Abstract
Purpose
In the present study, we investigated whether intra-islet GLP-1 production and its modulation have a role in apoptosis, proliferation or neogenesis that is compromised by protein restriction during the foetal and suckling periods.
Methods
Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist (treated groups), or saline (non-treated groups) was intraperitoneally administered for 15 days from 75 to 90 days of age in female adult rats consisting of offspring born to and suckled by mothers fed a control diet (control groups) and who had the same diet until 90 days of age or offspring born to and suckled by mothers fed a low-protein diet and who were fed the control diet after weaning until 90 days of age (protein-restricted group).
Results
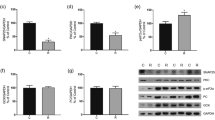
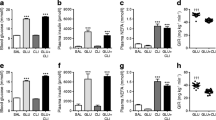
The β-cell mass was lower in the protein-restricted groups than in the control groups. Exendin-4 increased β-cell mass, regardless of the mother’s protein intake. The colocalization of GLP-1/glucagon was higher in the protein-restricted rats than in control rats in both the exendin-4-treated and non-treated groups. The frequency of cleaved caspase-3-labelled cells was higher in the non-treated protein-restricted group than in the non-treated control group and was similar in the treated protein-restricted and treated control groups. Regardless of treatment with exendin-4, Ki67-labelled cell frequency and β-catenin/DAPI colocalization were elevated in the protein-restricted groups. Exendin-4 increased the area of endocrine cell clusters and β-catenin/DAPI and FoxO1/DAPI colocalization regardless of the mother’s protein intake.
Conclusions
Protein restriction in early life increased intra-islet GLP-1 production and β-cell proliferation, possibly mediated by the β-catenin pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berney DM, Desai M, Palmer DJ, Greenwald S, Brown A, Hales CN et al (1997) The effects of maternal protein deprivation on the fetal rat pancreas: major structural changes and their recuperation. J Pathol 183:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199709)183:1%3c109:AID-PATH1091%3e3.0.CO;2-B
Bonner-Weir S (2001) beta-cell turnover: its assessment and implications. Diabetes 50:S20–S24. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.50.2007.s20
Fujimoto K, Hanson PT, Tran H, Ford EL, Han Z, Johnson JD et al (2009) Autophagy regulates pancreatic beta cell death in response to Pdx1 deficiency and nutrient deprivation. J Biol Chem 284:27664–27673. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.041616
Bonner-Weir S, Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Weir GC (2016) Dynamic development of the pancreas from birth to adulthood. Ups J Med Sci 121:155–158. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009734.2016.1154906
Bonner-Weir S, Guo L, Li WC, Ouziel-Yahalom L, Lysy PA, Weir GC et al (2012) Islet neogenesis: a possible pathway for beta-cell replenishment. Rev Diabet Stud 9:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2012.9.407
Renehan AG, Booth C, Potten CS (2001) What is apoptosis, and why is it important? BMJ 322:1536–1538. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7301.1536
Hirata H, Takahashi A, Kobayashi S, Yonehara S, Sawai H, Okazaki T et al (1998) Caspases are activated in a branched protease cascade and control distinct downstream processes in Fas-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med 187:587–600. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.187.4.587
Rojas J, Bermudez V, Palmar J, Martínez MS, Olivar LC, Nava M et al (2018) Pancreatic beta cell death: novel potential mechanisms in diabetes therapy. J Diabetes Res 2018:9601801. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9601801
Petrik J, Reusens E, Arany C, Remacle C, Coelho C, Hoet JJ et al (1999) A low protein diet alters the balance of islet cell replication and apoptosis in the fetal and neonatal rat. Endocrinology 140:4861–4873. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.140.10.7042
Lee Y, Jun H (2014) Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells. Metabolism 63:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010
Hui H, Nourparvar A, Zhao X, Perfetti R (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits apoptosis of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. Endocrinology 144:1444–1455. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2002-220897
Buteau J, Spatz ML, Accili D (2006) Peptide-1 effects on pancreatic b-cell mass. Diabetes 55:1190–1196. https://doi.org/10.2337/db05-0825
