Abstract
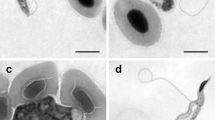
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of trypanosomes on cultured largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and describe the taxonomic identification of the parasite. The effects of the parasite on M. salmoides were examined based on clinical symptoms, hemograms, histopathology, and serum biochemistry. Diseased fish showed typical clinical symptoms of trypanosomiasis, which included lethargy, anorexia, and histopathological lesions in the liver, head kidney, and spleen. The serum of diseased fish had significantly lower concentrations of glucose, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein, and significantly higher alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activities. The morphology of the trypanosomes was also analyzed using light microscopy, and their 18S rDNA sequence was analyzed to establish genetic relationships with other known strains. We found that the trypomastigote form of the trypanosomes from M. salmoides was similar to those isolated from Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. The trypanosomes had a slender and narrow body with a relatively long free flagellum, not well-developed undulating membrane, and an oval kinetoplast located near the subterminal posterior end of the body. The 18S rDNA sequences of the trypanosome from M. salmoides had the highest similarity (99.8%) with that of P. fulvidraco, suggesting they are identical species. Based on the differences in morphological characteristics and 18S rDNA sequence compared to trypanosomes isolated from other freshwater fish, it is considered as a new species and we propose the name Trypanosoma micropteri n. sp.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MSK, Shafiq HA, Ollevier F (2011) Pathogenic effects associated with Trypanosoma danilewskyi strain FCC 1 infection in juvenile common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J Anim Plant Sci 21:800–806
Bai J, Lutz-Carrillo DJ, Quan Y, Liang SX (2008) Taxonomic status and genetic diversity of cultured largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides, in China. Aquacult 278:27–30
Chen YJ, Yuan RM, Liu YJ, Yang HJ, Liang GY, Tian LX (2015) Dietary vitamin C requirement and its effects on tissue antioxidant capacity of juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Aquacult 435:431–436
Corrêa LL, Oliveira MS, Tavares-Dias M, Ceccarelli PS (2016) Infections of Hypostomus spp. by Trypanosoma spp. and leeches: a study of hematology and record of these hirudineans as potential vectors of these hemoflagellates. Braz J Vet Parasitol 25:299–305
Coyle SD, Tidwell JH, Webster CD (2000) Response of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides to dietary supplementation of lysine, methionine, and highly unsaturated fatty acids. J World Aquacult Soc 31:89–95
Davies AJ, Gibson WC, Ferris VR, Basson L, Smit NJ (2005) Two genotypic groups of morphologically similar fish trypanosomes from the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Dis Aquat Org 66:215–220
Torre FRDL, Salibian A, Ferrari L (2000) Biomarkers assessment in juvenile Cyprinus carpio exposed to waterborne cadmium. Environ Pollut 109:277–282
Eiras JC, Takemoto RM, Pavanelli GC, Luque JL (2012) Checklist of protozoan parasites of fishes from Brazil. Zootaxa 3221:1–25
Fink IR, Ribeiro CMS, Forlenza M, Taverne TA, Rombout JHWM, Savelkoul HFJ et al (2015) Immune-relevant thrombocytes of common carp undergo parasite-induced nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis. Dev Comp Immunol 50:146–154
Fujimoto RY, Neves MS, Santos RFB, Souza NC, Couto MVS, Lopes JN et al (2013) Morphological and hematological studies of Trypanosoma spp. infecting ornamental armored catfish from Guamá River-PA, Brazil. An Acad Bras Cienc 85:1149–1156
Gibson WC, Lom J, Peckova H, Ferris VR, Hamilton PB (2005) Phylogenetic analysis of freshwater fish trypanosomes from Europe using SSU rRNA gene sequences and random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Parasitol 130:405–412
Grybchuk IA, Losev A, Kostygov AY, Lukeš J, Yurchenko V (2014) High prevalence of trypanosome co-infections in freshwater fishes. Folia Parasitol 61:495–504
Gu Z, Wang J, Li M, Zhang J, Gong X (2007b) Redescription of Trypanosoma siniperca Chang 1964 from freshwater fish of China based on morphological and molecular data. Parasitol Res 100:395–400
Gu Z, Wang J, Li M, Zhang J, Ke X, Gong X (2007a) Morphological and genetic differences of Trypanosoma in some Chinese freshwater fishes: difficulties of species identification. Parasitol Res 100:723–730
Gu ZM, Wang JG, Zhang JY, Gong XN (2006) Redescription of Trypanosoma ophiocephali Chen 1964 (Kinetoplastida: Trypanosomatina: Trypanosomatidae) and first record from the blood of dark sleeper (Odontobutis obscura Temminck and Schlegel) in China. Parasitol Res 100:149–154
Gupta N, Gupta DK (2012) Erythropenia in piscine trypanosomiasis. Trends Parasitol Res 1:1–6
