Abstract
Since its discovery well over 100 years ago (Flemming, in Sitzungsber Akad Wissensch Wien 71:81–147, 1875; Van Beneden, in Bull Acad R Belg 42:35–97, 1876) the centrosome is increasingly being recognized as a most impactful organelle for its role not only as primary microtubule organizing center (MTOC) but also as a major communication center for signal transduction pathways and as a center for proteolytic activities. Its significance for cell cycle regulation has been well studied and we now also know that centrosome dysfunctions are implicated in numerous diseases and disorders including cancer, Alstrom syndrome, Bardet–Biedl syndrome, Huntington’s disease, reproductive disorders, and several other diseases and disorders. The present review is meant to build on information presented in the previous review (Schatten, in Histochem Cell Biol 129:667–686, 2008) and to highlight functions of the mammalian centrosome in health, and dysfunctions in disorders, disease, and aging with six sections focused on (1) centrosome structure and functions, and new insights into the role of centrosomes in cell cycle progression; (2) the role of centrosomes in tumor initiation and progression; (3) primary cilia, centrosome-primary cilia interactions, and consequences for cell cycle functions in health and disease; (4) transitions from centrosome to non-centrosome functions during cellular polarization; (5) other centrosome dysfunctions associated with the pathogenesis of human disease; and (6) centrosome functions in oocyte germ cells and dysfunctions in reproductive disorders and reproductive aging.

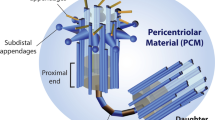
Modified from Schatten (2013)

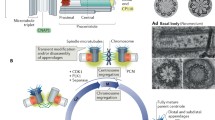
Modified from Schatten (2013)

Modified from Schatten (2014)


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acilan C, Saunders WS (2008) A tale of too many centrosomes. Cell 134:572–575
Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC (2015) Microtubule minus-end-targeting proteins. Curr Biol 25:R162–R171
Akhmanova A. Steinmetz MO (2008) Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:309–322
Alvarez Sedó CA, Schatten H, Combelles C, Rawe VY (2011) The nuclear mitotic apparatus protein NuMA: localization and dynamics in human oocytes, fertilization and early embryos. Mol Hum Reprod 17(6):392–398. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gar009
Andersen JS, Wilkinson CJ, Mayor T, Mortensen P, Nigg EA, Mann M (2003) Proteomic characterization of the human centrosome by protein correlation profiling. Nature 426:570–574
Ansley SJ et al (2003) Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Nature 425:628–633
Arquint C, Gabryjonczyk AM, Nigg EA (2014) Centrosomes as signalling centres. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369
Badano JL, Teslovich TM, Katsanis N (2005) The centrosome in human genetic disease. Nat Rev Genet 6:194–207
Baines AJ, Bignone PA, King MDA, Maggs AM, Bennett PM, Pinder JC, Phillips GW (2009) The CKK domain (DUF1781) binds microtubules and defines the CAMSAP/ssp4 family of animal proteins. Mol Biol Evol 26:2005–2014
Berbari NF, O’Connor AK, Haycraft CJ, Yoder BK (2009) The primary cilium as a complex signaling center. Curr Biol 19:R526–R535
Blacque OE et al (2004) Loss of C. elegans BBS-7 and BBS-8 protein function results in cilia defects and compromised intraflagellar transport. Genes Dev 18:1630–1642
Bornens M (2012) The centrosome in cells and organisms. Science 335:422–426
Boutros R (2012) Regulation of centrosomes by cyclin-dependent kinases. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap. 11. Springer, New York
Boveri T (1901) Zellen-Studien: Über die Natur der Centrosomen. Jena, Germany: Fisher Z Med Naturw 28:1–220
Boveri T (1914) Zur Frage der Entstehung maligner Tumoren. G. Fisher, Jena
Brinkley BR, Goepfert TM (1998) Supernumerary centrosomes and cancer: Boveri’s hypothesis resurrected. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 41:281–288
Can A, Semiz O, Cinar O (2005) Bisphenol-A induces cell cycle delay and alters centrosome and spindle microtubular organization in oocytes during meiosis. Mol Hum Reprod 11:389–396
Cande Z (1990) Centrosomes: composition and reproduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2:301–305
Carroll E, Okuda M, Horn HF, Biddinger P, Stambrook PJ, Gleich LL, Li YQ, Tarapore P, Fukasawa K (1999) Centrosome hyperamplification in human cancer: chromosome instability induced by p53 mutation and/or Mdm2 overexpression. Oncogene 18:1935–1944
Carvalho I, Milanezi F, Martins A, Reis RM, Schmitt F (2005) Overexpression of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha in breast cancer is associated with tumour progression. Breast Cancer Res 7:R788–R795
Chabin-Brion K, Marceiller J, Perez F, Settegrana C, Drechou A, Durand G, Pous C (2001) The Golgi complex is a microtubule-organizing organelle. Mol Biol Cell 12:2047–2060. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.12.7.2047
Chan JY (2011) A clinical overview of centrosome amplification in human cancers. Int J Biol Sci 7:1122–1144
Cheng J, Türkel N, Hemati N, Fuller MT, Hunt AJ, Yamashita YM (2008) Centrosome misorientation reduces stem cell division during ageing. Nature 456:599–604
Cheung CH, Coumar MS, Chang JY, Hsieh HP (2011) Aurora kinase inhibitor patents and agents in clinical testing: an update (2009–10). Expert Opin Ther Pat 21:857–884
