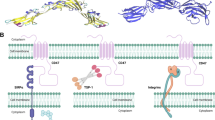
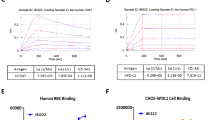
Abstract
CD47, a transmembrane protein, acts as a “do not eat me” signal that is overexpressed in many tumor cell types, thereby forming a signaling axis with its ligand signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) and enabling the tumor cells to escape from macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. Several clinical trials with CD47 targeting agents are underway and have achieved impressive results preliminarily. However, hematotoxicity (particularly anemia) has emerged as the most common side effect that cannot be neglected. In the development of CD47 targeting agents, various methods have been used to mitigate this toxicity. In this review, we summarized five strategies used to alleviate CD47 blockade-induced hematotoxicity, as follows: change in the mode of administration; dual targeting bispecific antibodies of CD47; CD47 antibodies/SIRPα fusion proteins with negligible red blood cell binding; anti-SIRPα antibodies; and glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase like inhibitors. With these strategies, the development of CD47 targeting agents can be improved.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ADCC:
-
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- ADCP:
-
Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis
- CD19:
-
Cluster of differentiation 19
- CD20:
-
Cluster of differentiation 20
- CD47:
-
Cluster of differentiation 47
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated molecule-4
- DLBCL:
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2
- MTD:
-
Maximum tolerated dose
- PD-1:
-
Programmed cell death receptor-1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed cell death ligand-1
- QPCT:
-
Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase
- QPCTL:
-
Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase like
- RBC:
-
Red blood cell
- SIRPα:
-
Signal regulatory protein alpha
- SIRPβ:
-
Signal regulatory protein beta
- SIRPγ:
-
Signal regulatory protein gamma
- TAA:
-
Tumor-associated antigens
References
Advani R, Flinn I, Popplewell L, Forero A, Bartlett NL, Ghosh N et al (2018) CD47 blockade by Hu5F9-G4 and rituximab in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 379(18):1711–1721
Agoram B, Wang B, Sikic BI, Lakhani NJ, Patnaik A, Liu J et al (2018) Pharmacokinetics of Hu5F9-G4, a first-in-class anti-CD47 antibody, in patients with solid tumors and lymphomas. J Clin Oncol 36(15_suppl):2525
Ansell S, Chen RW, Flinn IW, Maris MB, O’Connor OA, Johnson LD et al (2016) A phase 1 study of TTI-621, a novel immune checkpoint inhibitor targeting CD47, in patients with relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancies. Blood 128(22):1812
Ansell SM, Flinn IW, Maris MB, O’Connor OA, Lesokhin A, Advani AS et al (2017) TTI-621 (SIRPαFc), an immune checkpoint inhibitor blocking the CD47 “do not eat” signal, induces objective responses in patients with advanced, relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood 130(Supplement 1):4116
Ansell SM, Maris MB, Lesokhin AM, Chen RW, Flinn IW, Sawas A et al (2021) Phase I study of the CD47 blocker TTI-621 in patients with relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 27(8):2190–2199
Arias CF, Arias CF (2017) How do red blood cells know when to die? R Soc Open Sci 4(4):160850
Barazi HO, Li Z, Cashel JA, Krutzsch HC, Annis DS, Mosher DF et al (2002) Regulation of integrin function by CD47 ligands. Differential effects on alpha vbeta 3 and alpha 4beta1 integrin-mediated adhesion. J Biol Chem 277(45):42859–42866
Becker A, Eichentopf R, Sedlmeier R, Waniek A, Cynis H, Koch B et al (2016) IsoQC (QPCTL) knock-out mice suggest differential substrate conversion by glutaminyl cyclase isoenzymes. Biol Chem 397(1):45–55
