Abstract
Purpose
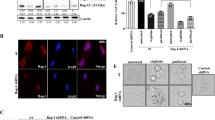
BCL2-associated athanogene 3 (BAG3), a co-chaperone of HSP70, is a cytoprotective and anti-apoptotic protein that acts against various stresses, including heat stress. Here, we examined the effect of BAG3 on the sensitivity of human retinoblastoma cells to hyperthermia (HT).
Methods
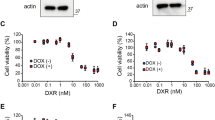
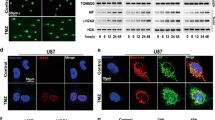
We examined the effects of BAG3 knockdown on the sensitivity of Y79 and WERI-Rb-1cells to HT (44 °C, 1 h) by evaluating apoptosis and cell proliferation using western blotting, real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR), flow cytometry, and a WST-8 assay kit. Furthermore, we examined the effects of activating nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) using western blotting and real time qPCR.
Results
HT induced considerable apoptosis along with the activation of caspase-3 and chromatin condensation. The sensitivity of Y79 and WERI-Rb-1 cells to HT was significantly enhanced by BAG3 knockdown. Compared to HT alone, the combination of BAG3 knockdown and HT reduced phosphorylation of the inhibitors of kappa B α (IκBα) and p65, a subunit of NF-κB, and degraded IκB kinase γ (IKKγ) during the recovery period after HT. Furthermore, BAG3 knockdown increased the HT-induced phosphorylation of ERK after HT treatment, and the ERK inhibitor U0126 significantly improved the viability of the cells treated with a combination of BAG3 knockdown and HT.
Conclusions
The silencing of BAG3 seems to enhance the effects of HT, at least in part, by maintaining HT-induced inactivity of NF-κB and the phosphorylation of ERK. These findings indicate that BAG3 may be a potential molecular target for modifying the outcomes of HT in retinoblastoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacCarthy A, Draper GJ, Steliarova-Foucher E, Kingston JE (2006) Retinoblastoma incidence and survival in European children (1978–1997). Report from the Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer 42:2092–2102
Classon M, Harlow E (2002) The retinoblastoma tumour suppressor in development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:910–917
Lin P, O'Brien JM (2009) Frontiers in the management of retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol 148:192–198
Shields CL, Lally SE, Leahey AM, Jabbour PM, Caywood EH, Schwendeman R, Shields JA (2014) Targeted retinoblastoma management: when to use intravenous, intra-arterial, periocular, and intravitreal chemotherapy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 5:374–385
Shields CL, De Potter P, Himelstein BP, Shields JA, Meadows AT, Maris JM (1996) Chemoreduction in the initial management of intraocular retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol 114:1330–1338
Shields CL, Shields JA, Needle M, de Potter P, Kheterpal S, Hamada A, Meadows AT (1997) Combined chemoreduction and adjuvant treatment for intraocular retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 104:2101–2111
Inomata M, Kaneko A, Kunimoto T, Saijo N (2002) In vitro thermo- and thermochemo-sensitivity of retinoblastoma cells from surgical specimens. Int J Hyperthermia 18:50–61
Choi EK, Park SR, Lee JH, Chung HS, Ahn HE, Rhee YH, Lim BU, Park HJ (2003) Induction of apoptosis by carboplatin and hyperthermia alone or combined in WERI human retinoblastoma cells. Int J Hyperth 19:431–443
Abramson DH, Schefler AC (2004) Transpupillary thermotherapy as initial treatment for small intraocular retinoblastoma: technique and predictors of success. Ophthalmology 111:984–991
Shields CL, Santos MC, Diniz W, Gündüz K, Mercado G, Cater JR, Shields JA (1999) Thermotherapy for retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol 117:885–893
Parsell DA, Lindquist S (1993) The function of heat-shock proteins in stress tolerance: degradation and reactivation of damaged proteins. Ann Rev Genet 27:437–496
Ohtsuka K, Hata M (2000) Molecular chaperone function of mammalian Hsp70 and Hsp40- A review. Int J Hyperth 16:231–245
Garrido C, Brunet M, Didelot C, Zermati Y, Schmitt E, Kroemer G (2006) Heat shock proteins 27 and 70: anti-apoptotic proteins with tumorigenic properties. Cell Cycle 5:2592–2601
Takayama S, Xie Z, Reed JC (1999) An evolutionarily conserved family of Hsp70/Hsc70 molecular chaperone regulators. J Biol Chem 274:781–786
