Abstract
Background
We aimed to compare patient characteristics and outcome of patients who had either undergone pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) or AV-node ablation (AVN) to control AF-related symptoms.
Methods
From the German Ablation Registry, we analyzed data of 4444 patients (95%) who had undergone PVI and 234 patients (5%) with AVN.
Results
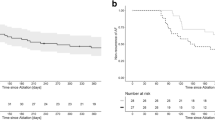
AVN patients were on average 10 years older than PVI patients (71 ± 10 vs. 61 ± 10 years, p < 0.001) with 33% aged > 75 years. AVN patients had significantly more cardiovascular comorbidities (diabetes 21% vs. 8%, renal insufficiency 24% vs. 3%, underlying heart disease 80% vs. 36%, severely reduced left ventricular function 28% vs. 1%, all p < 0.001). Significantly more PVI patients had paroxysmal AF (63% vs. 18%, p < 0.001), and more AVN patients had long-standing persistent AF (44% vs. 7%, p < 0.001). At 1-year follow-up, mortality in the AVN group was much higher (Kaplan–Meier estimates 9.8% vs. 0.5%). 20% of PVI patients had undergone another ablation vs. 3% AVN patients (p < 0.001). Symptomatic improvement was equally achieved in about 80%. Re-hospitalization for cardiovascular reasons occurred significantly more often in PVI vs. AVN patients (31% vs. 18%, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In the large German Ablation Registry, AVN ablation was performed much less frequently than PVI for symptomatic treatment of AF and typically in older patients with more comorbidity. Symptomatic improvement was similar in both groups. Hospitalizations for cardiovascular reasons were lower in AVN patients despite older age and more cardiovascular comorbidities. 20% of PVI patients had undergone at least one re-ablation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener HC, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks J, Hindricks G, Manolis AS, Oldgren J, Popescu BA, Schotten U, Van Putte B, Vardas P, Agewall S, Camm J, Baron Esquivias G, Budts W, Carerj S, Casselman F, Coca A, De Caterina R, Deftereos S, Dobrev D, Ferro JM, Filippatos G, Fitzsimons D, Gorenek B, Guenoun M, Hohnloser SH, Kolh P, Lip GY, Manolis A, McMurray J, Ponikowski P, Rosenhek R, Ruschitzka F, Savelieva I, Sharma S, Suwalski P, Tamargo JL, Taylor CJ, Van Gelder IC, Voors AA, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Zeppenfeld K (2016) 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J 37:2893–2962
January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC Jr, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Murray KT, Sacco RL, Stevenson WG, Tchou PJ, Tracy CM, Yancy CW, American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (2014) 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:e1–e76
Macle L, Cairns J, Leblanc K, Tsang T, Skanes A, Cox JL, Healey JS, Bell A, Pilote L, Andrade JG, Mitchell LB, Atzema C, Gladstone D, Sharma M, Verma S, Connolly S, Dorian P, Parkash R, Talajic M, Nattel S, Verma A, CCS Atrial Fibrillation Guidelines Committee (2016) 2016 Focused Update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Can J Cardiol 32:1170–1185
Hohnloser SH, Kuck KH, Lilienthal J (2000) Rhythm or rate control in atrial fibrillation—Pharmacological Intervention in Atrial Fibrillation (PIAF): a randomised trial. Lancet 356(9244):1789–1794
Wyse DG, Waldo AL, DiMarco JP, Domanski MJ, Rosenberg Y, Schron EB, Kellen JC, Greene HL, Mickel MC, Dalquist JE, Corley SD, Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Investigators (2002) A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 347:1825–1833
Van Gelder IC, Hagens VE, Bosker HA, Kingma JH, Kamp O, Kingma T, Said SA, Darmanata JI, Timmermans AJ, Tijssen JG, Crijns HJ (2002) Rate Control versus Electrical Cardioversion for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Study Group. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with recurrent persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 347:1834–1840
Roy D, Talajic M, Nattel S, Wyse DG, Dorian P, Lee KL, Bourassa MG, Arnold JM, Buxton AE, Camm AJ, Connolly SJ, Dubuc M, Ducharme A, Guerra PG, Hohnloser SH, Lambert J, Le Heuzey JY, O’Hara G, Pedersen OD, Rouleau JL, Singh BN, Stevenson LW, Stevenson WG, Thibault B, Waldo AL, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Investigators (2008) Rhythm control versus rate control for atrial fibrillation and heart failure. N Engl J Med 358:2667–2677
Eckardt L, Frommeyer G, Sommer P, Steven D, Deneke T, Estner HL, Kriatselis C, Kuniss M, Busch S, Tilz RR, Bonnemeier H, von Bary C, Voss F, Meyer C, Thomas D, Neuberger H-R (2018) Updated survey on interventional electrophysiology: 5-year follow-up of infrastructure, procedures, and training positions in Germany. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 4:820–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacep.2018.01.001
