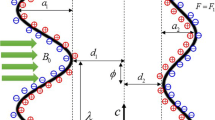
Abstract
The two-layered electro-osmotic peristaltic flow of Phan-Thien-Tanner (PTT) fluid in a flexible cylindrical tube is analyzed. The core (inner) layer fluid satisfies the constitutive equation of PTT fluid model and the peripheral (outer) layer is characterized as a Newtonian fluid. For each region, the two-dimensional conservation equations for mass and momentum with electro-osmotic body forces are transformed from the fixed frame to the moving frame of reference. These equations are further simplified by invoking the constraints of long wavelength and low Reynolds number. Closed-form expressions for velocity and stream function are derived and then employed to investigate the pressure variations, trapping, interface region, and reflux for a variety of the involved parameters. The analysis reveals that the reflux and trapping can be restrained by appropriately tuning the electro-kinetic slip parameter and Deborah number. Further, the pumping efficacy can also be improved by adjusting the rheological and the electro-kinetic effects. These results may be helpful for improving the performance of the microfluidic peristaltic pump.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- u, w :
-
Velocity components
- τ :
-
Shear stress
- λ :
-
Wavelength
- μ r :
-
Viscosity ratio between two regions
- μ 1 :
-
Viscosity in the core region
- μ 2 :
-
Viscosity in the peripheral region
- f :
-
Linear function
- R 1 :
-
Interface between the two fluids
- R 0 :
-
Boundary of the tube wall
- q 1 :
-
Flow rate over the inner cross-section
- q :
-
Flow rate over the outer cross-section
- ϵ c :
-
Dielectric constant in the inner region
- ϵ N :
-
Dielectric constant in the outer region
- De :
-
Deborah number
- κ :
-
Relaxation time
- U :
-
Velocity of the peristaltic wall
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- k :
-
Height of the interface at z = 0
- ϕ oc :
-
Occlusion parameter
- ψ ∗ :
-
Stream function in the fixed frame
- ψ :
-
Stream function in the wave frame
- ρ e :
-
Total charge density
- r 0 :
-
Characteristics radius of the tube
- δ :
-
Ratio of the characteristics radial length to the characteristics axial length scale
- T P :
-
Complete period
- c :
-
Core region
- N :
-
Peripheral region
References
Afonso AM, Alves MA, Pinho FT (2009) Analytical solution of mixed electro-osmotic pressure driven flows of viscoelastic fluids in microchannels. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 159:50–63
Afonso AM, Alves MA, Pinho FT (2013) Analytical solution of two-fluid electro-osmotic flow of viscoelastic fluid. J Colloid Interface Sci 395:277–286
Ali N, Hayat T (2008) Peristaltic flow of a micropolar fluid in an asymmetric channel. Computers and Mathematics with Applications 55:589–608
Ali N, Sajid M, Abbas Z, Javed T (2010) Non-Newtonian fluid flow induced by peristaltic waves in a curved channel. European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids 29:387–394
Brasseur JG, Corrsin S, Nan QL (1987) The influence of a peripheral layer of different viscosity on peristaltic pumping with Newtonian fluids. J Fluid Mech 174:495–519
Chakraborty S (2006) Augmentation of peristaltic micro-flows through electro-osmotic mechanisms. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:5356–5363
Chaube MK, Yadav A, Tripathi D (2018) Electro-osmotically induced alterations in peristaltic micro-flows of power law fluids through physiological vessels. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(423):1–9
Ferras LL, Nobrega JM, Pinho FT (2012) Analytical solutions for channel flows of Phan-Thien-Tanner and Giesekus fluids under slip. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 171-172:97–105
Ferras LL, Afonso AM, Alves MA, Pinho FT, Noberga JM (2014) Analytical and numerical study of the electro-osmotic annular flow of viscoelastic fluid. J Colloid Interface Sci 420:152–157
Goswami P, Chakraborty J, Bandopadhyay A, Chakraborty S (2016) Electrokinetically modulated peristaltic transport of power-law fluids. Microvasc Res 103:41–54
Hayat T, Ali N (2006) Peristaltically induced motion of a MHD third grade fluid in a deformable tube. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its applications 370:225–239
Hayat T, Noreen S, Ali N, Abbasbanday S (2009) Peristaltic motion of phan-Thien-Tanner fluid in a Planar Channel. Numerical Method for Partial Differential Equations 11:737–738
Hayat T, Noreen S, Ali N (2010) Effect of an induced magnetic field on the peristaltic motion of Phan-Thien-Tanner (PTT) fluid. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 65:665–676
Hayat T, Nawaz S, Alsaedi A, Rafiq M (2017a) Influence of radial magnetic field on the peristaltic flow of Williamson fluid in a curved complaint walls channel. Result in Physics 7:982–990
Hayat T, Tanveer A, Alsaedi A, Asghar S (2017b) Homogenous-hetrogenous reactions in peristaltic flow of prandtl fluid with thermal radiations. J Mol Liq 240:504–513
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta potential in colloid sciences: principles and applications. Academic Press, London
Jayavel P, Jhorar R, Tripathi D, Azese MN (2019) Electroosmotic flow of pseudoplastic nano-liquids via peristaltic pumping. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 61:1–18
Kavitha A, Reddy RH, Saravana R, Sreenadh S (2017) Peristaltic transport of a Jeffery fluid in contact with a Newtonian fluid in an inclined channel. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 8:683–687
Mekheimer KS (2004) Peristaltic flow of blood under effect of a magnetic field in a non-uniform channels. Appl Math Comput 153:763–777
