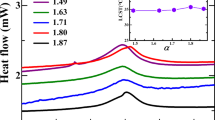
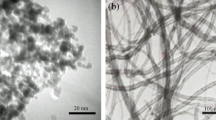
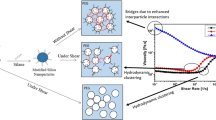
Abstract
MXenes constitute a new class of two-dimensional materials and have received considerable attention in the past decade from researchers in a wide variety of fields. In this study, we showed that the rheological properties of the concentrated (50 wt%) colloidal suspensions of the MXene sediment can be easily controlled by various water-soluble polymers to facilitate their solution processing in practical applications. The viscosity of the initially gelled polymer-free suspension at low shear rates was reduced by several orders of magnitudes by adding nonionic, anionic, and cationic polymers that can adsorb on the particle surface. The cationic poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA) afforded the highest reduction in viscosity, attributed to the decrease in the undesirable face-to-edge electrostatic attraction between the MXenes. The PDDA-doped concentrated suspensions exhibited remarkably low viscosities and elastic moduli and thus can be applied to spray coating process without clogging even at high particle loadings.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Naguib M, MOchalin VN, Barsoum MW, Gogotsi Y (2014) XenesM: A New Family of Two-dimensinoal Materials. Adv Mater 26:992–1005
Gogotsi Y, Anasori B (2019) The Rise of MXenes. ACS Nano 13:8491–8494
Vahidmohammadi A, Rosen J, Gogotsi Y (2021) The World of Two-dimensional Carbides and Nitrdies. Science 372:6547
Chaudhari NK, Jin H, Kim B, Baek DS, Joo SH, Lee K (2014) MXene: An Emerging Two-dimensional Material for Future Energy Conversion and Storage Applications. Adv Mater 26:992–1005
Murali G, Rawal J, Modigunta JKR, Park YH, Lee JH, Lee SY, Park SJ, In I (2021) A Review on MXenes: New-Generation 2D Materials for Supercapacitors, Sustain. Energy Fuels 5:5672–5693
Shahzad F, Alhabeb M, Hatter CB, Anasori B, Hong SM, Koo CM, Gogotsi Y (2016) Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with 2D Transition Metal Carbides (MXenes). Science 353:1137–1140
Iqbal A, Shahzad F, Hantanasirisakul K, Kim MK, Kwon J, Hong J, Kim H, Kim D, Gogotsi Y, Koo CM (2020) Anomalous Absorption of Electromagnetic Waves by 2D Transition Metal Carbonitride Ti3CNTx (MXene). Science 369:446–450
Sokolov A, Ali M, Li H, Jeon YR, Ko MJ, Choi C (2021) Partially Oxidized MXene Ti3C2Tx Sheets for Memristor Having Synapse and Threshold Resistive Switching Characteristics. Adv Electron Mater 7:2000866
Khot AC, Dongale TD, Park JH, Kesavan AV, Kim TG (2021) Ti3C2-Based MXene Oxide Nanosheets for Resistive Memory and Synaptic Learning Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:5216–5227
Ling Z, Ren CE, Zhao MQ, Gogotsi Y (2014) Flexible and Conductive MXene Films and Nanocomposites with High Capacitance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:16676–16681
Jimmy J, Kandasubramanian B (2020) MXene Functionalized Polymer Composites: Synthesis and Applications. Eur Polym J 122:109367
Wyatt BC, Nemani SK, Anasori B (2021) 2D Transition Metal Carbides (MXenes) in Metal and Ceramic Matrix Composites. Nano Converg 8:16