Bouchlaka MN, Puro R, Capoccia B, Donio M, Hiebsch R, Carter AJ et al (2018) Development of AO-176, a next generation humanized anti-CD47 antibody with novel anti-cancer properties and negligible binding to red blood cells. Eur J Cancer 103:76
Bruce LJ, Ghosh S, King MJ, Layton DM, Mawby WJ, Stewart GW et al (2002) Absence of CD47 in protein 4.2-deficient hereditary spherocytosis in man: an interaction between the Rh complex and the band 3 complex. Blood 100(5):1878–1885
Buatois V, Johnson Z, Salgado-Pires S, Papaioannou A, Hatterer E, Chauchet X et al (2018) Preclinical development of a bispecific antibody that safely and effectively targets CD19 and CD47 for the treatment of B-Cell lymphoma and leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther 17(8):1739–1751
Chen J, Zhong MC, Guo H, Davidson D, Mishel S, Lu Y et al (2017) SLAMF7 is critical for phagocytosis of haematopoietic tumour cells via Mac-1 integrin. Nature 544(7651):493–497
Chen JY, McKenna KM, Choi TS, Duan J, Brown L, Stewart JJ et al (2018) RBC-specific CD47 pruning confers protection and underlies the transient anemia in patients treated with anti-CD47 antibody 5F9. Blood 132(Supplement 1):2327
Chen Q, Wang C, Zhang X, Chen G, Hu Q, Li H et al (2019) In situ sprayed bioresponsive immunotherapeutic gel for post-surgical cancer treatment. Nat Nanotechnol 14(1):89–97
Dheilly E, Moine V, Broyer L, Salgado-Pires S, Johnson Z, Papaioannou A et al (2017) Selective blockade of the ubiquitous checkpoint receptor CD47 Is enabled by dual-targeting bispecific antibodies. Mol Ther 25(2):523–533
Dheilly E, Majocchi S, Moine V, Didelot G, Broyer L, Calloud S et al (2018) Tumor-directed blockade of CD47 with bispecific antibodies induces adaptive antitumor immunity. Antibodies (basel) 7(1):3
Durand J, Gauttier V, Morello A, Pengam S, Vanhove B, Poirier N (2018) Abstract 1753: SIRPa inhibition monotherapy leads to dramatic change in solid tumor microenvironment and prevents metastasis development. Cancer Res 78(13 Supplement):1753
Feng M, Jiang W, Kim BYS, Zhang CC, Fu YX, Weissman IL (2019) Phagocytosis checkpoints as new targets for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 19(10):568–586
Fernandes HP, Cesar CL, Barjas-Castro ML (2011) Electrical properties of the red blood cell membrane and immunohematological investigation. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter 33(4):297–301
Freeman SA, Grinstein S (2014) Phagocytosis: receptors, signal integration, and the cytoskeleton. Immunol Rev 262(1):193–215
Gauttier V, Pengam S, Durand J, Morello A, Conchon S, Vanhove B et al (2018) Abstract 1684: Selective SIRPa blockade potentiates dendritic cell antigen cross-presentation and triggers memory T-cell antitumor responses. Cancer Res 78(13 Supplement):1684
Gauttier V, Pengam S, Durand J, Biteau K, Mary C, Morello A et al (2020) Selective SIRPalpha blockade reverses tumor T cell exclusion and overcomes cancer immunotherapy resistance. J Clin Invest 130(11):6109–6123
Ingram JR, Blomberg OS, Sockolosky JT, Ali L, Schmidt FI, Pishesha N et al (2017) Localized CD47 blockade enhances immunotherapy for murine melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(38):10184–10189
Jaiswal S, Jamieson CH, Pang WW, Park CY, Chao MP, Majeti R et al (2009) CD47 is upregulated on circulating hematopoietic stem cells and leukemia cells to avoid phagocytosis. Cell 138(2):271–285
Jinnouchi F, Yamauchi T, Yurino A, Nunomura T, Nakano M, Iwamoto C et al (2020) Establishment of a human SIRPA knock-in xenograft mouse model to study human hematopoietic and cancer stem cells. Blood 135(19):1661–1672
Johnson LDS, Banerjee S, Kruglov O, Viller NN, Horwitz SM, Lesokhin A et al (2019) Targeting CD47 in Sezary syndrome with SIRPalphaFc. Blood Adv 3(7):1145–1153
