Abstract
Purpose
Recent studies raise an interesting possibility that resistance exercise also decreases passive muscle stiffness, as does stretching exercise. However, little is known about how program variables of resistance exercise acutely influence muscle stiffness. We aimed to examine the acute changes in passive stiffness of the individual hamstring muscles after resistance exercises using different combinations of contraction modes and ranges of motion (ROMs).
Methods
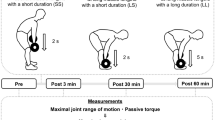
Thirteen healthy young male participants performed three sessions of resistance exercises that comprised stiff-leg deadlift with different contraction modes and exercise ROMs on separate days as follows: (1) eccentric contractions with a wide exercise ROM (EW); (2) eccentric contractions with a narrow exercise ROM (EN); and (3) concentric contractions with a wide exercise ROM (CW). Maximal joint ROM, passive torque, shear modulus of the individual hamstring muscles, and maximal isometric torque of knee flexion were measured before and 3 min, 30 min, and 60 min after completing each session.
Results
The shear modulus of the semimembranosus was significantly lower at 3 min post-exercise (121.8 ± 16.0 kPa) than at pre-exercise (129.0 ± 18.9 kPa, p = 0.021, r = 0.45) in EW, but not in EN or CW. There were no significant changes in the shear moduli of the biceps femoris long head or the semitendinosus at any timepoint in any exercise protocols.
Conclusions
The present results suggest that the combination of eccentric contraction and wide ROM during resistance exercise has the potential to acutely decrease passive stiffness (shear modulus) of a specific muscle.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data sets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Information on software application is available upon reasonable request.
Change history
05 July 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-04999-z
Abbreviations
- BFlh:
-
Biceps femoris long head
- CW:
-
Concentric contraction with wide range of motion
- EN:
-
Eccentric contraction with narrow range of motion
- EW:
-
Eccentric contraction with wide range of motion
- RMS :
-
Root-mean-square
- ROM:
-
Range of motion
- SDL:
-
Stiff-leg deadlift
- SM:
-
Semimembranosus
- ST:
-
Semitendinosus
References
Akagi R, Tanaka J, Shikiba T, Takahashi H (2015) Muscle hardness of the triceps brachii before and after a resistance exercise session: a shear wave ultrasound elastography study. Acta Radiol 56:1487–1493. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185114559765
Andrade RJ, Freitas SR, Hug F et al (2018) The potential role of sciatic nerve stiffness in the limitation of maximal ankle range of motion. Sci Rep 8:14532. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32873-6
Aune AAG, Bishop C, Turner AN et al (2019) Acute and chronic effects of foam rolling vs eccentric exercise on ROM and force output of the plantar flexors. J Sports Sci 37:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2018.1486000
Avrillon S, Lacourpaille L, Hug F et al (2020) Hamstring muscle elasticity differs in specialized high-performance athletes. Scand J Med Sci Sports 30:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13564
Barbosa GM, Trajano GS, Dantas GAF et al (2020) Chronic effects of static and dynamic stretching on hamstrings eccentric strength and functional performance: a randomized controlled trial. J Strength Cond Res 34:2031–2039. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000003080
Caliskan E, Akkoc O, Bayramoglu Z et al (2019) Effects of static stretching duration on muscle stiffness and blood flow in the rectus femoris in adolescents. Med Ultrason 21:136–143. https://doi.org/10.11152/mu-1859
Chalchat E, Gennisson JL, Peñailillo L et al (2020) Changes in the viscoelastic properties of the vastus lateralis muscle with fatigue. Front Physiol 11:307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00307
Chen TC, Nosaka K, Sacco P (2007) Intensity of eccentric exercise, shift of optimum angle, and the magnitude of repeated-bout effect. J Appl Physiol 102:992–999. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00425.2006
Ema R, Nosaka K, Kawashima R et al (2021) Muscle length influence on rectus femoris damage and protective effect in knee extensor eccentric exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 31:597–609. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13890
Fukaya T, Kiyono R, Sato S et al (2020) Effects of static stretching with high-intensity and short-duration or low-intensity and long-duration on range of motion and muscle stiffness. Front Physiol 11:601912. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.601912
García-Pinillos F, Ruiz-Ariza A, Moreno del Castillo R, Latorre-Román PÁ (2015) Impact of limited hamstring flexibility on vertical jump, kicking speed, sprint, and agility in young football players. J Sports Sci 33:1293–1297. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2015.1022577
Glickman ME, Rao SR, Schultz MR (2014) False discovery rate control is a recommended alternative to Bonferroni-type adjustments in health studies. J Clin Epidemiol 67:850–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.03.012
Hirata K, Yamadera R, Akagi R (2020) Can static stretching reduce stiffness of the triceps surae in older men? Med Sci Sports Exerc 52:673–679. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000002186
Ichihashi N, Umegaki H, Ikezoe T et al (2016) The effects of a 4-week static stretching programme on the individual muscles comprising the hamstrings. J Sports Sci 34:2155–2159. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2016.1172725
Kawama R, Takahashi K, Wakahara T (2021) Effect of hip joint position on electromyographic activity of the individual hamstring muscles during stiff-Leg deadlift. J Strength Cond Res 35:S38–S43. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000003442
Kisilewicz A, Madeleine P, Ignasiak Z et al (2020) Eccentric exercise reduces upper trapezius muscle stiffness assessed by shear wave elastography and myotonometry. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:928. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00928
Kumagai H, Miyamoto-Mikami E, Hirata K et al (2019) ESR1 rs2234693 polymorphism is associated with muscle injury and muscle stiffness. Med Sci Sports Exerc 51:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001750
Lacourpaille L, Nordez A, Hug F et al (2014) Time-course effect of exercise-induced muscle damage on localized muscle mechanical properties assessed using elastography. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 211:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12272
