Abstract
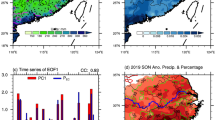
The predictability of precipitation in the Arabian Peninsula is of great importance for local agriculture and socio-economic development. In autumn, precipitation in the Arabian Peninsula is correlated with ENSO, but its predictive skill is limited. Here, we show that spring sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies in the southwest Pacific (SWP) exhibit a higher correlation with autumn precipitation in the Arabian Peninsula than ENSO, enhancing the predictability of local dry/wet variations. This cross-season and cross-hemispheric relationship is established through the western tropical Pacific (WTP). The spring SWP SST anomalies show a cross-hemispheric propagation embedded in the southerly monsoon flow by initiating the wind-evaporation-SST feedback, which sustains the progression of SST anomalies towards the WTP in autumn. The warming (cooling) of WTP SST enhances (suppresses) the convection in the Indo-western Pacific and leads to an anomalous cyclonic (anticyclonic) circulation in the northern Indian Ocean, which corresponds to northerly (southerly) anomalies and moisture divergence (convergence) over the northern Arabian Peninsula, causing precipitation decrease (increase). These results indicate that the SWP SST is a useful predictor of Arabian Peninsula precipitation six months in advance through the cross-hemispheric influence. A model based on the spring SWP SST and preceding winter ENSO (Niño3.4) shows a high predictive skill for the autumn precipitation anomalies in the Arabian Peninsula.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available to the public. Detailed information has been provided in the "Data and Method" section in the manuscript.
References
Abid MA, Kucharski F, Almazroui M, Kang IS (2016) Interannual rainfall variability and ECMWF-Sys4-based predictability over the Arabian Peninsula winter monsoon region. Q J Royal Meteorol Soc 142:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2648
Abid MA, Almazroui M, Kucharski F, O’Brien E, Yousef AE (2018) ENSO relationship to summer rainfall variability and its potential predictability over Arabian Peninsula region. Npj Clim Atmospheric Sci. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-017-0003-7
Abram NJ et al (2022) Coupling of Indo-Pacific climate variability over the last millennium (vol 579, pg 385, 2020). Nature 602:E20–E20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04318-0
Almazroui M (2011) Sensitivity of a regional climate model on the simulation of high intensity rainfall events over the Arabian Peninsula and around Jeddah (Saudi Arabia). Theor Appl Climatol 104:261–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-010-0387-3
Almazroui M, Islam MN, Athar H, Jones D, Rahman MA (2012) Recent climate change in the Arabian Peninsula: annual rainfall and temperature analysis of Saudi Arabia for 1978–2009. Int J Climatol 32:953–966. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3446
Almazroui M, Abid MA, Athar H, Islam MN, Ehsan MA (2013) Interannual variability of rainfall over the Arabian Peninsula using the IPCC AR4 global climate models. Int J Climato 33:2328–2340. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3600
Almazroui M, Islam MN, Saeed F, Alkhalaf AK, Dambul R (2017) Assessing the robustness and uncertainties of projected changes in temperature and precipitation in AR5 global climate models over the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos Res 194:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.05.005
Almazroui M et al (2022) Skill of the Saudi-KAU CGCM in forecasting ENSO and its comparison with NMME and C3S models Earth. Syst Env 6:327–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-022-00311-3
Aloe AM (2014) An empirical investigation of partial effect sizes in meta-analysis of correlational data. J General Psychol 141:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221309.2013.853021
Alsaaran NA, Alghamdi AS (2022) Precipitation climatology and spatiotemporal trends over the Arabian Peninsula. Theoret Appl Climatol 147:1133–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03878-5
Athar H (2015) Teleconnections and variability in observed rainfall over Saudi Arabia during 1978–2010. Atmos Sci Lett 16:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1002/asl2.570
Atif RM, Almazroui M, Saeed S, Abid MA, Islam MN, Ismail M (2020) Extreme precipitation events over Saudi Arabia during the wet season and their associated teleconnections. Atmos Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104655
Babu CA, Jayakrishnan PR, Varikoden H (2016) Characteristics of precipitation pattern in the Arabian Peninsula and its variability associated with ENSO. Arabian J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2265-x
Boyin Huang, Peter W, Thorne Viva F, Banzon Tim, Boyer Gennady, Chepurin Jay H, Lawrimore Matthew J, Menne Thomas M, Smith Russell S, Vose Huai-Min, Zhang (2017) Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature version 5 (ERSSTv5): upgrades validations and intercomparisons. J Clim 30(20):8179-8205. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0836.1
Chen SF, Wu RG, Chen W, Hu KM, Yu B (2020) Structure and dynamics of a springtime atmospheric wave train over the North Atlantic and Eurasia. Clim Dyn 54:5111–5126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05274-7
Chen SF, Wu RG, Chen W (2021) Influence of North Atlantic sea surface temperature anomalies on springtime surface air temperature variation over Eurasia in CMIP5 models. Clim Dyn 57:2669–2686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05826-5
