Abstract
Introduction
The connection between iron and excessive adiposity has received much research interest. Although children and adolescents have unique developmental phases and nutritional demands, to date, reviews of iron in the overweight (OW) and obese (OB) have combined studies of children and adults or have focussed on adults.
Purpose
The aim of this review was to critically evaluate studies of the relationship between iron and OW and obesity in children and adolescents, with emphasis on iron status, oral iron response, dietary intake and systemic inflammatory markers.
Methods
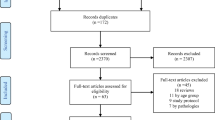
A PubMed search was conducted to identify relevant articles published up to December 2015. Combinations of the following keywords were used: iron, OW, OB, children, adolescents, diet, hepcidin, inflammation, fortification, supplementation, weight loss, trace elements, obesity, iron deficiency (ID), minerals.
Results and conclusion
A higher prevalence of ID, or risk of ID, among OW and OB children and adolescents has been consistently observed. Chronic inflammation caused by excessive adiposity offers a plausible explanation for this finding, rather than dietary factors. However, future studies must employ screening for the presence of both acute and chronic infections and inflammatory conditions and report other factors such as pubertal status. Intervention studies, although few, indicate that OW and OB children and adolescents have reduced response to oral iron. Further trials are needed to explore the connection between body fat mass, inflammatory proteins and iron absorption, together with the effect of weight loss on iron status in iron-deficient OW and OB children and adolescents.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGP:
-
α-1 Acid glycoprotein
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- ID:
-
Iron deficiency
- IDA:
-
Iron deficiency anaemia
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- OB:
-
Obese
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- OW:
-
Overweight
- NW:
-
Normal weight
- sTfR:
-
Serum soluble transferrin receptor
- SDS:
-
Standard deviation score
References
Olds T, Maher C, Zumin S, Péneau S, Lioret S, Castetbon K, Bellisle de Wilde J, Hohepa M, Maddison R, Lissner L, Sjöberg A, Zimmermann M, Aeberli I, Ogden C, Flegal K, Summerbell C (2011) Evidence that the prevalence of childhood overweight is plateauing: data from nine countries. Int J Pediatr Obes 6:342–360
Wabitsch M, Moss A, Kromeyer-Hauschild K (2014) Unexpected plateauing of childhood obesity rates in developed countries. BMC Med 12:17
Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, de Onis M, Ezzati M, Grantham-McGregor S, Katz J, Martorell R, Uauy R, Maternal and Child Nutrition Study Group (2013) Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 382:427–451
DeBoer MD (2013) Obesity, systemic inflammation, and increased risk for cardiovascular disease and diabetes among adolescents: a need for screening tools to target interventions. Nutrition 29:379–386
Coimbra S, Catarino C, Santos-Silva A (2013) The role of adipocytes in the modulation of iron metabolism in obesity. Obes Rev 14:771–779
Tussing-Humphreys L, Pusatcioglu C, Nemeth E, Braunschweig C (2012) Rethinking iron regulation and assessment in iron deficiency, anemia of chronic disease, and obesity: introducing hepcidin. J Acad Nutr Diet 112:391–400
Cepeda-Lopez AC, Aeberli I, Zimmermann MB (2010) Does obesity increase risk for iron deficiency? A review of the literature and the potential mechanisms. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 80:263–270
Zafon C, Lecube A, Simó R (2010) Iron in obesity. An ancient micronutrient for a modern disease. Obes Rev 11:322–328