Lacourpaille L, Nordez A, Hug F et al (2017) Early detection of exercise-induced muscle damage using elastography. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:2047–2056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3695-9
Maeda N, Urabe Y, Tsutsumi S et al (2017) The acute Effects of static and cyclic stretching on muscle stiffness and hardness of medial gastrocnemius muscle. J Sports Sci Med 16:514–520
Magnusson SP, Simonsen EB, Aagaard P et al (1997) Determinants of musculoskeletal flexibility: viscoelastic properties, cross-sectional area, EMG and stretch tolerance. Scand J Med Sci Sports 7:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.1997.tb00139.x
Miyamoto N, Hirata K, Kanehisa H (2017) Effects of hamstring stretching on passive muscle stiffness vary between hip flexion and knee extension maneuvers. Scand J Med Sci Sports 27:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12620
Miyamoto N, Hirata K, Miyamoto-Mikami E et al (2018) Associations of passive muscle stiffness, muscle stretch tolerance, and muscle slack angle with range of motion: individual and sex differences. Sci Rep 8:8274. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26574-3
Miyamoto N, Kimura N, Hirata K (2020) Non-uniform distribution of passive muscle stiffness within hamstring. Scand J Med Sci Sports 30:1729–1738. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13732
Morales-Artacho AJ, Lacourpaille L, Guilhem G (2017) Effects of warm-up on hamstring muscles stiffness: cycling vs foam rolling. Scand J Med Sci Sports 27:1959–1969. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12832
Nakamura M, Ikezoe T, Kobayashi T et al (2014) Acute effects of static stretching on muscle hardness of the medial gastrocnemius muscle belly in humans: an ultrasonic shear-wave elastography study. Ultrasound Med Biol 40:1991–1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2014.03.024
Nakamura M, Ikezoe T, Umegaki H et al (2017) Changes in passive properties of the gastrocnemius muscle–tendon unit during a 4-week routine static-stretching program. J Sport Rehabil 26:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2015-0198
Nelson RT (2006) A Comparison of the immediate effects of eccentric training vs static stretch on hamstring flexibility in high school and college athletes. N Am J Sports Phys Ther 1:56–61
Nosaka K, Sakamoto K, Newton M et al (2001) The repeated bout effect of reduced-load eccentric exercise on elbow flexor muscle damage. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210100430
Ono T, Okuwaki T, Fukubayashi T (2010) Differences in activation patterns of knee flexor muscles during concentric and eccentric exercises. Res Sports Med 18:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1080/15438627.2010.490185
Ono T, Higashihara A, Fukubayashi T (2011) Hamstring functions during hip-extension exercise assessed with electromyography and magnetic resonance imaging. Res Sports Med 19:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/15438627.2011.535769
Panoutsakopoulos V, Kotzamanidou MC, Papaiakovou G, Kollias IA (2021) The ankle joint range of motion and its effect on squat jump performance with and without arm swing in adolescent female volleyball players. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6010014
Pournot H, Tindel J, Testa R et al (2016) The acute effect of local vibration as a recovery modality from exercise-induced increased muscle stiffness. J Sports Sci Med 15:142–147
Seymore KD, Domire ZJ, DeVita P et al (2017) The effect of Nordic hamstring strength training on muscle architecture, stiffness, and strength. Eur J Appl Physiol 117:943–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3583-3
Umegaki H, Ikezoe T, Nakamura M et al (2015) Acute effects of static stretching on the hamstrings using shear elastic modulus determined by ultrasound shear wave elastography: differences in flexibility between hamstring muscle components. Man Ther 20:610–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2015.02.006
Vatovec R, Marušič J, Marković G et al (2021) Effects of Nordic hamstring exercise combined with glider exercise on hip flexion flexibility and hamstring passive stiffness. J Sports Sci 39:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2021.1933350
Watsford ML, Murphy AJ, McLachlan KA et al (2010) A prospective study of the relationship between lower body stiffness and hamstring injury in professional Australian rules footballers. Am J Sports Med 38:2058–2064. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546510370197
Witvrouw E, Danneels L, Asselman P et al (2003) Muscle flexibility as a risk factor for developing muscle injuries in male professional soccer players. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med 31:41–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/03635465030310011801
Woodley SJ, Mercer SR (2005) Hamstring muscles: architecture and innervation. Cells Tissues Organs 179:125–141. https://doi.org/10.1159/000085004
Xu J, Fu SN, Zhou D et al (2019) Relationship between pre-exercise muscle stiffness and muscle damage induced by eccentric exercise. Eur J Sport Sci 19:508–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2018.1535625
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 21J20128).
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 21J20128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RK, TH, and TW conceived and designed the study. RK conducted the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the original draft. KY, TH, and TW reviewed and edited the original draft. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
The present study was approved by the Doshisha University Research Ethics Review Committee regarding Human Subject Research (number: 21006). All experimental procedures involving human participants were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Consent to participate
All participants consented to participate in the present study.
Consent to publication
All authors consent to the publication of the manuscript in EJAP.
Additional information
Communicated by Oliver Seynnes.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawama, R., Yanase, K., Hojo, T. et al. Acute changes in passive stiffness of the individual hamstring muscles induced by resistance exercise: effects of contraction mode and range of motion. Eur J Appl Physiol 122, 2071–2083 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-04976-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-04976-6