Kim SJ, Koh HJ, Ren CE, Kwon O, Maleski K, Cho SY, Anasori B, Kim CK, Choi YK, Kim J, Gogotsi Y, Jung HT (2018) Metallic Ti3C2Tx MXene Gas Sensors with Ultrahigh Signal-to-Noise Ratio. ACS Nano 12:986–993
Ho DH, Choi YY, Jo SB, Myoung JM, Cho JH (2021) Sensing with MXenes: Progress and Prospects. Adv Mater 33:2005846
Zhong Q, Li Y, Zhang G (2021) Two-dimensional MXene-based and MXene-derived Photocatalysts: Recent Developments and Perspectives. Chem Eng J 409:128099
You Z, Liao Y, Li X, Fan J, Xiang Q (2021) State-of-the-art Recent Progress in MXene-based Photocatalysts: A Comprehensive Review. Nanoscale 13:9463–9504
Petukhov DI, Kan AS, Chumakov AP, Konovalov OV, Valeev RG, Eliseev AA (2021) MXene-based Gas Separation Membranes with Sorption Type Selectivity. J Membr Sci 621:218994
Li J, Li X, Bruggen BV (2020) An MXene-based Membrane for Molecular Separation. Environ Sci Nano 7:1289–1304
Karahan HE, Goh K, Zhang C, Yang E, Yildirim C, Chuah CY, Ahunbay MG, Lee J, Tantekin-Ersolmaz SB, Chen Y, Bae T-H (2020) MXene Materials for Designing Advanced Separation Membranes. Adv Mater 32:1906697
Rasool K, Helal M, Ali A, Ren CE, Gogotsi Y, Mahmoud KA (2016) Antibacterial Activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene. ACS Nano 10:3674–3684
Dwivedi N, Dhand C, Kumar P, Srivastava AK (2021) Emergent 2D Materials for Combating Infectious Diseases: the Potential of MXenes and MXene-Graphene Composites to Fight Against Pandemics. Mater Adv 2:2892–2905
Zhao J, Yang Y, Yang C, Tian Y, Han Y, Liu J, Yin X, Que X (2018) A Hydrophobic Surface Enabled Salt-Blocking 2D Ti3C2 MXene Membrane for Efficient and Stable Solar Desalination. J Mater Chem A 33:16196–16204
Xu D, Li Z, Li L, Wang J (2020) Insights into the Photothermal Conversion of 2D MXene Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Mechanism, and Applications. Adv Func Mater 30:2000712
Liu Y, Zhao J, Zhang S, Li D, Zhang X, Zhao Q, Xing B (2022) Advances and Challenges of Broadband Solar Absorbers for Efficient Solar Steam Generation. Environ Sci Nano 9:2264–2296
Aslfattahi N, Samylingam L, Abdelrazik AS, Arifutzzaman A, Saidur R (2020) MXene Based New Class of Silicone Oil Nanofluids for the Performance Improvement of Concentrated Photovoltaic Thermal Collector. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 211:110526
Bao Z, Bing N, Zhu X, Xie H, Yu W (2021) TI3C2Tx MXene Contained Nanofluids with High Thermal Conductivity, Super Colloidal Stability and Low Viscosity. Chem Eng J 406:126390
Ambreen T, Saleem A, Park CW (2022) Thermal Efficiency of Eco-Friendly MXene Based Nanofluid for Performance Enhancement of a Pin-Fin Heat Sink: Experimental and Numerical Analyses. Int J Heat Mass Transf 186:122451
Alhabeb M, Maleski K, Anasori B, Lelyukh P, Clark L, Sin S, Gogotsi Y (2017) Guidelines for Synthesis and Processing of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chem Mater 29:7633–7644
Abdolhosseinzadeh S, Schneider R, Verma A, Heler J, Nuesch F, Zhang C (2020) Turning Trash into Treasure: Additive Free MXene Sediment Inks for Screen-Printed Micro-Supercapacitors. Adv Mater 32:2000716
Xu H, Zhu W, Sun F, Qi H, Zou J, Laine R, Ding W (2021) Turning Trash into Treasure: MXene with Intrinsic LiF Solid Electrolyte Interfaces Performs Better and Better During Battery Cycling. Adv Mater Technol 6:2000882