Katz BZ, Herishanu Y (2014) Therapeutic targeting of CD19 in hematological malignancies: past, present, future and beyond. Leuk Lymphoma 55(5):999–1006
Kauder SE, Kuo TC, Harrabi O, Chen A, Sangalang E, Doyle L et al (2018) ALX148 blocks CD47 and enhances innate and adaptive antitumor immunity with a favorable safety profile. PLoS ONE 13(8):e0201832
Kaur S, Kuznetsova SA, Pendrak ML, Sipes JM, Romeo MJ, Li Z et al (2011) Heparan sulfate modification of the transmembrane receptor CD47 is necessary for inhibition of T cell receptor signaling by thrombospondin-1. J Biol Chem 286(17):14991–15002
Killian ML (2014) Hemagglutination assay for influenza virus. Methods Mol Biol 1161:3–9
Kwong LS, Brown MH, Barclay AN, Hatherley D (2014) Signal-regulatory protein alpha from the NOD mouse binds human CD47 with an exceptionally high affinity—implications for engraftment of human cells. Immunology 143(1):61–67
Lindberg FP, Gresham HD, Schwarz E, Brown EJ (1993) Molecular cloning of integrin-associated protein: an immunoglobulin family member with multiple membrane-spanning domains implicated in alpha v beta 3-dependent ligand binding. J Cell Biol 123(2):485–496
Liu J, Wang L, Zhao F, Tseng S, Narayanan C, Shura L et al (2015) Pre-clinical development of a humanized Anti-CD47 antibody with anti-cancer therapeutic potential. PLoS ONE 10(9):e0137345
Liu B, Guo H, Xu J, Qin T, Guo Q, Gu N et al (2018a) Elimination of tumor by CD47/PD-L1 dual-targeting fusion protein that engages innate and adaptive immune responses. Mabs 10(2):315–324
Liu X, Liu L, Ren Z, Yang K, Xu H, Luan Y et al (2018b) Dual targeting of innate and adaptive checkpoints on tumor cells limits immune evasion. Cell Rep 24(8):2101–2111
Liu Y, Chang Y, He X, Cai Y, Jiang H, Jia R et al (2020) CD47 enhances cell viability and migration ability but inhibits apoptosis in endometrial carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Oncol 10:1525
Logtenberg MEW, Jansen JHM, Raaben M, Toebes M, Franke K, Brandsma AM et al (2019) Glutaminyl cyclase is an enzymatic modifier of the CD47- SIRPalpha axis and a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Med 25(4):612–619
Ma L, Zhu M, Gai J, Li G, Chang Q, Qiao P et al (2020) Preclinical development of a novel CD47 nanobody with less toxicity and enhanced anti-cancer therapeutic potential. J Nanobiotechnology 18(1):12
Mair B, Aldridge PM, Atwal RS, Philpott D, Zhang M, Masud SN et al (2019) High-throughput genome-wide phenotypic screening via immunomagnetic cell sorting. Nat Biomed Eng 3(10):796–805
Majeti R, Chao MP, Alizadeh AA, Pang WW, Jaiswal S, Gibbs KD Jr et al (2009) CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and therapeutic antibody target on human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell 138(2):286–299
Matlung HL, Babes L, Zhao XW, van Houdt M, Treffers LW, van Rees DJ et al (2018) Neutrophils kill antibody-opsonized cancer cells by trogoptosis. Cell Rep 23(13):3946–59 e6
McCracken MN, Cha AC, Weissman IL (2015) Molecular pathways: activating T cells after cancer cell phagocytosis from blockade of CD47 “Don’t Eat Me” signals. Clin Cancer Res 21(16):3597–3601
Meng Z, Wang Z, Guo B, Cao W, Shen H (2019) TJC4, a differentiated anti-CD47 antibody with novel epitope and RBC sparing properties. Blood 134(Supplement_1):4063
Mohammed R, Milne A, Kayani K, Ojha U (2019) How the discovery of rituximab impacted the treatment of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. J Blood Med 10:71–84
Mouro-Chanteloup I, Delaunay J, Gane P, Nicolas V, Johansen M, Brown EJ et al (2003) Evidence that the red cell skeleton protein 4.2 interacts with the Rh membrane complex member CD47. Blood 101(1):338–344
Muramatsu M, Gonzalez HD, Cacciola R, Aikawa A, Yaqoob MM, Puliatti C (2014) ABO incompatible renal transplants: good or bad? World J Transplant 4(1):18–29