Choi JW, Kim IG, Kim JY, Park CH (2016) The recent strengthening of walker circulation. Sola. https://doi.org/10.2151/sola.2016-022
Cullen HM, Kaplan A, Arkin PA, Demenocal PB (2002) Impact of the North Atlantic Oscillation on middle eastern climate and streamflow. Clim Change 55:315–338. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020518305517
Dasari HP, Langodan S, Viswanadhapalli Y, Vadlamudi BR, Papadopoulos VP, Hoteit I (2018) ENSO influence on the interannual variability of the Red Sea convergence zone and associated rainfall. Int J Climatol 38:761–775. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5208
Dasari HP, Desamsetti S, Langodan S, Attada R, Ashok K, Hoteit I (2022) Long-term changes in the Arabian Peninsula rainfall and their relationship with the ENSO signals in the tropical Indo-Pacific. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-06062-7
Delacre M, Lakens D, Leys C (2017) Why psychologists should by default use Welch’s t-test instead of student’s t-test. Int Rev Soc Psychol 30:92–101. https://doi.org/10.5334/irsp.82
Ding R, Li J, Tseng YH, Ruan C (2015) Influence of the North Pacific Victoria mode on the Pacific ITCZ summer precipitation. J Geophys Res: Atmos 120(3):964–979. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD022364
Dogar MM, Sato T (2018) Analysis of climate trends and leading modes of climate variability for MENA region. J Geophys Res-Atmos 123:13074–13091. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jd029003
Fan K, Wang HJ (2007) Simulation of the AAO anomaly and its influence on the Northern Hemispheric circulation in boreal winter and spring Chinese. Chin J Geophys 50:397-403
Gelaro R et al (2017) The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J Clim 30:5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-16-0758.1
Gill AE (1980) Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q J R Meteorol Soc 106(449):447–462. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49710644905
Harris I, Jones PJUoEA-CfEDA (2017) CRU TS4. 01 Climatic research unit: time-series version 4.01 of high-resolution gridded data of month-by-month variation in climate 4
Hayashi M, Shiogama H, Emori S, Ogura T, Hirota N (2021) The Northwestern pacific warming record in August 2020 occurred under anthropogenic forcing. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020gl090956
Hersbach H et al (2020) The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J Royal Meteorol Soc 146:1999–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803
Huang JP, Yu HP, Guan XD, Wang GY, Guo RX (2016) Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2837
Huang YH, Liu XD, Yin ZY, An ZS (2021) Global impact of ENSO on dust activities with emphasis on the key region from the Arabian Peninsula to Central Asia. J Geophys Res-Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020jd034068
Kang IS, Rashid IU, Kucharski F, Almazroui M, Alkhalaf AK (2015) Multidecadal changes in the relationship between ENSO and wet-season precipitation in the Arabian Peninsula. J Clim 28:4743–4752. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-14-00388.1
Kotwicki V, Al Sulaimani Z (2009) Climates of the Arabian Peninsula-past, present, future. Int J Clim Change Strategies Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/17568690910977500
Kucharski F et al (2016) The teleconnection of the tropical Atlantic to Indo-Pacific sea surface temperatures on inter-annual to centennial time scales: a review of recent findings. Atmosphere 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7020029
Kumar KN, Entekhabi D, Molini A (2015) Hydrological extremes in hyperarid regions: a diagnostic characterization of intense precipitation over the Central Arabian Peninsula. J Geophys Res-Atmos 120:1637–1650. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014jd022341
Li J, Ruan C (2018) The North Atlantic–Eurasian teleconnection in summer and its effects on Eurasian climates. Environ Res Lett 13(2):024007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa9d33
Li JP, Zheng F, Sun C, Feng J, Wang J (2019) Pathways of influence of the northern hemisphere mid-high latitudes on east asian climate: a review. Adv Atmos Sci 36:902–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-8236-5
Li ZY, Holbrook NJ, Zhang XB, Oliver ECJ, Cougnon EA (2020) Remote forcing of tasman sea marine heatwaves. J Clim 33:5337–5354. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-19-0641.1
Liu ZY, Vavrus S, He F, Wen N, Zhong YF (2005) Rethinking tropical ocean response to global warming: The enhanced equatorial warming. J Clim 18:4684–4700. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli3579.1
Liu T, Li JP, Li YJ, Zhao S, Zheng F, Zheng JY, Yao ZX (2018) Influence of the May Southern annular mode on the South China Sea summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 51:4095–4107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3753-3
Liu YS, Gong ZQ, Sun C, Li JP, Wang L (2020) Multidecadal seesaw in Hadley circulation strength between the two hemispheres caused by the Atlantic multidecadal variability. Front Earth Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2020.580457
Liu YS, Sun C, Kucharski F, Li JP, Wang CZ, Ding RQ (2021) The North Pacific Blob acts to increase the predictability of the Atlantic warm pool. Env Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac0030
Mamalakis A, Yu JY, Randerson JT, AghaKouchak A, Foufoula-Georgiou E (2018) A new interhemispheric teleconnection increases predictability of winter precipitation in southwestern US. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04722-7
