Abstract
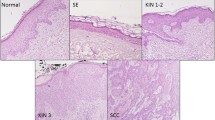
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is a malignant proliferation of keratinocytes with an uncertain molecular basis causing significant morbidity. MicroRNAs (miRs) are small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression on post- transcriptional level. MiRs are critical to various biological processes. To determine if miRs play a role in pathogenesis of invasive cSCC, we collected patients’ specimens from in situ and invasive cSCC (n = 19) and examined miRs expression levels using qPCR. Specifically, we evaluated miR-21, miR-103a, miR-186, miR-200b, miR-203, and miR-205 expression levels due to their role in skin biology and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. MiR levels were compared between in situ and invasive cSCCs. We found statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) upregulation of miR-21 and miR-205 in invasive cSCC compared to cSCC in situ. We concluded that miR-21 and miR-205 may have diagnostic value in determining the invasive properties of cSCCs and that each cSCC displays unique miR profile, underscoring the possibility of personalized medicine approach in developing potential novel, less invasive treatments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MRD (2001) Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 13:975–983
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355. doi:10.1038/nature02871
Baffa R, Fassan M, Volinia S, O’Hara B, Liu CG, Palazzo JP, Gardiman M, Rugge M, Gomella LG, Croce CM, Rosenberg A (2009) MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic cancers identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol 219:214–221. doi:10.1002/path.2586
Bostjancic E, Glavac D (2008) Importance of microRNAs in skin morphogenesis and diseases. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panon Adriat 17:95–102
Bruegger C, Kempf W, Spoerri I, Arnold AW, Itin PH, Burger B (2013) MicroRNA expression differs in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas and healthy skin of immunocompetent individuals. Exp Dermatol 22:426–428. doi:10.1111/exd.12153
Chen B, Pan W, Lin X, Hu Z, Jin Y, Chen H, Ma G, Qiu Y, Chang L, Hua C, Zou Y, Gao Y, Ying H, Lv D (2015) MicroRNA-346 functions as an oncogene in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4046-2
Chen D, Yan W, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zhu L, Liu W, Ding X, Wang A, Chen Y (2016) Downregulation of miR-221 enhances the sensitivity of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells to Adriamycin through upregulation of TIMP3 expression. Biomed Pharmacother 77:72–78. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2015.12.002
Chen S, Zhu J, Yu F, Tian Y, Ma S, Liu X (2015) Combination of miRNA and RNA functions as potential biomarkers for gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 36:9909–9918. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3756-9
Cheng YX, Chen GT, Chen C, Zhang QF, Pan F, Hu M, Li BS (2016) MicroRNA-200b inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration of cervical cancer cells by directly targeting RhoE. Mol Med Rep. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.4933
Cherpelis BS, Marcusen C, Lang PG (2002) Prognostic factors for metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Dermatol Surg 28:268–273
Dong W, Yongjun L, Nan D, Junyun W, Qiong Y, Yaran Y, Yanming L, Xiangdong F, Hua Z (2015) Molecular networks and mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulated by miRNAs in the malignant melanoma cell line. Yi Chuan 37:673–682. doi:10.16288/j.yczz.15-022
Dziunycz P, Iotzova-Weiss G, Eloranta JJ, Lauchli S, Hafner J, French LE, Hofbauer GF (2010) Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin shows a distinct microRNA profile modulated by UV radiation. J Investig Dermatol 130:2686–2689. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.169
Elsnerova K, Mohelnikova-Duchonova B, Cerovska E, Ehrlichova M, Gut I, Rob L, Skapa P, Hruda M, Bartakova A, Bouda J, Vodicka P, Soucek P, Vaclavikova R (2016) Gene expression of membrane transporters: importance for prognosis and progression of ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep. doi:10.3892/or.2016.4599
Foundation TSC (2016). http://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/skin-cancer-facts. Accessed 8 June 2016
Gao W, Shen H, Liu L, Xu J, Xu J, Shu Y (2011) MiR-21 overexpression in human primary squamous cell lung carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137:557–566. doi:10.1007/s00432-010-0918-4