McClung JP, Karl JP (2009) Iron deficiency and obesity: the contribution of inflammation and diminished iron absorption. Nutr Rev 67:100–104
Aigner E, Feldman A, Datz C (2014) Obesity as an emerging risk factor for iron deficiency. Nutrients 6:3587–3600
Cheng HL, Bryant C, Cook R, O’Connor H, Rooney K, Steinbeck K (2012) The relationship between obesity and hypoferraemia in adults: a systematic review. Obes Rev 13:150–161
Charles CV (2012) Iron deficiency anemia: a public health problem of global proportions. In: Maddock J (ed) Public health—methodology, environmental and systems, 1st edn. In Tech, Rijeka, pp 109–130
Gore FM, Bloem PJ, Patton GC, Ferguson J, Joseph V, Coffey C, Sawyer SM, Mathers CD (2011) Global burden of disease in young people aged 10–24 years: a systematic analysis. Lancet 377:2093–2102
Forsythe LK, Wallace JM, Livingstone MB (2008) Obesity and inflammation: the effects of weight loss. Nutr Res Rev 21:117–133
Wenzel BJ, Stults HB, Mayer J (1962) Hypoferraemia in obese adolescents. Lancet 2:327–328
Suliburska J, Cofta S, Gajewska E, Kalmus G, Sobieska M, Samborski W, Krejpcio Z, Drzymala-Czyz S, Bogdanski P (2013) The evaluation of selected serum mineral concentrations and their association with insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17:2396–2400
Tascilar ME, Ozgen IT, Abaci A, Serdar M, Aykut O (2011) Trace elements in obese Turkish children. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:188–195
García OP, Ronquillo D, del Carmen Caamaño M, Martínez G, Camacho M, López V, Rosado JL (2013) Zinc, iron and vitamins A, C and E are associated with obesity, inflammation, lipid profile and insulin resistance in Mexican school-aged children. Nutrients 5:5012–5030
Azab SFA, Saleh SH, Elsaeed WF, Elshafie MA, Sherief LM, Esh AMH (2014) Serum trace elements in obese Egyptian children: a case–control study. Ital J Pediatr 40:20
Błażewicz A, Klatka M, Astel A, Partyka M, Kocjan R (2013) Differences in trace metal concentrations (Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cd, And Ni) in whole blood, plasma, and urine of obese and nonobese children. Biol Trace Elem Res 155:190–200
Dale JC, Burritt MF, Zinsmeister AR (2002) Diurnal variation of serum iron, iron-binding capacity, transferrin saturation and ferritin levels. Am J Clin Pathol 117:802–808
Chiari MM, Bagnoli R, De Luca PD, Monti M, Rampoldi E, Cunietti E (1995) Influence of acute inflammation on iron and nutritional status indexes in older inpatients. J Am Geriatr Soc 43:767–771
Bagni UV, Luiz RR, da Veiga GV (2013) Overweight is associated with low hemoglobin levels in adolescent girls. Obes Res Clin Pract 7:e218–e229
Scheer JC, Guthrie HA (1981) Hemoglobin criteria with respect to obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 34:2748–2751
Chen K, Zhang X, Li TY, Chen L, Qu P, Liu YX (2009) Co-assessment of iron, vitamin A and growth status to investigate anemia in preschool children in suburb Chongqing, China. World J Pediatr 5:275–281
World Health Organization (2011) Haemoglobin concentrations for the diagnosis of anaemia and assessment of severity. WHO, Geneva. http://www.who.int/vmnis/indicators/haemoglobin.pdf Accessed 13 June 2014
Seltzer CC, Mayer J (1963) Serum iron and iron-binding capacity in adolescents. II. Comparison of obese and non-obese subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 13:354–361
Nead KG, Halterman JS, Kaczorowski JM, Auinger P, Weitzman M (2004) Overweight children and adolescents: a risk group for iron deficiency. Pediatrics 114:104–108
Brotanek JM, Gosz J, Weitzman M, Flores G (2007) Iron deficiency in early childhood in the United States: risk factors and racial/ethnic disparities. Pediatrics 120:568–575