Ip W, Chiang YA, Jin T (2012) The involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway and TCF7L2 in diabetes mellitus: the current understanding, dispute, and perspective. Cell Biosci 2:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-2-28
Liu Z, Habener JF (2008) Glucagon-like peptide-1 activation of TCF7L2-dependent Wnt signaling enhances pancreatic beta cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 283:8723–8735. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M706105200
Elghazi L, Gould AP, Weiss AJ, Barker DJ, Callaghan J, Opland D et al (2012) Importance of b-Catenin in glucose and energy homeostasis. Sci Rep 2:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00693
Figeac F, Uzan B, Faro M, Chelali N, Portha B, Movassat J (2010) Neonatal growth and regeneration of b-cells are regulated by the Wnt/b-catenin signaling in normal and diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 298:245–256. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00538.2009
Rouille Y, Westermarktt G, Martin SK, Steiner DF (1994) Proglucagon is processed to glucagon by prohormone convertase PC2 in aTC1-6 cells. Biochemistry 91:3242–3246
Hansen AMK, Nordestgaard DNE, Heller RS, Gotfredsen CF, Maedler K, Fels JJ et al (2011) Upregulation of alpha cell glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in Psammomys obesus—an adaptive response to hyperglycaemia? Diabetologia 54:1379–1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2080-1
Kilimnik G, Kim A, Steiner DF, Friedman TC, Hara M (2010) Intraislet production of GLP-1 by activation of prohormone convertase 1/3 in pancreatic α-cells in mouse models of β-cell regeneration. Islets 2:149–155
Nie Y, Nakashima M, Brubaker PL, Li Q, Perfetti R, Jansen E et al (2000) Regulation of pancreatic PC1 and PC2 associated with increased glucagon-like peptide 1 in diabetic rats. J Clin Invest 105:955–965. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI7456
O’Malley TJ, Fava GE, Zhang Y, Fonseca VA, Wu H (2014) Progressive change of intra-islet GLP-1 production during diabetes development. Diabetes Metab 30:661–668. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2534.PROGRESSIVE
Whalley NM, Pritchard LE, Smith DM, White A (2011) Processing of proglucagon to GLP-1 in pancreatic α-cells: Is this a paracrine mechanism enabling GLP-1 to act on β-cells? J Endocrinol 211:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-11-0094
Huang C, Yuan L, Cao S (2015) Endogenous GLP-1 as a key self-defense molecule against lipotoxicity in pancreatic islets. Int J Mol Med 36:173–185. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2015.2207
Liu Z, Stanojevic V, Avadhani S, Yano T, Habener JF (2011) Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4) axis activation induces intra-islet glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) production and enhances beta cell survival. Diabetologia 54:2067–2076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2181-x
Moffett RC, Vasu S, Thorens B, Drucker DJ, Flatt PR (2014) Incretin receptor null mice reveal key role of GLP-1 but not GIP in pancreatic beta cell adaptation to pregnancy. PLoS One 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096863
Marin L, Silva HBF, Damin G, Ignacio-Souza LM, Reis SRL, de Oliveira CAM et al (2018) Nutritional recovery from a low-protein diet during pregnancy does not restore the kinetics of insulin secretion and Ca(2+) or alterations in the cAMP/PKA and PLC/PKC pathways in islets from adult rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43:1257–1267. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2017-0629
Marin BK, Reis SRL, Ramalho AFS, Lemes SF, Marin L, Vanzela EC et al (2019) Protein restriction in early life increases intracellular calcium and insulin secretion, but does not alter SNARE proteins expression during pregnancy. Exp Physiol 104:1029–1037. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP087045
Matveyenko AV, Singh I, Shin BC, Georgia S, Devaskar SU (2010) Differential effects of prenatal and postnatal nutritional environment on ß-cell mass development and turnover in male and female rats. Endocrinology 151:5647–5656. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2010-0978
Scaglia L, Cahill CJ, Finegood DT, Bonner-Weir S (1997) Apoptosis participates in the remodeling of the endocrine pancreas in the neonatal rat. Endocrinology 138:1736–1741. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.138.4.5069
Movassat J, Saulnier C, Portha B (1995) Beta-cell mass depletion precedes the onset of hyperglycemia in the GK rat, a genetic model of non-insulindependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab 21:365–370
