Abstract
Purpose
A preoperative estimate of the risk of malignancy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) is important. The present study carries out an external validation of the Shin score in a European multicenter cohort.
Methods
An observational multicenter European study from 2010 to 2015. All consecutive patients undergoing surgery for IPMN at 35 hospitals with histological-confirmed IPMN were included.
Results
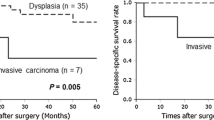
A total of 567 patients were included. The score was significantly associated with the presence of malignancy (p < 0.001). In all, 64% of the patients with benign IPMN had a Shin score < 3 and 57% of those with a diagnosis of malignancy had a score ≥ 3. The relative risk (RR) with a Shin score of 3 was 1.37 (95% CI: 1.07–1.77), with a sensitivity of 57.1% and specificity of 64.4%.
Conclusion
Patients with a Shin score ≤ 1 should undergo surveillance, while patients with a score ≥ 4 should undergo surgery. Treatment of patients with Shin scores of 2 or 3 should be individualized because these scores cannot accurately predict malignancy of IPMNs. This score should not be the only criterion and should be applied in accordance with agreed clinical guidelines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roth S, Bose P, Alhamdani MSS, Mustafa SA, Tjaden C, Zamzow K et al (2020) Noninvasive discrimination of low and high-risk pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Ann Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004066
Attiyeh MA, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Al Efishat MA, Eaton A, Gönen M, Batts R et al (2018) Development and validation of a multi-institutional preoperative nomogram for predicting grade of dysplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas: a report from the Pancreatic Surgery Consortium. Ann Surg 1:157–163
Tanaka M, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Kamisawa T, Jang JY, Levy P, Ohtsuka T et al (2017) Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 17:738–753
Correa-Gallego C, Do R, Lafemina J, Gönen M, D’Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP et al (2013) Predicting dysplasia and invasivecarcinoma in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: development of a preoperative nomogram. Ann Surg Oncol 20:4348–4355
Tanaka M, Fernández-del Castillo C, Adsay V, Chari S, Falconi M, Jang JY et al (2012) International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 12:183–197
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernández-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M et al (2006) International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 6:17–32
Xu B, Ding WX, Jin DY, Wang DS, Lou WH (2013) Decision making for pancreatic resection in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 7 19(9):1451–7. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i9.1451
Berland L, Silverman SG, Gore R, Mayo-Smith WW, Megibow AJ, Yee J et al (2010) Managing incidental findings on abdominal CT: white paper of the ACR incidental findings committee. J Am Coll Radiol 7:754–773
Vege SS, Ziring B, Jain R, Moayyedi P (2015) American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 148:819–822
Shin SH, Han DJ, Park KT, Kim YH, Park JB, Lim C (2010) Validating a simple scoring system to predict malignancy and invasiveness of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. World J Surg 34:776–783
Keshishian J, Ambuji K, Athanasios T, Mokenge M, Shivakumar V (2017) Evaluating utility of scoring system to predict malignancy and invasiveness of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas at a single center. J Gastroenterol Hepatol Endoscop 2(6):1–4
Robles EP, Maire F, Cros J, Vullierme MP, Rebours V, Sauvanet A et al (2016) Accuracy of 2012 International Consensus Guidelines for the prediction of malignancy of branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. United European Gastroent J 4:580–586
Dortch JD, Stauffer JA, Asbun HJ (2015) Pancreatic resection for side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (SB-IPMN): a contemporary single-institution experience. J Gastrointest Surg 19:1603–1609
Nguyen AH, Toste PA, Farrell JJ, Clerkin BM, Williams J, Muthusamy VR et al (2015) Current recommendations for surveillance and surgery of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms may overlook some patients with cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 19:258–265
Fritz S, Klauss M, Bergmann F, Strobel O, Schneider L, Werner J et al (2014) Pancreatic main-duct involvement in branch-duct IPMNs: an underestimated risk. Ann Surg 260:848–855
Aso T, Ohtsuka T, Matsunaga T, Kimura H, Watanabe Y, Tamura K et al (2014) “High-risk stigmata” of the 2012 international consensus guidelines correlate with the malignant grade of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreas 43:1239–1243