Oldenborg PA, Zheleznyak A, Fang YF, Lagenaur CF, Gresham HD, Lindberg FP (2000) Role of CD47 as a marker of self on red blood cells. Science 288(5473):2051–2054
Olsson M, Oldenborg PA (2008) CD47 on experimentally senescent murine RBCs inhibits phagocytosis following Fcgamma receptor-mediated but not scavenger receptor-mediated recognition by macrophages. Blood 112(10):4259–4267
Olsson M, Bruhns P, Frazier WA, Ravetch JV, Oldenborg PA (2005) Platelet homeostasis is regulated by platelet expression of CD47 under normal conditions and in passive immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 105(9):3577–3582
Oronsky B, Cabrales P, Caroen S, Guo X, Scribner C, Oronsky A et al (2021) RRx-001, a downregulator of the CD47- SIRPalpha checkpoint pathway, does not cause anemia or thrombocytopenia. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 17(4):355–357
Petrova PS, Viller NN, Wong M, Pang X, Lin GH, Dodge K et al (2017) TTI-621 (SIRPalphaFc): a CD47-blocking innate immune checkpoint inhibitor with broad antitumor activity and minimal erythrocyte binding. Clin Cancer Res 23(4):1068–1079
Pettersen RD, Hestdal K, Olafsen MK, Lie SO, Lindberg FP (1999) CD47 signals T cell death. J Immunol 162(12):7031–7040
Piccione EC, Juarez S, Liu J, Tseng S, Ryan CE, Narayanan C et al (2015) A bispecific antibody targeting CD47 and CD20 selectively binds and eliminates dual antigen expressing lymphoma cells. Mabs 7(5):946–956
Piccione EC, Juarez S, Tseng S, Liu J, Stafford M, Narayanan C et al (2016) SIRPalpha-antibody fusion proteins selectively bind and eliminate dual antigen-expressing tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res 22(20):5109–5119
Puro RJ, Bouchlaka MN, Hiebsch RR, Capoccia BJ, Donio MJ, Manning PT et al (2020) Development of AO-176, a next-generation humanized anti-CD47 antibody with novel anticancer properties and negligible red blood cell binding. Mol Cancer Ther 19(3):835–846
Ribas A, Wolchok JD (2018) Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 359(6382):1350–1355
Ring NG, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Weiskopf K, Shan L, Volkmer JP, George BM et al (2017) Anti-SIRPalpha antibody immunotherapy enhances neutrophil and macrophage antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(49):E10578–E10585
Rizzo C, Caruso C, Vasto S (2014) Possible role of ABO system in age-related diseases and longevity: a narrative review. Immun Ageing 11:16
Sallman DA, Asch AS, Al Malki MM, Lee DJ, Donnellan WB, Marcucci G et al (2019) The first-in-class anti-CD47 antibody magrolimab (5F9) in combination with azacitidine is effective in MDS and AML patients: ongoing phase 1b results. American Society of Hematology, Washington
Sallman DA, Malki MA, Asch AS, Lee DJ, Kambhampati S, Donnellan WB et al (2020) Tolerability and efficacy of the first-in-class anti-CD47 antibody magrolimab combined with azacitidine in MDS and AML patients: phase Ib results. J Clin Oncol 38(15_suppl):7507
Scheltens P, Hallikainen M, Grimmer T, Duning T, Gouw AA, Teunissen CE et al (2018) Safety, tolerability and efficacy of the glutaminyl cyclase inhibitor PQ912 in Alzheimer’s disease: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2a study. Alzheimers Res Ther 10(1):107
Schwartz AL, Nath PR, Allgauer M, Lessey-Morillon EC, Sipes JM, Ridnour LA et al (2019) Antisense targeting of CD47 enhances human cytotoxic T-cell activity and increases survival of mice bearing B16 melanoma when combined with anti-CTLA4 and tumor irradiation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 68(11):1805–1817
Sharma P, Allison JP (2015) The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 348(6230):56–61