Manios Y, Moschonis G, Chrousos C, Lionis C, Mougios V, Kantilafti M, Tzotzola V, Skenderi KP, Petridou A, Tsalis G, Sakellaropoulou A, Skouli G, Katsarou C (2013) The double burden of obesity and iron deficiency in children and adolescents in Greece: the Healthy Growth Study. J Hum Nutr Diet 26:470–478
Moschonis G, Chrousos GP, Lionis C, Mougios V, Manios Y, Healthy Growth Study group (2012) Association of total body and visceral fat mass with iron deficiency in preadolescents: the Healthy Growth Study. Br J Nutr 108:710–719
Aeberli I, Hurrell RF, Zimmerman MB (2009) Overweight children have higher circulating hepcidin concentrations and lower iron status but have dietary iron intakes and bioavailability comparable with normal-weight children. Int J Obes 33:1111–1117
Cook JD, Flowers CH, Skikne BS (1998) An assessment of dried blood-spot technology for identifying iron deficiency. Blood 92:1807–1813
Sharma AP, McKenna AM, Lepage N, Nieuwenhuys E, Filler G (2009) Relationships among serum iron, inflammation, and body mass index in children. Adv Pediatr 56:135–144
Tussing-Humphreys LM, Liang H, Nemeth E, Freels S, Braunschweig CA (2009) Excess adiposity, inflammation, and iron-deficiency in female adolescents. J Am Diet Assoc 109:297–302
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Newfield RS, Koren I, Agmon A, Lilos P, Philip M (2003) Greater prevalence of iron deficiency in overweight and obese children and adolescents. Int J Obes 27:416–418
Ferrari M, Cuenca-García M, Valtueña J, Moreno LA, Censi L, González-Gross M, Androutsos O, Gilbert CC, Huybrechts I, Dallongeville J, Sjöström M, Molnar D, De Henauw S, Gómez-Martínez S, de Moraes AC, Kafatos A, Widhalm K, Leclercq C, HELENA Study Group (2015) Inflammation profile in overweight/obese adolescents in Europe: an analysis in relation to iron status. Eur J Clin Nutr 69:247–255 Epub 2014 Sep 10
Chang JS, Li YL, Lua CH, Owaga E, Chen WY, Chiou HY (2014) Interleukin-10 as a potential regulator of hepcidin homeostasis in overweight and obese children: a cross-sectional study in Taiwan. Nutrition 30:1165–1170
Chang JS, Chang CC, Chien E, Lin SS, Cheng-Shiuan T, Bai CH, Chao KC (2013) Association between interleukin 1β and interleukin 10 concentrations: a cross-sectional study in young adolescents in Taiwan. BMC Pediatr 13:123
Huang YF, Tok TS, Lu CL, Ko HC, Chen MY, Chen SC (2015) Relationship between being overweight and iron deficiency in adolescents. Pediatr Neonatol 56:386–392
Eftekhari M, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Shidfar F (2009) The relationship between BMI and iron status in iron-deficient adolescent Iranian girls. Public Health Nutr 12:2377–2381
Moayeri H, Bidad K, Zadhoush S, Gholami N, Anari S (2006) Increasing prevalence of iron deficiency in overweight and obese children and adolescents (Tehran Adolescent Obesity Study). Eur J Pediatr 165:813–814
Gibson RS, Bailey KB, Williams S, Houghton L, Costa-Ribeiro HC, Mattos AP, Barreto DL, Lander RL (2014) Tissue iron deficiency and adiposity-related inflammation in disadvantaged preschoolers from NE Brazil. Eur J Clin Nutr 68:887–891
Cepeda-Lopez AC, Osendarp SJM, Melse-Boonstra A, Aeberli I, Gonzalez-Salazar F, Feskens E, Villalpando S, Zimmermann MB (2011) Sharply higher rates of iron deficiency in obese Mexican women and children are predicted by obesity-related inflammation rather than by differences in dietary iron intake. Am J Clin Nutr 93:975–983
Demircioğlu F, Görünmez G, Dağıstan E, Göksügür SB, Bekdaş M, Tosun M (2014) Serum hepcidin levels and iron metabolism in obese children with and without fatty liver: case–control study. Eur J Pediatr 173:947–951
Adair LS (2008) Child and adolescent obesity: epidemiology and developmental perspectives. Physiol Behav 94:8–16