Roch AM, Ceppa EP, DeWitt JM, Al-Haddad MA, House MG, Nakeeb A et al (2014) International Consensus Guidelines parameters for the prediction of malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm are not properly weighted and are not cumulative. HPB 16:929–935
Goh BK, Thng CH, Tan DM, Low ASC, Wong JS, Cheow PC et al (2014) Evaluation of the Sendai and 2012 International Consensus Guidelines based on cross-sectional imaging findings performed for the initial triage of mucinous cystic lesions of the pancreas: a single institution experience with 114 surgically treated patients. Am J Surg 208:202–209
Jang JY, Park T, Lee S, Kang MJ, Lee SY, Lee KB et al (2014) Validation of international consensus guidelines for the resection of branch duct-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Br J Surg 101:686–692
Sahora K, Mino-Kenudson M, Brugge W, Thayer SP, Ferrone CR, Sahani D et al (2013) Branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: does cyst size change the tip of the scale? A critical analysis of the revised international consensus guidelines in a large single-institutional series. Ann Surg 258:466–475
Hirono S, Tani M, Kawai M, Okada K, Miyazawa M, Shimizu A et al (2012) The carcinoembryonic antigen level in pancreatic juice and mural nodule size are predictors of malignancy for branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Ann Surg 255:517–522
Xu MM, Yin S, Siddiqui AA, Salem RR, Schrope B, Sethi A et al (2017) Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of three current guidelines for the evaluation of asymptomatic pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(35):e7900. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007900
Shimizu Y, Kanemitsu Y, Sano T, Senda Y, Mizuno N, Yamao K (2010) A nomogram for predicting the probability of carcinoma in patients with intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm. World J Surg 34(12):2932–2938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0785-9
Shimizu Y, Yamaue H, Maguchi H, Yamao K, Hirono S, Osanai M et al (2015) Validation of a nomogram for predicting the probability of carcinoma in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in 180 pancreatic resection patients at 3 high-volume centers. Pancreas 44:459–464
Suzuki Y, Nakazato T, Yokoyama M, Kogure M, Matsuki R, Abe N et al (2016) Development and potential utility of a new scoring formula for prediction of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Pancreas 45(9):1227–1232. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000649
Jang JY, Park T, Lee S, Kim Y, Lee SY, Kim SW et al (2017) Proposed nomogram predicting the individual risk of malignancy in the patients with branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Ann Surg 266:1062–1068
Shimizu Y, Hijioka S, Hirono S, Kin T, Ohtsuka T, Kanno A et al (2020) New model for predicting malignancy in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Ann Surg 272(1):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000003108
Lee SJ, Park SY, Hwang DW, Lee JH, Song KB, Lee W et al (2020) Surgical decisions based on a balance between malignancy probability and surgical risk in patients with branch and mixed-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. J Clin Med 26 9(9):2758–123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092758
Sugimoto M, Elliott IA, Nguyen AH, Kim S, Muthusamy VR, Watson R et al (2017) Assessment of a revised management strategy for patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms involving the main pancreatic duct. JAMA Surg 18 152(1):e163349. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2016.3349
Hwang DW, Jang JY, Lim CS, Lee SE, Yoon YS, Ahn YJ et al (2011) Determination of malignant and invasive predictors in branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a suggested scoring formula. J Korean Med Sci 26(6):740–746. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
Study conception and design: Alba Manuel-Vázquez, José Manuel Ramia. Acquisition of data: all the authors. Analysis and interpretation of data: Alba Manuel-Vázquez A, Anita Balakrishnan, José Manuel Ramia. Drafting of manuscript: Alba Manuel-Vázquez A, Anita Balakrishnan, Mickaël Lesurtel, José Manuel Ramia. Critical revision of manuscript: all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Manuel-Vázquez, A., Balakrishnan, A., Agami, P. et al. A scoring system for predicting malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a multicenter EUROPEAN validation. Langenbecks Arch Surg 407, 3447–3455 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-022-02687-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-022-02687-2