Shi R, Chai Y, Duan X, Bi X, Huang Q, Wang Q et al (2020) The identification of a CD47-blocking “hotspot” and design of a CD47/PD-L1 dual-specific antibody with limited hemagglutination. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:16
Sikic BI, Lakhani N, Patnaik A, Shah SA, Chandana SR, Rasco D et al (2019) First-in-human, first-in-class phase I trial of the anti-CD47 antibody Hu5F9-G4 in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol 37(12):946–953
Sim J, Sockolosky JT, Sangalang E, Izquierdo S, Pedersen D, Harriman W et al (2019) Discovery of high affinity, pan-allelic, and pan-mammalian reactive antibodies against the myeloid checkpoint receptor SIRPalpha. Mabs 11(6):1036–1052
Subramanian S, Tsai R, Sen S, Dahl KN, Discher DE (2006) Membrane mobility and clustering of Integrin Associated Protein (IAP, CD47)–major differences between mouse and man and implications for signaling. Blood Cells Mol Dis 36(3):364–372
Veillette A, Chen J (2018) SIRPalpha-CD47 immune checkpoint blockade in anticancer therapy. Trends Immunol 39(3):173–184
Velliquette RW, Aeschlimann J, Kirkegaard J, Shakarian G, Lomas-Francis C, Westhoff CM (2019) Monoclonal anti-CD47 interference in red cell and platelet testing. Transfusion 59(2):730–737
Voets E, Parade M, Lutje Hulsik D, Spijkers S, Janssen W, Rens J et al (2019) Functional characterization of the selective pan-allele anti-SIRPalpha antibody ADU-1805 that blocks the SIRPalpha-CD47 innate immune checkpoint. J Immunother Cancer 7(1):340
Wang Y, Ni H, Zhou S, He K, Gao Y, Wu W et al (2020a) Tumor-selective blockade of CD47 signaling with a CD47/PD-L1 bispecific antibody for enhanced anti-tumor activity and limited toxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70(2):365–376
Wang H, Sun Y, Zhou X, Chen C, Jiao L, Li W et al (2020b) CD47/SIRPalpha blocking peptide identification and synergistic effect with irradiation for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer 8(2):e000905
Willingham SB, Volkmer JP, Gentles AJ, Sahoo D, Dalerba P, Mitra SS et al (2012) The CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPa) interaction is a therapeutic target for human solid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(17):6662–6667
Wu Z, Weng L, Zhang T, Tian H, Fang L, Teng H et al (2019) Identification of Glutaminyl Cyclase isoenzyme isoQC as a regulator of SIRPalpha-CD47 axis. Cell Res 29(6):502–505
Yanagita T, Murata Y, Tanaka D, Motegi SI, Arai E, Daniwijaya EW et al (2017) Anti-SIRPalpha antibodies as a potential new tool for cancer immunotherapy. JCI Insight 2(1):e89140
Yang Y, Guo R, Chen Q, Liu Y, Zhang P, Zhang Z et al (2018) A novel bispecific antibody fusion protein co-targeting EGFR and CD47 with enhanced therapeutic index. Biotechnol Lett 40(5):789–795
Yu WB, Ye ZH, Chen X, Shi JJ, Lu JJ (2020) The development of small-molecule inhibitors targeting CD47. Drug Discov Today 26(2):561–568
Acknowledgements
We express great thanks to Dr. Le-Le Zhang for the language polishing to our manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by The Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (File no. 0129/2019/A3) and was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81973516).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y-CC and WS wrote the main manuscript text. Y-CC drew the figures. J-JS, Y-CC and WS collected and analyzed the data. J-JL and J-JS provided suggestions and revisions. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the final manuscript for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YC., Shi, W., Shi, JJ. et al. Progress of CD47 immune checkpoint blockade agents in anticancer therapy: a hematotoxic perspective. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 1–14 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03815-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03815-z