Abstract
Purpose
A previous study revealed that resistance exercise with eccentric contraction and a wide range of motion (ROM) can acutely decrease muscle stiffness of a specific muscle. To explore further approaches to decrease the stiffness, we examined the acute changes in passive stiffness of the individual hamstring muscles after eccentric-only resistance exercise with different combinations of muscle lengths and exercise durations.
Methods
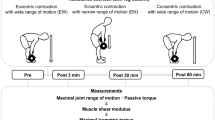
Thirteen healthy young male participants performed three sessions of eccentric-only exercises that comprised stiff-leg deadlift with different muscle lengths and exercise durations (duration per repetition × the total number of repetitions) on separate days as follows: (1) short muscle lengths with a short duration (SS); (2) long muscle lengths with a short duration (LS); and (3) long muscle lengths with a long duration (LL). Maximal joint ROM, passive torque, shear modulus of each hamstring muscle, and maximal isometric torque of knee flexion were measured before, and at 3, 30, and 60 min after each session.
Results
The shear modulus of the semimembranosus was significantly lower at 3 min post-exercise (129.8 ± 22.7 kPa) than at pre-exercise (140.5 ± 19.1 kPa, p < 0.01) in LL, but not in SS or LS. No significant differences were observed in the shear moduli of the biceps femoris long head or semitendinosus between pre-exercise and 3 min post-exercise in any session.
Conclusion
The combination of long muscle lengths and a long duration during eccentric-only resistance exercise is important to immediately decrease the stiffness (shear modulus) of a specific muscle.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Information on software application is available upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- BFlh:
-
Biceps femoris long head
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- EN:
-
Eccentric-only contractions and a narrow exercise range of motion
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- LL:
-
Eccentric contraction at long muscle lengths with a long duration
- LS:
-
Eccentric contraction at long muscle lengths with a short duration
- RMS :
-
Root-mean-square
- ROM:
-
Range of motion
- SDL:
-
Stiff-leg deadlift
- SM:
-
Semimembranosus
- SS:
-
Eccentric contraction at short muscle lengths with a short duration
- ST:
-
Semitendinosus
References
Barbosa GM, Trajano GS, Dantas GAF, Silva BR, Vieira WHB (2020) Chronic effects of static and dynamic stretching on hamstrings eccentric strength and functional performance: a randomized controlled trial. J Strength Cond Res 34:2031–2039. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000003080
Bergh U, Ekblom B (1979) Influence of muscle temperature on maximal muscle strength and power output in human skeletal muscles. Acta Physiol Scand 107:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06439.x
Caliskan E, Akkoc O, Bayramoglu Z et al (2019) Effects of static stretching duration on muscle stiffness and blood flow in the rectus femoris in adolescents. Med Ultrason 21:136–143. https://doi.org/10.11152/mu-1859
Chen TC, Nosaka K, Sacco P (2007) Intensity of eccentric exercise, shift of optimum angle, and the magnitude of repeated-bout effect. J Appl Physiol 102:992–999. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00425.2006
Cramer JT, Housh TJ, Weir JP, Johnson GO, Coburn JW, Beck TW (2005) The acute effects of static stretching on peak torque, mean power output, electromyography, and mechanomyography. Eur J Appl Physiol 93:530–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1199-x
Freitas SR, Andrade RJ, Larcoupaille L, Mil-homens P, Nordez A (2015) Muscle and joint responses during and after static stretching performed at different intensities. Eur J Appl Physiol 115:1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3104-1
Fridén J, Lieber RL (1992) Structural and mechanical basis of exercise-induced muscle injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:521–530
Fridén J, Sfakianos PN, Hargens AR, Akeson WH (1988) Residual muscular swelling after repetitive eccentric contractions. J Orthop Res 6:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.1100060404
Glickman ME, Rao SR, Schultz MR (2014) False discovery rate control is a recommended alternative to Bonferroni-type adjustments in health studies. J Clin Epidemiol 67:850–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.03.012
Ichihashi N, Umegaki H, Ikezoe T et al (2016) The effects of a 4-week static stretching programme on the individual muscles comprising the hamstrings. J Sports Sci 34:2155–2159. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2016.1172725
Kawama R, Yanase K, Hojo T, Wakahara T (2022) Acute changes in passive stiffness of the individual hamstring muscles induced by resistance exercise: effects of contraction mode and range of motion. Eur J Appl Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-04976-6
Kenny GP, Reardon FD, Zaleski W et al (2003) Muscle temperature transients before, during, and after exercise measured using an intramuscular multisensor probe. J Appl Physiol 94:2350–2357. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01107.2002
Kumagai H, Miyamoto-Mikami E, Hirata K et al (2019) ESR1 rs2234693 polymorphism is associated with muscle injury and muscle stiffness. Med Sci Sports Exerc 51:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001750
Lacourpaille L, Nordez A, Hug F, Couturier A, Dibie C, Guilhem G (2014) Time-course effect of exercise-induced muscle damage on localized muscle mechanical properties assessed using elastography. Acta Physiol (oxf) 211:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12272
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Magnusson SP, Simonsen EB, Aagaard P, Boesen J, Johannsen F, Kjaer M (1997) Determinants of musculoskeletal flexibility: viscoelastic properties, cross-sectional area, EMG and stretch tolerance. Scand J Med Sci Sports 7:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.1997.tb00139.x
