Abstract
Main conclusion
We analyzed the synthetic full-length transcript promoter of Blueberry red ringspot virus (BRRV) and developed two chimeric promoters (MBR3 and FBR3). Transcriptional activities of these chimeric promoters were found equivalent to that of the CaMV35S2 promoter. Chimeric promoters driven plant-derived PaDef protein showed high antimicrobial activities against several pathogens.
Abstract
Blueberry red ringspot virus (BRRV) is a pararetrovirus under the genus, Soymovirus belongs to the Caulimoviridae family. We have made a synthetic version of the BRRV-Flt promoter and analyzed its activity in detail. A 372 bp promoter fragment BR3 (− 212 to + 160) showed the strongest transcriptional activity compared with other fragments in both transient and transgenic assays; its activity was found near equivalent to that of the CaMV35S promoter. We constructed two chimeric promoters; MBR3 and FBR3 by fusing the UASs (Upstream activation sequences) of Mirabilis mosaic virus (MUAS; − 297 to − 38; 335 bp) and Figwort mosaic virus (FUAS; − 249 to − 54; 303 bp) respectively to the core promoter domain of BR3 (BR3; − 212 to + 160; 372 bp). The activities of MBR3 and FBR3 promoters were found equivalent to that of the activity of the CaMV35S2 promoter and approximately 4.0 (four) times stronger than that of the CaMV35S promoter. Histochemical and fluorometric GUS assays confirmed the above observation. The transcriptional efficacies of these recombinant promoters were tested by evaluating the antibacterial and antifungal activities of recombinant plant-derived antimicrobial peptide Persea americana var. drymifolia defensin (PaDef) driven under these promoters. Bioassays showed promising antifungal activities of the plant made PaDef against Alternaria alternata and antibacterial property against Gram-positive (S. aureus and R. fascians) and Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli and P. aeruginosa). Based upon the above results, MBR3 and FBR3 could be useful promoters for plant genetic engineering and can become useful substitutes for the widely used CaMV35S2 promoter in plant biology.




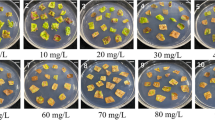
taken from transgenic flowers, (d) 3 week-old whole transgenic tobacco seedlings, (e) Root tips of above-mentioned promoters. f Transient GFP expression analysis of BR3, MBR3, FBR3 promoter along with CaMV35S(35S) and CaMV35S2(35S2) promoters by agro-infiltration of tobacco leaves and pictures taken under a UV. g Transient GFP expression analysis of above promoters measured using ImageJ software in agro-infiltrated N. tabacum Samsun NN leaves, presented with respective standard deviation and statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001)


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BRRV:
-
Blueberry red ringspot virus
- CP:
-
Core promoter
- UAS:
-
Upstream activation sequence
- MMV:
-
Mirabilis mosaic virus
- FMV:
-
Figwort mosaic virus
- MBR3:
-
Chimeric promoter developed by fusing MMV (−297 to −38) and BRRV (−212 to + 160)
- FBR3:
-
Chimeric promoter developed by fusing FMV (−249 to −54) and BRRV (−212 to + 160)
- KanR :
-
Kanamycin resistant
- KanS :
-
Kanamycin susceptible
- X-gluc:
-
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl β-d-glucopyranosiduronic acid
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- AMP:
-
Antimicrobial peptide
- PaDef:
-
Persea americana Var. drymifolia defensin
References
Acharya S, Ranjan R, Pattanaik S, Maiti IB, Dey N (2014) Efficient chimeric plant promoters derived from plant infecting viral promoter sequences. Planta 239(2):381–396
Bhattacharyya S, Dey N, Maiti IB (2002) Analysis of cis-sequence of subgenomic transcript promoter from the Figwort mosaic virus and comparison of promoter activity with the cauliflower mosaic virus promoters in monocot and dicot cells. Virus Res 90(1–2):47–62
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Chatterjee A, Das NC, Raha S, Maiti IB, Shrestha A, Khan A, Acharya S, Dey N (2017) Enrichment of apoplastic fluid with therapeutic recombinant protein for efficient biofarming. Biotechnol Prog 33(3):726–736
Chen H, Nelson R, Sherwood J (1994) Enhanced recovery of transformants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens after freeze-thaw transformation and drug selection. Biotechniques 16(4):664–668
Deb D, Dey N (2019) Synthetic salicylic acid inducible recombinant promoter for translational research. J Biotechnol 297:9–18
Deb D, Shrestha A, Maiti IB, Dey N (2018) Recombinant promoter (MUASCsV8CP) driven totiviral killer protein 4 (KP4) imparts resistance against fungal pathogens in transgenic tobacco. Front Plant Sci 9:278
