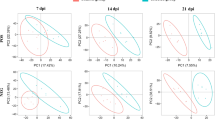
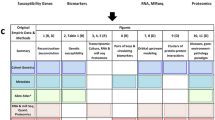
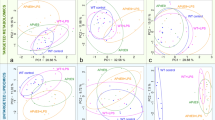
Toxoplasma gondii can cross the blood-brain barrier and infect different regions of the brain including the hippocampus. In the present study, we examined the impact of Toxoplasma gondii infection on the metabolism of the hippocampus of female BALB/c mice compared to control mice using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Multivariate analysis revealed significant differences between infected and control hippocampi and identified 25, 82, and 105 differential metabolites (DMs) in the infected hippocampi at 7, 14, and 21 days post-infection (dpi), respectively. One DM (sphingosyl-phosphocholine in the sphingolipid metabolism pathway) and 11 dysregulated pathways were detected at all time points post-infection, suggesting their important roles in the neuropathogenesis of T. gondii infection. These pathways were related to neural activity, such as inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels, retrograde endocannabinoid signaling, and arachidonic acid metabolism. Weighted correlation network analysis and receiver operating characteristic analysis identified 33 metabolites significantly associated with T. gondii infection in the hippocampus, and 30 of these were deemed as potential biomarkers for T. gondii infection. This study provides, for the first time, a global view of the metabolic perturbations that occur in the mouse hippocampus during T. gondii infection. The potential relevance of the identified metabolites and pathways to the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment and psychiatric disorders are discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The metabolomics raw data have been deposited in the MetaboLights database (Access number: MTBLS1890).
References
Abdoli A, Dalimi A (2014) Are there any relationships between latent Toxoplasma gondii infection, testosterone elevation, and risk of autism spectrum disorder? Front Behav Neurosci 8:339
Balboa MA, de Pablo N, Meana C, Balsinde J (2019) The role of lipins in innate immunity and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1864(10):1328–1337
Bedny M, Caramazza A, Grossman E, Pascual-Leone A, Saxe R (2008) Concepts are more than percepts: the case of action verbs. J Neurosci 28(44):11347–11353
Berenreiterova M, Flegr J, Kubena AA, Nemec P (2011) The distribution of Toxoplasma gondii cysts in the brain of a mouse with latent toxoplasmosis: implications for the behavioral manipulation hypothesis. PLoS One 6(12):e28925
Berger A, Rosenthal D, Spiegel S (1995) Sphingosylphosphocholine, a signaling molecule which accumulates in Niemann-Pick disease type A, stimulates DNA-binding activity of the transcription activator protein AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(13):5885–5889
Binder JR, Westbury CF, McKiernan KA, Possing ET, Medler DA (2005) Distinct brain systems for processing concrete and abstract concepts. J Cogn Neurosci 17(6):905–917
Bittleman DB, Casale TB (1995) 5-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE)-induced neutrophil transcellular migration is dependent upon enantiomeric structure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 12(3):260–267
Boillat M et al (2020) Neuroinflammation-associated aspecific manipulation of mouse predator fear by Toxoplasma gondii. Cell Reports 30(2):320–334.e326
Bosetti F (2007) Arachidonic acid metabolism in brain physiology and pathology: lessons from genetically altered mouse models. J Neurochem 102(3):577–586
Chen XQ, Elsheikha HM, Hu RS, Hu GX, Guo SL, Zhou CX, Zhu XQ (2018) Hepatic metabolomics investigation in acute and chronic murine toxoplasmosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:189
Chen XQ, Zhou CX, Elsheikha HM, He S, Hu GX, Zhu XQ (2017) Profiling of the perturbed metabolomic state of mouse spleen during acute and chronic toxoplasmosis. Parasit Vectors 10(1):339
Chiulli N, Codazzi F, Di Cesare A, Gravaghi C, Zacchetti D, Grohovaz F (2007) Sphingosylphosphocholine effects on cultured astrocytes reveal mechanisms potentially involved in neurotoxicity in Niemann-Pick type A disease. Eur J Neurosci 26(4):875–881