Di Toro A, Marotta A, Todisco N, Ponticiello E, Collini R, Di Lascio R, Perrone L (1997) Unchanged iron and copper and increased zinc in the blood of obese children after two hypocaloric diets. Biol Trace Elem Res 57:97–104
Amato A, Santoro N, Calabro P, Grandone A, Swinkels DW, Perrone L, del Giudice EM (2010) Effect of body mass index reduction on serum hepcidin levels and iron status in obese children. Int J Obes 34:1772–1774
Conway RE, Geissler CA, Hider RC, Thompson RP, Powell JJ (2006) Serum iron curves can be used to estimate dietary iron bioavailability in humans. J Nutr 136:1910–1914
Gong L, Yuan F, Teng J, Li X, Zheng S, Lin L, Deng H, Ma G, Sun C, Li Y (2014) Weight loss, inflammatory markers, and improvements of iron status in overweight and obese children. J Pediatr 164:795–800
Baumgartner J, Smuts CM, Aeberli I, Malan L, Tjalsma H, Zimmerman MB (2013) Overweight impairs efficacy of iron supplementation in iron-deficient South African children: a randomised controlled intervention. Int J Obes 37:24–30
Sanad M, Osman M, Gharib A (2011) Obesity modulates serum hepcidin and treatment outcome of iron deficiency anaemia in children: a case–control study. Ital J Pediatr 37:34–39
Zimmerman MB, Zeder C, Muthayya S, Winichagoon P, Chaouki N, Aeberli I, Hurrell RF (2008) Adiposity in women and children from transition countries predicts decreased iron absorption, iron deficiency and reduced response to iron fortification. Int J Obes 32:1098–1104
Swinburn BA, Caterson I, Seidell JC, James WP (2004) Diet, nutrition and the prevention of excess weight gain and obesity. Public Health Nutr 7:123–146
Poti JM, Duffey KJ, Popkin BM (2014) The association of fast food consumption with poor dietary outcomes and obesity among children: Is it the fast food or the remainder of the diet? Am J Clin Nutr 99:162–171
Ortega RM, Requejo AM, López-Sobaler AM, Quintas ME, Andrés P, Redondo MR, Navia B, López-Bonilla MD, Rivas T (1998) Difference in the breakfast habits of overweight/obese and normal weight schoolchildren. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 68:125–132
Hassapidou M, Fotiadou E, Maglara E, Papadopoulou SK (2006) Energy intake, diet composition, energy expenditure, and body fatness of adolescents in northern Greece. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14:855–862
Tornaritis MJ, Philippou E, Hadjigeorgiou C, Kourides YA, Panayi A, Savva SC (2014) A study of the dietary intake of Cypriot children and adolescents aged 6–18 years and the association of mother’s educational status and children’s weight status on adherence to nutritional recommendations. BMC Public Health 14:13
Manios Y, Moschonis G, Papandreou C, Politidou E, Naoumi A, Peppas D, Mavrogianni C, Lionis C, Chrousos GP, On behalf of the ‘Healthy Growth Study’ group (2015) Revised Healthy Lifestyle-Diet Index and associations with obesity and iron deficiency in school children: the Healthy Growth Study. J Hum Nutr Diet 28:50–58
Vandevijvere S, Michels N, Verstraete S, Ferrari M, Leclercq C, Cuenca-García M, Grammatikaki E, Manios Y, Gottrand F, Valtueña J, Kersting M, Gonzalez-Gross M, Moreno L, Mouratidou T, Stevens K, Meirhaeghe A, Dallongeville J, Sjöström M, Hallstrom L, Kafatos A, Widhalm K, Molnar D, De Henauw S, Huybrechts I, HELENA study group (2013) Intake and dietary sources of haem and non-haem iron among European adolescents and their association with iron status and different lifestyle and socio-economic factors. Eur J Clin Nutr 67:765–772
Rossander L, Hallberg L, Bjorn-Rasmussen E (1979) Absorption of iron from breakfast meals. Am J Clin Nutr 32:2484–2489
Densupsoontorn N, Jirapinyo P, Kangwanpornsiri C (2013) Micronutrient deficiencies in obese Thai children. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 22:497–503
