Abstract
Background
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive neuroendocrine cancer with a high risk of early mortality (i.e., survival time less than 1 month). This study aimed to identify relevant risk factors and predict early mortality in SCLC patients.
Methods
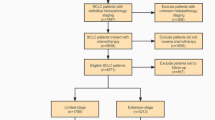
A total of 27,163 SCLC cases registered between 2010 and 2019 were extracted from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data. Significant independent risk factors were identified by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. Nomograms for all-causes and cancer-specific early death were constructed and evaluated.
Results
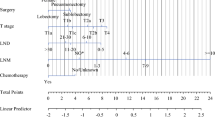
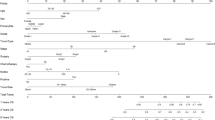
Age, sex, clinical stage, presence of metastasis (liver and lung), and absence of treatment (surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy) were identified for significant association with all-causes and cancer-specific early death. Nomograms based on these predictors exhibited high accuracy (area under ROC curve > 0.850) and potential clinical practicality in the prediction of early mortality.
Conclusion
We identified a set of factors associated with early mortality from SCLC and developed a clinically useful nomogram to predict high-risk patients. This nomogram could aid oncologists in the administration of individualized treatment regimens, potentially improving clinical outcomes of SCLC patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://seer.cancer.gov.
References
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP (2015) Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol 16(4):e173–e180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71116-7
Bennett BM, Wells JR, Panter C, Yuan Y, Penrod JR (2017) The humanistic burden of Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): a systematic review of Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) Literature. Front Pharmacol 8:339. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00339
Bertagnolli MM, Anderson B, Norsworthy K, Piantadosi S, Quina A et al (2020) Status update on data required to build a learning health system. J Clin Oncol 38(14):1602–1607. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.03094
Chen S, Liu Y, Yang J, Liu Q, You H et al (2019) Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in male patients with breast cancer. Front Oncol 9:361. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00361
Chen H, Huang Z, Chen L, Li Y, Zhao T et al (2021) Characteristics of early death in patients with localized nasopharyngeal cancer: a population-based SEER analysis. Front Oncol 11:580220. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.580220
Correa AF, Jegede O, Haas NB, Flaherty KT, Pins MR et al (2019) Predicting renal cancer recurrence: defining limitations of existing prognostic models with prospective trial-based validation. J Clin Oncol 37(23):2062–2071. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.00107
Cortinovis D, Bidoli P, Canova S, Colonese F, Gemelli M et al (2021) Novel cytotoxic chemotherapies in small cell lung carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051152
Dyba T, Randi G, Bray F, Martos C, Giusti F et al (2021) The European cancer burden in 2020: Incidence and mortality estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers. Eur J Cancer 157:308–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2021.07.039
Gao J, Wang S, Li F, Xu H, Li X et al (2022) Nomograms for predicting overall survival and cancer-specific survival of young patients with epithelial ovarian cancer: analysis based on SEER program. Adv Ther 39(1):257–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01955-9
Hristov B, Eguchi T, Bains S, Dycoco J, Tan KS et al (2019) Minimally invasive lobectomy is associated with lower noncancer-specific mortality in elderly patients: a propensity score matched competing risks analysis. Ann Surg 270(6):1161–1169. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000002772
Hsu W-H, Zhao X, Zhu J, Kim I-K, Rao G et al (2019) Checkpoint kinase 1 inhibition enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity and overcomes cisplatin resistance in SCLC by promoting mitotic cell death. J Thor Oncol 14(6):1032–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.01.028
Iams WT, Shiuan E, Meador CB, Roth M, Bordeaux J et al (2019) Improved prognosis and increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients who have SCLC with neurologic Paraneoplastic syndromes. Jf Thor Oncol 14(11):1970–1981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.05.042
Iasonos A, Schrag D, Raj GV, Panageas KS (2008) How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol 26(8):1364–1370. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.12.9791
Janssens ACJW, Martens FK (2020) Reflection on modern methods: Revisiting the area under the ROC Curve. Int J Epidemiol 49(4):1397–1403. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyz274
Jones GS, McKeever TM, Hubbard RB, Khakwani A, Baldwin DR (2018) Factors influencing treatment selection and 30-day mortality after chemotherapy for people with small-cell lung cancer: An analysis of national audit data. Eur J Cancer 103:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2018.07.133
Li J, Zhu H, Sun L, Xu W, Wang X (2019) Prognostic value of site-specific metastases in lung cancer: A population based study. J Cancer 10(14):3079–3086. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.30463
Miranda-Filho A, Piñeros M, Soerjomataram I, Deltour I, Bray F (2017) Cancers of the brain and CNS: global patterns and trends in incidence. Neuro Oncol 19(2):270–280. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now166
Rudin CM, Brambilla E, Faivre-Finn C, Sage J (2021) Small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00235-0
Sabari JK, Lok BH, Laird JH, Poirier JT, Rudin CM (2017) Unravelling the biology of SCLC: implications for therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(9):549–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.71
SEER Incidence Data, 1975–2019. Available at: https://seer.cancer.gov/data/ (Accessed 15 April 2022).
Shen X, Zhu G, Liu R, Viola D, Elisei R et al (2018) Patient age-associated mortality risk is differentiated by BRAF V600E status in papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol 36(5):438–445. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.74.5497
Song Z, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang D (2020) A novel predictive tool for determining the risk of early death from stage IV endometrial carcinoma: a large cohort study. Front Oncol 10:620240. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.620240
Song Z, Wang Y, Zhang D, Zhou Y (2020) A Novel tool to predict early death in uterine sarcoma patients: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results-based study. Front Oncol 10:608548. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.608548
Van Calster B, Wynants L, Verbeek JFM, Verbakel JY, Christodoulou E et al (2018) Reporting and interpreting decision curve analysis: a guide for investigators. Eur Urol 74(6):796–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.038
Wang S, Yang L, Ci B, Maclean M, Gerber DE et al (2018) Development and validation of a nomogram prognostic model for SCLC patients. J Thor Oncol 13(9):1338–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.05.037
Wu S, Wang J, Zhang W, Li J, Wu H et al (2020) Analysis of factors affecting brain metastasis in limited-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with definitive thoracic irradiation. Front Oncol 10:556634. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.556634
Zhang Z, Pu J, Zhang H (2021) Development and validation of a simple-to-use nomogram to predict early death in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol 11:729175. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.729175
Zhu Y, Fang X, Wang L, Zhang T, Yu D (2020) A predictive nomogram for early death of metastatic gastric cancer: a retrospective study in the SEER database and China. J Cancer 11(18):5527–5535. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.46563
Funding
This study was jointly supported by Shandong medical and health science and technology development plan project (202009030079, 202009030080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design: YA, ZL and LS. Methodological development: ZL, MP, XL, YZ, WZ and WH. Statistical analysis: ZL, YA, and MP. Manuscript writing: All authors. Study research guidance and supervision: YA and LS. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors of this article declared that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Pang, M., Liang, X. et al. Risk factors of early mortality in patients with small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study in the SEER database. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 11193–11205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05003-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05003-7