Ma J, Yang K, Jiang Y, Shen L, Ma H, Cui Z, Du Y, Lin J, Liu J, Zhu N (2022) Integrating MXene Waste Materials into Value-added Products for Smart Wearable Self-powered Healthcare Monitoring. Cell Rep Phys Sci 3:100908
Yuan M, Wang L, Liu X, Du X, Zhang G, Chang Y, Xia Q, Hu Q, Zhou A (2023) 3D Printing Quasi-Solid-State Micro-Supercapacitors with Ultrahigh Areal Energy Density Based on High Concentration MXene Sediment. Chem Eng J 451:138686
Peng YY, Akuzum B, Kurra N, Zhao MQ, Alhabeb M, Anasori B, Kumbur EC, Alshareef HN, Ger MD, Gogotsi Y (2016) All-MXene (2D titanium carbide) Solid-State Microsupercapacitors for On-Chip Energy Storage. Energy Environ Sci 9:2847–2854
Couly C, Alhabeb M, Van Aken KL, Kurra N, Gomes L, Navarro-Suarez AM, Anasori B, Alshareef HN, Gogotsi Y (2018) Asymmetric Flexible MXene-Reduced Graphene Oxide Micro-Supercapacitor. Adv Electron Mater 4:1700339
Hantanasirisakul K, Zhao MQ, Urbankowski P, Halim J, Anasori B, Kota S, Ren CE, Barsoum MW, Gogotsi Y (2016) Fabrication of Ti3C2Tx MXene Transparent Thin Films with Tunable Optoelectronic Properties. Adv Electron Mater 2:1600050
Zhang YZ, Wang Y, Jiang Q, El-Demellawi JK, Kim H, Alshareef HN (2020) MXene Printing and Patterned Coating for Device Applications. Adv Mater 1908486
Aydin E, El-Demellawi JK, Yarali E, Aljamaan F, Sansoni S, Rehman A, Harrison G, Kang J, Labban AE, Bastiani MD, Razzaq A, Kerschaver EV, Allen TG, Mahammed OF, Anthopoulos T, Alshareef HN, Wolf SD (2022) Scaled Deposition of Ti3C2Tx MXene on Complex Surfaces: Application Assessment as Rear Electrodes for Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cells. ACS Nano 16:2419–2428
Dillon AD, Ghidiu MJ, Krick AL, Griggs J, May SJ, Gogotsi Y, Barsoum MW, Fafarman AT (2016) Highly Conductive Optical Quality Solution-Processes Films of 2D Titanium Carbide. Adv Func Mater 26:4162–4168
Uzun S, Schelling M, Hantanasirisakul K, Mathis TS, Askeland R, Dion G, Gogotsi Y (2021) Additive-Free Aqueous MXene Inks for Thermal Inkjet Printing on Textiles. Small 17:2006376
Zhang C, Mckeon L, Kremer MP, Park SH, Ronan O, Seral-Ascaso A, Barwich S, Coileain CO, McEvoy N, Nerl HC, Anasori B, Coleman JN, Gogotsi Y, Nicolosi V (2019) Additive-free MXene Inks and Direct Printing of Micro-supercapacitors. Nat Commun 10:1795
Orangi J, Hamade F, Davis VA, Beidaghi M (2020) 3D Printing of Additive-Free 2D Ti3C2Tx (MXene) Ink for Fabrication of Micro-Supercapacitors with Ultra-High Energy Densities. ACS Nano 14:640–650
Yang W, Yang J, Byun JJ, Moissinac FP, Xu J, Haigh SJ, Domingos M, Bissett MA, Dryfe RAW, Barg S (2019) 3D Printing of Freestanding MXene Architectures for Current-Collector-Free Supercapacitors. Adv Mater 31:1902725
Eom W, Shin H, Ambade RB, Lee SH, Lee KH, Kang DJ, Han TH (2020) Large-scale Wet-spinning of Highly Electroconductive MXene Fibers. Nat Commun 11:2825
Lim S, Park H, Yang J, Kwak C, Lee J (2019) Stable Colloidal Dispersion of Octylated Ti3C2-MXenes in a Nonpolar Solvent. Colloids Surf A 579:123648
Maleski K, Mochalin VN, Gogotsi Y (2017) Dispersion of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide MXene in Organic Solvents. Chem Mater 29:1632–1640
Zhang Q, Lai H, Fan R, Ji P, Fu X, Li H (2021) High Concentration of Ti3C2Tx MXene in Organic Solvent. ACS Nano 15:5249–5262