Miyamoto N, Hirata K, Kanehisa H (2017) Effects of hamstring stretching on passive muscle stiffness vary between hip flexion and knee extension maneuvers. Scand J Med Sci Sports 27:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12620
Miyamoto N, Hirata K, Inoue K, Hashimoto T (2019) Muscle stiffness of the vastus lateralis in sprinters and long-distance runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc 51:2080–2087. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000002024
Miyamoto N, Kimura N, Hirata K (2020) Non-uniform distribution of passive muscle stiffness within hamstring. Scand J Med Sci Sports 30:1729
Mizumoto A, Plonsky L (2016) R as a Lingua Franca: advantages of using R for quantitative Research in applied linguistics. Appl Linguist 37:284–291. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/amv025
Morales-Artacho AJ, Lacourpaille L, Guilhem G (2017) Effects of warm-up on hamstring muscles stiffness: cycling vs foam rolling. Scand J Med Sci Sports 27:1959–1969. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12832
Murayama M, Inami T, Shima N, Yoneda T, Nosaka K (2022) Changes in biceps brachii muscle hardness assessed by a push-in meter and strain elastography after eccentric versus concentric contractions. Sci Rep 12:9214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13184-3
Nelson RT (2006) A Comparison of the immediate effects of eccentric training vs static stretch on hamstring flexibility in high school and college athletes. N Am J Sports Phys Ther 1:56–61
Nosaka K, Lavender A, Newton M, Sacco P (2003) Muscle damage in resistance training—is muscle damage necessary for strength gain and muscle hypertrophy? Int J Sport Health Sci 1:1–8
Nosaka K, Newton M, Sacco P et al (2005) Partial protection against muscle damage by eccentric actions at short muscle lengths. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:746–753. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000162691.66162.00
Sapin-de Brosses E, Gennisson JL, Pernot M, Fink M, Tanter M (2010) Temperature dependence of the shear modulus of soft tissues assessed by ultrasound. Phys Med Biol 55:1701–1718. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/55/6/011
Seymore KD, Domire ZJ, DeVita P, Rider PM, Kulas AS (2017) The effect of Nordic hamstring strength training on muscle architecture, stiffness, and strength. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:943–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3583-3
Umegaki H, Ikezoe T, Nakamura M et al (2015) Acute effects of static stretching on the hamstrings using shear elastic modulus determined by ultrasound shear wave elastography: differences in flexibility between hamstring muscle components. Man Ther 20:610–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2015.02.006
Vatovec R, Marušič J, Marković G, Šarabon N (2021) Effects of Nordic hamstring exercise combined with glider exercise on hip flexion flexibility and hamstring passive stiffness. J Sports Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2021.1933350
Voglar M, Vatovec R, Kozinc Ž, Šarabon N (2022) The effects of eccentric exercise on passive hamstring muscle stiffness: comparison of shear-wave elastography and passive knee torque outcomes. Eur J Transl Myol. https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10567
Warren GL, Hayes DA, Lowe DA, Armstrong RB (1993) Mechanical factors in the initiation of eccentric contraction-induced injury in rat soleus muscle. J Physiol 464:457–475. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019645
Watanabe Y, Madarame H, Ogasawara R, Nakazato K, Ishii N (2014) Effect of very low-intensity resistance training with slow movement on muscle size and strength in healthy older adults. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 34:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12117
Woodley SJ, Mercer SR (2005) Hamstring muscles: architecture and innervation. Cells Tissues Organs 179:125–141. https://doi.org/10.1159/000085004
Xu J, Fu SN, Zhou D, Huang C, Hug F (2019) Relationship between pre-exercise muscle stiffness and muscle damage induced by eccentric exercise. Eur J Sport Sci 19:508–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2018.1535625
Zhi L, Miyamoto N, Naito H (2022) Passive muscle stiffness of biceps femoris is acutely reduced after eccentric knee flexion. J Sports Sci Med 21:487–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13732
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted with the support a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 21J20128).
Funding
This work was conducted with a grant support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 21J20128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RK, TH, and TW conceived and designed the study. RK conducted the experiments, analyzed the data, wrote the original draft, and reviewed its draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
The present study was approved by the Doshisha University Research Ethics Review Committee regarding Human Subject Research (number: 21006). All experimental procedures involving human participants were based on the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
The authors affirmed that research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in figures and experimental data.
Additional information
Communicated by Olivier Seynnes.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kawama, R., Hojo, T. & Wakahara, T. Acute changes in passive stiffness of the individual hamstring muscles induced by resistance exercise: effects of muscle length and exercise duration. Eur J Appl Physiol 123, 655–666 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05092-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05092-1