Abstract
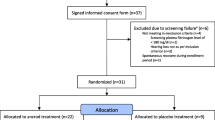
Higher levels of fibrinogen or cholesterol were associated with improved hearing recovery in SSHL patients after treatment with HELP-apheresis (Heparin-induced extracorporeal LDL precipitation apheresis). The present trial was performed to demonstrate HELP-related effects on relevant metabolic and inflammatory parameters in the context of SSHL treatment. In the framework of a single arm non-controlled trial, we investigated the variation of metabolic and inflammatory parameters using HELP-apheresis for a defined group of 100 patients with SSHL. Based on cut off inclusion criteria (Serum LDL-cholesterol >1.6 g/l and/or fibrinogen >2.0 g/l, SSHL in minimum three frequencies more than 30 dB, time after event not longer than 6 days), the protocol followed a strict time line with one single shot HELP-apheresis and follow-up monitoring including laboratory parameters at six defined time points. If HELP-apheresis could not effect improvement of hearing on day 5, additional corticosteroid treatment was applied. Concentration of anti-inflammatory IL-10 increased while other proinflammatory parameters declined. Serum levels of all measured sterols and apolipoproteins decreased significantly. None of the investigated parameters were suitable to predict hearing improvement of the patients. Levels of fibrinogen and LDL-cholesterol were not prognostic for outcome after HELP-apheresis. A significant (p < 0.001) increase of anti-inflammatory IL-10 after apheresis was notable, while most of the proinflammatory parameters declined. Despite the limited validity of a single arm non-controlled trial, these alterations on immune modulating factors indicate possible secondary pleiotropic effects caused by HELP-apheresis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM, Rosenfeld RM, Schwartz SR, Barrs DM, Brown SR, Fife TD, Ford P, Ganiats TG, Hollingsworth DB, Lewandowski CA, Montano JJ, Saunders JE, Tucci DL, Valente M, Warren BE, Yaremchuk KL, Robertson PJ (2012) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146(3 Suppl):S1–S35
Rauch SD (2008) Clinical practice: idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. N Engl J Med 359(8):833–840
Conlin AE, Parnes LS (2007) Treatment of sudden sensorineural hear- ing loss, I: a systematic review. Arch Otolaryngol Neck Surg 133:573–581
Ballesteros F, Alobid I, Tassies D, Reverter JC, Scharf RE, Guilemany JM, Bernal-Sprekelsen M (2009) Is there an overlap between sudden neurosensorial hearing loss and cardiovascular risk factors? Audiol Neurootol 14(3):139–145
Lin RJ, Krall R, Westerberg BD, Chadha NK, Chau JK (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk factors for sudden sensorineural hearing loss in adults. Laryngoscope 122(3):624–635
Suckfüll M, Wimmer C, Reichel O, Mees K, Schorn K (2002) Hyperfibrinogenemia as a risk factor for sudden hearing loss. Otol Neurotol Off lication Am Otol Soc Am Neurotol Soc Eur Acad Otol Neurotol 23(3):309–311
Lane DW, l’Anson S (1994) Viscosimetric effect of fibrinogen. J Clin Pathol 47(11):1004–1005
Mösges R, Köberlein J, Heibges A, Erdtracht B, Klingel R, Lehmacher W (2009) Rheopheresis for idiopathic sudden hearing loss: results from a large prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266(7):943–953
Suckfüll M (2002) Fibrinogen and LDL apheresis in treatment of sudden hearing loss: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet 360(9348):1811–1817
Bianchin G, Russi G, Romano N, Fioravanti P (2011) Role of H. E. L. P. -apheresis in the treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in a group of 230 patients. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, pp 395–398
Ullrich H, Kleinjung T, Steffens T, Jacob P, Schmitz G, Strutz J (2004) Improved treatment of sudden hearing loss by specific fibrinogen aphaeresis. J Clin Apher 19(2):71–78
Kirschkamp T, Schmid-Schönbein H, Weinberger A, Smeets R (2008) Effects of fibrinogen and alpha2-macroglobulin and their apheretic elimination on general blood rheology and rheological characteristics of red blood cell aggregates. Ther Apher Dial Off Peer reviewed J Int Soc Apher Japanese Soc Apher Japanese Soc Dial Ther 12(5):360–367
