Abstract
Purpose
Pancreas transplantation (PT) is one of the few ways to restore euglycemia within diabetic patients; however, the high morbidity caused by surgical complications and the need for immunosuppressive therapy has raised controversy about PT improving the health-related quality-of-life (HRQoL). The aim of this study is to assess the long-term (≥ 5 years after PT) HRQoL and to identify the factors affecting it.
Methods
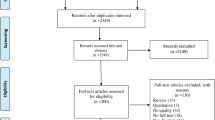
A single-center, cross-sectional study of 49 sequential PT was performed. All patients conducted a telephone interview to fulfill the modification of Medical Outcome Health Survey Short Form questionnaire (SF-36v2) and were compared to similar post-PT studies from the literature.
Results
Patients with a history of replacement renal therapy (RRT) or neuropathy undergoing a PT were associated to a worse bodily pain (P = 0.03) and physical function (P = 0.04), respectively, whereas those with retinopathy showed an improved Role Emotional (P = 0.04). Multivariate analysis revealed the presence of RRT as the only independent prognostic factor for a worse bodily pain [relative risk = 3.9; 95% confidence interval (1.1–14.6)], (P = 0.04). Furthermore, nearly all PT recipients (91.8%) claimed an overall better health than prior to PT.
Conclusion
Our study confirms that PT recipients’ HRQoL improves after PT, showing similar HRQoL scores across different populations and suggests that patients in predialysis could benefit from an improved HRQoL if transplanted on the early stages of the disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data are available.
References
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ (2009) Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87(1):4–14
Marcuello C, Calle-Pascual AL, Fuentes M, Runkle I, Soriguer F, Goday A, Bosch-Comas A, Bordiú E, Carmena R, Casamitjana R, Castaño L, Castell C, Catalá M, Delgado E, Franch J, Gaztambide S, Girbés J, Gomis R, Gutiérrez G, López-Alba A, Martínez-Larrad MT, Rojo Martínez G, Serrano-Rios M, Valdés S, Vázquez JA, Vendrell J (2012) Evaluation of health-related quality of life according to carbohydrate metabolism status: a Spanish population-based study (Di@bet.es study). Int J Endocrinol 2012:1–7
WHO | (2019) World Health Organization. https://w.who.int/. Accessed January 3, 2019.
Mathers CD, Loncar D (2006) Projections of Global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med 3(11):2011–2030
American Diabetes Association (2018) Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 41:86–104
Yu S, Du J (2017) Selenoprotein S: a therapeutic target for diabetes and macroangiopathy? Cardiovasc Diabetol 16(1):101
American Diabetes Association (2018) Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 41(1):105–118
US renal data system 2016 annual data report (2017) epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 69(3):A4
Samoylova ML, Borle D, Ravindra KV (2019) Pancreas transplantation. Indications, techniques, and outcomes. Surg Clin North Am 99:87–101
Smith GC, Trauer T, Kerr PG, Chadban SJ (2010) Prospective quality-of-life monitoring of simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplant recipients using the 36-item short form health survey. Am J Kidney Dis 55(4):698–707
Hanlon M, Cooper M, Abrams P (2019) Quality of life after pancreas transplantation: time to look again. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 24(4):451–455
Speight J, Reaney MD, Woodcock AJ, Smith RM, Shaw JAM (2010) Patient-reported outcomes following islet cell or pancreas transplantation (alone or after kidney) in Type 1 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabet Med 27(7):812–822
Organización Nacional de Trasplantes (2005). Documento de consenso sobre trasplante de páncreas e islotes. Aula Médica.
Muñoz-Bellvís L, Esteban MC, Iglesias M, González L, González-Muñoz JI, Muñoz-González C, Quiñones JE, Tabernero G, Iglesias RA, Sayagués JM, Fraile P (2018) Development and results of a novel pancreas transplant program in spain: the surgeon's point of view. Cir Esp 96(4):205–212
OPTN: organ procurement and transplantation network (2019) https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/search-results?q = graft functin. Accessed January 8, 2019.
