Abstract
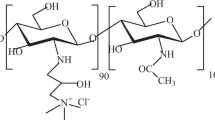
O-carboxymethyl chitosan (O-CMC) is a water-soluble derivative of chitosan. In this work, the formation of polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) between O-CMC and sodium alginate (SAL) was explored by investigating the effects of medium pH, polyelectrolytes mixing ratio, and ionic strength on the yield of O-CMC–SAL PECs. Meanwhile, the rheological, thermal, and microstructural properties of the PECs prepared at various medium acidities were characterized as well. The results indicated that the strongest complexation between O-CMC and SAL occurred in medium pH 6.5 and biopolymer ratio (R O-CMC/SAL) 1.5:1 (w/w) in the absence of added NaCl. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis revealed that both electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding were involved in PEC formation. The PECs possessed the porous structure and displayed predominately the elastic property with the highest moduli values being recorded at medium pH 3.5. It was concluded that the O-CMC–SAL PECs have potential biomedical applications due to the nearly neutral complexation pH and the porous structure for drug inclusion.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luo Y, Wang Q (2014) Recent development of chitosan-based polyelectrolyte complexes with natural polysaccharides for drug delivery. Int J Biol Macromol 64C:353–367
Cui L, Jia JF, Xiong ZH, Zhang CJ, Ye ZT, Zhu P (2014) Preparation and properties of carboxymethyl chitosan and sodium alginate semi-interpenetrating hydrogels. Acta Polym Sin 0:361–368
Meng X, Tian F, Yang J, He CN, Xing N, Li F (2010) Chitosan and alginate polyelectrolyte complex membranes and their properties for wound dressing application. J Mater Sci-Mater Med 21:1751–1759
Dai YN, Li P, Zhang JP, Wang AQ, Wei Q (2008) A novel pH sensitive N-succinyl chitosan/alginate hydrogel bead for nifedipine delivery. Biopharm Drug Dispos 29:173–184
Motwani SK, Chopra S, Talegaonkar S, Kohli K, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK (2008) Chitosan–sodium alginate nanoparticles as submicroscopic reservoirs for ocular delivery: formulation, optimisation and in vitro characterisation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 68:513–525
Chen SC, Wu YC, Mi FL, Lin YH, Yu LC, Sung HW (2004) A novel pH-sensitive hydrogel composed of N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan and alginate cross-linked by genipin for protein drug delivery. J Control Release 96:285–300
Lucinda SRM, Salgado HRN, Evangelista RC (2010) Alginate-chitosan systems: in vitro controlled release of triamcinolone and in vivo gastrointestinal transit. Carbohydr Polym 81:260–268
Mi FL, Liang HF, Wu YC, Lin YS, Yang TF, Sung HW (2005) pH-sensitive behavior of two-component hydrogels composed of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan and alginate. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 16:1333–1345
Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Nair SV, Tokura S, Tamura H, Selvamurugan N (2010) Novel carboxymethyl derivatives of chitin and chitosan materials and their biomedical applications. Prog Mater Sci 55:675–709
Douglas KL, Tabrizian M (2005) Effect of experimental parameters on the formation of alginate-chitosan nanoparticles and evaluation of their potential application as DNA carrier. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 16:43–56
Takahashi T, Takayama K, Machida Y, Nagai T (1990) Characteristics of polyion complexes of chitosan with sodium alginate and sodium polyacrylate. Int J Pharm 61:35–41
Sæther HV, Holme HK, Maurstad G, Smidsrød O, Stokke BT (2008) Polyelectrolyte complex formation using alginate and chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 74:813–821
Florczyk SJ, Kim DJ, Wood DL, Zhang M (2011) Influence of processing parameters on pore structure of 3D porous chitosan–alginate polyelectrolyte complex scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A 98A:614–620
Huang GQ, Xiao JX, Jia L, Yang J (2014) Complex coacervation of O-carboxymethylated chitosan and gum arabic. Intern J Polym Mater. doi:10.1080/00914037.2014.936591
Ge HC, Luo DK (2005) Preparation of carboxymethyl chitosan in aqueous solution under microwave irradiation. Carbohydr Res 340:1351–1356
Berger J, Reist M, Mayer JM, Felt O, Peppas NA, Gurny R (2004) Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 57:19–34
Feng C, Wang Z, Jiang C, Kong M, Zhou X, Li Y, Cheng X, Chen X (2013) Chitosan/o-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles for efficient and safe oral anticancer drug delivery: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm 457:158–167
Liu S, Cao YL, Ghosh S, Rousseau D, Low NH, Nickerson MT (2010) Intermolecular interactions during complex coacervation of pea protein isolate and gum arabic. J Agric Food Chem 58:552–556
Ye A (2008) Complexation between milk proteins and polysaccharides via electrostatic interaction: principles and applications a review. Int J Food Sci Technol 43:406–415
Espinosa-Andrews H, Sandoval-Castilla O, Vázquez-Torres H, Vernon-Carter EJ, Lobato-Calleros C (2010) Determination of the gum Arabic-chitosan interactions by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and characterization of the microstructure and rheological features of their coacervates. Carbohydr Polym 79:541–546
Fan L, Du Y, Zhang B, Yang J, Zhou J, Kennedy JF (2006) Preparation and properties of alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan blend fibers. Carbohydr Polym 65:447–452
Shon SO, Ji BC, Han YA, Park DJ, Kim IS, Choi JH (2007) Viscoelastic sol–gel state of the chitosan and alginate solution mixture. J Appl Polym Sci 104:1408–1414
Weinbreck F, Wientjes RHW, Nieuwenhuijse H, Robijn GW, de Kruif CG (2004) Rheological properties of whey protein/gum arabic coacervates. J Rheol 48:1215–1228
Ru Q, Wang Y, Lee J, Ding Y, Huang Q (2012) Turbidity and rheological properties of bovine serum albumin/pectin coacervates: effect of salt concentration and initial protein/polysaccharide ratio. Carbohydr Polym 88:838–846
Espinosa-Andrews H, Baez-Gonzalez JG, Cruz-Sosa F, Vernon-Carter EJ (2007) Gum arabic-chitosan complex coacervation. Biomacromolecules 8:1313–1318
Kittur FS, Harish-Prashanth KV, Udaya-Sankar K, Tharanathan RN (2002) Characterization of chitin, chitosan and their carboxymethyl derivatives by differential scanning calorimetry. Carbohydr Polym 49:185–193
Honary S, Maleki M, Karami M (2009) The effect of chitosan molecular weight on the properties of alginate/chitosan microparticles containing prednisolone. Trop J Pharm Res 8:53–61
Tığlı RS, Gümüşderelioğlu M (2009) Evaluation of alginate-chitosan semi IPNs as cartilage scaffolds. J Mater Sci-Mater M 20:699–709
Chen L, Remondetto GE, Subirad M (2006) Food protein-based materials as nutraceutical delivery systems. Trends Food Sci Technol 17:272–283
Acknowledgment
We thank the financial support from the National Science Foundation of China (31101391), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2010CQ032), and the Shenzhen Key Fundamental Project Program (JC201105201225A).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, GQ., Cheng, LY., Xiao, JX. et al. Preparation and characterization of O-carboxymethyl chitosan–sodium alginate polyelectrolyte complexes. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 401–407 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3432-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3432-4