Cole NB, Sciaky N, Marotta A, Song J, Lippincott- Schwartz J (1996) Golgi dispersal during microtubule disruption: regeneration of Golgi stacks at peripheral endoplasmic reticulum exit sites. Mol Biol Cell 7:631–650. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.7.4.631
Corthesy-Theulaz I, Pauloin A, Pfeffer SR (1992) Cytoplasmic dynein participates in the centrosomal localization of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol 118:1333–1345. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.118.6.1333
D’Angelo A, Franco B (2009) The dynamic cilium in human diseases. PathoGenetics 2(3):1–15
Davenport JR, Yoder BK (2005) An incredible decade for the primary cilium: a look at a once-forgotten organelle. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1159–F1169
De Brabander M, Geuens G, Nuydens R, Willebrords R, De Mey J (1981) Taxol induces the assembly of free microtubules in living cells and blocks the organizing capacity of the centrosomes and kinetochores. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5608–5612
Del Castillo U, Winding M, Lu W, Gelfand VI (2015) Interplay between kinesin-1 and cortical dynein during axonal outgrowth and microtubule organization in Drosophila neurons. eLife 4:e10140
Delgehyr N, Sillibourne J, Bornens M (2005) Microtubule nucleation and anchoring at the centrosome are independent processes linked by ninein function. J Cell Sci 118:1565–1575. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02302
DiAntonio A, Hicke L (2004) Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of the synapse. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:223–246
Dictenberg J, Zimmerman W, Sparks C, Young A, Vidair C, Zheng Y, Carrington W, Fay F, Doxsey SJ (1998) Pericentrin and gamma tubulin form a protein complex and are organized into a novel lattice at the centrosome. J Cell Biol 141:163–174
Dimitriadis I, Katsaros C, Galatis B (2001) The effect of taxol on centrosome function and microtubule organization in apical cells of Sphacelaria rigidula (Phaeophyceae). Phycol Res 49:23–34
Doxsey SJ, Stein P, Evans L, Calarco P, Kirschner M (1994) Pericentrin, a highly conserved protein of centrosomes involved in microtubule organization. Cell 76:639–650
Duensing S, Munger K (2003) Centrosome abnormalities and genomic instability induced by human papillomavirus oncoproteins. Prog Cell Cycle Res 5:383–391
Duensing S, Lee LY, Duensing A, Basile J, Piboonniyom S, Gonzalez S, Crum CP, Munger K (2000) The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins cooperate to induce mitotic defects and genomic instability by uncoupling centrosome duplication from the cell division cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10002–10007
Efimov A et al (2007) Asymmetric CLASP-dependent nucleation of noncentrosomal microtubules at the trans-Golgi network. Dev Cell 12:917–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2007.04.002
Eichenlaub-Ritter U, Vogt E, Cukurcam S, Sun F, Pacchierotti F, Parry J (2008) Exposure of mouse oocytes to bisphenol A causes meiotic arrest but not aneuploidy. Mutat Res 651:82–92
Fabunmi RP, Wigley WC, Thomas PJ, DeMartin GN (2000) Activity and regulation of the centrosome-associated proteasome. J Biol Chem 275:409–413
Fan HY, Sun QY (2004) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade during oocyte maturation and fertilization in mammals. Biol Reprod 70:535–547
Fisk HA (2012) Many pathways to destruction: the centrosome and its control by and role in regulated proteolysis. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap, 8. Springer, New York
Flemming W (1875) Studien über die Entwicklungsgeschichte der Najaden. Sitzungsber Akad Wissensch Wien 71:81–147
Flemming W (1891) Verhandlungen der anatomischen Gesellschaft, Jahrg. 6, München (found as item 60 vol II in Collected Papers of Walther Flemming in M.B.L. Library, reprint collection)
Fukasawa K (2012) Molecular links between centrosome duplication and other cell cycle associated events. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap, 10. Springer, New York
Fukasawa K, Choi T, Kuriyama R, Rulong S, Vande Woude GF (1996) Abnormal centrosome amplification in the absence of p53. Science 271:1744–1747
Gauthier LR et al (2004) Huntingtin controls neurotrophic support and survival of neurons by enhancing BDNF vesicular transport along microtubules. Cell 118:127–138
George MA, Pickering SJ, Braude PR, Johnson MH (1996) The distribution of α- and γ-tubulin in fresh and aged human and mouse oocytes exposed to cryoprotectant. Mol Hum Reprod 2(6):445–456
Gillingham AK, Munro S (2000) The PACT domain, a conserved centrosomal targeting motif in the coiled-coil proteins AKAP450 and pericentrin. EMBO Rep 1:524–529
Goldspink DA, Rookyard C, Tyrrell BJ, Gadsby J, Perkins J, Lund EK, Galjart N, Thomas P, Wileman T, Mogensen MM (2017) Ninein is essential for apico-basal microtubule formation and CLIP-170 facilitates its redeployment to non-centrosomal microtubule organizing centres. Open Biol
Goodwin SS, Vale RD (2010) Patronin regulates the microtubule network by protecting microtubule minus ends. Cell 143:263–274
Gopalakrishnan J et al (2011) Sas-4 provides a scaffold for cytoplasmic complexes and tethers them in a centrosome. Nat Commun 2:359
Goud AP, Goud PT, Diamond MP, Abu-Soud HM (2005a) Nitric oxide delays oocyte aging. Biochemistry 44:11361–11368
Goud AP, Goud PT, Diamond MP, Van Oostveldt P, Hughes MR (2005b) Microtubule turnover in ooplasm biopsy reflects ageing phenomena in the parent oocyte. Reprod Biomed Online 11:43–52
Habermann K, Lange BM (2012) New insights into subcomplex assembly and modifications of centrosomal proteins. Cell Div 7:17
