Abstract
Purpose
To conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated the surgical outcomes of type-1 tympanoplasty with and without gelfoam middle ear packing.
Methods
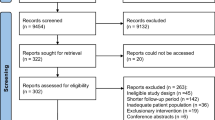
PubMed, CENTRAL, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases were screened from inception until October 2022. The included RCTs were evaluated for risk of bias, and the quality of each outcome was assessed according to the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) system.
Results
Nine RCTs with 773 participants (gelfoam = 381 and non-gelfoam = 392) were analyzed. The overall study quality varied: low risk (n = 4 RCTs), some concerns (n = 3 RCTs), and high risk (n = 2 RCTs). There were no significant differences between both arms regarding the graft uptake rate (moderate certainty), hearing improvement rate (moderate certainty), type of impedance audiometry (moderate certainty), and ear discharge (low certainty). The mean change in air–bone gap was significantly higher in the non-gelfoam arm compared with the gelfoam arm (low certainty). However, the non-gelfoam group had superior hearing improvement in only the early postoperative period (i.e., one month); however, after two, three, and six months, there were no significant differences between both arms. The rate of ear fullness was significantly higher in the gelfoam arm compared with the non-gelfoam arm (moderate certainty).
Conclusion
Among patients undergoing type-1 tympanoplasty, the surgical outcomes did not significantly differ between both arms. The practice of middle ear packing with gelfoam needs to be standardized.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data are available within the manuscript and its supplemental files.
Code availability
Review Manager Software version 5.4.0. for Windows.
References
Joseph RB (1962) The effect of absorbable gelatin sponge preparations and other agents on scar formation in the dog’s middle ear. An experimental histopathologic study. The Laryngoscope 72(11):1528–1548
Krupala JL, Gianoli GJ, Smith RA (1998) The efficacy of hyaluronic acid foam as a middle ear packing agent in experimental tympanoplasty. Otol Neurotol 19(5):546–50
Revesz G (1961) The use of lyophilized plasma substance in tympanoplasty. J Laryngol Otol 75(11):985–989
Hellström S, Salén B, Stenfors L-E (1983) Absorbable gelatin sponge (Gelfoam) in Otosurgery: one cause of undesirable postoperative results? an experimental study in the rat. Acta Otolaryngol 96(3–4):269–275
Correll JT (1945) Biologic investigations of a new absorbable sponge. Surg Gynecol Obstet 81:585–589
Shen Y, Mei Teh B, Friedland PL, Eikelboom RH, Atlas MD (2011) To pack or not to pack? A contemporary review of middle ear packing agents. Laryngoscope 121(5):1040–1048
Wagner WR, Pachence JM, Ristich J, Johnson PC (1996) Comparativein vitroanalysis of topical hemostatic agents. J Surg Res 66(2):100–108
Goncalves S, Chiossone-Kerdel JA, Bianco AS, Ercolino JM, Hernandez-Rojas J (2015) Effect of absorbable gelatin sponge in the middle ear: in vitro and in vivo animal model. Acta Otolaryngol 135(1):14–25
Liening DA, Lundy L, Silberberg B, Finstuen K (1997) A comparison of the biocompatibility of three absorbable hemostatic agents in the rat middle ear. Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 116(4):454–457
Higgins JPT, Green S, Collaboration C (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley-Blackwell, NewYork
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev 10(1):1–11
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366:l4898
Handbook G, Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A (2013) Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). GRADE Working Group 2013
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(7109):629–634
Higgins JPT (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Bhavana K, Jha RK, Majumdar S, Nikhil (2022) Is gelfoam necessary for middle ear surgery: a comparative study of the results of tympanoplasty with and without gelfoam in the middle ear. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74:281–7
Ghiasi S, Seyed TSJ (2008) Tympanoplasty without use of gelfoam in the middle ear. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74(Suppl 1):281–7
Han JS, Han JJ, AlAhmari YD, Park JM, Seo JH, Park SY et al (2021) Effect of middle ear gelfoam on hearing and healing process after tympanoplasty: a prospective randomized case-control study. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg 42(1):102767
Kumar S, Ambastha R, Thakur RP (2021) Type 1 tympanoplasty in the middle ear with and without gelfoam: a comparative assessment of the outcome. Int J Pharm Clin Res 13(5):101–106
Malick N, Gadag RP, Vidyashree KM, Puthukulangara S (2017) Comparative study of type 1 tympanoplasty with and without gelfoam in the middle ear. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 3(4):1036
Ramalingam V, Ramanathan M, Muraleedharan A, Kamindan K, Ramkumar T, Venugopal M et al (2019) A study on outcome of myringoplasty in dry ear (Quiescent/Inactive CSOM) without using gelfoam in middle ear. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71:1609–1614
Rohit Kumar Jha (2014) A comparative study of the results of tympanoplasty with and without gel foam. [Master of surgery in otorhinolaryngology, BLDE University, India].
Sahoo SR, Tripathi J, Kumari S, Rastogi S (2021) Efficacy of middle-ear packing in success of type 1 tympanoplasty: a prospective randomised study. J Laryngol Otol 135(10):864–868
Wang D, Ren T, Wang W (2020) The outcomes of endoscopic myringoplasty: packing with gelatin sponge versus packing with nothing. Acta Otolaryngol 140(4):292–296
Albazee E, Abdelaziz A, Magzoub H, Alanzi A, Aldosari N, Al-Qudah M et al (2022) Dry versus wet temporalis fascia graft in type-I tympanoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 280(3):1005–1015
Malhotra M, Malhotra R, Varshney S, Priya M, Bhardwaj A, Tyagi A et al (2020) A historical review of Indian perspectives on techniques of tympanoplasty. Int J Otolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1408270
Kim WJ, Kong JS, Jamil ALS, Park SY, Jeong CY, Kim DK et al (2016) Do we always need gelfoam packing in the middle ear cavity during tympanoplasty? Presenting Author: Woo Jin Kim. J Laryngol Otol 130(S3):S191
Li G, Feghali JG, Dinces E, McElveen J, Van de Water TR (2001) Evaluation of esterified hyaluronic acid as middle ear–packing material. Arch Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 127(5):534–9
Aihara Y, Ohyama Y, Ushio K, Kamio T, Sakuma A, Ohkawara D et al (2002) Patient’s satisfaction with tympanoplasty. Otology Japan 12(2):103–108
Blaine G (1951) Absorbable gelatin sponge in experimental surgery. The Lancet 258(6680):427–429
Jang CH, Park H, Cho YB, Choi CH (2008) The effect of anti-adhesive packing agents in the middle ear of guinea pig. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 72(11):1603–1608
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EA and AA-Z contributed to study conception, literature review, data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing. BA, ANA, and AAA contributed to literature review, data collection, data analysis, and revision of manuscript for editorial and intellectual contents. MS and AH contributed to study conception, study supervision, data interpretation, and revision of manuscript for editorial and intellectual contents. All authors read and approved the final draft of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
Not required as this research does not involve direct patient or animal contact.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
405_2023_7975_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplemental Table 1. The exact literature search strategy used in every database. Supplemental Table 2. Summary of the GRADE rating of the outcomes. Supplementary file1 (DOCX 15 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Albazee, E., Abu-Zaid, A., Alshammari, B. et al. Efficacy of gelfoam middle ear packing in type-1 tympanoplasty: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 3503–3514 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07975-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07975-1