Teupser D, Baber R, Ceglarek U, Scholz M, Illig T, Gieger C, Holdt LM, Leichtle A, Greiser KH, Huster D, Linsel-Nitschke P, Schäfer A, Braund PS, Tiret L, Stark K, Raaz-Schrauder D, Fiedler GM, Wilfert W, Beutner F, Gielen S, Grosshennig A, König IR, Lichtner P, Heid IM, Kluttig A, El Mokhtari NE, Rubin D, Ekici AB, Reis A, Garlichs CD, Hall AS, Matthes G, Wittekind C, Hengstenberg C, Cambien F, Schreiber S, Werdan K, Meitinger T, Loeffler M, Samani NJ, Erdmann J, Wichmann H-E, Schunkert H, Thiery J (2010) Genetic regulation of serum phytosterol levels and risk of coronary artery disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 3(4):331–339
Ramunni A, Quaranta N, Saliani MT, Fallacara RA, Ria R, Ranieri G (2006) Does a reduction of adhesion molecules by LDL-apheresis have a role in the treatment of sudden hearing loss? Ther Apher Dial 10(3):282–286
Fujioka M, Kanzaki S, Okano HJ, Masuda M, Ogawa K, Okano H (2006) Proinflammatory cytokines expression in noise-induced damaged cochlea. J Neurosci Res 83(4):575–583
Miyao M, Firestein GS, Keithley EM (2008) Acoustic trauma augments the cochlear immune response to antigen. Laryngoscope 118(10):1801–1808
Adams JC, Seed B, Lu N, Landry A, Xavier RJ (2009) Selective activation of nuclear factor kappa B in the cochlea by sensory and inflammatory stress. Neuroscience 160(2):530–539
Masuda M (2013) Cause of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: the stress response theory. World J Otorhinolaryngol 3(3):42
Armstrong VW, Schuff-Werner P, Eisenhauer T, Helmhold M, Stix M, Seidel D (1994) Heparin extracorporeal LDL precipitation (HELP): an effective apheresis procedure for lowering Lp(a) levels. Chem Phys Lipids 67–68:315–321
Armstrong VW, Schleef J, Thiery J, Muche R, Schuff-Werner P, Eisenhauer T, Seidel D (1989) Effect of HELP-LDL-apheresis on serum concentrations of human lipoprotein(a): kinetic analysis of the post-treatment return to baseline levels. Eur J Clin Invest 19(3):235–240
Seidel D (1996) H.E.L.P. apheresis therapy in the treatment of severe hypercholesterolemia: 10 years of clinical experience. [Review] [30 refs]. Artif Organs 20(4):303–310
Oreskovic Z, Shejbal D, Bicanic G, Kekic B (2011) Influence of lipoproteins and fibrinogen on pathogenesis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Laryngol Otol 125(3):258–261
Cadoni G, Scorpecci A, Cianfrone F, Giannantonio S, Paludetti G, Lippa S (2010) Serum fatty acids and cardiovascular risk factors in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a case-control study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119(2):82–88
Ernst E, Resch KL (1993) Fibrinogen as a cardiovascular risk factor: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Ann Intern Med 118(12):956–963
Miller JM, Ren TY, Nuttall AL (1995) Studies of inner ear blood flow in animals and human beings. Otolaryngol Neck Surg Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol Neck Surg 112(1):101–113
Sillman JS, LaRouere MJ, Nuttall AL, Lawrence M, Miller JM (1988) Recent advances in cochlear blood flow measurements. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 97(1):1–8
Shiraishi T, Kubo T, Matsunaga T (1991) Chronological study of recovery of sudden deafness treated with defibrinogenation and steroid therapies
Suckfüll M (2001) Heparin-Induced extracorporeal low-density lipoprotein precipitation apheresis: a new therapeutic concept in the treatment of sudden hearing loss. Ther Apher 5(5):377–383
Mellwig K-P, Pulawski E, Horstkotte D, Buuren F (2012) Lipid apheresis: oxidative stress, rheology, and vasodilatation. Clini Res Cardiol Suppl 7(S1):45–49
Hovland A, Lappegård KT, Mollnes TE (2012) LDL apheresis and inflammation–implications for atherosclerosis. Scand J Immunol 76(3):229–236
Stefanutti C, Morozzi C, Petta A (2011) Lipid and low-density-lipoprotein apheresis. Effects on plasma inflammatory profile and on cytokine pattern in patients with severe dyslipidemia. Cytokine 56(3):842–849
Masuda M, Kanzaki S, Minami S, Kikuchi J, Kanzaki J, Sato H, Ogawa K (2012) Correlations of inflammatory biomarkers with the onset and prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 33(7):1142–1150
Trune D, Nguyen-Huynh A (2012) Vascular pathophysiology in hearing disorders. Semin Hear 33(3):242–250
Zenti MG, Grazia ZM, Stefanutti C, Claudia S (2011) Effects of selective H.E.L.P. LDL-apheresis on plasma inflammatory markers concentration in severe dyslipidemia: implication for anti-inflammatory response. Cytokine 56(3):850–854
Scherer EQ, Yang J, Canis M, Reimann K, Ivanov K, Diehl CD, Backx PH, Wier WG, Strieth S, Wangemann P, Voigtlaender-Bolz J, Lidington D, Bolz SS (2010) TNFα enhances microvascular tone and reduces blood flow in the cochlea via enhanced S1P signaling. Stroke 41(11):2618–2624