Harada A, Takei Y, Kanai Y, Tanaka Y, Nonaka S, Hirokawa N (1998) Golgi vesiculation and lysosome dispersion in cells lacking cytoplasmic dynein. J Cell Biol 141:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.141.1.51
Harjes P, Wanker EE (2003) The hunt for huntingtin function: interaction partners tell many different stories. Trends Biochem Sci 28:425–433
Hassounah NB, Bunch TA, McDermott KM (2012) Molecular pathways: the role of primary cilia in cancer progression and therapeutics with a focus on hedgehog signaling. Clin Cancer Res 18(9):2429–2435
He Y, Francis F, Myers KA, Yu W, Black MM, Baas PW (2005) Role of cytoplasmic dynein in the axonal transport of microtubules and neurofilaments. J Cell Biol 168:697–703
Hildebrandt F, Otto E (2005) Cilia and centrosomes: a unifying pathogenic concept for cystic kidney disease? Nat Rev Genet 6:928–940
Ho YS, Duh JS, Jeng JH, Wang YJ, Liang YC, Lin CH, Tseng CJ, Yu CF, Chen RJ, Lin JK (2001) Griseofulvin potentiates antitumorigenesis effects of nocodazole through induction of apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer 91:393–401
Ho SM, Tang WY, Belmonte de FJ, Prins GS (2006) Developmental exposure to estradiol and bisphenol A increases susceptibility to prostate carcinogenesis and epigenetically regulates phosphodiesterase type 4 variant 4. Cancer Res 66:5624–5632
Hoppeler-Lebel A, Celati C, Bellett G, Mogensen MM, Klein-Hitpass L, Bornens M, Tassin AM (2007) Centrosomal CAP350 protein stabilises microtubules associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci 120:3299–3308. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.013102
Huang B (1990) Genetics and biochemistry of centrosomes and spindle poles. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2:28–32
Huang JC, Yan LY, Lei ZL, Miao YL, Shi LH, Yang JW, Wang Q, Ouyang YC, Sun QY, Chen DY (2007) Changes in histone acetylation during postovulatory aging of mouse oocyte. Biol Reprod 77:666–670
Hyder CL, Isoniemi KO, Torvaldson ES, Eriksson JE (2011) Insights into intermediate filament regulation from development to ageing. J Cell Sci 124:1363–1372
Imai Y, Soda M, Takahashi R (2000) Parkin suppresses unfolded protein stress-induced cell death through its E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity. J Biol Chem 275:35661–35664
Infante C, Ramos-Morales F, Fedriani C, Bornens M, Rios RM (1999) GMAP-210, A cis-Golgi networkassociated protein, is a minus end microtubulebinding protein. J Cell Biol 145:83–98. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.145.1.83
Inoko A, Matsuyama M, Goto H, Ohmuro-Matsuyama Y, Hayashi Y, Enomoto M, Ibi M, Urano T, Yonemura S, Kiyono T, Izawa I, Inagaki M (2012) Trichoplein and Aurora A block aberrant primary cilia assembly in proliferating cells. J Cell Biol 197(3):391–405
Ishikawa H, Marshall WF (2011) Ciliogenesis: building the cell’s antenna. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:222–234
Ishikawa A, Tsuji S (1996) Clinical analysis of 17 patients in 12 Japanese families with autosomal-recessive type juvenile parkinsonism. Neurology 47:160–166
Izzi L, Attisano L (2004) Regulation of the TGFβ signaling pathway by ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Oncogene 23:2071–2078
Jechlinger M, Sommer A, Moriggl R et al (2006) Autocrine PDGFR signaling promotes mammary cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest 116:1561–1570
Jenkins S, Wang J, Eltoum I, Desmond R, Lamartiniere CA (2011) Chronic oral exposure to bisphenol A results in a nonmonotonic dose response in mammary carcinogenesis and metastasis in MMTV-erbB2 mice. Environ Health Perspect 119:1604–1609
Jeseta M, Petr J, Krejcova T, Chmelikova E, Jilek F (2008) In vitro ageing of pig oocytes: effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A. Zygote 16:145–152
Kadavath H, Hofele RV, Biernat J, Kumar S, Tepper K, Urlaub H, Mandelkow E, Zweckstetter M (2015) Tau stabilizes microtubules by binding at the interface between tubulin heterodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:7501–7506
Kammerer S, Roth RB, Hoyal CR, Reneland R, Marnellos G, Kiechle M, Schwarz-Boeger U, Griffiths LR, Ebner F, Rehbock J, Cantor CR, Nelson MR, Brown A (2005) Association of the NuMA region on chromosome 11q13 with breast cancer susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(6):2004–2009
Karanikolas B, Sütterlin C (2012) Functional associations between the Golgi apparatus and the centrosome in mammalian cells. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap. 7. Springer, New York
Katsanis N (2004) The oligogenic properties of Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 13:R65–R71
Keri RA, Ho SM, Hunt PA, Knudsen KE, Soto AM et al (2007) An evaluation of evidence for the carcinogenic activity of bisphenol A. Reprod Toxicol 24:240–252
Kikuchi K, Naito K, Noguchi J, Shimada A, Kaneko H, Yamashita M, Aoki F, Tojo H, Toyoda Y (2000) Maturation/M-phase promoting factor: a regulator of aging in porcine oocytes. Biol Reprod 63:715–722
Kikuchi K, Naito K, Noguchi J, Kaneko H, Tojo H (2002) Maturation/M-phase promoting factor regulates aging of porcine oocytes matured in vitro. Cloning Stem Cells 4:211–222
Kim NH, Moon SJ, Prather RS, Day BN (1996) Cytoskeletal alteration in aged porcine oocytes and parthenogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev 43:513–518
Kim JC et al (2004) The Bardet–Biedl protein BBS4 targets cargo to the pericentriolar region and is required for microtubule anchoring and cell cycle progression. Nat Genet 36:462–470