Mishra M, Rao AR (2005) Peristaltic transport in a channel with a porous peripheral layer: model of a flow in gastrointestinal tract. J Biomech 38:779–789
Misra JC, Pandey SK (1999) Peristaltic transport of a non-Newtonian fluid with a peripheral layer. Int J Eng Sci 37:1841–1858
Narahari M, Sreenadh S (2010) Peristalatic transport of a Bingham fluid in contact with a Newtonian fluid. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 6(11):41–54
Narla VK, Tripathi D (2019) Electro-osmosis modulated transient blood flow in curved microvessels: study of a mathematical model. Microvasc Res 123:25–34
Narla VK, Tripathi D, Beg OA (2018) Electro-osmosis modulated viscoelastic embryo transport in uterine hydrodynamics: mathematical modeling. J Biomech Eng 141(2):021003(10)
Oliveira PJ, Pinho FT (1999) Analytical solution for fully developed channel and pipe flow of Phan-Thien-Tanner fluids. J Fluid Mech 387:271–280
Prabakaran HP, Hemadri RR, Sreenadh S, Saravana R, Kavitha A (2013) Peristaltic pumping of a Bingham fluid in contact with a Newtonian fluid in an inclined channel under long wave length approximation. Advances and Application in Fluid Mechanics 13(2):127–139
Prakash J, Tripathi D (2018) Electroosmotic flow of Williamson ionic nano-liquids in a tapered microfluidic channel in presence of thermal radiation and peristalsis. J Mol Liq 256:352–371
Raju KK, Devanathan R (1972) Peristaltic motion of a non-Newtonian fluid. Rheol Acta 11:170–178
Rao AR, Mishra M (2004) Peristaltic transport of a power-law fluid in a porous tube. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 121:163–174
Rao AR, Usha S (1995) Peristaltic transport of two immiscible viscous fluid in a circular tube. J Fluid Mech 298:271–285
Shapiro AH, Jaffrin MY, Weinberg SL (1969) Peristaltic pumping with long wavelength at low Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 37:799–825
Shukla JB, Parihar RS, Rao BRP, Gupta SP (1980) Effects of peripheral layer viscosity on peristaltic transport of a bio-fluid. J Fluid Mech 97:225–237
Siddiqui AM, Schwarz WH (1994) Peristaltic flow of second-order fluid in a tube. Journal non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics 53:257–284
Srivastava VP, Saxena M (1995) A two-fluid of non-Newtonain blood flow induced by peristaltic waves. Rheol Acta 34:406–414
Takagi D, Balmforth NJ (2011a) Peristaltic pumping of rigid objects in an elastic tube. J Fluid Mech 672:219–244
Takagi D, Balmforth NJ (2011b) Peristaltic pumping of viscous fluid in an elastic tube. J Fluid Mech 672:196–218
Tripathi D (2011) A mathematical model for the peristaltic flow of chyme movement in small intestine. Math Biosci 233:90–97
Tripathi D, Bhushan S, Bég OA (2016) Transverse magnetic field driven modification in unsteady peristaltic transport with electrical double layer effects. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 506:32–39
Tripathi D, Borode A, Jhorar R, Bég OA, Tiwari AK (2017a) Computer modelling of electro-osmotically augmented three-layered microvascular peristaltic blood flow. Microvasc Res 114:65–83
Tripathi D, Sharma A, Bég OA, Tiwari A (2017b) Electro-thermal transport in biological systems: an analytical approach for electro-kinetically modulated peristaltic flow. Journal of Thermal Science and Engineering Applications 9:041010–041011
Tripathi D, Jhorar R, Beg OA, Shaw S (2018a) Electro-osmosis modulated peristaltic biorheological flow through an asymmetric microchannel: mathematical model. Meccanica 53:2079–2090
Tripathi D, Jhorar R, Borode A, Bég OA (2018b) Three-layered electro-osmosis modulated blood flow through a micro-channel. European Journal of Mechanics / B Fluids 72:391–402
Tripathi D, Sharma A, Bég OA (2018c) Joule heating and buoyancy effects in electro-osmotic peristaltic transport of aqueous nanofluids through a microchannel with complex wave propagation. Adv Powder Technol 29:639–653
Vajravelu K, Sreenadh S, Babu VR (2006) Peristaltic pumping of a Herschel-Bulkley fluid in contact with a Newtonian fluid. Q Appl Math 64:593–604
Vajravelu K, Sreenadh S, Hemadri RR, Murugeshan K (2009) Peristaltic transport of a Casson fluid in contact with a Newtonian fluid in a circular tube with permeable wall. International Journal Fluid Mechanics Research 36:244–254
Walker SW, Shelley MJ (2010) Shape optimization of peristaltic pumping. J Comput Phys 229:1260–1291
Zhao C, Yang C (2013) Electro-osmotic flows of non-Newtonian power-law fluids in a cylindrical microchannel. Electrophoresis 34:662–667
Zhao M, Wang S, Wei S (2013) Transient electro-osmotic flow of Oldroyd-B fluids in a straight pipe of circular cross section. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 201:135–139
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the reviewer for his valuable comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Here, we provide the values of coefficients appearing in the interface polynomial Eq. (67):
From Eq. (65), the real solution of P0 can be obtained by employing Cardan-Tartaglia formula of algebraic cubic equation as follows:
where \( S={\left(-d+\sqrt{A^3{B}^3+{d}^2}\right)}^{\frac{1}{3}} \),
with d = 12(q − (UE − 1))A2, B = 1 + (μr − 1)k4 and A = b2μrk6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, S., Ali, N. & Ullah, K. Peristaltic flow of Phan-Thien-Tanner fluid: effects of peripheral layer and electro-osmotic force. Rheol Acta 58, 603–618 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-019-01158-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-019-01158-8