Abstract
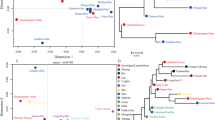
A total of 39 Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat (Y-STR) loci included in the advanced commercial six-dye multiplex system (AGCU Database Y30 kit) and a custom-designed four-dye multiplex system were investigated in 259 unrelated healthy Chinese males residing in Henan Province, central China. The haplotype diversity (HD) values were 0.99997 and 1.0000 for the six and four fluorescent-multiplex amplification systems, respectively. The discrimination capacity (DC) values were 0.9961 and 1.0000, respectively. When the 39 Y-STR loci were considered, 259 unique haplotypes were obtained in Henan Han individuals with both the haplotype diversity and discrimination capacity being 1.000. The gene diversity (GD) of 39 Y-STR loci in the studied group ranged from 0.3956 (DYS588) to 0.9990 (DYF403S1). Population comparisons between the Henan Han and 24 reference groups were performed. Both multidimensional scaling plots and phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that significant genetic differences existed between Henan Han and reference ethnic minorities of China, particularly the Tibetan, Uighur, and Mongolian populations. Moreover, the results indicated that 39 Y-STRs included in the two fluorescent-multiplex amplification systems are highly polymorphic and informative in the studied populations and can be employed as complementary tools for forensic application and human genetics research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kayser M (2017) Forensic use of Y-chromosome DNA: a general overview. Hum Genet 136:621–635
Alghafri R, Zupanič PI, Zupanc T et al (2017) Rapidly mutating Y-STR analyses of compromised forensic samples. Int J Legal Med 132:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-017-1600-z
Ballantyne KN, Ralf A, Aboukhalid R, Achakzai NM, Anjos MJ, Ayub Q, Balažic J, Ballantyne J, Ballard DJ, Berger B, Bobillo C, Bouabdellah M, Burri H, Capal T, Caratti S, Cárdenas J, Cartault F, Carvalho EF, Carvalho M, Cheng B, Coble MD, Comas D, Corach D, D’Amato ME, Davison S, de Knijff P, de Ungria MCA, Decorte R, Dobosz T, Dupuy BM, Elmrghni S, Gliwiński M, Gomes SC, Grol L, Haas C, Hanson E, Henke J, Henke L, Herrera-Rodríguez F, Hill CR, Holmlund G, Honda K, Immel UD, Inokuchi S, Jobling MA, Kaddura M, Kim JS, Kim SH, Kim W, King TE, Klausriegler E, Kling D, Kovačević L, Kovatsi L, Krajewski P, Kravchenko S, Larmuseau MHD, Lee EY, Lessig R, Livshits LA, Marjanović D, Minarik M, Mizuno N, Moreira H, Morling N, Mukherjee M, Munier P, Nagaraju J, Neuhuber F, Nie S, Nilasitsataporn P, Nishi T, Oh HH, Olofsson J, Onofri V, Palo JU, Pamjav H, Parson W, Petlach M, Phillips C, Ploski R, Prasad SPR, Primorac D, Purnomo GA, Purps J, Rangel-Villalobos H, Rębała K, Rerkamnuaychoke B, Gonzalez DR, Robino C, Roewer L, Rosa A, Sajantila A, Sala A, Salvador JM, Sanz P, Schmitt C, Sharma AK, Silva DA, Shin KJ, Sijen T, Sirker M, Siváková D, Škaro V, Solano-Matamoros C, Souto L, Stenzl V, Sudoyo H, Syndercombe-Court D, Tagliabracci A, Taylor D, Tillmar A, Tsybovsky IS, Tyler-Smith C, van der Gaag KJ, Vanek D, Völgyi A, Ward D, Willemse P, Yap EPH, Yong RYY, Pajnič IZ, Kayser M (2014) Toward male individualization with rapidly mutating y-chromosomal short tandem repeats. Hum Mutat 35:1021–1032. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22599
Ballantyne KN, Keerl V, Wollstein A, Choi Y, Zuniga SB, Ralf A, Vermeulen M, de Knijff P, Kayser M (2012) A new future of forensic Y-chromosome analysis: rapidly mutating Y-STRs for differentiating male relatives and paternal lineages. Forensic Sci Int Genet 6:208–218
Gopinath S, Zhong C, Nguyen V, Ge J, Lagacé RE, Short ML, Mulero JJ (2016) Developmental validation of the Yfiler(®) Plus PCR Amplification Kit: an enhanced Y-STR multiplex for casework and database applications. Forensic Sci Int Genet 24:164–175
D’Amato ME, Bajic VB, Davison S (2011) Design and validation of a highly discriminatory 10-locus Y-chromosome STR multiplex system. Forensic Sci Int Genet 5:122–125
Huang Y, Ma Y, Mo X et al (2016) Establishment of fluorescent-multiplex amplification system of 10 Y-STR loci and its application. Chin J Forensic Med 31:238–241. https://doi.org/10.13618/j.issn.1001-5728.2016.03.005
Köchl S, Niederstätter H, Parson W (2005) DNA extraction and quantitation of forensic samples using the phenol-chloroform method and real-time PCR. Methods Mol Biol 297:13–29
Poetsch M, Bajanowski T, Pfeiffer H (2012) The publication of population genetic data in the International Journal of Medicine: guidelines. Int J Legal Med 126:489–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-012-0700-z14.
Wang M, Wang Z, Zhang Y, He G, Liu J, Hou Y (2017) Forensic characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of two Han populations from the southern coastal regions of China using 27 Y-STR loci. Forensic Sci Int Genet 31:e17–e23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.10.009
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Acknowledgments
We thank all sample donors for their contribution to this work and all those who helped with sample collection. In addition, we would like to thank all contributors of the YHRD database. We also would like to express our acknowledgment to Senior Research Fellow, PhD, Sharon O’Toole, Department of Histopathology, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland, for improving the English presentation.
Funding
This study was supported by Key scientific research projects of Henan Province (13A310849), Key Project of Henan Education Science during the 12th Five-Year Plan (2013-JKGHB-0035), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671873, 81273347).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Xinxiang Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Multidimensional Scaling plots of our studied populations (bold and red) and 24 reference Chinese populations based on PPY23 haplotypes. (GIF 16 kb)
Fig. S2
The phylogenetic tree between the studied populations (bold and red) and 24 reference Chinese populations based on PPY23 haplotypes. (GIF 30 kb)
Table S1
The haplotype distributions and corresponding haplotype frequencies of 30 Y-chromosomal STRs included in AGCU Database Y30 Kit in the Han Chinese population residing in Henan Province (N = 259). (XLSX 48 kb)
Table S2
The haplotype distributions and corresponding haplotype frequencies of 10 Y-chromosomal STRs included in four-dye multiplex system in the Han Chinese population residing in Henan Province (N = 259). (XLSX 32 kb)
Table S3
The haplotype distributions and corresponding haplotype frequencies of 39 Y-chromosomal STRs in the Han Chinese population residing in Henan Province (N = 259). (XLSX 63 kb)
Table S4
Allele frequencies and GD values for 32 single-copy Y-STRs in the Chinese Han population residing in Henan Province (n = 259). (XLSX 19 kb)
Table S5
Allelic combinations frequencies and GD values for multi-copy Y-STRs in the Chinese Han populations residing in Henan Province (n = 259). (XLSX 23 kb)
Table S6
The pairwise genetic distances between Henan Han and 24 reference Chinese population. (XLSX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Guo, L., Wang, M. et al. Genetic analysis of 39 Y-STR loci in a Han population from Henan province, central China. Int J Legal Med 133, 95–97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1852-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1852-2