da Silva RC, Langoni H (2009) Toxoplasma gondii: host-parasite interaction and behavior manipulation. Parasitol Res 105(4):893–898
Daniels BP, Sestito SR, Rouse ST (2015) An expanded task battery in the Morris water maze reveals effects of Toxoplasma gondii infection on learning and memory in rats. Parasitol Int 64(1):5–12
David CN, Frias ES, Szu JI, Vieira PA, Hubbard JA, Lovelace J, Michael M, Worth D, McGovern KE, Ethell IM, Stanley BG, Korzus E, Fiacco TA, Binder DK, Wilson EH (2016) GLT-1-dependent disruption of CNS glutamate homeostasis and neuronal function by the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog 12(6):e1005643
Elsheikha HM, Busselberg D, Zhu XQ (2016) The known and missing links between Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia. Metab Brain Dis 31(4):749–759
Evans AK, Strassmann PS, Lee IP, Sapolsky RM (2014) Patterns of Toxoplasma gondii cyst distribution in the forebrain associate with individual variation in predator odor avoidance and anxiety-related behavior in male Long-Evans rats. Brain Behav Immun 37:122–133
Farfel-Becker T, Vitner EB, Kelly SL, Bame JR, Duan J, Shinder V, Merrill AH, Dobrenis K, Futerman AH (2014) Neuronal accumulation of glucosylceramide in a mouse model of neuronopathic Gaucher disease leads to neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet 23(4):843–854
Farkas I, Kalló I, Deli L, Vida B, Hrabovszky E, Fekete C, Moenter SM, Watanabe M, Liposits Z (2010) Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling reduces GABAergic synaptic transmission to gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Endocrinology 151(12):5818–5829
Gale SD, Brown BL, Berrett A, Erickson LD, Hedges DW (2014) Association between latent toxoplasmosis and major depression, generalised anxiety disorder and panic disorder in human adults. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 61(4):285–292
Gerdeman G, Lovinger DM (2001) CB1 cannabinoid receptor inhibits synaptic release of glutamate in rat dorsolateral striatum. J Neurophysiol 85(1):468–471
Gertow J, Kjellqvist S, Ståhlman M, Cheung L, Gottfries J, Werngren O, Borén J, Franco-Cereceda A, Eriksson P, Fisher RM (2014) Ceramides are associated with inflammatory processes in human mediastinal adipose tissue. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 24(2):124–131
Grimble RF, Tappia PS (1998) Modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine biology by unsaturated fatty acids. Z Ernahrungswiss 37(Suppl 1):57–65
Groer MW et al (2011) Prenatal depression and anxiety in Toxoplasma gondii-positive women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 204(5):433 e431–433 e437
Gu H, Zhang P, Zhu J, Raftery D (2015) Globally optimized targeted mass spectrometry: Reliable metabolomics analysis with broad coverage. Anal Chem 87(24):12355–12362
He JJ, Ma J, Wang JL, Zhang FK, Li JX, Zhai BT, Wang ZX, Elsheikha HM, Zhu XQ (2019) Global transcriptome profiling of multiple porcine organs reveals Toxoplasma gondii-induced transcriptional landscapes. Front Immunol 10:1531
Hoffman AF, Lupica CR (2000) Mechanisms of cannabinoid inhibition of GABA(A) synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 20(7):2470–2479
Hsu PC, Groer M, Beckie T (2014) New findings: depression, suicide, and Toxoplasma gondii infection. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract 26(11):629–637
Huth AG, de Heer WA, Griffiths TL, Theunissen FE, Gallant JL (2016) Natural speech reveals the semantic maps that tile human cerebral cortex. Nature 532(7600):453–458
Ingram WM, Goodrich LM, Robey EA, Eisen MB (2013) Mice infected with low-virulence strains of Toxoplasma gondii lose their innate aversion to cat urine, even after extensive parasite clearance. PLoS One 8(9):e75246
Leung D, Saghatelian A, Simon GM, Cravatt BF (2006) Inactivation of N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D reveals multiple mechanisms for the biosynthesis of endocannabinoids. Biochemistry 45(15):4720–4726
Levick SP, Loch DC, Taylor SM, Janicki JS (2007) Arachidonic acid metabolism as a potential mediator of cardiac fibrosis associated with inflammation. J Immunol 178(2):641–646