Kitada T et al (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Kobayashi T, Dynlacht BD (2011) Regulating the transition from centriole to basal body. J Cell Biol 193:435–444
Korzeniewski N, Duensing S (2012) Disruption of centrosome duplication control and induction of mitotic instability by the high-risk human papillomavirus oncoproteins E6 and E7. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap, 12. Springer, New York
Korzeniewski N, Wheeler S, Chatterjee P et al (2010) A novel role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in centrosome amplification—implications for chemoprevention. Mol Cancer 9:153
Krämer A, Maier B, Bartek J (2011) Centrosome clustering and chromosomal (in)stability: a matter of life and death. Mol Oncol 5:324–335
Krämer A, Anderhub S, Maier B (2012) Mechanisms and consequences of centrosome clustering in cancer cells. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap, 17. Springer, New York
Kulaga HM et al (2004) Loss of BBS proteins causes anosmia in humans and defects in olfactory cilia structure and function in the mouse. Nat Genet 36:994–998
Leber B, Maier B, Fuchs F, Chi J, Riffel P, Anderhub S, Wagner L, Ho AD, Salisbury JL, Boutros M, Krämer A (2010) Proteins required for centrosome clustering in cancer cells. Sci Transl Med 2(33ra38):1–11
Lee JH, Campbell KH (2008) Caffeine treatment prevents age-related changes in ovine oocytes and increases cell numbers in blastocysts produced by somatic cell nuclear transfer. Cloning Stem Cells 10:381–390
Levy YY, Lai EY, Remillard SP, Heintzelman MB, Fulton C (1996) Centrin is a conserved protein that forms diverse associations with centrioles and MTOCs in Naegleria and other organisms. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 33:298–323
Li Y, Hu J (2015) Small GTPases act as cellular switches in the context of Cilia. In: Schatten H (ed) The cytoskeleton in health and disease. Springer, New York
Li Y, Lu W, Chen D, Boohaker RJ, Zhai L, Padmalayam I, Wennerberg K, Xu B, Zhang W (2015) KIFC1 is a novel potential therapeutic target for breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 16:1316–1322
Liang CG, Su YQ, Fan HY, Schatten H, Sun QY (2007) Mechanisms regulating oocyte meiotic resumption: roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol 21(9):2037–2055
Ling H, Peng L, Seto E, Fukasawa K (2012) Suppression of centrosome duplication and amplification by deacetylases. Cell Cycle 11:3779–3791
Lingle WL, Salisbury JL (1999) Altered centrosome structure is associated with abnormal mitoses in human breast tumors. Am J Pathol 155:1941–1951
Lingle WL, Salisbury JL (2000) The role of the centrosome in the development of malignant tumors. Curr Top Dev Biol 49:313–329
Liu S, Ginestier C, Ou SJ et al (2011) Breast cancer stem cells are regulated by mesenchymal stem cells through cytokine networks. Cancer Res 71(2):614–624
Lutz W, Lingle WL, McCormick D, Greenwood TM, Salisbury JL (2001) Phosphorylation of centrin during the cell cycle and its role in centriole separation preceding centrosome duplication. J Biol Chem 276:20774–20780
Ly DH, Lockhart DJ, Lerner RA, Schultz PG (2000) Mitotic misregulation and human aging. Science 287:2486–2492
Manandhar G, Schatten H, Sutovsky P (2005) Centrosome reduction during gametogenesis and its significance. Biol Repro 72:2–13
Marchetti F, Mailhes JB, Bairnsfather L, Nandy I, London SN (1996) Dose-response study and threshold estimation of griseofulvin induced aneuploidy during female mouse meiosis I and II. Mutagenesis 11:195–200
Maro B, Howlett SK, Webb M (1985) Non-spindle microtubule organizing centers in metaphase II-arrested mouse oocytes. J Cell Biol 101:1665–1672
Mazia D, Harris PJ, Bibring T (1960) The multiplicity of the mitotic centers and the time-course of their duplication and separation. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 7:l–20
Meng W, Mushika Y, Ichii T, Takeichi M (2008) Anchorage of microtubule minus ends to adherens junctions regulates epithelial cell-cell contacts. Cell 135:948–959
Mennella V, Agard DA, Huang B, Laurence Pelletier L (2013) Amorphous no more: subdiffraction view of the pericentriolar material architecture. Trends Cell Biol 1–10
Merdes A, Cleveland DA (1998) The role of NuMA in the interphase nucleus. J Cell Sci 111:71–79
Miao YL, Kikuchi K, Sun QY, Schatten H (2009a) Oocyte aging: cellular and molecular changes, developmental potential and reversal possibility. Human Reprod Update 15(5):573–585
Miao YL, Sun Q-Y, Zhang X, Zhao JG, Zhao MT, Spate L, Prather RS, Schatten H (2009b) Centrosome abnormalities during porcine oocyte aging. Environ Mol Mutagen 50(8):666–671
Miao Y-L, Zhang X, Zhao JG, Spate L, Zhao MT, Murphy CN, Prather RS, Sun Q-Y, Schatten H (2012) Effects of griseofulvin on in vitro porcine oocyte maturation and embryo development. Environ Mol Mutagen 53(7):561–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.21717
Michaud EJ, Yoder BK (2006) The primary cilium in cell signaling and cancer. Cancer Res 66:6463–6467
Mittal K, Choi DH, Klimov S, Pawar S, Kaur R, Mitra AK, Gupta MV, Sams R, Cantuaria G, Rida PCG, Aneja R (2016) A centrosome clustering protein, KIFC1, predicts aggressive disease course in serous ovarian adenocarcinomas. J Ovar Res 9:17:1–11
Mogensen MM (2004) Microtubule organizing centers in polarized epithelial cells. In: Nigg E (ed) Centrosomes in development and disease. Wiley, Weinheim, pp 299–319