Akuzum B, Maleski K, Anasori B, Lelyukh P, Alvarez NJ, Kumbur EC, Gogotsi Y (2018) Rheological Characteristics of 2D Titanium Carbide (MXene) Dispersions: A Guide for Processing MXenes. ACS Nano 12:2685–2694
Tezel GB, Arole K, Holta DE, Radovic M, Green MJ (2022) Interparticle Interactions and Rheological Signatures of Ti3C2Tz MXene Dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 605:120–128
Wei TS, Fan FY, Helal A, Smith KC, McKinley GH, Chiang YM, Lewis JA (2015) Biphasic Electrode Suspensions for Li-Ion Semi-solid Flow Cells with High Energy Density, Fast Charge Transport, and Low-Dissipation Flow. Adv Energy Mater 5:1500535
Zhang L, Wu X, Qian W, Zhang H, Zhang S (2021) Lithium Slurry Flow Cell, a Promising Device for the Future Energy Storage, Green. Energy Environ 6:5–8
Rueb CJ, Zukoski CF (1997) Viscoelastic Properties of Colloidal Gels. J Rheol 41:197–218
Okonkwo EC, Wole-Osho I, Almanassra IW, Abdullatif YM, Al-Ansari T (2021) An Updated Review of Nanofluids in Various Heat Transfer Devices. J Therm Anal Calorim 145:2817–2872
Nielsen LE (1973) Thermal Conductivity of Particulate-Filled Polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 17:3819–3820
Asakura S, Oosawa F (1958) Interaction Between Particles Suspended in Solutions. J Polym Sci 33:183–192
Tuinier R, Rieger J, de Kruif CG (2003) Depletion-Induced Phase Separation in Colloid-Polymer Mixture. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 103:1–31
Zhulina EB, Borisov OV, Priamitsyn VA (1990) Theory of Steric Stabilization of Colloid Dispersions by Grafted Polymers. J Colloid Interface Sci 137:495–511
Guo X, Ballauff M (2001) Spherical Polyelectrolyte Brushes: Comparison Between Annealed and Quanched Brushes. Phys Rev E 64:051406
Lim S, Park H, Kim JH, Yang J, Kwak C, Kim J, Ryu SY, Lee J (2020) Polyelectrolyte-grafted Ti3C2-MXenes Stable in Extreme Salinity Aquatic Conditions for Remediation of Contaminated Subsurface Environments. RSC Adv 10:25966–25978
Larson RG (1999) The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids. Oxford University Press, New York
Krieger IM, Dougherty TJ (1959) A Mechanism for Non-Newtonian Flow in Suspensions of Rigid Spheres. Trans Soc Rheol 3:137–152
Batchelor GK (1977) The Effect of Brownian Motion on the Bulk Stress in a Suspension of Spherical Particles. J Fluid Mech 83:97–117
Russel WB (1980) Review of the Role of Colloidal Forces in the Rheology of Suspensions. J Rheol 287:287–316
Shoaib M, Khan S, Wani OB, Abdala A, Seiphoori A, Bobicki ER (2022) Modulation of Soft Glassy Dynamics in Aqueous Suspensions of an Anisotropic Charged Swelling Clay Through pH Adjustment. J Colloid Interface Sci 606:860–872
Mason TG, Weitz DA (1995) Linear Viscoelasticity of Colloidal Hard Sphere Suspensions near the Glass Transition. Phys Rev Lett 75:2770
Yang J, Park H, Kim J, Mok J, Kim T, Shin E, Kwak C, Lim S, Kim CB, Park J-S, Na HB, Choi D, Lee J (2020) Yield Stress Enhancement of a Ternary Colloidal Suspension via the Addition of Minute Amounts of Sodium Alginate to the Interparticle Capillary Bridges. Langmuir 36:9424–9435
Cooper CL, Cosgrove T, van Duijneveldt JS, Murray M, Prescott SW (2013) The Use of Solvent Relaxation NMR to Study Colloidal Suspensions. Soft Matter 9:7211–7228