Hayes PM, Lawton SP, Smit NJ, Gibson WC, Davies AJ (2014) Morphological and molecular characterization of a marine fish trypanosome from South Africa, including its development in a leech vector. Parasit Vectors 7:50
Islam AKMN, Woo PTK (1991) Anemia and its mechanism in goldfish Carassius auratus infected with Trypanosoma danilewskyi. Dis Aquat Org 11:37–43
Jamalzadeh HR, Keyvan A, Ghomi MR, Gheradi F (2009) Comparison of blood indices in healthy and fungal infected Caspian salmon (Salmo trutta caspius). Afr J Biotechnol 8:319–322
Jesus RBD, Gallani SU, Valladão GMR, Pala G, Silva TFAD, Costa JCD et al (2018) Trypanosomiasis causing mortality outbreak in Nile tilapia intensive farming: identification and pathological evaluation. Aquacult 491:169–176
Jones SRM, Woo PTK (1991) Development and infectivity of Trypanosoma phalera in leech and fish hosts. Can J Zool 68:1951–1955
Khan RA (1985) Pathogenesis of Trypanosoma murmanensis in marine fish of the northwestern Atlantic following experimental transmission. Can J Zool 63:2141–2144
Lemos M, Fermino BR, Rodrigues CS, Hoffmann L, Silva R, Camargo EP et al (2015) Phylogenetic and morphological characterization of trypanosomes from Brazilian armoured catfishes and leeches reveal high species diversity, mixed infections and a new fish trypanosome species. Parasit Vectors 8:573
Li L, Wang J (1996) The life cycle of Trypanosoma lichuanensis Li in blood of Rana boulengeri Gunther. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 20:66–73
Li SJ, Bai JJ, Zhao L, Zhu B, Zhu XP (2018) Development of EST-SNPs in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and analysis of their correlation with growth traits. Mar Fish 2:34–38 (In China)
Lom J, Dykova I (1992) Flagellates (phylum Mastigophora). In: Protozoan parasites of fishes. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 32–38
Ma DM, Deng GC, Bai JJ, Li SG, Yu LG, Quan XJ et al (2013) A strain of Siniperca chuatsi Rhabdovirus causes high mortality among cultured largemouth bass in South China. J Aquat Anim Health 25:197–204
Maqbool A, Ahmed I (2016) Haematological response of snow barbell, Schizothorax plagiostomus Heckel, naturally infected with a new Trypanosoma species. J Parasit Dis 40:1–10
Maslov DA, Lukes J, Jirku M, Simpson L (1996) Phylogeny of trypanosomes as inferred from the small and large subunit rRNAs: implications for the evolution of parasitism in the trypanosomatid protozoa. Mol Biochem Parasitol 75:197–205
Molina JP, Madi RR, Solferini VN, Ceccarelli PS, Pinheiro HP, Ueta MT (2016) Trypanosomatids (Protozoa: Kinetoplastida) in three species of armored catfish from Mogi-Guaçu River, Pirassununga, São Paulo. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 25:131–141
Newman SH, Piatt JF, White J (1997) Hematological and plasma biochemical reference ranges of Alaskan seabirds: their ecological significance and clinical importance. Colon Waterbirds 20:492–504
Percin F, Konyalioglu S (2008) Serum biochemical profiles of captive and wild northern bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus L. 1758) in the Eastern Mediterranean. Aquac Res 39:945–953
Rodrigues RN, Oliveira MSB, Tavaresdias M, Corrêa LL (2017) First record of infection by Trypanosoma sp. of Colossoma macropomum (Serrasalmidae), a Neotropical fish cultivated in the Brazilian Amazon. J Appl Aquac 4:29–38
Su Y, Feng J, Jiang J, Guo Z, Liu G, Xu L (2014) Trypanosoma epinepheli n. sp. (Kinetoplastida) from a farmed marine fish in China, the brown-marbled grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus). Parasitol Res 113:11–18
Vaglio A, Landriscina C (1999) Changes in liver enzyme activity in the teleost Sparus aurata in response to cadmium intoxication. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 43:111–116
Woo PTK (1998) Diplomonadida, Kinetoplastida and Amoebida (Phylum Sarcomastigophora). In: Woo PTK (ed) Fish Diseases and Disorders: Noninfectious disorders. CABI, Oxfordshire, pp 46–115
Woo PTK, Black GA (1984) Trypanosoma danilewskyi: host specificity and host’s effect on morphometrics. J Parasitol 70:788–793
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China Agriculture Research System (The Control of Parasites Infection on Marine Fish, CARS-47-18) to Pro. Anxing Li.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All protocols were approved by China Institute of Veterinary Drug Control and the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee at Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, China.
Additional information
Section Editor: Astrid Holzer
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 295 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, B., Lu, G., Du, J. et al. First report of trypanosomiasis in farmed largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) from China: pathological evaluation and taxonomic status. Parasitol Res 118, 1731–1739 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06323-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06323-9