Abstract
Objective
To investigate the impact of histological variants (HV) in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) and analyze the potential association between HV and postoperative bladder recurrence.
Materials and methods
The medical records of UTUC patients treated with RNU at our center from January 2012 to December 2019 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were grouped according to the types of HV. Clinicopathological features and prognostic factors were compared among groups.
Results
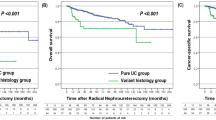
A total of 629 patients were included in the study: 458 (73%) patients had pure urothelial carcinoma (PUC) and 171 (27%) patients had UTUC with HV. Squamous differentiation was the most common type (124 cases, 19%), followed by glandular differentiation (29 cases, 5.0%). Patients with HV had a higher proportion of T3 and T4 pathologic stages (P < 0.001) as well as high-grade disease (P = 0.002). In the univariate analysis, squamous differentiation and glandular differentiation were significantly associated with worse cancer-specific survival (CSS) (HR 2.22, 95% CI 1.62–3.04, P < 0.001; HR 1.90, 95% CI 1.13–3.20, P = 0.016). However, the multivariate analysis showed that this association became non-significant. We found that HV were associated with recurrent muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) after RNU and all patients had T2 and T3 initial tumor stages (P = 0.008, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
We found that UTUC patients with HV were associated with biologically aggressive disease and recurrent MIBC after RNU. The detection of bladder recurrence following surgery needs to be given more attention in advanced UTUC patients with HV.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article and its tables and figures. Further enquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- HV:
-
Histological variants
- UTUC:
-
Upper tract urothelial carcinoma
- RNU:
-
Radical nephroureterectomy
- UC:
-
Urothelial carcinoma
- MIBC:
-
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- CSS:
-
Cancer-Specific Survival
- AJCC:
-
American Joint Committee on Cancer
- HRs:
-
Hazard ratios
- NMIBC:
-
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- CSM:
-
Cancer-specific mortality
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
References
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK et al (2017) The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin 67(2):93–99. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21388
Chen XP, Xiong GY, Li XS, Matin SF, Garcia M, Fang D et al (2013) Predictive factors for worse pathological outcomes of upper tract urothelial carcinoma: experience from a nationwide high-volume centre in China. BJU Int 112(7):917–924. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.12238
Chung HS, Hwang EC, Kim MS, Yu SH, Jung SI, Kang TW et al (2019) Effects of variant histology on the oncologic outcomes of patients with upper urinary tract carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy: a propensity score-matched analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer 17(3):e394–e407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2018.11.015
Compérat EM, Burger M, Gontero P, Mostafid AH, Palou J, Rouprêt M et al (2019) Grading of urothelial carcinoma and the new “World Health Organisation Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs 2016.” Eur Urol Focus 5(3):457–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2018.01.003
Deuker M, Stolzenbach LF, Collà Ruvolo C, Nocera L, Tian Z, Roos FC et al (2021) Upper urinary tract tumors: variant histology versus urothelial carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 19(2):117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2020.11.004
Hayashi H, Mann S, Kao CS, Grignon D, Idrees MT (2017) Variant morphology in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: a 14-year case series of biopsy and resection specimens. Hum Pathol 65:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2017.05.001
Hsieh MC, Sung MT, Chiang PH, Huang CH, Tang Y, Su YL (2015) The prognostic impact of histopathological variants in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0129268. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129268
Kim JK, Moon KC, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH (2017) Variant histology as a significant predictor of survival after radical nephroureterectomy in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol Oncol 35(7):458.e459-458.e415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.02.010
Kim SH, Song MK, Joung JY, Chung J, Lee KH, Seo HK (2019) Significant clinicopathologic prognostic factors for bladder recurrence, progression, and cancer-specific survival after surgery among patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Investig Clin Urol 60(6):432–442. https://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2019.60.6.432
Lee YJ, Moon KC, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH (2014) Impact of squamous and glandular differentiation on oncologic outcomes in upper and lower tract urothelial carcinoma. PLoS ONE 9(9):e107027. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107027
Mori K, Janisch F, Parizi MK, Mostafaei H, Lysenko I, Kimura S et al (2020) Prognostic value of variant histology in upper tract urothelial carcinoma treated with nephroureterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Urol 203(6):1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.1097/ju.0000000000000523
Moschini M, D’Andrea D, Korn S, Irmak Y, Soria F, Compérat E, Shariat SF (2017) Characteristics and clinical significance of histological variants of bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol 14(11):651–668. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2017.125
