Abstract
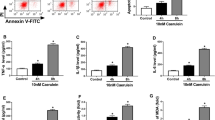
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common clinical critical disease with high mortality and the exact pathogenesis is not fully elucidated. The present study aimed to uncover the function of miR-135a in the proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammatory characteristics of diseased pancreatic cells and the potential molecular mechanisms. The expression patterns of miR-135a and family with sequence similarity 129 member A (FAM129A) in patients with AP were analyzed on the basis of the GEO database. The transfection efficiency and expression level of miR-135a in AR42J cells were determined by qRT-PCR. The biological characteristics of AR42J cells treated with cerulein were detected by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), flow cytometry, and western blot assays. The potential interaction between miR-135a and FAM129A was confirmed by bioinformatics prediction softwares and luciferase reporter assay. MiR-135a inhibitor and pcDNA3.1-FAM129A were co-transfected to determine the regulation of miR-135a/FAM129A on inflammatory AR42J cell injury. We observed that miR-135a was highly expressed in AP samples. Depletion of miR-135a could alleviate the condition so that the AR42J cells proliferation increased, apoptosis decreased, and the expression of inflammatory cytokines enhanced. In addition, mRNA and protein expression of FAM129A were negatively regulated by miR-135a, and over-expression of FAM129A could strengthen the relief effect of miR-135a inhibitor in AP induced by cerulein. In summary, our data demonstrates that silencing miR-135a reduces AR42J cells injury and inflammatory response in AP induced by cerulein through targeting FAM129A.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi H, Majima S, Kon S, Kobayashi T, Kajino K, Mitani H, Hirayama Y, Shiina H, Igawa M, Hino O (2004) Niban gene is commonly expressed in the renal tumors: a new candidate marker for renal carcinogenesis. Oncogene 23:3495–3500. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207468
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Schapira AH, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Obeso JA, Cooper JM (2013) Influence of microRNA deregulation on chaperone-mediated autophagy and alpha-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis 4:e545. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.73
Baulina NM, Kulakova OG, Favorova OO (2016) MicroRNAs: the role in autoimmune inflammation. Acta Nat 8:21–33
Berger P, Mollema R, Girbes AR, van Dullemen H, Bosscha K, Gooszen HG, Ploeg RJ (2001) Acute pancreatitis--a protocol for diagnosis and treatment. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 145:1970–1975
Bhatia M, Wong FL, Cao Y, Lau HY, Huang J, Puneet P, Chevali L (2005) Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 5:132–144. https://doi.org/10.1159/000085265
Carvalheira G, Nozima BH, Cerutti JM (2015) microRNA-106b-mediated down-regulation of C1orf24 expression induces apoptosis and suppresses invasion of thyroid cancer. Oncotarget 6:28357–28370. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4947
Cerutti JM, Delcelo R, Amadei MJ, Nakabashi C, Maciel RM, Peterson B, Shoemaker J, Riggins GJ (2004) A preoperative diagnostic test that distinguishes benign from malignant thyroid carcinoma based on gene expression. J Clin Invest 113:1234–1242. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci19617
Dang Z, Xu WH, Lu P, Wu N, Liu J, Ruan B, Zhou L, Song WJ, Dou KF (2014) MicroRNA-135a inhibits cell proliferation by targeting Bmi1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Biol Sci 10:733–745. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.8097
Frossard JL, Hadengue A, Pastor CM (2001) New serum markers for the detection of severe acute pancreatitis in humans. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.164.1.2008026
Fu Q, Qin T, Chen L, Liu CJ, Zhang X, Wang YZ, Hu MX, Chu HY, Zhang HW (2016) miR-29a up-regulation in AR42J cells contributes to apoptosis via targeting TNFRSF1A gene. World J Gastroenterol 22:4881–4890. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4881
Gukovskaya AS, Perkins P, Zaninovic V, Sandoval D, Rutherford R, Fitzsimmons T, Pandol SJ, Poucell-Hatton S (1996) Mechanisms of cell death after pancreatic duct obstruction in the opossum and the rat. Gastroenterology 110:875–884. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8608898
Hu MX, Zhang HW, Fu Q, Qin T, Liu CJ, Wang YZ, Tang Q, Chen YX (2016) Functional role of microRNA-19b in acinar cell necrosis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. 36:221–225
Ito S, Fujii H, Matsumoto T, Abe M, Ikeda K, Hino O (2010) Frequent expression of Niban in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and squamous dysplasia. Head Neck 32:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.21153
Jiang X (2014) Different signal pathways regulate IL-1beta-induced mature and primary miRNA-146a expression in human alveolar epithelial cells. Acta Physiol Hung 101:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1556/APhysiol.101.2014.3.3
Kaiser AM, Saluja AK, Sengupta A, Saluja M, Steer ML (1995) Relationship between severity, necrosis, and apoptosis in five models of experimental acute pancreatitis. Am J Phys 269:C1295–C1304. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.5.C1295
Kannangai R, Diehl AM, Sicklick J, Rojkind M, Thomas D, Torbenson M (2005) Hepatic angiomyolipoma and hepatic stellate cells share a similar gene expression profile. Hum Pathol 36:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2005.01.002
Kinney TP, Freeman ML (2008) Approach to acute, recurrent, and chronic pancreatitis. Minn Med 91:29–33
Lankisch PG, Apte M, and Banks PA (2015) Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 386:85-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60649-8