Lissner L, Troiano RP, Midthune D, Heitmann BL, Kipnis V, Subar AF, Potischman N (2007) OPEN about obesity: recovery biomarkers, dietary reporting errors and BMI. Int J Obes (Lond) 31:956–961
Collins CE, Watson J, Burrows T (2010) Measuring dietary intake in children and adolescents in the context of overweight and obesity. Int J Obes (Lond) 34:1103–1115
Livingstone MBE, Robson PJ, Wallace JM (2004) Issues in dietary intake assessment of children and adolescents. Br J Nutr 92:S213–S222
Livingstone MBE, Robson PJ (2000) Measurement of dietary intake in children. Proc Nutr Soc 59:279–293
Bingham SA (1987) The dietary assessment of individuals: methods, accuracy, new techniques and recommendations. Nutr Abstr Rev 57:705–742
Bingham SA, Gill C, Welch A, Cassidy A, Runswick SA, Oakes S, Lubin R, Thurnham DI, Key TJ, Roe L, Khaw KT, Day NE (1997) Validation of dietary assessment methods in the UK arm of EPIC using weighed records, and 24-hour urinary nitrogen and potassium and serum vitamin C and carotenoids as biomarkers. Int J Epidemiol 26:S137–S151
Block G (1982) A review of validations of dietary assessment methods. Am J Epidemiol 115:492–505
Monsen ER, Balfinity JL (1982) Calculating dietary iron bio-availability—refinement and computerisation. J Am Diet Assoc 80:307–311
Tseng M, Chakraborty H, Robinson DT, Mendez M, Kohlmeier L (1997) Adjustment of iron intake for dietary enhancers and inhibitors in population studies: bioavailable iron in rural and urban residing Russian women and children. J Nutr 127:1456–1468
Reddy MB, Hurrell RF, Cook JD (2000) Estimation of nonheme-iron bioavailability from meal composition. Am J Clin Nutr 71:937–943
Hallberg L, Hulthén L (2000) Prediction of dietary iron absorption: an algorithm for calculating absorption and bio-availability of dietary iron. Am J Clin Nutr 71:1147–1160
Conway RE, Powell JJ, Geissler CA (2007) A food-group based algorithm to predict non-heme iron absorption. Int J Food Sci Nutr 58:29–41
Rickard AP, Chatfield MD, Conway RE, Stephen AM, Powell JJ (2009) An algorithm to assess intestinal iron availability for use in dietary surveys. Br J Nutr 102:1678–1685
Dandona P, Aljada A, Bandyopadhyay A (2004) Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol 25:4–7
Wrighting DM, Andrews NC (2006) Interleukin-6 induces hepcidin expression through STAT3. Blood 108:3204–3209
Verga Falzacappa MV, Vujic Spasic M, Kessler R, Stolte J, Hentze MW, Muckenthaler MU (2007) STAT3 mediates hepatic hepcidin expression and its inflammatory stimulation. Blood 109:353–358
Hintze KJ, Snow D, Nabor D, Timbimboo H (2011) Adipocyte hypoxia increases hepatocyte hepcidin expression. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:764–771
Bekri SS, Gual PP, Anty RR, Luciani NN, Dahman MM, Ramesh BB, Iannelli A, Staccini-Myx A, Casanova D, Ben Amor I, Saint-Paul MC, Huet PM, Sadoul JL, Gugenheim J, Srai SK, Tran A, Le Marchand-Brustel Y (2006) Increased adipose tissue expression of hepcidin in severe obesity is independent from diabetes and NASH. Gastroenterology 131:788–796
Ganz T (2007) Molecular control of iron transport. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:394–400
Nemeth E, Ganz T (2006) Regulation of iron metabolism by hepcidin. Annu Rev Nutr 26:323–342
Nemeth E, Ganz T (2009) The role of hepcidin in iron metabolism. Acta Haematol 122:78–86
Bouglé DL, Bureau F, Laroche D (2009) Trace element status in obese children: relationship with metabolic risk factors. E Spen Eur E J Clin Nutr Metab 4:e98–e100
del Giudice EM, Santoro N, Amato A, Brienza C, Calabro P, Wiegerinck ET, Cirillo G, Tartaglione N, Grandone A, Swinkels DW, Perrone L (2009) Hepcidin in obese children as a potential mediator of the association between obesity and iron deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:5102–5107
