Abstract
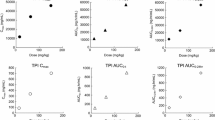
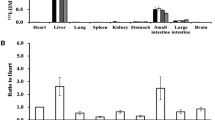
Detection of synthetic thymidine analogues after their incorporation into replicating DNA during the S-phase of the cell cycle is a widely exploited methodology for evaluating proliferative activity, tracing dividing and post-mitotic cells, and determining cell-cycle parameters both in vitro and in vivo. To produce valid quantitative readouts for in vivo experiments with single intraperitoneal delivery of a particular nucleotide, it is necessary to determine the time interval during which a synthetic thymidine analogue can be incorporated into newly synthesized DNA, and the time by which the nucleotide is cleared from the blood serum. To date, using a variety of methods, only the bioavailability time of tritiated thymidine and 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) have been evaluated. Recent advances in double- and triple-S-phase labeling using 5-iodo-2′-deoxyuridine (IdU), 5-chloro-2′-deoxyuridine (CldU), and 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) have raised the question of the bioavailability time of these modified nucleotides. Here, we examined their labeling kinetics in vivo and evaluated label clearance from blood serum after single intraperitoneal delivery to mice at doses equimolar to the saturation dose of BrdU (150 mg/kg). We found that under these conditions, all the examined thymidine analogues exhibit similar labeling kinetics and clearance rates from the blood serum. Our results indicate that all thymidine analogues delivered at the indicated doses have similar bioavailability times (approximately 1 h). Our findings are significant for the practical use of multiple S-phase labeling with any combinations of BrdU, IdU, CldU, and EdU and for obtaining valid labeling readouts.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alexiades MR, Cepko C (1996) Quantitative analysis of proliferation and cell cycle length during development of the rat retina. Dev Dyn 205:293–307. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199603)205:3%3c293::AID-AJA9%3e3.0.CO;2-D
Angevine JB, Sidman RL (1961) Autoradiographic study of cell migration during histogenesis of cerebral cortex in the mouse. Nature 192:766–768. https://doi.org/10.1038/192766b0
Aten JA, Bakker PJ, Stap J et al (1992) DNA double labelling with IdUrd and CldUrd for spatial and temporal analysis of cell proliferation and DNA replication. Histochem J 24:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01046839
Barker JM, Charlier TD, Ball GF, Balthazart J (2013) A new method for in vitro detection of bromodeoxyuridine in serum: a proof of concept in a songbird species, the canary. PLoS One 8:e63692. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063692
Brandt MD, Hübner M, Storch A (2012) Brief report: adult hippocampal precursor cells shorten S-phase and total cell cycle length during neuronal differentiation. STEM CELLS 30:2843–2847. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1244
Burns KA, Kuan C-Y (2005) Low doses of bromo- and iododeoxyuridine produce near-saturation labeling of adult proliferative populations in the dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 21:803–807. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03907.x
Cai L, Hayes NL, Nowakowski RS (1997) Local homogeneity of cell cycle length in developing mouse cortex. J Neurosci 17:2079–2087
Encinas JM, Enikolopov G (2008) Identifying and quantitating neural stem and progenitor cells in the adult brain. Methods in cell biology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 243–272
Encinas JM, Michurina TV, Peunova N et al (2011) Division-coupled astrocytic differentiation and age-related depletion of neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell 8:566–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2011.03.010
Fischer TJ, Walker TL, Overall RW et al (2014) Acute effects of wheel running on adult hippocampal precursor cells in mice are not caused by changes in cell cycle length or S phase length. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00314
Gratzner HG (1982) Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine: a new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science 218:474–475. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7123245
Hayes NL, Nowakowski RS (2000) Exploiting the dynamics of S-phase tracers in developing brain: interkinetic nuclear migration for cells entering versus leaving the S-phase. Dev Neurosci 22:44–55. https://doi.org/10.1159/000017426
Hayes NL, Nowakowski RS (2002) Dynamics of cell proliferation in the adult dentate gyrus of two inbred strains of mice. Dev Brain Res 134:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-3806(01)00324-8
Kriss JP, Revesz L (1962) The distribution and fate of bromodeoxyuridine and bromodeoxycytidine in the mouse and rat. Cancer Res 22:254–265
Kuhn H, Dickinson-Anson H, Gage F (1996) Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci 16:2027–2033. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-06-02027.1996
Liboska R, Ligasová A, Strunin D et al (2012) Most anti-BrdU antibodies react with 2’-deoxy-5-ethynyluridine—the method for the effective suppression of this cross-reactivity. PLoS One 7:e51679. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051679
Ma H, Samarabandu J, Devdhar RS et al (1998) Spatial and temporal dynamics of DNA replication sites in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 143:1415–1425. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.143.6.1415
Manders EM, Stap J, Brakenhoff GJ et al (1992) Dynamics of three-dimensional replication patterns during the S-phase, analysed by double labelling of DNA and confocal microscopy. J Cell Sci 103(Pt 3):857–862
Manders EMM, Stap J, Strackee J et al (1996) Dynamic behavior of DNA replication domains. Exp Cell Res 226:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1996.0233
Mandyam CD, Harburg GC, Eisch AJ (2007) Determination of key aspects of precursor cell proliferation, cell cycle length and kinetics in the adult mouse subgranular zone. Neuroscience 146:108–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.064
Matiašová A, Ševc J, Mikeš J et al (2014) Flow cytometric determination of 5-bromo-2ʹ-deoxyuridine pharmacokinetics in blood serum after intraperitoneal administration to rats and mice. Histochem Cell Biol 142:703–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1253-7