Mogensen MM, Malik A, Piel M, Bouckson-Castaing V, Bornens M (2000) Microtubule minus-end anchorage at centrosomal and non-centrosomal sites: the role of ninein. J Cell Sci 113:3013–3023
Moritz M, Agard DA (2001) Gamma-tubulin complexes and microtubule nucleation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11:174–181
Moritz M, Zheng Y, Alberts BM, Oegema K (1998) Recruitment of the g-tubulin ring complex to Drosophila salt stripped centrosomes. J Cell Biol 142:775e786
Muroyama A, Lechler T (2017) Microtubule organization, dynamics and functions in differentiated cells. Development 144:3012–3021. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.153171
Muroyama A, Seldin L, Lechler T (2016) Divergent regulation of functionally distinct gamma-tubulin complexes during differentiation. J Cell Biol 213:679–692
Müsch A (2004) Microtubule organization and function in epithelial cells. Traffic 5:1–9
Nauli SM et al (2003) Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells. Nature Genet 33:129–137
Nigg EA (2002) Centrosome aberrations: cause or consequence of cancer progression? Nat Rev Cancer 2:815–825
Nigg EA, Raff JW (2009) Centrioles, centrosomes, and cilia in health and disease. Cell 139:663–678
Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE (2003) Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 348:1356–1364
Oddoux S, Zaal KJ, Tate V, Kenea A, Nandkeolyar SA, Reid E, Liu W, Ralston E (2013) Microtubules that form the stationary lattice of muscle fibers are dynamic and nucleated at Golgi elements. J Cell Biol 203:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201304063
Pacchierotti F, Ranaldi R, Eichenlaub-Ritter U, Attia S, Adler ID (2008) Evaluation of aneugenic effects of bisphenol A in somatic and germ cells of the mouse. Mutat Res 651(1–2):64–70
Paintrand et al (1992) Centrosome organization their sensitivity and centriole architecture: to divalent cations. J Struct Biol 108:107e128
Pan J, Snell W (2007) The primary cilium: keeper of the key to cell division. Cell 129:1255–1257
Panda D, Rathinasamy K, Santra MK, Wilson L (2005) Kinetic suppression of microtubule dynamic instability by griseofulvin: implications for its possible use in the treatment of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9878–9883
Peters JM (2002) The anaphase-promoting complex: proteolysis in mitosis and beyond. Mol Cell 9:931–943
Pickart CM, Cohen RE (2004) Proteasomes and their kin: proteases in the machine age. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:177–187
Pihan GA et al (1998) Centrosome defects and genetic instability in malignant tumors. Cancer Res 58:3974–3985
Pihan GA, Wallace J, Zhou Y, Doxsey SJ (2003) Centrosome abnormalities and chromosome instability occur together in pre-invasive carcinomas. Cancer Res 63:1398–1404
Pimenta-Marques A, Bento I, Lopes CA, Duarte P, Jana SC, Bettencourt-Dias M (2016) A mechanism for the elimination of the female gamete centrosome in Drosophila melanogaster. Science 353:aaf4866
Prins GS, Ye SH, Birch L, Ho SM, Kannan K (2011) Serum bisphenol A pharmacokinetics and prostate neoplastic responses following oral and subcutaneous exposures in neonatal Sprague–Dawley rats. Reprod Toxicol 31:1–9
Prosser SL, Fry AM (2012) Regulation of the centrosome cycle by protein degradation. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap. 9. Springer, New York
Qiao J, Wang ZB, Feng HL, Miao YL, Wang Q, Yu Y, Wei YC, Yan J, Wang WH, Shen W, Sun SC, Schatten H, Sun QY (2014) The root of reduced fertility in aged women and possible therapeutic options: current status and future perspectives. Mol Aspects Med 38:54–85
Quarmby LM, Parker JDK (2005) Cilia and the cell cycle? J Cell Biol 169(5):707–710
Rausell F, Pertusa JF, Gomez-Piquer V, Hermenegildo C, Garcia-Perez MA, Cano A, Tarin JJ (2007) Beneficial effects of dithiothreitol on relative levels of glutathione S-transferase activity and thiols in oocytes, and cell number, DNA fragmentation and allocation at the blastocyst stage in the mouse. Mol Reprod Dev 74:860–869
Rebacz B, Larsen TO, Clausen MH, Ronnest MH, Loffler H, Ho AD, Krämer A (2007) Identification of griseofulvin as an inhibitor of centrosomal clustering in a phenotype-based screen. Cancer Res 67:6342–6350
Rios RM (2014) The centrosome–Golgi apparatus nexus. Phil Trans R Soc B 369:20130462. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0462
Rios RM, Sanchis A, Tassin AM, Fedriani C, Bornens M (2004) GMAP-210 recruits gamma-tubulin complexes to cis-Golgi membranes and is required for Golgi ribbon formation. Cell 118:323–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.012
Roll-Mecak A, McNally FJ (2010) Microtubule-severing enzymes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:96–103
Roth J, Yam GH, Fan J, Hirano K, Gaplovska-Kysela K, Le Fourn V, Guhl B, Santimaria R, Torossi T, Ziak M, Zuber C (2008) Protein quality control: the who’s who, the where’s and therapeutic escapes. Histochem Cell Biol 129:163–177
Saladino C, Bourke E, Morrison CG (2012) Centrosomes, DNA damage and aneuploidy. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome, Chap. 13. Springer, New York
Salisbury JL (1995) Centrin, centrosomes, and mitotic spindle poles. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:39–45
Salisbury JL (2004) Centrosomes: Sfi1p and centrin unravel a structural riddle. Curr Biol 14:R27–R29
Salisbury JL, Suino KM, Busby R, Springett M (2002) Centrin-2 is required for centriole duplication in mammalian cells. Curr Biol 12:1287–1292