Li X, Lin Z, Wang L, Liu Q, Cao Z, Huang Z, Zhong M, Peng S, Zhang Y, Li Y, Ma X (2018) RNA-Seq Analyses of the role of miR-21 in acute pancreatitis. Cell Physiol Biochem 51:2198–2211. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495866
Lippai D, Bala S, Catalano D, Kodys K, Szabo G (2014) Micro-RNA-155 deficiency prevents alcohol-induced serum endotoxin increase and small bowel inflammation in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38:2217–2224. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12483
Liu J, Qin J, Mei W, Zhang H, Yuan Q, Peng Z, Luo R, Yuan X, Huang L, Tao L (2014) Expression of Niban in renal interstitial fibrosis. Nephrology (Carlton) 19:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.12266
Liu S, Zou H, Wang Y, Duan X, Chen C, Cheng W, Wang L, Ning N, Tang H, Chen M, Mao X, Peng C, Li H, Jiang Y, Jiang B (2018) miR-155-5p is negatively associated with acute pancreatitis and inversely regulates pancreatic acinar cell progression by targeting Rela and Traf3. Cell Physiol Biochem 51:1584–1599. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495648
Majima S, Kajino K, Fukuda T, Otsuka F, Hino O (2000) A novel gene “Niban” upregulated in renal carcinogenesis: cloning by the cDNA-amplified fragment length polymorphism approach. Jpn J Cancer Res 91:869–874
Mareninova OA, Sendler M, Malla SR, Yakubov I, French SW, Tokhtaeva E, Vagin O, Oorschot V, Lullmann-Rauch R, Blanz J, Dawson D, Klumperman J, Lerch MM, Mayerle J, Gukovsky I, Gukovskaya AS (2015) Lysosome associated membrane proteins maintain pancreatic acinar cell homeostasis: LAMP-2 deficient mice develop pancreatitis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:678–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.07.006
Matsumoto F, Fujii H, Abe M, Kajino K, Kobayashi T, Matsumoto T, Ikeda K, Hino O (2006) A novel tumor marker, Niban, is expressed in subsets of thyroid tumors and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Hum Pathol 37:1592–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2006.06.022
Nagaraj S, Zoltowska KM, Laskowska-Kaszub K, Wojda U (2019) microRNA diagnostic panel for Alzheimer's disease and epigenetic trade-off between neurodegeneration and cancer. Ageing Res Rev 49:125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2018.10.008
Qin T, Fu Q, Pan YF, Liu CJ, Wang YZ, Hu MX, Tang Q, Zhang HW (2014) Expressions of miR-22 and miR-135a in acute pancreatitis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 34:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1263-7
Saunders LR, Sharma AD, Tawney J, Nakagawa M, Okita K, Yamanaka S, Willenbring H, Verdin E (2010) miRNAs regulate SIRT1 expression during mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation and in adult mouse tissues. Aging (Albany NY) 2:415–431. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100176
Shi H, Ji Y, Zhang D, Liu Y, Fang P (2015) MiR-135a inhibits migration and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting KLF8 in lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 465:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.145
Sun Y, Qin Z, Li Q, Wan JJ, Cheng MH, Wang PY, Su DF, Yu JG, Liu X (2016) MicroRNA-124 negatively regulates LPS-induced TNF-alpha production in mouse macrophages by decreasing protein stability. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:889–897. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.16
Teichenne J, Morro M, Casellas A, Jimenez V, Tellez N, Leger A, Bosch F, Ayuso E (2015) Identification of miRNAs involved in reprogramming acinar cells into insulin producing cells. PLoS One 10:e0145116. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145116
Vonlaufen A, Wilson JS, Apte MV (2008) Molecular mechanisms of pancreatitis: current opinion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:1339–1348. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05520.x
Yuki R, Aoyama K, Kubota S, Yamaguchi N, Kubota S, Hasegawa H, Morii M, Huang X, Liu K, Williams R, Fukuda MN, Yamaguchi N (2015) Overexpression of zinc-finger protein 777 (ZNF777) inhibits proliferation at low cell density through down-regulation of FAM129A. J Cell Biochem 116:954–968. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25046
Zhang T, Shao Y, Chu TY, Huang HS, Liou YL, Li Q, Zhou H (2016) MiR-135a and MRP1 play pivotal roles in the selective lethality of phenethyl isothiocyanate to malignant glioma cells. Am J Cancer Res 6:957–972
Zhang XX, Deng LH, Chen WW, Shi N, Jin T, Lin ZQ, Ma Y, Jiang K, Yang XN, Xia Q (2017) Circulating microRNA 216 as a marker for the early identification of severe acute pancreatitis. Am J Med Sci 353:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjms.2016.12.007
Zhao J, Li X, Zou M, He J, Han Y, Wu D, Yang H, Wu J (2014) miR-135a inhibition protects A549 cells from LPS-induced apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 452:951–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.09.025
Zhou W, Bi X, Gao G, Sun L (2016) miRNA-133b and miRNA-135a induce apoptosis via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in human renal carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 84:722–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.074
Zhou W, Li X, Liu F, Xiao Z, He M, Shen S, Liu S (2012) MiR-135a promotes growth and invasion of colorectal cancer via metastasis suppressor 1 in vitro. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai 44:838–846. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gms071
Zhu HJ, Wang DG, Yan J, Xu J (2015) Up-regulation of microRNA-135a protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by decreasing TXNIP expression in diabetic mice. Am J Transl Res 7:2661–2671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, KK., Yu, SS., Li, GY. et al. miR-135a deficiency inhibits the AR42J cells damage in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis through targeting FAM129A. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 471, 1519–1527 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-019-02329-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-019-02329-5