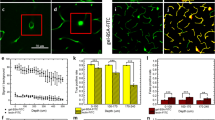
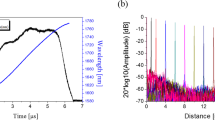
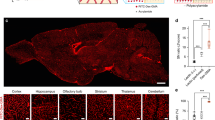
Abstract
Fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography (fMOST) is a three-dimensional (3d) imaging method at the mesoscopic level. The whole-brain of mice can be imaged at a high resolution of 0.32 × 0.32 × 1.00 μm3. It is useful for revealing the fine morphology of intact organ tissue, even for positioning the single vessel connected with a complicated vascular network across different brain regions in the whole mouse brain. Featuring its 3d visualization of whole-brain cross-scale connections, fMOST has a vast potential to decipher brain function and diseases. This article begins with the background of fMOST technology including a widespread 3D imaging methods comparison and the basic technical principal illustration, followed by the application of fMOST in cerebrovascular research and relevant vascular labeling techniques applicable to different scenarios.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Bearer EL, Zhang X, Jacobs RE (2007) Live imaging of neuronal connections by magnetic resonance: robust transport in the hippocampal-septal memory circuit in a mouse model of Down syndrome. Neuroimage 37:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.05.010
Briggman KL, Helmstaedter M, Denk W (2011) Wiring specificity in the direction-selectivity circuit of the retina. Nature 471:183–188. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09818
Di Giovanna AP, Tibo A, Silvestri L, Mullenbroich MC, Costantini I, Allegra Mascaro AL et al (2018) Whole-brain vasculature reconstruction at the single capillary level. Sci Rep 8:12573. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30533-3
Fontaine R, Weltzien FA (2019) Labeling of blood vessels in the teleost brain and pituitary using cardiac perfusion with a DiI-fixative. J vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/59768
Gong H, Zeng S, Yan C, Lv X, Yang Z, Xu T et al (2013) Continuously tracing brain-wide long-distance axonal projections in mice at a one-micron voxel resolution. Neuroimage 74:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.02.005
Gong H, Xu D, Yuan J, Li X, Guo C, Peng J et al (2016) High-throughput dual-colour precision imaging for brain-wide connectome with cytoarchitectonic landmarks at the cellular level. Nat Commun 7:12142. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12142
Huang Q, Chen Y, Liu S, Xu C, Cao T, Xu Y et al (2020) Weakly Supervised Learning of 3D Deep Network for Neuron Reconstruction. Front Neuroanat 14:38. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2020.00038
Ito D, Imai Y, Ohsawa K, Nakajima K, Fukuuchi Y, Kohsaka S (1998) Microglia-specific localisation of a novel calcium binding protein, Iba1. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 57:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-328x(98)00040-0
Jahrling N, Becker K, Dodt HU (2009) 3D-reconstruction of blood vessels by ultramicroscopy. Organogenesis 5:227–230. https://doi.org/10.4161/org.5.4.10403
Ji X, Ferreira T, Friedman B, Liu R, Liechty H, Bas E et al (2021) Brain microvasculature has a common topology with local differences in geometry that match metabolic load. Neuron 109(1168–87):e13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.02.006
Jing D, Zhang S, Luo W, Gao X, Men Y, Ma C et al (2018) Tissue clearing of both hard and soft tissue organs with the PEGASOS method. Cell Res 28:803–818. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0049-z
Kandel ER (2001) The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 294:1030–1038. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1067020
Khouri K, Xie DF, Crouzet C, Bahani AW, Cribbs DH, Fisher MJ et al (2021) Simple methodology to visualize whole-brain microvasculature in three dimensions. Neurophotonics. 8:025004. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.NPh.8.2.025004
Kirst C, Skriabine S, Vieites-Prado A, Topilko T, Bertin P, Gerschenfeld G et al (2020) Mapping the fine-scale organization and plasticity of the brain vasculature. Cell 180(780–95):e25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.01.028
Konno A, Matsumoto N, Tomono Y, Okazaki S (2020) Pathological application of carbocyanine dye-based multicolour imaging of vasculature and associated structures. Sci Rep 10:12613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69394-0
Lacalle-Aurioles M, Mateos-Perez JM, Guzman-De-Villoria JA, Olazaran J, Cruz-Orduna I, Aleman-Gomez Y et al (2014) Cerebral blood flow is an earlier indicator of perfusion abnormalities than cerebral blood volume in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:654–659. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.241