Sathasivam K et al (2001) Centrosome disorganization in fibroblast cultures derived from R6/2 Huntington’s disease (HD) transgenic mice and HD patients. Hum Mol Genet 10:2425–2435
Satir P, Christensen ST (2008) Structure and function of mammalian cilia. Histochem Cell Biol 129:687–693
Schatten H (1977) Untersuchungen über die Wirkung von Griseofulvin in Seeigeleiern und in Mammalierzellen. Universität Heidelberg; (effects of griseofulvin on sea urchin eggs and on mammalian cells. University of Heidelberg)
Schatten H (1994) Dithiothreitol prevents membrane fusion but not centrosome or microtubule organization during the first cell cycles in sea urchins. Cell Motil Cytoskel 27:59–68
Schatten H (2008) The mammalian centrosome and its functional significance. Histochem Cell Biol 129:667–686
Schatten H (2013) The Impact of Centrosome Abnormalities on Breast Cancer Development and Progression with a Focus on Targeting Centrosomes for Breast Cancer Therapy. Chapter 12. In: Cell and Molecular Biology of Breast Cancer. Edited by Heide Schatten, published by Springer Science and Business Media, LLC
Schatten H (2014) The role of centrosomes in cancer stem cell functions. In: Schatten H (ed) Cell and molecular biology and imaging of stem cells, first edition. Wiley, USA, chap 12, pp 259–279
Schatten H, Chakrabarti A (2004) Detection of centrosome structure in fertilized and artificially activated sea urchin eggs using immunofluorescence microscopy and isolation of centrosomes followed by structural characterization with field emission scanning electron microscopy. In: Schatten H (ed) Methods in molecular biology, vol 253: germ cell protocols: vol 1 sperm and oocyte analysis. Humana Press Inc, Totowa, pp 151–164
Schatten H, Ripple M (2018) The impact of centrosome pathologies on prostate cancer development and progression. In: Schatten H (ed) Cell and molecular biology of prostate cancer: updates, insights and new frontiers. Springer, New York
Schatten H, Sun QY (2010) The role of centrosomes in fertilization, cell division and establishment of asymmetry during embryo development. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:174–184
Schatten H, Sun QY (2011a) Centrosome dynamics during meiotic spindle formation in oocyte maturation. Mol Reprod Dev 78:757–768
Schatten H, Sun QY (2011b) New insights into the role of centrosomes in mammalian fertilisation and implications for ART. Reproduction 142:793–801
Schatten H, Sun QY (2011c) The significant role of centrosomes in stem cell division and differentiation. Microsc Microanal 17(4):506–512
Schatten H, Sun Q-Y (2012) Nuclear-centrosome relationships during fertilization, cell division, embryo development, and in somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) embryos. In: Schatten H (ed) The centrosome. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC
Schatten H, Sun QY (2013) Chromosome behavior and spindle formation in mammalian oocytes. In: Trounson (ed) Biology and pathology of the oocyte. Gosden & Eichenlaub-Ritter: Biology & Pathology of the Oocyte 2nd Edition. Cambridge University Press, New York
Schatten H, Sun QY (2014) Posttranslationally modified tubulins and other cytoskeletal proteins: Their role in gametogenesis, oocyte maturation, fertilization and pre-implantation embryo development. In Sutovsky P (ed) Posttranslational protein modifications in the reproductive system. Springer, New York
Schatten H, Sun QY (2015a) Centrosome and microtubule functions and dysfunctions in meiosis: implications for age-related infertility and developmental disorders. Reprod Fertil Dev 27(6):934–943. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD14493
Schatten H, Sun Q-Y (2015b) Centrosome-microtubule interactions in health, disease, and disorders. In: Schatten H (ed) The cytoskeleton in health and disease. Springer, New York
Schatten H, Sun QY (2017) Cytoskeletal functions, defects, and dysfunctions affecting human fertilization and embryo development. In: Schatten H (ed) Human reproduction: updates and new horizons. Wiley, Hoboken
Schatten G, Schatten H, Bestor T, Balczon R (1982a) Taxol inhibits the nuclear movements during fertilization and induces asters in unfertilized sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol 94:455–465
Schatten H, Schatten G, Petzelt C, Mazia D (1982b) Effects of griseofulvin on fertilization and early development of sea urchins. Independence of DNA synthesis, chromosome condensation, and cytokinesis cycles from microtubule-mediated events. Eur J Cell Biol 27:74–87
Schatten G, Simerly C, Schatten H (1985) Microtubule configurations during fertilization, mitosis and early development in the mouse and the requirement for egg microtubule-mediated motility during mammalian fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4152–4156
Schatten H, Schatten G, Mazia D, Balczon R, Simerly C (1986) Behavior of centrosomes during fertilization and cell division in mouse oocytes and in sea urchin eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:105–109
Schatten H, Walter M, Mazia D, Biessmann H, Paweletz N, Coffe G, Schatten G (1987) Centrosome detection in sea urchin eggs with a monoclonal antibody against Drosophila intermediate filament proteins: characterization of stages of the division cycle of centrosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8488–8492
Schatten G, Simerly C, Asai DJ, Szöke E, Cooke P, Schatten H (1988) Acetylated α-tubulin in microtubules during mouse fertilization and early development. Dev Biol 130:74–86
Schatten H, Walter M, Biessmann H, Schatten G (1992) Activation of maternal centrosomes in unfertilized sea urchin eggs. Cell Motil Cytoskel 23:61–70
