Abstract
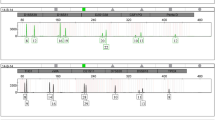
Forensic entomological evidence is employed to estimate minimum postmortem interval (PMImin), location, and identification of fly samples or human remains. Traditional forensic DNA analysis (i.e., STR, mitochondrial DNA) has been used for human identification from the larval gut contents. Forensic DNA phenotyping (FDP), predicting human appearance from DNA-based crime scene evidence, has become an established approach in forensic genetics in the past years. In this study, we aimed to recover human DNA from Lucilia sericata (Meigen 1826) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) gut contents and predict the eye and hair color of individuals using the HIrisPlex system. Lucilia sericata larvae and reference blood samples were collected from 30 human volunteers who were under maggot debridement therapy. The human DNA was extracted from the crop contents and quantified. HIrisPlex multiplex analysis was performed using the SNaPshot minisequencing procedure. The HIrisPlex online tool was used to assess the prediction of the eye and hair color of the larval and reference samples. We successfully genotyped 25 out of 30 larval samples, and the most SNP genotypes (87.13%) matched those of reference samples, though some alleles were dropped out, producing partial profiles. The prediction of the eye colors was accurate in 17 out of 25 larval samples, and only one sample was misclassified. Fourteen out of 25 larval samples were correctly predicted for hair color, and eight were misclassified. This study shows that SNP analysis of L. sericata gut contents can be used to predict eye and hair color of a corpse.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amendt J, Krettek R, Zehner R (2004) Forensic entomology. Naturwissenschaften. 91:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-003-0493-5
Gunn A (2001) Essential Forensic Biology, 2nd edn
Amendt J, Campobasso CP, Gaudry E, Reiter C, LeBlanc HN, Hall MJR (2007) Best practice in forensic entomology—standards and guidelines. Int J Legal Med 121:90–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-006-0086-x
Catts EP, Goff ML (1992) Forensic entomology in criminal investigations. Annu Rev Entomol 37:253–272. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.001345
Kulshrestha P, Satpathy D (2001) Use of beetles in forensic entomology. Forensic Sci Int 120:15–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-0738(01)00410-8
Amendt J, Richards CS, Campobasso CP, Zehner R, Hall MJR (2011) Forensic entomology: applications and limitations. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 7:379–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-010-9209-2
Amendt J (2010) Current concepts in forensic entomology. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-9684-6
Kondakci GO, Bulbul O, Shahzad MS, Polat E, Cakan H, Altuncul H, Filoglu G (2009) STR and SNP analysis of human DNA from Lucilia sericata larvae’s gut contents. Forensic Sci Int Genet Suppl Ser 2:178–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigss.2009.08.147
Di Luise E, Magni P, Staiti N, Spitaleri S, Romano C (2008) Genotyping of human nuclear DNA recovered from the gut of fly larvae. Forensic Sci Int Genet Suppl Ser 1:591–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigss.2007.10.075
Njau DG, Muge EKK, Kinyanjui PWW, Omwandho COAOA, Mukwana S (2016) STR analysis of human DNA from maggots fed on decomposing bodies: Assessment of the time period for successful analysis. Egypt J Forensic Sci 6:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejfs.2015.04.002
Powers J, van Oorschot RAH, Durdle A (2019) Investigation into the presence of human DNA in the various life stages of forensically relevant Calliphorid species. Aust J Forensic Sci 51:S234–S237. https://doi.org/10.1080/00450618.2019.1569143
Campobasso CP, Linville JG, Wells JD, Introna F (2005) Forensic genetic analysis of insect gut contents. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 26:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.paf.0000163832.05939.59
Vanin S (2016) Advances in forensic entomology in missing persons investigations. In: Handbook of Missing Persons. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40199-7_20
Li X, Cai JF, Guo YD, Xiong F, Zhang L, Feng H, Meng FM, Fu Y, Li JB, Chen YQ (2011) Mitochondrial DNA and STR analyses for human DNA from maggots crop contents: a forensic entomology case from central-southern China. Trop Biomed 28:333–338 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22041753
Zehner R, Amendt J, Krettek R (2004) STR typing of human DNA from fly larvae fed on decomposing bodies. J Forensic Sci 49:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1520/JFS2003248
Marchetti D, Arena E, Boschi I, Vanin S (2013) Human DNA extraction from empty puparia. Forensic Sci Int 229:e26–e29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2013.03.043
Chamoun CA, Couri MS, Garrido RG, Moura-Neto RS, Oliveira-Costa J (2020) Recovery & identification of human Y-STR DNA from immatures of chrysomya albiceps (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Simulation of sexual crime investigation involving victim corpse in state of decay. Forensic Sci Int 310:110239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2020.110239