Perrone L, Gialanella G, Moro R, Feng SL, Boccia E, Palombo G, Carbone MT, Di Toro R (1998) Zinc, copper, and iron in obese children and adolescents. Nutr Res 18:183–189
Bouglé D, Brouard J (2013) Iron in child obesity. Relationships with inflammation and metabolic risk factors. Nutrients 5:2222–2230
Torti FM, Torti SV (2002) Regulation of ferritin genes and protein. Blood 99:3505–3516
Gabay C, Kushner I (1999) Acute phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 340:448–454
Murer SB, Aeberli I, Braegger CP, Gittermann M, Hersberger M, Leonard SW, Taylor AW, Traber MG, Zimmermann MB (2014) Antioxidant supplements reduced oxidative stress and stabilized liver function tests but did not reduce inflammation in a randomized controlled trial in obese children and adolescents. J Nutr 144:193–201
Skinner AC, Steiner MJ, Henderson FW, Perrin EM (2010) Multiple markers of inflammation and weight status: cross-sectional analyses throughout childhood. Pediatrics 125:e801–e809
Richardson MW, Ang L, Visintainer PF, Wittcopp CA (2009) The abnormal measures of iron homeostasis in pediatric obesity are associated with the inflammation of obesity. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 2009:713269. doi:10.1155/2009/713269
Fried SK, Bunkin DA, Greenberg AS (1998) Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:847–850
Fain JN, Madan AK, Hiler ML, Cheema P, Bahouth SW (2004) Comparison of the release of adipokines by adipose tissue, adipose tissue matrix, and adipocytes from visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues of obese humans. Endocrinology 145:2273–2282
Mathieu P, Lemieux I, Després JP (2010) Obesity, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87:407–416
Hamza RT, Hamed AI, Kharshoum RR (2013) Iron homeostasis and serum hepcidin-25 levels in obese children and adolescents: relation to body mass index. Horm Res Paediatr 80:11–17
Nazif HK, El-Shaheed AA, El-Shamy KA, Mohsen MA, Fadl NN, Moustafa RS (2015) Study of serum hepcidin as a potential mediator of the disrupted iron metabolism in obese adolescents. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 9:172–178
Mehta K, Van Thiel DH, Shah N, Mobarhan S (2002) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathogenesis and the role of antioxidants. Nutr Rev 60:289–293
Mandato C, Lucariello S, Licenziati MR, Franzese A, Spagnuolo MI, Ficarella R, Pacilio M, Amitrano M, Capuano G, Meli R, Vajro P (2005) Metabolic, hormonal, oxidative, and inflammatory factors in pediatric obesity-related liver disease. J Pediatr 147:62–66
Garanty-Bogacka B, Syrenicz M, Goral J, Krupa B, Syrenicz J, Walczak M, Syrenicz A (2011) Changes in inflammatory biomarkers after successful lifestyle intervention in obese children. Endokrynol Pol 62:499–505
Van Hoorenbeeck K, Franckx H, Debode P, Aerts P, Wouters K, Ramet J, Van Gaal LF, Desager KN, De Backer WA, Verhulst SL (2012) Weight loss and sleep-disordered breathing in childhood obesity: effects on inflammation and uric acid. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20:172–177
Reinehr T, Stoffel-Wagner B, Roth CL, Andler W (2005) High-sensitive C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and cardiovascular risk factors before and after weight loss in obese children. Metabolism 54:1155–1161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutchinson, C. A review of iron studies in overweight and obese children and adolescents: a double burden in the young?. Eur J Nutr 55, 2179–2197 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1155-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1155-7