Neef AB, Luedtke NW (2011) Dynamic metabolic labeling of DNA in vivo with arabinosyl nucleosides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:20404–20409. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1101126108
Neef AB, Luedtke NW (2014) An azide-modified nucleoside for metabolic labeling of DNA. ChemBioChem 15:789–793. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201400037
Newton PT, Li L, Zhou B et al (2019) A radical switch in clonality reveals a stem cell niche in the epiphyseal growth plate. Nature 567:234–238. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0989-6
Nowakowski RS, Rakic P (1974) Clearance rate of exogenous 3H-thymidine from the plasma of pregnant rhesus monkeys. Cell Tissue Kinet 7:189–194. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2184.1974.tb00411.x
Nowakowski RS, Lewin SB, Miller MW (1989) Bromodeoxyuridine immunohistochemical determination of the lengths of the cell cycle and the DNA-synthetic phase for an anatomically defined population. J Neurocytol 18:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01190834
Packard DS, Menzies RA, Skalko RG (1973) Incorportaiton of thymidine and its analogue, bromodeoxyuridine, into embryos and maternal tissues of the mouse. Differentiation 1:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-0436.1973.tb00137.x
Phuphanich S, Levin VA (1985) Bioavailability of bromodeoxyuridine in dogs and toxicity in rats. Cancer Res 45:2387–2389
Podgorny O, Peunova N, Park J-H, Enikolopov G (2018) Triple S-phase labeling of dividing stem cells. Stem Cell Rep 10:615–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.12.020
Rieder U, Luedtke NW (2014) Alkene-tetrazine ligation for imaging cellular DNA. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:9168–9172. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201403580
Rubini JR, Cronkite EP, Bond VP, Fliedner TM (1960) The metabolism and fate of tritiated thymidine in man. J Clin Invest 39:909–918. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI104111
Saffhill R, Hume WJ (1986) The degradation of 5-iododeoxyuridine and 5-bromodeoxyuridine by serum from different sources and its consequences for the use of the compounds for incorporation into DNA. Chem Biol Interact 57:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2797(86)90008-6
Salic A, Mitchison TJ (2008) A chemical method for fast and sensitive detection of DNA synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2415–2420. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0712168105
Schweyer K, Rüschoff-Steiner C, Arias-Carrión O et al (2019) Neuronal precursor cells with dopaminergic commitment in the rostral migratory stream of the mouse. Sci Rep 9:13359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49920-5
Staroscik RN, Jenkins WH, Mendelsohn ML (1964) Availability of tritiated thymidine after intravenous administration. Nature 202:456–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/202456a0
Steinhauser ML, Bailey AP, Senyo SE et al (2012) Multi-isotope imaging mass spectrometry quantifies stem cell division and metabolism. Nature 481:516–519. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10734
Stetson PL, Shukla UA, Amin PR, Ensminger WD (1985) High-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of bromodeoxyuridine and its major metabolite, bromouracil, in biological fluids. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 341:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(00)84032-3
Takahashi T, Nowakowski RS, Caviness VS (1993) Cell cycle parameters and patterns of nuclear movement in the neocortical proliferative zone of the fetal mouse. J Neurosci 13:820–833
Takahashi T, Nowakowski RS, Caviness VS (1994) Mode of cell proliferation in the developing mouse neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:375–379. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.1.375
Taylor JH, Woods PS, Hughes WL (1957) The organization and duplication of chromosomes as revealed by autoradiographic studies using tritium-labeled thymidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 43:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.43.1.122
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR et al (2002) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415:1030–1034. https://doi.org/10.1038/4151030a
Vega CJ, Peterson DA (2005) Stem cell proliferative history in tissue revealed by temporal halogenated thymidine analog discrimination. Nat Methods 2:167–169. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth741
Verdoodt F, Willems M, Mouton S et al (2012) Stem cells propagate their DNA by random segregation in the flatworm Macrostomum lignano. PLoS One 7:e30227. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030227
Zeng C, Pan F, Jones LA et al (2010) Evaluation of 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine staining as a sensitive and reliable method for studying cell proliferation in the adult nervous system. Brain Res 1319:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.092
Funding
This study was funded by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant no. 19-29-04016 (to O.V.P.), the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation grant no. 075-15-2019-1789 to the Center for Precision Genome Editing and Genetic Technologies for Biomedicine (to O.V.P.), NIH (NIA grant AG057705 to G.E.), and Russian Science Foundation, grant no. 19-15-00247 (to G.E.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All experiments on mice were performed according to European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and other Scientific Purposes (1986, ETS 123) and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shemyakin-Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry (protocol no. 281).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maltsev, D.I., Mellanson, K.A., Belousov, V.V. et al. The bioavailability time of commonly used thymidine analogues after intraperitoneal delivery in mice: labeling kinetics in vivo and clearance from blood serum. Histochem Cell Biol 157, 239–250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-021-02048-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-021-02048-y