Wells JD, Introna F, Di Vella G, Campobasso CP, Hayes J, Sperling FAH (2001) Human and insect mitochondrial DNA analysis from Maggots. J Forensic Sci 46. https://doi.org/10.1520/jfs15022j
Linville JG, Hayes J, Wells JD (2004) Mitochondrial DNA and STR analyses of maggot crop contents: effect of specimen preservation technique. J Forensic Sci 49:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1520/jfs2003266
Butler JM (2012) Single nucleotide polymorphisms and applications. In: Advanced Topics in Forensic DNA Typing. Elsevier, pp 347–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374513-2.00012-9
Pontes L, de Sousa JC, Medeiros R (2017) SNPs and STRs in forensic medicine. A strategy for kinship evaluation. Arch Med Sadowej Kryminol 67:226–240. https://doi.org/10.5114/amsik.2017.73194
Kayser M (2015) Forensic DNA Phenotyping: predicting human appearance from crime scene material for investigative purposes. Forensic Sci Int Genet 18:33–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.02.003
Walsh S, Liu F, Ballantyne KN, van Oven M, Lao O, Kayser M (2011) IrisPlex: A sensitive DNA tool for accurate prediction of blue and brown eye colour in the absence of ancestry information. Forensic Sci Int Genet 5:170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2010.02.004
Walsh S, Liu F, Wollstein A, Kovatsi L, Ralf A, Kosiniak-Kamysz A, Branicki W, Kayser M (2013) The HIrisPlex system for simultaneous prediction of hair and eye colour from DNA. Forensic Sci Int Genet 7:98–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.07.005
Chaitanya L, Breslin K, Zuñiga S, Wirken L, Pośpiech E, Kukla-Bartoszek M, Sijen T, de Knijff P, Liu F, Branicki W, Kayser M, Walsh S (2018) The HIrisPlex-S system for eye, hair and skin colour prediction from DNA: introduction and forensic developmental validation. Forensic Sci Int Genet 35:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.04.004
Bulbul O, Zorlu T, Filoglu G (2020) Prediction of human eye colour using highly informative phenotype SNPs (PISNPs). Aust J Forensic Sci 52:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/00450618.2018.1484161
Walsh S, Chaitanya L, Clarisse L, Wirken L, Draus-Barini J, Kovatsi L, Maeda H, Ishikawa T, Sijen T, de Knijff P, Branicki W, Liu F, Kayser M (2014) Developmental validation of the HIrisPlex system: DNA-based eye and hair colour prediction for forensic and anthropological usage. Forensic Sci Int Genet 9:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2013.12.006
Chaitanya L, Pajnič IZ, Walsh S, Balažic J, Zupanc T, Kayser M (2017) Bringing colour back after 70 years: predicting eye and hair colour from skeletal remains of World War II victims using the HIrisPlex system. Forensic Sci Int Genet 26:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.10.004
Walsh S, Kayser M (2016) A practical guide to the HIrisPlex system: simultaneous prediction of eye and hair color from DNA. In: Methods in Molecular Biology, pp 213–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3597-0_17
Zupanič Pajnič I (2021) Identification of a Slovenian prewar elite couple killed in the Second World War. Forensic Sci Int 327:110994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2021.110994
Clark K, Evans L, Wall R (2006) Growth rates of the blowfly, Lucilia sericata, on different body tissues. Forensic Sci Int 156:145–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2004.12.025
Buckland PC, Smith KGV (1988) A manual of forensic entomology. Am J Archaeol 92:287. https://doi.org/10.2307/505635
Polat E (2010) Larva debridement therapy (LDT). Türk Aile HekDerg 14:188–191. https://doi.org/10.2399/tahd.10.188
Grassberger M, Reiter C (2001) Effect of temperature on Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae) development with special reference to the isomegalen- and isomorphen-diagram. Forensic Sci Int 120:32–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-0738(01)00413-3
Mukherjee S, Singh P, Tuccia F, Pradelli J, Giordani G, Vanin S (2019) DNA characterization from gut content of larvae of Megaselia scalaris (Diptera, Phoridae). Sci Justice 59:654–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scijus.2019.06.006
Chamoun CA, Couri MS, Louro ID, Garrido RG, Moura-Neto RS, Oliveira-Costa J (2019) Research Article In vitro recovery and identification of Y-STR DNA from Chrysomya albiceps ( Diptera, Calliphoridae) larvae fed a decomposing mixture of human semen and ground beef. Genet Mol Res 18:1–11. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr18189
Sanavio M, Tozzo P, Nespeca P, Caenazzo L (2019) “Mummified” human DNA extraction from larvae: a difficult genetic analysis. A case report and a brief review of the literature. Romanian J Leg Med 27:297–299. https://doi.org/10.4323/rjlm.2019.297
Qiagen (2012) QIAamp DNA investigator handbook, pp 1–55
Qiagen, QIAamp DNA Mini Kit, Genomic DNA. (2019). https://www.qiagen.com/us/products/discovery-translational-research/dna-rna-purification/dna/qiaamp-dna-mini-kit/#orderinginformation.