Rickels MR, Stock PG, de Koning EJP, Piemonti L, Pratschke J, Alejandro R, Bellin MD, Berney T, Choudhary P, Johnson PR, Kandaswamy R, Kay TWH, Keymeulen B, Kudva YC, Lastres E, Langer RM, Lehmann R, Barbara L, Markmann JF, Marinac M, Odorico JS, Pattou F, Senior PA, Shaw JAM, Vantyghem MC, White S (2018) Defining outcomes for β-cell replacement therapy in the treatment of diabetes: a consensus report on the Igls criteria from the IPITA/EPITA opinion leaders workshop. Transpl Int 31(4):343–352
Ware JE, Kosinski M, Dewey JE (2002). How to Score Version 2 of the SF-36 Health Survey (Standard and Acute Forms). 3rd ed. (Lincoln R, ed.). QualityMetric.
Garratt A, Schmidt L, Mackintosh A, Fitzpatrick R (2002) Quality of life measurement: bibliographic study of patient assessed health outcome measures. BMJ 324(7251):1417
Cohen DJ, Van Hout B, Serruys PW, Mohr FW, Macaya C, den Heijer P, Vrakking MM, Wang K, Mahoney EM, Audi S, Leadley K, Dawkins KD, Kappetein AP (2011) Quality of life after PCI with drug-eluting stents or coronary-artery bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 364(11):1016–1026
Vilagut G, Ferrer M, Rajmil L, Rebollo P, Permanyer-Miralda G, Quintana J (2006) El cuestionario de salud SF-36 español: una década de experiencia y nuevos desarrollos. Gac Sanit 19(2):135–150
Pera PI, Vasallo JM, Rabasa AT, Salinas FO, Pérez LFC, Brulles MJR (2009) Quality of life in simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant recipients. Clin Transpl 23(5):600–605
Sureshkumar KK, Patel BM, Markatos A, Nghiem DD, Marcus RJ (2006) Quality of life after organ transplantation in type 1 diabetics with end-stage renal disease. Clin Transpl 20(1):19–25
Drognitz O, Benz S, Pfeffer F, Fischer C, Makowiec F, Schareck W, Hopt UT (2004) Long-term follow-up of 78 simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants at a single-center institution in Europe. Transplantation 78(12):1802–1808
Díaz-Quijano FA (2012) A simple method for estimating relative risk using logistic regression. BMC Med Res Methodol 15(12):14
Dindo D, Dermartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proporal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213
Martins L, Outerelo C, Malheiro J, Fonseca IM, Henriques AC, Dias LS, Rodriguez AS, Cabrita AM, Noronha IL (2015) Health-related quality of life may improve after transplantation in pancreas-kidney recipients. Clin Transpl 29(3):242–251
Zehrer CL, Gross CR (1991) Quality of life of pancreas transplant recipients. Diabetología 34(Suppl.1):S145–S149
Gross CR, Limwattananon C, Matthees BJ (1998) Quality of life after pancreas transplantation: a review. Clin Transpl 12(4):351–361
Matas AJ, McHugh L, Payne WD, Wrenshall LE, Dunn DL, Gruessner RW, Sutherland DE, Najarian JS (1998) Long-term quality of life after kidney and simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Clin Transpl 12(3):233–242
Gross CR, Limwattananon C, Matthees B, Zehrer JL, Savik K (2000) Impact of transplantation on quality of life in patients with diabetes and renal dysfunction. Transplantation 70(12):1736–1746
Adang EM, Engel GL, van Hooff JP, Kootstra G (1996) Comparison before and after transplantation of pancreas-kidney and pancreas-kidney with loss of pancreas--a prospective controlled quality of life study. Transplantation 62(6):754–758
Sutherland DER, Gruessner RWG, Dunn DL, Matas AJ, Humar A, Kandaswamy R, Mauer SM, Kennedy WR, Goetz FC, Robertson RP, Gruessner AC, Najarian JS (2001) Lessons learned from more than 1,000 pancreas transplants at a single institution. Ann Surg 233(4):463–501
Eypasch E, Williams JI, Wood-Dauphinee S, Ure DM, Schmülling C, Neugebauer E, Troidl H (1995) Gastrointestinal quality of life index: development, validation and application of a new instrument. Br J Surg 82(2):216–222
Humar A, Ramcharan T, Kandaswamy R, Gruessner RWG, Gruessner AC, Sutherland DER (2004) Technical failures after pancreas transplants: why grafts fail and the risk factors--a multivariate analysis. Transplantation 78(8):1188–1192
Troppman C (2010) Complications after pancreas transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 15(1):112–118