He W, Zhang MG, Wang XJ, Zhong S, Shao Y, Zhu Y, Shen ZJ (2013) KAT5 and KAT6B are in positive regulation on cell proliferation of prostate cancer through PI3K-AKT signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6:2864–2871
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2016). http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/skin/statistics/race.htm. Accessed 20 Aug 2016
Huang Y, Kesselman D, Kizub D, Guerrero-Preston R, Ratovitski EA (2013) Phospho-deltaNp63alpha/microRNA feedback regulation in squamous carcinoma cells upon cisplatin exposure. Cell Cycle 12:684–697. doi:10.4161/cc.23598
Hufbauer M, Lazic D, Reinartz M, Akgul B, Pfister H, Weissenborn SJ (2011) Skin tumor formation in human papillomavirus 8 transgenic mice is associated with a deregulation of oncogenic miRNAs and their tumor suppressive targets. J Dermatol Sci 64:7–15. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.06.008
Karia PS, Han J, Schmults CD (2013) Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: estimated incidence of disease, nodal metastasis, and deaths from disease in the United States, 2012. J Am Acad Dermatol 68:957–966. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.11.037
Kramer A, Green J, Pollard J Jr, Tugendreich S (2014) Causal analysis approaches in ingenuity pathway analysis. Bioinformatics 30:523–530. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btt703
Li X, Huang K, Yu J (2014) Inhibition of microRNA-21 upregulates the expression of programmed cell death 4 and phosphatase tensin homologue in the A431 squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Oncol Lett 8:203–207. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2066
Liao F, Ji MY, Shen L, Qiu S, Guo XF, Dong WG (2013) Decreased EGR3 expression is related to poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. J Mol Histol 44:463–468. doi:10.1007/s10735-013-9493-8
Luo Q, Li W, Zhao T, Tian X, Liu Y, Zhang X (2015) Role of miR-148a in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by repression of MAPK pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 583:47–54. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2015.07.022
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, Inoue N, Machida H, Nakayama T, Hayashi T, Kunizaki M, Hidaka S, Nagayasu T, Nakashima M, Ujifuku K, Mitsutake N, Ohtsuru A, Yamashita S, Korpal M, Kang Y, Gregory PA, Goodall GJ, Kohno S, Nakao K (2011) MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Transl Med 9:30. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-9-30
Mitsui H, Suarez-Farinas M, Gulati N, Shah KR, Cannizzaro MV, Coats I, Felsen D, Krueger JG, Carucci JA (2014) Gene expression profiling of the leading edge of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: IL-24-driven MMP-7. J Investig Dermatol 134:1418–1427. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.494
Obayashi M, Yoshida M, Tsunematsu T, Ogawa I, Sasahira T, Kuniyasu H, Imoto I, Abiko Y, Xu D, Fukunaga S, Tahara H, Kudo Y, Nagao T, Takata T (2016) microRNA-203 suppresses invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction via targeting NUAK1 in head and neck cancer. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6972
Okamura Y, Nomoto S, Hayashi M, Hishida M, Nishikawa Y, Yamada S, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Takeda S, Kodera Y, Nakao A (2011) Identification of the bleomycin hydrolase gene as a methylated tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel triple-combination array method. Cancer Lett 312:150–157. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.07.028
Okumura K, Saito M, Isogai E, Aoto Y, Hachiya T, Sakakibara Y, Katsuragi Y, Hirose S, Kominami R, Goitsuka R, Nakamura T, Wakabayashi Y (2014) Meis1 regulates epidermal stem cells and is required for skin tumorigenesis. PLoS One 9:e102111. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102111
Paiva I, Gil da Costa RM, Ribeiro J, Sousa H, Bastos MM, Faustino-Rocha A, Lopes C, Oliveira PA, Medeiros R (2015) MicroRNA-21 expression and susceptibility to HPV-induced carcinogenesis—role of microenvironment in K14-HPV16 mice model. Life Sci 128:8–14. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2015.02.020
Pastar I, Khan AA, Stojadinovic O, Lebrun EA, Medina MC, Brem H, Kirsner RS, Jimenez JJ, Leslie C, Tomic-Canic M (2012) Induction of specific microRNAs inhibits cutaneous wound healing. J Biol Chem 287:29324–29335. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.382135