Mariotti A, Ballabrera-Poy J, Zeng N (2005) Tropical influence on Euro-Asian autumn rainfall variability. Clim Dyn 24:511–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-004-0498-6
Michaelsen J (1987) Cross-validation in statistical climate forecast models. J Clim Appl Meteorol 26:1589–1600. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1987)026%3c1589:Cviscf%3e2.0.Co;2
Nan S, Li JP (2003) The relationship between the summer precipitation in the Yangtze River valley and the boreal spring Southern Hemisphere annular mode. Geophys Res Lett 30. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003gl018381
Nnamchi HC, Li JP, Kang IS, Kucharski F (2013) Simulated impacts of the South Atlantic Ocean Dipole on summer precipitation at the Guinea Coast. Clim Dyn 41:677–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1629-0
Patlakas P, Stathopoulos C, Flocas H, Bartsotas NS, Kallos G (2021) Precipitation climatology for the arid region of the Arabian Peninsula-variability, trends and extremes. Climate. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli9070103
Saeed S, Almazroui M (2019) Impacts of mid-latitude circulation on winter precipitation over the Arabian Peninsula. Clim Dyn 53:5253–5264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04862-6
Salinger MJ et al (2019) The unprecedented coupled ocean-atmosphere summer heatwave in the New Zealand region 2017/18: drivers, mechanisms and impacts. Env Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab012a
Shears NT, Bowen MM (2017) Half a century of coastal temperature records reveal complex warming trends in western boundary currents. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14944-2
Shi N, Tian PY, Zhang LY (2019) Simultaneous influence of the Southern Hemisphere annular mode on the atmospheric circulation of the Northern Hemisphere during the boreal winter. Int J Climatol 39:2685–2696. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5981
Sohn BJ, Yeh SW, Schmetz J, Song HJ (2013) Observational evidences of walker circulation change over the last 30 years contrasting with GCM results. Clim Dyn 40:1721–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1484-z
Sun C, Li JP, Zhao S (2015) Remote influence of Atlantic multidecadal variability on Siberian warm season precipitation. Sci Rep 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16853
Sun C et al (2019) Recent Acceleration of Arabian Sea Warming Induced by the Atlantic-Western Pacific Trans-basin Multidecadal Variability. Geophys Res Lett 46:1662–1671. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018gl081175
Sun C, Liu Y, Wei T, Kucharski F, Li J, Wang C (2022) Cross-hemispheric SST propagation enhances the predictability of tropical western Pacific climate. NPJ Clim Atmos Sci 5:38. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-022-00262-6
Wu ZW, Dou J, Lin H (2015) Potential influence of the November-December Southern Hemisphere annular mode on the East Asian winter precipitation: a new mechanism. Clim Dyn 44:1215–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2241-2
Xie SP, Hu KM, Hafner J, Tokinaga H, Du Y, Huang G, Sampe T (2009) Indian Ocean Capacitor Effect on Indo-Western Pacific Climate during the Summer following El Nino. J Clim 22:730–747 https://doi.org/10.1175/2008jcli2544.1
Xie W, Fan GZ, Ding RQ, Li JP, Li BS, Qin JH, Zhou XJ (2019) Interdecadal change in the lagged relationship between the Victoria mode and ENSO. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 12:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2019.1620081
Xu K, Zhu C, Wang W (2016) The cooperative impacts of the El Nino-Southern oscillation and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the interannual variability of autumn rainfall in China. Int J Climatol 36:1987–1999. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4475
Yamagata T, Behera SK, Luo JJ, Masson S, Jury MR, Rao SA (2004) Coupled ocean-atmosphere variability in the tropical Indian ocean. In: Conference on Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction and Climate Variability, San Francisco, CA, Dec 2002. Geophysical Monograph Book Series. pp 189–211
Zhang TT, Yang S, Jiang XW, Dong SR (2016) Sub-seasonal prediction of the maritime continent rainfall of wet-dry transitional seasons in the NCEP climate forecast version 2. Atmosphere. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7020028
Zhao W, Chen SF, Chen W, Yao SL, Nath D, Yu B (2019) Interannual variations of the rainy season withdrawal of the monsoon transitional zone in China. Clim Dyn 53:2031–2046. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04762-9
Zheng F, Li JP (2012) Impact of preceding boreal winter southern hemisphere annular mode on spring precipitation over south China and related mechanism. Chin J Geophys 55:3542–3557. https://doi.org/10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.004
Zheng F, Li J, Liu T (2014a) Some advances in studies of the climatic impacts of the Southern Hemisphere annular mode. Acta Meteorol Sin 72:926–939
Zheng F, Li JP, Liu T (2014b) Some advances in studies of the climatic impacts of the Southern Hemisphere annular mode. J Meteorol Res 28:820–835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4079-2
Funding
This work is jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41790474, and 41975082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, T., Sun, C., Liu, Y. et al. Cross-season and cross-hemispheric influence of southwest Pacific SST on Arabian Peninsula precipitation. Clim Dyn 61, 669–686 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06572-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06572-y