Deb D, Khan A, Dey N (2020) Phoma diseases: epidemiology and control. Plant Pathol 69(7):1203–1217
Dey N, Maiti IB (1999) Structure and promoter/leader deletion analysis of mirabilis mosaic virus (MMV) full-length transcript promoter in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 40(5):771–782
Dey N, Sarkar S, Acharya S, Maiti IB (2015) Synthetic promoters in planta. Planta 242(5):1077–1094
Gao A-G, Hakimi SM, Mittanck CA, Wu Y, Woerner BM, Stark DM, Shah DM, Liang J, Rommens CM (2000) Fungal pathogen protection in potato by expression of a plant defensin peptide. Nat Biotechnol 18(12):1307–1310
Gardiner-Garden M, Frommer M (1987) CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol 196(2):261–282
Glasheen B, Polashock J, Lawrence D, Gillett J, Ramsdell D, Vorsa N, Hillman B (2002) Cloning, sequencing, and promoter identification of Blueberry red ringspot virus, a member of the family Caulimoviridae with similarities to the “Soybean chlorotic mottle-like” genus. Adv Virol 147(11):2169–2186
Guzmán-Rodríguez JJ, López-Gómez R, Suárez-Rodríguez LM, Salgado-Garciglia R, Rodríguez-Zapata LC, Ochoa-Zarzosa A, López-Meza JE (2013) Antibacterial activity of defensin PaDef from avocado fruit (Persea americana var. drymifolia) expressed in endothelial cells against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. BioMed Res Internat 2013:10–34
Guzmán-Rodríguez JJ, López-Gómez R, Salgado-Garciglia R, Ochoa-Zarzosa A, López-Meza JE (2016) The defensin from avocado (Persea americana var. drymifolia) PaDef induces apoptosis in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Biomed Pharmacother 82:620–627
Jauvion V, Rivard M, Bouteiller N, Elmayan T, Vaucheret H (2012) RDR2 partially antagonizes the production of RDR6-dependent siRNA in sense transgene-mediated PTGS. PLoS ONE 7(1):e29785
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6(13):3901–3907
Karjee S, Islam MN, Mukherjee SK (2008) Screening and identification of virus-encoded RNA silencing suppressors. RNAi. Springer, London, pp 187–203
Kim E, Lee HM, Kim YH (2017) Morphogenetic alterations of Alternaria alternata exposed to dicarboximide fungicide, iprodione. Plant Pathol J 33(1):95
Köhl J, Kolnaar R, Ravensberg WJ (2019) Mode of action of microbial biological control agents against plant diseases: relevance beyond efficacy. Front Plant Sci 10:845
Kroumova AB, Sahoo DK, Raha S, Goodin M, Maiti IB, Wagner GJ (2013) Expression of an apoplast-directed, T-phylloplanin-GFP fusion gene confers resistance against Peronospora tabacina disease in a susceptible tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 32(11):1771–1782
Kumar D, Patro S, Ranjan R, Sahoo DK, Maiti IB, Dey N (2011) Development of useful recombinant promoter and its expression analysis in different plant cells using confocal laser scanning microscopy. PLoS ONE 6(9):e24627
Kumar D, Patro S, Ghosh J, Das A, Maiti IB, Dey N (2012) Development of a salicylic acid inducible minimal sub-genomic transcript promoter from Figwort mosaic virus with enhanced root-and leaf-activity using TGACG motif rearrangement. Gene 503(1):36–47
Lefkowitz EJ, Dempsey DM, Hendrickson RC, Orton RJ, Siddell SG, Smith DB (2018) Virus taxonomy: the database of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D708–D717
Li L-C, Dahiya R (2002) MethPrimer: designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 18(11):1427–1431
Maiti IB, Shepherd RJ (1998) Isolation and expression analysis of peanut chlorotic streak caulimovirus (PClSV) full-length transcript (FLt) promoter in transgenic plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 244(2):440–444
Maiti IB, Gowda S, Kiernan J, Ghosh SK, Shepherd RJ (1997) Promoter/leader deletion analysis and plant expression vectors with the figwort mosaic virus (FMV) full length transcript (FLt) promoter containing single or double enhancer domains. Transgenic Res 6(2):143–156
Maiti S, Patro S, Purohit S, Jain S, Senapati S, Dey N (2014) Effective control of Salmonella infections by employing combinations of recombinant antimicrobial human β-defensins hBD-1 and hBD-2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(11):6896–6903
Martins PM, Merfa MV, Takita MA, De Souza AA (2018) Persistence in phytopathogenic bacteria: do we know enough? Front Microbiol 9:1099