Tavacı İ, Şimşek SZ, Sapan V, Arslan C, Aşıcıoğlu F, Filoğlu G, Bülbül Ö (2021) Optimization and validation of HIrisPlex panel for predicting of the eye and hair color, Turkiye Klin. J Forensic Med Forensic Sci 18:10–20. https://doi.org/10.5336/forensic.2020-79686
Houck MM, Siegel JA (2015) Entomology. In: Fundam Forensic Science. Elsevier, pp 215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800037-3.00009-1
Stehr FW (2009) Pupa and puparium. In: Encyclopedia of Insects, 2nd edn. Elsevier, pp 862–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374144-8.00225-3
Canales Serrano A (2020) Forensic DNA phenotyping: a promising tool to aid forensic investigation. Current situation. Span J Leg Med 46:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.remle.2020.01.002
Bulbul O, Filoglu G (2018) Development of a SNP panel for predicting biogeographical ancestry and phenotype using massively parallel sequencing. Electrophoresis 39:2743–2751. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201800243
Sari OI, Simsek SZ, Filoglu G, Bulbul O (2022) Predicting eye and hair color in a Turkish population using the HIrisPlex system. Genes (Basel) 13:2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112094
Straube D, Juen A (2013) Storage and shipping of tissue samples for DNA analyses: a case study on earthworms. Eur J Soil Biol 57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2013.04.001
Skowronek R, Tomsia M, Droździok K, Kabiesz J (2014) Insects feeding on cadavers as an alternative source of human genetic material. Arch Med Sadowej Kryminol 64:254–267. https://doi.org/10.5114/amsik.2014.50530
Cantu C, Bucheli S, Houston R (2022) Comparison of DNA extraction techniques for the recovery of bovine DNA from fly larvae crops. J Forensic Sci 67:1651–1659. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.15010
Kukla-Bartoszek M, Szargut M, Pośpiech E, Diepenbroek M, Zielińska G, Jarosz A, Piniewska-Róg D, Arciszewska J, Cytacka S, Spólnicka M, Branicki W, Ossowski A (2020) The challenge of predicting human pigmentation traits in degraded bone samples with the MPS-based HIrisPlex-S system. Forensic Sci Int Genet 47:102301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2020.102301
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are due to the individuals who volunteered to give larval and saliva samples. The authors would like to thank Sumeyye Zulal Simsek for technical help during the laboratory experiments.
Funding
The Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa Scientific Research and Projects Unit funded our research (Project No: 35843). ED and OB have received this grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Emre Deymenci, Gonul Filoglu, Erdal Polat, and Ozlem Bulbul contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Emre Deymenci and İlksen Sarı O. The first draft of the manuscript was written Emre Deymenci, İlksen Sarı O, and Ozlem Bulbul, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa, Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty (24.05.2021, number 96774), and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(XLSX 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deymenci, E., Sarı O, I., Filoglu, G. et al. Eye and hair color prediction of human DNA recovered from Lucilia sericata larvae. Int J Legal Med 138, 627–637 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-023-03112-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-023-03112-z