Rosati A, Ammirante M, Gentilella A, Basile A, Festa M, Pascale M, Marzullo L, Melisario MA, Tosco A, Franceschelli S, Moltedo O, Paqliuca G, Lerose R, Turco MC (2007) Apoptosis inhibition in cancer cells: a novel molecular pathway that involves BAG3 protein. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:1337–1342
Franceschelli S, Rosati A, Lerose R, De Nicola S, Turco MC, Pascale M (2008) Bag3 gene expression is regulated by heat shock factor 1. J Cell Physiol 215:575–577
Liao Q, Ozawa F, Friess H, Zimmermann A, Takayama S, Reed JC, Kleeff J, Büchler MW (2001) The anti-apoptotic protein BAG-3 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and induced by heat stress in pancreatic cancer cell lines. FEBS Lett 503:151–157
Kariya A, Tabuchi Y, Yunoki T, Kondo T (2013) Identification of common gene networks responsive to mild hyperthermia in human cancer cells. Int J Mol Med 32:195–202
Chiappetta G, Ammirante M, Basile A, Rosati A, Festa M, Monaco M, Vuttariello E, Pasquinelli R, Arra C, Zerilli M, Todaro M, Stassi G, Pezzullo L, Gentilella A, Tosco A, Pascale M, Marzullo L, Belisario MA, Turco MC, Leone A (2007) The antiapoptotic protein BAG3 is expressed in thyroid carcinomas and modulates apoptosis mediated by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:1159–1163
Staibano S, Mascolo M, Di Benedetto M, Vecchione ML, Ilardi G, Di Lorenzo G, Autorino R, Salerno V, Morena A, Rocco A, Turco MC, Morelli E (2010) BAG3 protein delocalisation in prostate carcinoma. Tumor Biol 31:461–469
Wang HQ, Liu BQ, Gao YY, Meng X, Guan Y, Zhang HY, Du ZX (2009) Inhibition of the JNK signalling pathway enhances proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis of kidney cancer cells by suppression of BAG3 expression. Br J Pharmacol 158:1405–1412
Festa M, Del Valle L, Khalili K, Franco R, Scognamiglio G, Graziano V, De Laurenzi V, Turco MC, Rosati A (2011) BAG3 protein is overexpressed in human glioblastoma and is a potential target for therapy. Am J Pathol 178:2504–2512
Suzuki M, Iwasaki M, Sugio A, Hishiya A, Tanaka R, Endo T, Takayama S, Saito T (2011) BAG3 (BCL2-associated athanogene 3) interacts with MMP-2 to positively regulate invasion by ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 303:65–71
Liu P, Xu B, Li J, Lu H (2009) BAG3 gene silencing sensitizes leukemic cells to Bortezomib-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett 583:401–406
Du ZX, Meng X, Zhang HY, Guan Y, Wang HQ (2008) Caspase-dependent cleavage of BAG3 in proteasome inhibitors-induced apoptosis in thyroid cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:894–898
Wang HQ, Liu HM, Zhang HY, Guan Y, Du ZX (2007) Transcriptional upregulation of BAG3 upon proteasome inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:381–385
Yunoki T, Kariya A, Kondo T, Hayashi A, Tabuchi Y (2013) The combination of silencing BAG3 and inhibition of the JNK pathway enhances hyperthermia sensitivity in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 335:52–57
Chuma M, Sakamoto N, Nakai A, Hige S, Nakanishi M, Natsuizaka M, Suda G, Sho T, Hatanaka K, Matsuno Y, Yokoo H, Kamiyama T, Taketomi A, Fujii G, Tashiro K, Hikiba Y, Fujimoto M, Asaka M, Maeda S (2014) Heat shock factor 1 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma development by activating nuclear factor-κB/mitogen-activated protein kinase. Carcinogenesis 35:272–281
Bassères DS, Baldwin AS (2006) Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 25:6817–6830
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS Jr (1996) TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science 274:784–787
Ammirante M, Rosati A, Arra C, Basile A, Falco A, Festa M, Pascale M, d'Avenia M, Marzullo L, Belisario MA, De Marco M, Barbieri A, Giudice A, Chiappetta G, Vuttariello E, Monaco M, Bonelli P, Salvatore G, Di Benedetto M, Deshmane SL, Khalili K, Turco MC, Leone A (2010) IKK{gamma} protein is a target of BAG3 regulatory activity in human tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:7497–7502
Rosati A, Basile A, Falco A, Avenia M, Festa M, Graziano V, De Laurenzi V, Arra C, Pascale M, Turco MC (2012) Role of BAG3 protein in leukemia cell survival and response to therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1826:365–369