Li C, Wang A, Wang C, Ramamurthy J, Zhang E, Guadagno E, Trakadis Y (2018) Metabolomics in patients with psychosis: a systematic review. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 177(6):580–588
Liang W, Huang Y, Tan X, Wu J, Duan J, Zhang H, Yin B, Li Y, Zheng P, Wei H, Xie P (2019) Alterations of glycerophospholipid and fatty acyl metabolism in multiple brain regions of schizophrenia microbiota recipient mice. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 15:3219–3229
Lin CY, Wu H, Tjeerdema RS, Viant MR (2007) Evaluation of metabolite extraction strategies from tissue samples using NMR metabolomics. Metabolomics 3(1):55–67
Luchicchi A, Pistis M (2012) Anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol: pharmacological properties, functional features, and emerging specificities of the two major endocannabinoids. Mol Neurobiol 46(2):374–392
Lutz B, Marsicano G, Maldonado R, Hillard CJ (2015) The endocannabinoid system in guarding against fear, anxiety and stress. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(12):705–718
Ma J, He JJ, Hou JL, Zhou CX, Elsheikha HM, Zhu XQ (2020) Ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolomics reveals metabolic alterations in the mouse cerebellum during Toxoplasma gondii infection. Front Microbiol 11:1555
Ma J, He JJ, Hou JL, Zhou CX, Zhang FK, Elsheikha HM, Zhu XQ (2019) Metabolomic signature of mouse cerebral cortex following Toxoplasma gondii infection. Parasit Vectors 12(1):373
Mahmoudvand H, Ziaali N, Aghaei I, Sheibani V, Shojaee S, Keshavarz H, Shabani M (2015) The possible association between Toxoplasma gondii infection and risk of anxiety and cognitive disorders in BALB/c mice. Pathog Glob Health 109(8):369–376
Marra CM (2018) Central nervous system infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Handb Clin Neurol 152:117–122
Mencarelli C, Martinez-Martinez P (2013) Ceramide function in the brain: when a slight tilt is enough. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(2):181–203
Mendez OA, Koshy AA (2017) Toxoplasma gondii: Entry, association, and physiological influence on the central nervous system. PLoS Pathog 13(7):e1006351
Mendoza J, Pevet P, Felder-Schmittbuhl MP, Bailly Y, Challet E (2010) The cerebellum harbors a circadian oscillator involved in food anticipation. J Neurosci 30(5):1894–1904
Murphy EJ (2010) Brain fixation for analysis of brain lipid-mediators of signal transduction and brain eicosanoids requires head-focused microwave irradiation: an historical perspective. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 91(3-4):63–67
Nixon GF, Mathieson FA, Hunter I (2008) The multi-functional role of sphingosylphosphorylcholine. Prog Lipid Res 47(1):62–75
Odorizzi L, Moreira NM, Goncalves GF, da Silva AV, Sant’ana Dde M, Araujo EJ (2010) Quantitative and morphometric changes of subpopulations of myenteric neurons in swines with toxoplasmosis. Auton Neurosci 155(1-2):68–72
Piomelli D (2003) The molecular logic of endocannabinoid signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(11):873–884
Reeber SL, Otis TS, Sillitoe RV (2013) New roles for the cerebellum in health and disease. Front Syst Neurosci 7:83
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez JC, Müller M (2011) pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12:77
Sathyanesan M, Haiar JM, Watt MJ, Newton SS (2017) Restraint stress differentially regulates inflammation and glutamate receptor gene expression in the hippocampus of C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. Stress 20(2):197–204
Shibasaki K, Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Tominaga M (2007) Effects of body temperature on neural activity in the hippocampus: regulation of resting membrane potentials by transient receptor potential vanilloid 4. J Neurosci 27(7):1566–1575
Spassieva S, Bieberich E (2016) Lysosphingolipids and sphingolipidoses: psychosine in Krabbe’s disease. J Neurosci Res 94(11):974–981
Sugiyama E, Uemura K, Hara A, Taketomi T (1993) Metabolism and neurite promoting effect of exogenous sphingosylphosphocholine in cultured murine neuroblastoma cells. J Biochem 113(4):467–472
Tenter AM, Heckeroth AR, Weiss LM (2000) Toxoplasma gondii: from animals to humans. Int J Parasitol 30(12-13):1217–1258