Khan MN, Jaïs P, Cummings J, Di Biase L, Sanders P, Martin DO, Kautzner J, Hao S, Themistoclakis S, Fanelli R, Potenza D, Massaro R, Wazni O, Schweikert R, Saliba W, Wang P, Al-Ahmad A, Beheiry S, Santarelli P, Starling RC, Dello Russo A, Pelargonio G, Brachmann J, Schibgilla V, Bonso A, Casella M, Raviele A, Haïssaguerre M, Natale A, PABA-CHF Investigators (2008) Pulmonary-vein isolation for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure. N Engl J Med 359:1778–1785
Brachmann J, Lewalter T, Kuck KH, Andresen D, Willems S, Spitzer SG, Straube F, Schumacher B, Eckardt L, Danilovic D, Thomas D, Hochadel M, Senges J (2017) Long-term symptom improvement and patient satisfaction following catheter ablation of supraventricular tachycardia: insights from the German Ablation Registry. Eur Heart J 38:1317–1326
Allen LaPointe NM, Lokhnygina Y, Rimmler J, Sanders GD, Peterson ED, Al-Khatib SM (2014) Use of rate and rhythm control drugs in patients younger than 65 years with atrial fibrillation. J Atr Fibrillation 7(1):1062
Chatterjee S, Sardar P, Lichstein E, Mukherjee D, Aikat S (2013) Pharmacologic rate versus rhythm-control strategies in atrial fibrillation: an updated comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 36:122–133
Marrouche NF, Brachmann J, Andresen D, Siebels J, Boersma L, Jordaens L, Merkely B, Pokushalov E, Sanders P, Proff J, Schunkert H, Christ H, Vogt J, Bänsch D, CASTLE-AF Investigators (2018) Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with heart failure. N Engl J Med 378:417–427
Friberg L, Tabrizi F, Englund A (2016) Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation is associated with lower incidence of stroke and death: data from Swedish health registries. Eur Heart J 37:2478–2487
Saliba W, Schliamser JE, Lavi I, Barnett-Griness O, Gronich N, Rennert G (2017) Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation is associated with reduced risk of stroke and mortality: a propensity score-matched analysis. Heart Rhythm 14:635–642
Aliot E, Brandes A, Eckardt L, Elvan A, Gulizia M, Heidbuchel H, Kautzner J, Mont L, Morgan J, Ng A, Szumowski L, Themistoclakis S, Van Gelder IC, Willems S, Kirchhof P (2015) The EAST study: redefining the role of rhythm control therapy in atrial fibrillation: EAST, the Early treatment of Atrial fibrillation for Stroke prevention Trial. Eur Heart J 36:255–256. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu476
Moreno J, Zamorano JL (2014) The CABANA trial. Eur Heart J 35:1908–1909
Ammar-Busch S, Bourier F, Reents T, Semmler V, Telishevska M, Kathan S, Hofmann M, Hessling G, Deisenhofer I (2017) Ablation of Complex Fractionated Electrograms With or Without ADditional LINEar Lesions for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (The ADLINE Trial). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 28:636–641
Fink T, Schlüter M, Heeger CH, Lemes C, Maurer T, Reissmann B, Riedl J, Rottner L, Santoro F, Schmidt B, Wohlmuth P, Mathew S, Sohns C, Ouyang F, Metzner A, Kuck KH (2017) Stand-alone pulmonary vein isolation versus pulmonary vein isolation with additional substrate modification as index ablation procedures in patients with persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: the randomized Alster-Lost-AF Trial (Ablation at St. Georg Hospital for Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation). Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 10(7):28687670. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCEP.117.005114 pii: e005114.
Verma A, Jiang CY, Betts TR, Chen J, Deisenhofer I, Mantovan R, Macle L, Morillo CA, Haverkamp W, Weerasooriya R, Albenque JP, Nardi S, Menardi E, Novak P, Sanders P, STAR AF II Investigators (2015) Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 372:1812–1822. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1408288
Vogler J, Willems S, Sultan A, Schreiber D, Lüker J, Servatius H, Schäffer B, Moser J, Hoffmann BA, Steven D (2015) Pulmonary vein isolation versus defragmentation: the CHASE-AF Clinical Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 66:2743–2752
Funding
The work was supported by an unrestricted grant from foundation ‘Stiftung Institut für Herzinfarktforschung Ludwigshafen’ (IHF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) and minor unrestricted grants from Medtronic, Biosense Webster, and Biotronik.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wasmer, K., Hochadel, M., Wieneke, H. et al. Long-term symptom improvement and patient satisfaction after AV-node ablation vs. pulmonary vein isolation for symptomatic atrial fibrillation: results from the German Ablation Registry. Clin Res Cardiol 108, 395–401 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-018-1368-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-018-1368-2