Lee ES, Yoon JH, Choi J, Andika FR, Lee T, Jeong Y (2019) A mouse model of subcortical vascular dementia reflecting degeneration of cerebral white matter and microcirculation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 39:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17736963
Li Y, Song Y, Zhao L, Gaidosh G, Laties AM, Wen R (2008) Direct labeling and visualization of blood vessels with lipophilic carbocyanine dye DiI. Nat Protoc 3:1703–1708. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.172
Li A, Gong H, Zhang B, Wang Q, Yan C, Wu J et al (2010) Micro-optical sectioning tomography to obtain a high-resolution atlas of the mouse brain. Science 330:1404–1408. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1191776
Liu L, Shi GP (2012) CD31: beyond a marker for endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 94:3–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvs108
Micheva KD, Smith SJ (2007) Array tomography: a new tool for imaging the molecular architecture and ultrastructure of neural circuits. Neuron 55:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.014
Miyawaki T, Morikawa S, Susaki EA, Nakashima A, Takeuchi H, Yamaguchi S et al (2020) Visualization and molecular characterization of whole-brain vascular networks with capillary resolution. Nat Commun 11:1104. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14786-z
Motoike T, Loughna S, Perens E, Roman BL, Liao W, Chau TC et al (2000) Universal GFP reporter for the study of vascular development. Genesis 28:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1002/1526-968x(200010)28:2%3c75::aid-gene50%3e3.0.co;2-s
Mustapha M, Nassir C, Aminuddin N, Safri AA, Ghazali MM (2019) Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD)—lessons from the animal models. Front Physiol 10:1317. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01317
Pan C, Liu N, Zhang P, Wu Q, Deng H, Xu F et al (2018) EGb761 ameliorates neuronal apoptosis and promotes angiogenesis in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage via RSK1/GSK3beta pathway. Mol Neurobiol 55:1556–1567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0363-8
Pantoni L (2010) Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 9:689–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70104-6
Patel AS, Smith A, Nucera S, Biziato D, Saha P, Attia RQ et al (2013) TIE2-expressing monocytes/macrophages regulate revascularization of the ischemic limb. EMBO Mol Med 5:858–869. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201302752
Qi Y, Yu T, Xu J, Wan P, Ma Y, Zhu J et al (2019) FDISCO: advanced solvent-based clearing method for imaging whole organs. Sci Adv 5:eaau8355. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aau8355
Robertson RT, Levine ST, Haynes SM, Gutierrez P, Baratta JL, Tan Z et al (2015) Use of labeled tomato lectin for imaging vasculature structures. Histochem Cell Biol 143:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1301-3
Salehi A, Jullienne A, Wendel KM, Hamer M, Tang J, Zhang JH et al (2018) A novel technique for visualizing and analyzing the cerebral vasculature in rodents. Transl Stroke Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-018-0632-0
Santosa SM, Guo K, Yamakawa M, Ivakhnitskaia E, Chawla N, Nguyen T et al (2020) Simultaneous fluorescence imaging of distinct nerve and blood vessel patterns in dual Thy1-YFP and Flt1-DsRed transgenic mice. Angiogenesis 23:459–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-020-09724-y
Sun Q, Li X, Ren M, Zhao M, Zhong Q, Ren Y et al (2019) A whole-brain map of long-range inputs to GABAergic interneurons in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci 22:1357–1370. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0429-9
Tang J, Zhu H, Tian X, Wang H, Liu S, Liu K et al (2022) Extension of endocardium-derived vessels generate coronary arteries in neonates. Circ Res 130:352–365. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.320335
Taranda J, Turcan S (2021) 3D whole-brain imaging approaches to study brain Tumors. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081897
Todorov MI, Paetzold JC, Schoppe O, Tetteh G, Shit S, Efremov V et al (2020) Machine learning analysis of whole mouse brain vasculature. Nat Methods 17:442–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-0792-1
Tsai PS, Kaufhold JP, Blinder P, Friedman B, Drew PJ, Karten HJ et al (2009) Correlations of neuronal and microvascular densities in murine cortex revealed by direct counting and colocalization of nuclei and vessels. J Neurosci 29:14553–14570. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3287-09.2009
Vidal M, Morris R, Grosveld F, Spanopoulou E (1990) Tissue-specific control elements of the Thy-1 gene. EMBO J 9:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08180.x