Schatten H, Chakrabarti A, Hedrick J (1999) Centrosome and microtubule instability in cells during aging. J Cell Biochem 74:229–241
Schatten H, Hueser CN, Chakrabarti A (2000a) From fertilization to cancer: the role of centrosomes in the union and separation of genomic material. Microsc Res Tech 49:420–427
Schatten H, Ripple M, Balczon R, Weindruch R, Taylor M (2000b) Androgen and taxol cause cell type specific alterations of centrosome and DNA organization in androgen-responsive LNCaP and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 76:463–477
Schatten H, Wiedemeier A, Taylor M, Lubahn D, Greenberg MN, Besch-Williford C, Rosenfeld C, Day K, Ripple M (2000c) Centrosome-centriole abnormalities are markers for abnormal cell divisions and cancer in the transgenic adenocarcinoma mouse prostate (TRAMP) model. Biol Cell 92:331–340
Schatten H, Hueser C, Chakrabarti A (2000d) Centrosome alterations induced by formamide cause abnormal spindle pole formations. Cell Biol Internat 24(9):611–620
Schatten H, Rawe VY, Sun QY (2012) Cytoskeletal architecture of human oocytes with focus on centrosomes and their significant role in fertilization. In: Nagy ZP, Varghese AC, Agarwal A (eds) Practical manual of in vitro fertilization: advanced methods and novel devices. Humana Press (Springer), New York
Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB (1979) Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature 277:665–667
Schnackenberg BJ, Palazzo RE (1999) Identification and function of the centrosome centromatrix. Biol Cell 91(6):429–438
Schnackenberg BJ, Hull DR, Balczon RD, Palazzo RE (2000) Reconstitution of microtubule nucleation potential in centrosomes isolated from Spisula solidissima oocytes. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 6):943–953
Schneider L, Clement CA, Teilmann SC et al (2005) PDGFR alpha signaling is regulated through the primary cilium in fibroblasts. Curr Biol 15:1861–1866
Schoffski P (2009) Polo-like kinase (PLK) inhibitors in preclinical and early clinical development in oncology. Oncologist 14:559–570
Sen GL, Reuter JA, Webster DE, Zhu L, Khavari PA (2010) DNMT1 maintains progenitor function in self-renewing somatic tissue. Nature 463:563–567
Sharma N, Berbari NF, Yoder BK (2008) Ciliary dysfunction in developmental abnormalities and diseases. Curr Top Dev Biol (85):371–427
Shimura H et al (2000) Familial Parkinson disease gene product, parkin, is a ubiquitin-protein ligase. Nat Genet 25:302–305
Sluder G, Begg DA (1985) Experimental analysis of the reproduction of spindle poles. J Cell Sci 76:35–51
Ślusarz A, Shenouda NS, Sakla MS, Drenkhahn SK, Narula AS, MacDonald RS, Besch-Williford CL, Lubahn DB (2010) Common botanical compounds inhibit the hedgehog signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 70(8):3382–3390
Son Y, Brady ST (2015) Post-translational modifications of tubulin: pathways to functional diversity of microtubules. Trends Cell Biol 25:125–136
Stinchcombe JC, Griffiths GM (2014) Communication, the centrosome and the immunological synapse. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369
Sun QY, Schatten H (2006) Multiple roles of NuMA in vertebrate cells: review of an intriguing multifunctional protein. Front Biosci 11:1137–1146
Sun Q-Y, Schatten H (2007) Centrosome inheritance after fertilization and nuclear transfer in mammals. In: Sutovsky P (ed) Somatic cell nuclear transfer, Landes Bioscience. Adv Exp Med Biol 591:58–71
Sütterlin C, Colanzi A (2010) The Golgi and the centrosome: building a functional partnership. J Cell Biol 188(5):621–628
Takahashi H et al (1994) Familial juvenile parkinsonism: clinical and pathologic study in a family. Neurology 44:437–441
Takahashi M, Shibata H, Shimakawa M, Miyamoto M, Mukai H, Ono Y (1999) Characterization of a novel giant scaffolding protein, CG-NAP, that anchors multiple signaling enzymes to centrosome and the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem 274:17:267–217 274. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.24.17267
Tang N, Marshall WF (2012) Centrosome positioning in vertebrate development. J Cell Sci 125:4951e4961
Tang WY, Morey LM, Cheung YY, Birch L, Prins GS et al (2012) Neonatal exposure to estradiol/bisphenol A alters promoter methylation and expression of Nsbp1 and Hpcal1 genes and transcriptional programs of Dnmt3a/b and Mbd2/4 in the rat prostate gland throughout life. Endocrinology 153:42–55
Tarapore P, Ying J, Ouyang B, Burke B, Bracken B, Ho S-M (2014) Exposure to bisphenol A correlates with early-onset prostate cancer and promotes centrosome amplification and anchorage-independent growth in vitro. PLoS One 9(3):e90332. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090332
Tarin JJ, Ten J, Vendrell FJ, Cano A (1998) Dithiothreitol prevents age-associated decrease in oocyte/conceptus viability in vitro. Hum Reprod 13:381–386
Tatone C, Carbone MC, Gallo R, Delle Monache S, Di Cola M, Alesse E, Amicarelli F (2006) Age-associated changes in mouse oocytes during postovulatory in vitro culture: possible role for meiotic kinases and survival factor BCL2. Biol Reprod 74:395–402
Thyberg J, Moskalewski S (1999) Role of microtubules in the organization of the Golgi complex. Exp Cell Res 246:263–279. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1998.4326
Tian XC, Lonergan P, Jeong BS, Evans AC, Yang X (2002) Association of MPF, MAPK, and nuclear progression dynamics during activation of young and aged bovine oocytes. Mol Reprod Dev 62:132–138