Torres L, Robinson SA, Kim DG, Yan A, Cleland TA, Bynoe MS (2018) Toxoplasma gondii alters NMDAR signaling and induces signs of Alzheimer’s disease in wild-type, C57BL/6 mice. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):57
Vyas A (2015) Mechanisms of host behavioral change in Toxoplasma gondii rodent association. PLoS Pathog 11(7):e1004935
Wasek B, Arning E, Bottiglieri T (2018) The use of microwave irradiation for quantitative analysis of neurotransmitters in the mouse brain. J Neurosci Methods 307:188–193
Wilkins JM, Trushina E (2017) Application of metabolomics in alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurol 8:719
Yin B, Gu C, Lu Y, Hegab IM, Yang S, Wang A, Wei W (2017) Repeated exposure to cat urine induces complex behavioral, hormonal, and c-fos mRNA responses in Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus). Naturwissenschaften 104(7-8):64
Yu Q, He Z, Zubkov D, Huang S, Kurochkin I, Yang X, Halene T, Willmitzer L, Giavalisco P, Akbarian S, Khaitovich P (2020) Lipidome alterations in human prefrontal cortex during development, aging, and cognitive disorders. Mol Psychiatry 25(11):2952–2969
Zaka M, Wenger DA (2004) Psychosine-induced apoptosis in a mouse oligodendrocyte progenitor cell line is mediated by caspase activation. Neurosci Lett 358(3):205–209
Zhang H, He W, Huang Y, Zeng Z, Yang X, Huang H, Wen J, Cao Y, Sun H (2019) Hippocampal metabolic alteration in rat exhibited susceptibility to prenatal stress. J Affect Disord 259:458–467
Zhang X, Dong J, Raftery D (2020a) Five easy metrics of data quality for LC-MS-based global metabolomics. Anal Chem 92(19):12925–12933
Zhang Z et al (2020b) Identification of Toxoplasma gondii tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) activity and molecular immunoprotection against toxoplasmosis. Vaccines (Basel) 8(2)
Zhou CX, Zhou DH, Elsheikha HM, Liu GX, Suo X, Zhu XQ (2015) Global metabolomic profiling of mice brains following experimental infection with the cyst-forming Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS One 10(10):e0139635
Zhou CX, Zhou DH, Elsheikha HM, Zhao Y, Suo X, Zhu XQ (2016) Metabolomic profiling of mice serum during toxoplasmosis progression using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci Rep 6:19557
Zhou DH, Zhao FR, Huang SY, Xu MJ, Song HQ, Su C, Zhu XQ (2013) Changes in the proteomic profiles of mouse brain after infection with cyst-forming Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit Vectors 6:96
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the technical assistance, including metabolite extraction, identification, and quantification, provided by BGI-Shenzhen, China.
Funding
This work was supported, in part, by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31902291), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFD0500403), the Yunnan Expert Workstation (Grant No. 202005AF150041), and the Veterinary Public Health Innovation Team of Yunnan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All mice were handled strictly in accordance with the Animal Ethics Procedures and Guidelines of the People’s Republic of China. The study’s protocol was reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Permit No. LVRIAEC2017-06).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Una Ryan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Table S1
Details of the identified differentially abundant metabolites. (XLSX 50 kb)
Fig. S1
Agarose gel electrophoresis showing the presence of PCR products of Toxoplasma gondii B1 gene in the hippocampi of infected mice at 7, 14 and 21 days post infection (dpi). As anticipated, no amplicons were detected in the hippocampus of uninfected (control) mice. N: PCR negative control; P: T. gondii PCR positive control; M: DL1000 DNA marker (TAKARA, Dalian, China). (PNG 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., He, JJ., Wang, M. et al. Toxoplasma gondii induces metabolic disturbances in the hippocampus of BALB/c mice. Parasitol Res 120, 2805–2818 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07222-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07222-8