Murakami Y, Matsumoto K, Ikeda M, Hirayama T, Utsunomiya T, Koguchi D et al (2019) Impact of histologic variants on the oncological outcomes of patients with upper urinary tract cancers treated with radical surgery: a multi-institutional retrospective study. Int J Clin Oncol 24(11):1412–1418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01486-y
Nogueira LM, Yip W, Assel MJ, Tracey AT, Wong NC, Alvim RG et al (2022) Survival impact of variant histology diagnosis in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. J Urol 208(4):813–820. https://doi.org/10.1097/ju.0000000000002799
Rink M, Robinson BD, Green DA, Cha EK, Hansen J, Comploj E et al (2012) Impact of histological variants on clinical outcomes of patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. J Urol 188(2):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.04.009
Rolim I, Henriques V, Rolim N, Blanca A, Marques RC, Volavšek M et al (2020) Clinicopathologic analysis of upper urinary tract carcinoma with variant histology. Virchows Arch 477(1):111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-020-02745-4
Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D, Compérat EM et al (2021) European Association of Urology Guidelines on upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2020 update. Eur Urol 79(1):62–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.042
Sakano S, Matsuyama H, Kamiryo Y, Hayashida S, Yamamoto N, Kaneda Y et al (2015) Impact of variant histology on disease aggressiveness and outcome after nephroureterectomy in Japanese patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol 20(2):362–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0721-3
Sato G, Yoshida T, Yanishi M, Saito R, Murota T, Kawa G et al (2020) Preoperative pyuria predicts for intravesical recurrence in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract after radical nephroureterectomy without a history of bladder cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer 18(2):e167–e173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc2019.09.017
Shah RB, Montgomery JS, Montie JE, Kunju LP (2013) Variant (divergent) histologic differentiation in urothelial carcinoma is under-recognized in community practice: impact of mandatory central pathology review at a large referral hospital. Urol Oncol 31(8):1650–1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2012.04.009
Shibing Y, Turun S, Qiang W, Junhao L, Haichao Y, Shengqiang Q et al (2015) Effect of concomitant variant histology on the prognosis of patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy. Urol Oncol 33(5):204.e209-216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.02.010
Soria F, Shariat SF, Lerner SP, Fritsche HM, Rink M, Kassouf W et al (2017) Epidemiology, diagnosis, preoperative evaluation and prognostic assessment of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). World J Urol 35(3):379–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-016-1928-x
Takemoto K, Teishima J, Kohada Y, Ikeda K, Nagamatsu H, Goriki A et al (2020) The impact of histological variant on oncological outcomes in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder treated with radical cystectomy. Anticancer Res 40(8):4787–4793. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.14481
Tang Q, Xiong G, Li X, Fang D, Xi C, Zhang L et al (2016) The prognostic impact of squamous and glandular differentiation for upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients after radical nephroureterectomy. World J Urol 34(6):871–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1715-0
Wang Q, Zhang T, Wu J, Wen J, Tao D, Wan T, Zhu W (2019) Prognosis and risk factors of patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma and postoperative recurrence of bladder cancer in central China. BMC Urol 19(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12894-019-0457-5
Zamboni S, Foerster B, Abufaraj M, Seisen T, Roupret M, Colin P et al (2019) Incidence and survival outcomes in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma diagnosed with variant histology and treated with nephroureterectomy. BJU Int 124(5):738–745. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14751
Funding
This study was supported by Integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine Research project of Tianjin Municipal Health Commission (Grant no. 2021172), the Technology Project of the Tianjin Binhai New Area Health Commission (Grant no. 2019BWKY026) and Tianjin “131” Innovative Talent Cultivation Project. The funding source had no role in the study design, data curation, analysis, or interpretation of data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation: CW, DT, JW; methodology: CW, DT, JW; investigation: JW, XZ, WW, YZ, DZ, GH; data curation: JW, DZ, XZ, WW, YZ, WL; formal analysis: JW, WW, YZ, XZ; visualisation: JW, WL, YZ, WW; writing—original draft: JW, DZ, YZ, XZ, WW, WL; writing–review and editing: JW, YZ, XZ, WL, WW, DZ, DT; supervision, CW, DT, JW, GH. All authors have read and agreed to the current version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This is an observational study and no ethical approval is required. The retrospective cohort study was conducted in accordance with the “Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects” of the current version of the Declaration of Helsinki. Data collected for this study were obtained as part of routine medical care.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zuo, X., Zhang, Y. et al. The impact of histological variants in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma treated with radical nephroureterectomy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 8279–8288 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04763-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04763-6