Schettler V, Wieland E (2007) Effects of LDL-apheresis–more than reduction of cholesterol? Dtsch Med Wochenschr 132(11):575–578
Thanaraj S, Hamlin PJ, Ford AC (2010) Systematic review: granulocyte/monocyte adsorptive apheresis for ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 32(11–12):1297–1306
Kobayashi S, Moriya H, Maesato K, Okamoto K, Ohtake T (2005) LDL-apheresis improves peripheral arterial occlusive disease with an implication for anti-inflammatory effects. J Clin Apher 20(4):239–243
Stefanutti C, Vivenzio A, Di Giacomo S, Ferraro PM (2011) Cytokines profile in serum of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia is changed by LDL-apheresis. Cytokine 55(2):245–250
Peter K, Weirich U, Nordt TK, Ruef J, Bode C (1999) Soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) as potential marker of atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost 82(Suppl 1):38–43
Demirhan E, Eskut NP, Zorlu Y, Cukurova I, Tuna G, Kirkali FG (2013) Blood levels of TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-12 in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 123(7):1778–1781
Hiramatsu M, Teranishi M, Uchida Y, Nishio N, Suzuki H, Kato K, Otake H, Yoshida T, Tagaya M, Suzuki H, Sone M, Sugiura S, Ando F, Shimokata H, Nakashima T (2012) Polymorphisms in Genes Involved in Inflammatory Pathways in Patients with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. J Neurogenet 26(3–4):387–396
Hovland A, Hardersen R, Sexton J, Mollnes TE, Lappegård KT (2009) Different inflammatory responses induced by three ldl-lowering apheresis columns. 253:247–253
Gesser B, Leffers H, Jinquan T, Vestergaard C, Kirstein N, Sindet-Pedersen S, Jensen SL, Thestrup-Pedersen K, Larsen CG (1997) Identification of functional domains on human interleukin 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(26):14620–14625
Lio D, Candore G, Crivello A, Scola L, Colonna-Romano G, Cavallone L, Hoffmann E, Caruso M, Licastro F, Caldarera CM, Branzi A, Franceschi C, Caruso C (2004) Opposite effects of interleukin 10 common gene polymorphisms in cardiovascular diseases and in successful ageing: genetic background of male centenarians is protective against coronary heart disease. J Med Genet 41(10):790–794
Gateva V, Sandling JK, Hom G, Taylor KE, Chung SA, Sun X, Ortmann W, Kosoy R, Ferreira RC, Nordmark G, Gunnarsson I, Svenungsson E, Padyukov L, Sturfelt G, Jönsen A, Bengtsson AA, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Baechler EC, Brown EE, Alarcón GS, Edberg JC, Ramsey-Goldman R, McGwin G, Reveille JD, Vilá LM, Kimberly RP, Manzi S, Petri MA, Lee A, Gregersen PK, Seldin MF, Rönnblom L, Criswell LA, Syvänen A-C, Behrens TW, Graham RR (2009) A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 41(11):1228–1233
Egli Gallo D, Khojasteh E, Gloor M, Hegemann SCA (2013) Effectiveness of systemic high-dose dexamethasone therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol Neurootol 18(3):161–170
Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Hultcrantz E (2012) Corticosteroid treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: randomized triple-blind placebo-controlled trial. Otol Neurotol 33(4):523–531
Xenellis J, Papadimitriou N, Nikolopoulos T, Maragoudakis P, Segas J, Tzagaroulakis A, Ferekidis E (2006) Intratympanic steroid treatment in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a control study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134(6):940–945
Ho HG-M, Lin H-C, Shu M-T, Yang C-C, Tsai H-T (2004) Effectiveness of intratympanic dexamethasone injection in sudden-deafness patients as salvage treatment
Plontke SK (2010) Intratympanic glucocorticoid therapy of sudden hearing loss. HNO 58(10):1025–1030
Coutinho AE, Chapman KE (2011) The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol Cell Endocrinol 335(1):2–13
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by the Roland Ernst Foundation for public health care, Dresden and B Braun Avitum AG, Melsungen.
Conflict of interest
Thomas Berger and Andreas Dietz have spoken at congresses sponsored by B Braun Avitium AG and have received honoraria for lecturing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, T., Kaiser, T., Scholz, M. et al. Fibrinogen is not a prognostic factor for response to HELP-apheresis in sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 3693–3703 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3449-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3449-9