Wang X, Xiong H, Liu Y, Yang T, Li A, Huang F et al (2021a) Chemical sectioning fluorescence tomography: high-throughput, high-contrast, multicolor, whole-brain imaging at subcellular resolution. Cell Rep 34:108709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108709
Wang J, Li Y, Yu H, Li G, Bai S, Chen S et al (2021b) Dl-3-N-Butylphthalide promotes angiogenesis in an optimized model of transient ischemic attack in C57BL/6 mice. Front Pharmacol 12:751397. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.751397
Wu Y, Ke J, Ye S, Shan LL, Xu S, Guo SF et al (2023) 3D visualization of whole brain vessels and quantification of vascular pathology in a chronic hypoperfusion model causing white matter damage. Transl Stroke Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-023-01157-1
Wu YT, Bennett HC, Chon U, Vanselow DJ, Zhang Q, Munoz-Castaneda R et al (2022) Quantitative relationship between cerebrovascular network and neuronal cell types in mice. Cell Rep 39:110978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110978
Xiong B, Li A, Lou Y, Chen S, Long B, Peng J et al (2017) Precise cerebral vascular atlas in stereotaxic coordinates of whole mouse brain. Front Neuroanat 11:128. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2017.00128
Yang B, Lange M, Millett-Sikking A, Zhao X, Bragantini J, VijayKumar S et al (2022a) DaXi-high-resolution, large imaging volume and multi-view single-objective light-sheet microscopy. Nat Methods 19:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01417-2
Yang AC, Vest RT, Kern F, Lee DP, Agam M, Maat CA et al (2022b) A human brain vascular atlas reveals diverse mediators of Alzheimer’s risk. Nature 603:885–892. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04369-3
Yuan J, Gong H, Li A, Li X, Chen S, Zeng S et al (2015) Visible rodent brain-wide networks at single-neuron resolution. Front Neuroanat 9:70. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00070
Zhang X, Yin X, Zhang J, Li A, Gong H, Luo Q et al (2019) High-resolution mapping of brain vasculature and its impairment in the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease mice. Natl Sci Rev 6:1223–1238. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz124
Zhang B, Qiu L, Xiao W, Ni H, Chen L, Wang F et al (2021) Reconstruction of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system and functional dissection of magnocellular oxytocin neurons in the brain. Neuron 109:331–46 e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.10.032
Zheng T, Yang Z, Li A, Lv X, Zhou Z, Wang X et al (2013) Visualization of brain circuits using two-photon fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography. Opt Express 21:9839–9850. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.21.009839
Zhong W, Gao X, Wang S, Han K, Ema M, Adams S et al (2017) Prox1-GFP/Flt1-DsRed transgenic mice: an animal model for simultaneous live imaging of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Angiogenesis 20:581–598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9572-7
Zhong Q, Li A, Jin R, Zhang D, Li X, Jia X et al (2021) High-definition imaging using line-illumination modulation microscopy. Nat Methods 18:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01074-x
Zhou C, Yang X, Wu S, Zhong Q, Luo T, Li A et al (2022) Continuous subcellular resolution three-dimensional imaging on intact macaque brain. Sci Bull (beijing) 67:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.08.003
Zhu J, Yu T, Li Y, Xu J, Qi Y, Yao Y et al (2020) MACS: rapid aqueous clearing system for 3d mapping of intact organs. Adv Sci (weinh) 7:1903185. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201903185
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Han and Dr. Liu for their help with the guidance in this paper. The authors thank Mr. Yang of the Institute of Science and Technology for Brain-Inspired Intelligence of Fudan University for helpful discussions on topics related to this work. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFC1711603) and the Clinical Research Plan of SHDC (no. SHDC2020CR2046B). Thank people all over the world for their efforts to combat the epidemic.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFC1711603) and the Clinical Research Plan of SHDC (no. SHDC2020CR2046B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW and ZY wrote the main manuscript text and ML and YH revised the manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors have agreed on this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Yang, Z., Liu, M. et al. Application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the cerebrovasculature and applicable vascular labeling methods. Brain Struct Funct 228, 1619–1627 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02684-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-023-02684-1