Posegger K, Linhares M, Mucci S, Romano TM, Gonzalez AM, Netto AA, Rangel E, Filho J, Silva-Junior HT, Medina-Pestana J (2020) The quality of life in type I diabetic patients with end-stage kidney disease before and after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: a single-center prospective study. Transpl Int 33(3):330–339
Rajkumar T, Mazid S, Vucak-Dzumhur M, Sykes TM, Elder GJ (2019) Health-related quality of life following kidney and simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation. Nephrology (Carlton) 4(9):975–982
Antonucci E, Lamanna I, Fagnoul D, Vincent J-L, De Backer D, Silvio Taccone F (2016) The impact of renal failure and renal replacement therapy on outcome during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy. Artif Organs 40(8):746–754
Hu FB, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Ascherio A, Rexrode KM, Willett WC, Manson JE (2000) Physical activity and risk of stroke in women. JAMA 283(22):2961–2967
Chou CY (2015) Determinants of the health-related quality of life for stroke survivors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24(3):655–662
Díaz-Buxo JA, Lowrie EG, Lew NL, Zang H, Lazarus JM (2000) Quality-of-life evaluation using short form 36: comparison in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 35(2):293–300
Giannarelli R, Coppelli A, Sartini MS, Aragona M, Boggi U, Mosca F, Nardi M, Del Prato S, Marchetti P (2002) Early improvement of unstable diabetic retinopathy after solitary pancreas transplantation. Diabetes Care 25(12):2358–2359
Giannarelli R, Coppelli A, Sartini M, Aragona M, Boggi U, Vistoli F, Rizzo G, Del Prato S, Mosca F, Marchetti P (2005) Effects of pancreas-kidney transplantation on diabetic retinopathy. Transpl Int 18(5):619–622
Won JC, Im YJ, Lee JH, Kim CH, Kwon HS, Cha BY, Park TS (2017) Clinical phenotype of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and relation to symptom patterns: cluster and factor analysis in patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea. J Diabetes Res 2017:5751687
Brod M, Blum SI, Bushnell DM, Ramasamy A (2015) Development and validation of the diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain impact (DPNPI) measure, a patient-reported outcome measure. Qual Life Res 24(12):3001–3014
Dermanovic Dobrota V, Hrabac P, Skegro D, Smiljanic R, Dobrota S, Prkacin I, Brkljacic N, Peros K, Tomix M, Lukinovix-Skudar V, Kes VB (2014) The impact of neuropathic pain and other comorbidities on the quality of life in patients with diabetes. Health Qual Life Outcomes 12(1):171
Watson JM, Behnke MK, Fabrizio MD, McCune TR (2013) Recipient graft failure or death impact on living kidney donor quality of life based on the living organ donor network database. J Endourol 27(12):1525–1529
McCormick BB, Bargman JM (2007) Noninfectious complications of peritoneal dialysis: implications for patient and technique survival. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(12):3023–3025
Mihalache O, Doran H, Mustăţea P, Bobirca F, Georgescu D, Birligea A, Agache A, Patrascu T (2018) Surgical complications of peritoneal dialysis. Chirurgia (Bucur) 113(5):611–624
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. L-S performed data collection, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript; CE, MI, LG, JQ, JI. G-M, GT, RAI, and PF provided patient’s clinical data, performed data collection, and reviewed the manuscript; JI. M-G supported the statistical analyses, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript; L. M-B designed the study, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the local institutional Ethics Committees. No organs/tissues were obtained from prisoners.
Consent to participate
Yes.
Consent to publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Sánchez, J., Esteban, C., Iglesias, M.J. et al. Factors affecting diabetic patient’s long-term quality of life after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: a single-center analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 406, 873–882 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02059-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02059-8