Matzke M, Kanno T, Huettel B, Daxinger L, Matzke A (2006) RNA-directed DNA methylation and Pol IVb in ArabidopsisCold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Meng D-M, Dai H-X, Gao X-F, Zhao J-F, Guo Y-J, Ling X, Dong B, Zhang Z-Q, Fan Z-C (2016) Expression, purification and initial characterization of a novel recombinant antimicrobial peptide Mytichitin-A in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 127:35–43
Meng D-M, Zhao J-F, Ling X, Dai H-X, Guo Y-J, Gao X-F, Dong B, Zhang Z-Q, Meng X, Fan Z-C (2017) Recombinant expression, purification and antimicrobial activity of a novel antimicrobial peptide PaDef in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 130:90–99
Odell JT, Dudley RK, Howell SH (1981) Structure of the 19 S RNA transcript encoded by the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Virology 111(2):377–385
Patro S, Maiti S, Panda SK, Dey N (2015) Utilization of plant-derived recombinant human β-defensins (hBD-1 and hBD-2) for averting salmonellosis. Transgenic Res 24(2):353–364
Pattanaik S, Dey N, Bhattacharyya S, Maiti IB (2004) Isolation of full-length transcript promoter from the Strawberry vein banding virus (SVBV) and expression analysis by protoplasts transient assays and in transgenic plants. Plant Sci 167(3):427–438
Petrzik K, Pribylova J, Pleško IM, Spak J (2011) Complete genome sequences of blueberry red ringspot virus (Caulimoviridae) isolates from the Czech Republic and Slovenia. Arch Virol 156(10):1901
Polashock JJ, Ehlenfeldt MK, Crouch JA (2009) Molecular detection and discrimination of Blueberry red ringspot virus strains causing disease in cultivated blueberry and cranberry. Plant Dis 93(7):727–733
Rajeev Kumar S, Anunanthini P, Ramalingam S (2015) Epigenetic silencing in transgenic plants. Front Plant Sci 6:693
Ranjan R, Patro S, Kumari S, Kumar D, Dey N, Maiti IB (2011) Efficient chimeric promoters derived from full-length and sub-genomic transcript promoters of Figwort mosaic virus (FMV). J Biotechnol 152(1–2):58–62
Saad N, Alcalá-Briseño R, Polston J, Olmstead J, Varsani A, Harmon P (2020) Blueberry red ringspot virus genomes from Florida inferred through analysis of blueberry root transcriptomes. Sci Rep 10(1):1–10
Sahoo DK, Sarkar S, Raha S, Das NC, Banerjee J, Dey N, Maiti IB (2015) Analysis of dahlia mosaic virus full-length transcript promoter-driven gene expression in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol Report 33(2):178–199
Sarkar S, Jain S, Rai V, Sahoo DK, Raha S, Suklabaidya S, Senapati S, Rangnekar VM, Maiti IB, Dey N (2015) Plant-derived SAC domain of PAR-4 (prostate apoptosis response 4) exhibits growth inhibitory effects in prostate cancer cells. Front Plant Sci 6:822
Sathoff AE, Lewenza S, Samac DA (2020) Plant defensin antibacterial mode of action against Pseudomonas species. BMC Microbiol 20(1):1–11
Schardl CL, Byrd AD, Benzion G, Altschuler MA, Hildebrand DF, Hunt AG (1987) Design and construction of a versatile system for the expression of foreign genes in plants. Gene 61(1):1–11
Sharma P, Deep S, Sharma M, Bhati DS (2013) Genetic variation of Alternaria brassicae (Berk) Sacc causal agent of dark leaf spot of cauliflower and mustard in India. J General Plant Pathol 79(1):41–45
Song G-q, Yamaguchi K-i (2003) Efficient agroinfiltration-mediated transient GUS expression system for assaying different promoters in rice. Plant Biotechnol 20(3):235–239
Tsuchiya T, Eulgem T (2013) Mutations in EDM2 selectively affect silencing states of transposons and induce plant developmental plasticity. Sci Rep 3(1):1–9
Van der Weerden NL, Anderson MA (2013) Plant defensins: common fold, multiple functions. Fungal Biol Rev 26(4):121–131
Velásquez AC, Castroverde CDM, He SY (2018) Plant–pathogen warfare under changing climate conditions. Curr Biol 28(10):R619–R634
Verdaguer B, de Kochko A, Beachy RN, Fauquet C (1996) Isolation and expression in transgenic tobacco and rice plants, of the cassava vein mosaic virus (CVMV) promoter. Plant Mol Biol 31(6):1129–1139
Acknowledgment
We are greatly thankful to Dr. Indu B. Maiti, KTRDC, University of Kentucky, for providing the genetic materials for this research. We sincerely thank the Director, Institute of Life Sciences, for his interest and support in this study. We are sincerely thankful to Dr. Noohi Nasim and Dr. I. Sriram Sandeep for their kind technical help and support. We also thank Mr. Abhimanyu Das for his technical assistance and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Anastasios Melis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, L., Deb, D., Khadanga, B. et al. Synthetic promoters from blueberry red ringspot virus (BRRV). Planta 253, 121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03624-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03624-1