Elliott LN, Bourne RA, Hassanpour A, Edwards JL, Sutcliffe S, Hunter TN (2018) Salt Enhanced Solvent Relaxation and Particle Surface Area Determination via Rapid Spin-lattice NMR. Powder Technol 333:458–467
Marchesini S, Paton KR, Brennan B, Turner P, Pollard AJ (2021) Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Proton Relaxation to Probe the Surface Chemistry of Carbon 2D Materials. Nanoscale 13:6389–6393
Lee J, Moesari E, Dandamudi CB, Beniah G, Chang B, Iqbal M, Fei Y, Zhou N, Ellison CJ, Johnston KP (2017) Behavior of Spherical Poly(2-acrylamido-2-metylpropanesulfonate) Polyelectrolyte Brushes on Silica Nanoparticles up to Extreme Salinity with Weak Divalent Cation Binding at Ambient and High Temperature. Macromolecules 50:7699–7711
Park H, Lim S, Yang J, Kwak C, Kim J, Kim J, Choi SS, Kim CB, Lee J (2020) A Systematic Investigation on the Properties of Silica Nanoparticles “Multipoint”-Grafted with Poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonate-co-acrylic Acid) in Extreme Salinity Brines and Brine-Oil Interfaces. Langmuir 36:3174–3183
Biver C, Hariharan R, Mays J, Russel WB (1997) Neutral and Charged Polymer Brushes: A Model Unifying Curvature Effects from Micelles to Flat Surfaces. Macromolecules 30:1787–1792
Zhou Z, Solomon MJ, Scale PJ, Boger DV (1999) The Yield Stress of Concentrated Flocculated Suspensions of Size Distributed Particles. J Rheol 43:651–671
Lim S, Kim JH, Park H, Kwak C, Yang J, Kim J, Ryu SY, Lee J (2021) Role of Electrostatic Interactions in the Adsorption of Dye Molecules by Ti3C2-MXenes. RSC Adv 11:6201–6211
Natu V, Sokol M, Verger L, Barsoum MW (2018) Effect of Edge Charges on Stability and Aggregation of Ti3C2Tz MXene Colloidal Suspensions. J Phys Chem C 122:27745–27753
Rozmyslowska-Wojciechowska A, Mitrzak J, Szuplewska A, Chudy M, Wozniak J, Petrus M, Wojciechowski T, Vasilchenko AS, Jastzebska AM (2020) Engineering of 2D Ti3C2 MXene Surface Charge and its Influence on Biological Properties. Materials 13:2347
Rand B, Melton IE (1976) Particle Interactions in Aqueous Kaolinite Suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci 60:308–320
Du J, Morris G, Pushkarova RA, St R. Smart C (2010) Effect of Surface Structure of Kaolinite on Aggregation, Settling Rate, and Bed Density. Langmuir 26:13227–13235
Buron H, Mengual O, Meunier G, Cayre I, Sabre P (2004) Optical Characterization of Concentrated Dispersions: Applications to Laboratory Analyses and On-line Process Monitoring and Control. Polym Int 53:1205–1209
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2018R1D1A1A02085492). This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2021R1F1A1048634). This research was supported by Nano·Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (2009–0082580).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 2174 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 6015 KB)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 7930 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, H., Lim, S., Kim, G. et al. Control of the rheological properties of concentrated aqueous MXene sediment suspensions using polymeric additives. Colloid Polym Sci 301, 357–370 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05076-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05076-3