Dunn KW, Kamocka MM, McDonald JH (2011) A practical guide to evaluating colocalization in biological microscopy. Am J Physiol Physiol 300:C723–C742. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00462.2010
Charan J, Kantharia ND (2013) How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J Pharmacol Pharmacother 4:303–306. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.119726
Rabah N, Gauthier D, Dikeakos JD, Reudelhuber TL, Lazure C (2007) The C-terminal region of the proprotein convertase 1⁄3(PC1⁄3) exerts a bimodal regulation of the enzyme activity in vitro. FEBS J 3:3482–3491. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05883.x
Poulsen MD, Hansen GH, Dabelsteen E, Hoyer PE, No OVE, Sjt H et al (1993) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV is sorted to the secretory granules in pancreatic islet A-cells. J Histochem Cytochem 41:81–88
Plagemann A, Waas T, Harder T, Rittel F, Ziska T, Rohde W (2000) Hypothalamic neuropeptide Y levels in weaning offspring of low-protein malnourished mother rats. Neuropeptides 34:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1054/npep.1999.0778
Krolow R, Noschang C, Arcego DM, Huffell AP, Marcolin ML, Benitz AN et al (2013) Sex-specific effects of isolation stress and consumption of palatable diet during the prepubertal period on metabolic parameters. Metabolism 62:1268–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.04.009
Henquin JC, Nenquin M, Stiernet P, Ahren B (2006) In vivo and in vitro glucose-induced biphasic insulin secretion in the mouse: pattern and role of cytoplasmic Ca2+ and amplification signals in beta-cells. Diabetes 55:441–451. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-1051
Thomaseth K, Pavan A, Pacini G, Ahre B, Glucagon-like B (2007) Glucagon-like peptide-1 accelerates the onset of insulin action on glucose disappearance in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00303.2006
Kimball SR, Jefferson LS (2006) New functions for amino acids : effects on gene transcription and translation. Am J Clin Nutr 83:500–507. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/83.2.500S
Kitamura T, Nakae J, Kitamura Y, Kido Y, Iii WHB, Wright CVE et al (1839) The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 links insulin signaling to Pdx1 regulation of pancreatic β cell growth. Rapid Publ 110:1839–1847. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI200216857.tion
Lv L, Chen H, Sun J, Lu D, Chen C, Liu D (2015) PRMT1 promotes glucose toxicity-induced b cell dysfunction by regulating the nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of PDX-1 in a FOXO1-dependent manner in INS-1 cells. Endocrine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0543-8
Ignácio-Souza LM, Reis SR, Arantes VC, Botosso BL, Veloso RV, Ferreira F et al (2013) Protein restriction in early life is associated with changes in insulin sensitivity and pancreatic β-cell function during pregnancy. Br J Nutr 109:236–247. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451200089X
Prigeon RL, Quddusi S, Paty B, D’Alessio DA (2003) Suppression of glucose production by GLP-1 independent of islet hormones: a novel extrapancreatic effect. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:701–707. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00024.2003
Hou G, Li C, Huan Y, Liu S, Liu Q, Liu M et al (2017) The PI3K/Akt1-FoxO1 translocation pathway mediates EXf effects on NIT-1 cell survival. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 125:669–676. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-117048
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the american institute of nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/123.11.1939
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Celso Roberto Afonso for his excellent technical assistance and Carlos Henrique Fregadolli for their contribution to the statistical analyses.
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian foundation CAPES-Brasil (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil, Finance Code 001; PROCAD 160638) and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Grant no. 308588/2016-9). This work is part of a dissertation presented by Chaiane Aline da Rosa as a partial requirement for a Master’s degree in Nutrition, Food and Metabolism at the College of Nutrition, UFMT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Rosa-Santos, C.A., da Costa Rodrigues, P., Silva, L.R. et al. Early protein restriction increases intra-islet GLP-1 production and pancreatic β-cell proliferation mediated by the β-catenin pathway. Eur J Nutr 59, 3565–3579 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-020-02192-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-020-02192-6