Uen YH, Liu DZ, Weng MS, Ho YS, Lin SY (2007) NF-kappaB pathway is involved in griseofulvin-induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis in HL-60 cells. J Cell Biochem 101(5):1165–1175
Valenstein ML, Roll-Mecak A (2016) Graded control of microtubule severing by tubulin glutamylation. Cell 164:911–921
Van Beneden E (1876) Contribution al’histoire de la vesiculaire germinative et du premier embryonnaire. Bull Acad R Belg 42:35–97
Veland IR, Awan A, Pedersen LB, Yoder BK, Christensen ST (2009) Primary cilia and signaling pathways in mammalian development, health and disease. Nephron Physiol 111:39–53
Verde I, Pahlke G, Salanova M, Zhang G, Wang S, Coletti D, Onuffer J, Jin SL, Conti M (2001) Myomegalin is a novel protein of the Golgi/centrosome that interacts with a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 276:11189–11198. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M006546200
Walsh CA (1999) Genetic malformations of the human cerebral cortex. Neuron 23:19–29
Wang Z, Wu T, Shi L, Zhang L, Zheng W, Qu JY, Niu R, Qi RZ (2010) Conserved motif of CDK5RAP2 mediates its localization to centrosomes and the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem 285:22658–22665. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.105965
Wang ZB, Schatten H, Sun QY (2011) Why is chromosome segregation error in oocytes increased with maternal. aging? Physiology 26(5):314–325
Wehland J, Herzog W, Weber K (1977) Interaction of griseofulvin with microtubules, microtubule protein and tubulin. J Mol Biol 111:329–342
Wheatley DN, Wang AM, Strugnell GE (1996) Expression of primary cilia in mammalian cells. Cell Biol Int 20:73–81
Wigley WC et al (1999) Dynamic association of proteasomal machinery with the centrosome. J Cell Biol 145:481–490
Wilkinson CJ, Andersen JS, Mann M, Nigg EA (2004) A proteomic approach to the inventory of the human centrosome. In: Nigg E (ed) Centrosomes in development and disease. Wiley, Weinheim, pp 125–142
Wojcik C, DeMartino GN (2003) Intracellular localization of proteasomes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:579–589
Wojcik C, Schroeter D, Wilk S, Lamprecht J, Paweletz N (1996) Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis centers in HeLa cells: indication from studies of an inhibitor of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome. Eur J Cell Biol 71:311–318
Woodruff JB, Wueseke O, Hyman AA (2014) Pericentriolar material structure and dynamics. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369
Wueseke O, Bunkenborg J, Hein MY, Zinke A, Viscardi V, Woodruff JB et al (2014) The Caenorhabditis elegans pericentriolar material components SPD-2 and SPD-5 are monomeric in the cytoplasm before incorporation into the PCM matrix. Mol Biol Cell 25:2984e2992
Wynshaw-Boris A, Gambello MJ (2001) LIS1 and dynein motor function in neuronal migration and development. Genes Dev 15:639–651
Xiao Y-X, Yang W-X (2016) KIFC1: a promising chemotherapy target for cancer treatment? Oncotarget 7(30):48656–48670
Xu Z, Abbott A, Kopf GS, Schultz RM, Ducibella T (1997) Spontaneous activation of ovulated mouse eggs: time-dependent effects on M-phase exit, cortical granule exocytosis, maternal messenger ribonucleic acid recruitment, and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate sensitivity. Biol Reprod 57:743–750
Xu X et al (1999) Centrosome amplification and a defective G2-M cell cycle checkpoint induce genetic instability in BRCA1 exon 11 isoform-deficient cells. Mol Cell 3:389–395
Yadav S, Puri S, Linstedt AD (2009) A primary role for Golgi positioning in directed secretion, cell polarity, wound healing. Mol Biol Cell 20:1728–1736. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E08-10-1077
Yadav S, Puthenveedu MA, Linstedt AD (2012) Golgin160 recruits the dynein motor to position the Golgi apparatus. Dev Cell 23:153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.05.023
Yang R, Feldman JL (2015) SPD-2/CEP192 and CDK are limiting for microtubule-organizing center function at the centrosome. Curr Biol 25:1924–1931
Yoder BK, Hou X, Guay-Woodford LM (2002) The polycystic kidney disease proteins, polycystin-1, polycystin-2, polaris, and cystin, are co-localized in renal cilia. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2508–2516
Young A, Dictenberg JB, Purohit A, Tuft R, Doxsey S (2000) Cytoplasmic dynein-mediated assembly of pericentrin and γ tubulin onto centrosomes. Mol Biol Cell 11:2047–2056
Zhang X, Chen MH, Wu X, Kodani A, Fan J, Doan R, Ozawa M, Ma J, Yoshida N, Reiter JF et al (2016) Cell-type-specific alternative splicing governs cell fate in the developing cerebral cortex. Cell 166:1147–1162. e1115
Zhao J, Ren Y, Jiang Q, Feng J (2003) Parkin is recruited to the centrosome in response to inhibition of proteasomes. J Cell Sci 116:4011–4019
Zhu X, Kaverina I (2013) Golgi as an MTOC: making microtubules for its own good. Histochem Cell Biol 140:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1119-4
Zilberman Y, Ballestrem C, Carramusa L, Mazitschek R, Khochbin S, Bershadsky A (2009) Regulation of microtubule dynamics by inhibition of the tubulin deacetylase HDAC6. J Cell Science 122:3531–3541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schatten, H., Sun, QY. Functions and dysfunctions of the mammalian centrosome in health, disorders, disease, and aging. Histochem Cell Biol 150, 303–325 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-018-1698-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-018-1698-1