Poulaki V, Mitsiades CS, Joussen AM, Lappas A, Kirchhof B, Mitsiades N (2002) Constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB activity is crucial for human retinoblastoma cell viability. Am J Pathol 161:2229–2240
Qu Y, Zhou F, Dai X, Wang H, Shi J, Zhang X, Wang Y, Wei W (2011) Clinicopathologic significances of nuclear expression of nuclear factor-κB transcription factors in retinoblastoma. J Clin Pathol 64:695–700
Falco A, Festa M, Basile A, Rosati A, Pascale M, Florenzano F, Nori SL, Nicolin V, Di Benedetto M, Vecchione ML, Arra C, Barbieri A, De Laurenzi V, Turco MC (2012) BAG3 controls angiogenesis through regulation of ERK phosphorylation. Oncogene 31:5153–5161
Xiao H, Cheng S, Tong R, Lv Z, Ding C, Du C, Xie H, Zhou L, Wu J, Zheng S (2014) BAG3 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest 94:252–261
Aravindan N, Shanmugasundaram K, Natarajan M (2009) Hyperthermia induced NFkappaB mediated apoptosis in normal human monocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 327:29–37
Kokura S, Yoshida N, Ueda M, Imamoto E, Ishikawa T, Takagi T, Naito Y, Okanoue T, Yoshikawa T (2003) Hyperthermia enhances tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis of a human gastric cancer cell line. Cancer Lett 201:89–96
Mattson D, Bradbury CM, Bisht KS, Curry HA, Spitz DR, Gius D (2004) Heat shock and the activation of AP-1 and inhibition of NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity: possible role of intracellular redox status. Int J Hyperth 20:224–233
Pajonk F, van Ophoven A, McBride WH (2005) Hyperthermia-induced proteasome inhibition and loss of androgen receptor expression in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:4836–4843
Yunoki T, Tabuchi Y, Hayashi A, Kondo T (2013) Inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 promotes hyperthermia sensitivity via inactivation of heat shock transcription factor 1 in human retinoblastoma cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:8353–8363
Park JB (2011) Protective effects of veskamide, enferamide, becatamide, and oretamide on H2O2-induced apoptosis of PC-12 cells. Phytomedicine 18:843–847
Furusawa Y, Iizumi T, Fujiwara Y, Zhao QL, Tabuchi Y, Nomura T, Kondo T (2012) Inhibition of checkpoint kinase 1 abrogates G2/M checkpoint activation and promotes apoptosis under heat stress. Apoptosis 17:102–112
Tabuchi Y, Sugahara Y, Ikegame M, Suzuki N, Kitamura K, Kondo T (2013) Genes responsive to low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast cells. Int J Mol Sci 14:22721–22740
Xia H, Karasawa K, Hanyu N, Chang TC, Okamoto M, Kiguchi Y, Kawakami M, Itazawa T (2006) Hyperthermia combined with intra-thoracic chemotherapy and radiotherapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int J Hyperth 22:613–621
Aktas M, de Jong D, Nuyttens JJ, van der Zee J, Wielheesen DH, Batman E, Burger CW, Ansink AC (2007) Concomitant radiotherapy and hyperthermia for primary carcinoma of the vagina: a cohort study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 133:100–104
Boiani M, Daniel C, Liu X, Hogarty MD, Marnett LJ (2013) The stress protein BAG3 stabilizes Mcl-1 protein and promotes survival of cancer cells and resistance to antagonist ABT-737. J Biol Chem 288:6980–6990
Zhang Y, Wang JH, Lu Q, Wang YJ (2012) Bag3 promotes resistance to apoptosis through BCL-2 family members in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep 27:109–113
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18:2195–2224
Rubinfeld H, Seger R (2005) The ERK cascade: a prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol 31:151–174
Park SW, Kim YI (2013) Triptolide induces apoptosis of PMA-treated THP-1 cells through activation of caspases, inhibition of NF-κB and activation of MAPKs. Int J Oncol 43:1169–1175
Wang X, Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2000) Requirement for ERK activation in cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275:39435–39443
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research B (24310046) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yunoki, T., Tabuchi, Y., Hayashi, A. et al. BAG3 protects against hyperthermic stress by modulating NF-κB and ERK activities in human retinoblastoma cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 253, 399–407 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2874-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2874-1