Patani N, Jiang WG, Newbold RF, Mokbel K (2011) Histone-modifier gene expression profiles are associated with pathological and clinical outcomes in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res 31:4115–4125
Patnaik S, Mallick R, Kannisto E, Sharma R, Bshara W, Yendamuri S, Dhillon SS (2015) MiR-205 and miR-375 microRNA assays to distinguish squamous cell carcinoma from adenocarcinoma in lung cancer biopsies. J Thorac Oncol 10:446–453. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000423
Petter G, Haustein UF (2000) Histologic subtyping and malignancy assessment of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg 26:521–530
Pio R, Jia Z, Baron VT, Mercola D, Cancer UNSCotSPftEoCS-P (2013) Early growth response 3 (Egr3) is highly over-expressed in non-relapsing prostate cancer but not in relapsing prostate cancer. PLoS One 8:e54096. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054096
Sand M, Skrygan M, Georgas D, Sand D, Hahn SA, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P, Bechara FG (2012) Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Sci 68:119–126. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2012.09.004
Schwartz DR, Homanics GE, Hoyt DG, Klein E, Abernethy J, Lazo JS (1999) The neutral cysteine protease bleomycin hydrolase is essential for epidermal integrity and bleomycin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4680–4685
Sonkoly E, Wei T, Janson PC, Saaf A, Lundeberg L, Tengvall-Linder M, Norstedt G, Alenius H, Homey B, Scheynius A, Stahle M, Pivarcsi A (2007) MicroRNAs: novel regulators involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis? PLoS One 2:e610. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000610
Sun SS, Zhou X, Huang YY, Kong LP, Mei M, Guo WY, Zhao MH, Ren Y, Shen Q, Zhang L (2015) Targeting STAT3/miR-21 axis inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating CDK5 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer 14:213. doi:10.1186/s12943-015-0487-x
Taube JH, Malouf GG, Lu E, Sphyris N, Vijay V, Ramachandran PP, Ueno KR, Gaur S, Nicoloso MS, Rossi S, Herschkowitz JI, Rosen JM, Issa JP, Calin GA, Chang JT, Mani SA (2013) Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 is required for EMT and cancer stem cell properties. Sci Rep 3:2687. doi:10.1038/srep02687
Wald AI, Hoskins EE, Wells SI, Ferris RL, Khan SA (2011) Alteration of microRNA profiles in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cell lines by human papillomavirus. Head Neck 33:504–512. doi:10.1002/hed.21475
Yao K, He L, Gan Y, Zeng Q, Dai Y, Tan J (2015) MiR-186 suppresses the growth and metastasis of bladder cancer by targeting NSBP1. Diagn Pathol 10:146. doi:10.1186/s13000-015-0372-3
Yu J, Peng H, Ruan Q, Fatima A, Getsios S, Lavker RM (2010) MicroRNA-205 promotes keratinocyte migration via the lipid phosphatase SHIP2. FASEB J 24:3950–3959. doi:10.1096/fj.10-157404
Yu X, Li Z (2016) The role of miRNAs in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 20:3–9. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12649
Zhang L, Xiang P, Han X, Wu L, Li X, Xiong Z (2015) Decreased expression of microRNA-20a promotes tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:11446–11451
Zhao W, Wang H, Han X, Ma J, Zhou Y, Chen Z, Zhou H, Xu H, Sun Z, Kong B, Fang H (2016) DeltaNp63alpha attenuates tumor aggressiveness by suppressing miR-205/ZEB1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-016-4921-5
Zheng N, Yang P, Wang Z, Zhou Q (2017) OncomicroRNAs-mediated tumorigenesis: implication in cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 17(1):40–47
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Michael McLeod for assistance in specimen collection, Shari Jackson for technical support and all members of Tomic-Canic laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing financial interests. This work is supported by the University of Miami SAC Award SAC 2013-19 (MTC).
This study has been approved by the University of Miami institutional ethics committee (IRB protocol # 20090614) and performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stojadinovic, O., Ramirez, H., Pastar, I. et al. MiR-21 and miR-205 are induced in invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. Arch Dermatol Res 309, 133–139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1705-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1705-0