Abstract
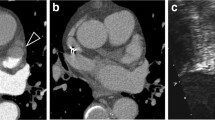
Filling defects of the left atrial appendage (LAA) on multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) are known to occur, not only due to LAA thrombi formation, but also due to the disturbance of blood flow in the LAA of patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the impact of the maintenance of sinus rhythm via ablation on the incidence of LAA filling defects on MDCT in patients with AF. A total of 459 consecutive patients were included in the present study. Prior to ablation, MDCT and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) were performed. AF ablation was performed in patients without LAA thrombi confirmed on TEE. The LAA filling defects were evaluated on MDCT at 3 months after ablation. LAA filling defects were detected on MDCT in 51 patients (11.1 %), among whom the absence of LAA thrombi was confirmed in 42 patients using TEE. The LAA Doppler velocity in patients with LAA filling defects was lower than that of patients without filling defects (0.61 ± 0.19 vs. 0.47 ± 0.21 m/s; P < 0.0001). The sensitivity, specificity and negative predictive value of MDCT in the detection of thrombi were 100, 91 and 100 %, respectively. No LAA filling defects were observed on MDCT at 3 months after ablation in any of the patients, including the patients in whom filling defects were noted prior to the procedure. MDCT is useful for evaluating the presence of LAA thrombi and the blood flow of the LAA. The catheter ablation of AF not only suppresses AF, but also eliminates LAA filling defect on MDCT suggesting the improvement of LAA blood flow.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haissaguerre M, Shah DC, Jais P, Hocini M, Yamane T, Deisenhofer I, Chauvin M, Garrigue S, Clementy J (2000) Electrophysiological breakthroughs from the left atrium to the pulmonary veins. Circulation 102:2463–2465
Lüker J, Sultan A, Sehner S, Hoffmann B, Servatius H, Willems S, Steven D (2015) Use of antiarrhythmic drugs during ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: observations from a large single-centre cohort. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-015-0771-0
Vazquez SR, Johnson SA, Rondina MT (2010) Peri-procedural anticoagulation in patients undergoing ablation for atrial fibrillation. Thromb Res 126:e69–e77
Spragg DD, Dalal D, Cheema A, Scherr D, Chilukuri K, Cheng A, Henrikson CA, Marine JE, Berger RD, Dong J, Calkins H (2008) Complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation:incidence and predictors. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 19:627–631
Vasamreddy CR, Dalal D, Eldadah Z, Dickfeld T, Jayam VK, Henrickson C, Meininger G, Dong J, Lickfett L, Berger R, Calkins H (2005) Safety and efficacy of circumferential pulmonary vein catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2:42–48
Tokuda M, Yamane T, Tokutake K, Yokoyama K, Hioki M, Narui R, Tanigawa SI, Yamashita S, Inada K, Matsuo S, Yoshimura M (2014) Catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation in a patient with cor triatriatum sinister demonstrating a total common trunk of the pulmonary vein. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-014-0580-x
Tada H, Oral H, Knight BP, Morady F (2002) Three-dimensional computed tomography of the pulmonary veins. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 13:521
Patel A, Au E, Donegan K, Kim RJ, Lin FY, Stein KM, Markowitz SM, Iwai S, Weinsaft JW, Min JK, Lerman BB (2008) Multidetector row computed tomography for identification of left atrial appendage filling defects in patients undergoing pulmonary vein isolation for treatment of atrial fibrillation: comparison with transesophageal echocardiography. Heart Rhythm 5:253–260
Martinez MW, Kirsch J, Williamson EE, Syed IS, Feng D, Ommen S, Packer DL, Brady PA (2009) Utility of nongated multidetector computed tomography for detection of left atrial thrombus in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2:69–76
Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, Schotten U, Savelieva I, Ernst S, Van Gelder IC, Al-Attar N, Hindricks G, Prendergast B, Heidbuchel H, Alfieri O, Angelini A, Atar D, Colonna P, De Caterina R, De Sutter J, Goette A, Gorenek B, Heldal M, Hohloser SH, Kolh P, Le Heuzey JY, Ponikowski P, Rutten FH (2010) Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the task force for the management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 31:2369–2429
Di Biase L, Santangeli P, Anselmino M, Mohanty P, Salvetti I, Gili S, Horton R, Sanchez JE, Bai R, Mohanty S, Pump A, Cereceda Brantes M, Gallinghouse GJ, Burkhardt JD, Cesarani F, Scaglione M, Natale A, Gaita F (2012) Does the left atrial appendage morphology correlate with the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation? Results from a multicenter study. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:531–538
Nedios S, Koutalas E, Kornej J, Rolf S, Arya A, Sommer P, Husser D, Hindricks G, Bollmann A (2015) Cardiogenic stroke despite low CHA2 DS2-VASc score: assessing stroke risk by left atrial appendage anatomy (ASK LAA). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 26:915–921
Agmon Y, Khandheria BK, Gentile F, Seward JB (1999) Echocardiographic assessment of the left atrial appendage. J Am Coll Cardiol 34:1867–1877
Sadanandan S, Sherrid MV (2000) Clinical and echocardiographic characteristics of left atrial spontaneous echo contrast in sinus rhythm. J Am Coll Cardiol 35:1932–1938
Yamane T, Matsuo S, Date T, Lellouche N, Hioki M, Narui R, Ito K, Tanigawa S, Yamashita S, Tokuda M, Yoshida H, Inada K, Shibayama K, Miyanaga S, Miyazaki H, Abe K, Sugimoto K, Yoshimura M (2011) Repeated provocation of time- and ATP-induced early pulmonary vein reconnections after pulmonary vein isolation: eliminating paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in a single procedure. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 4(5):601–608
Haïssaguerre M, Sanders P, Hocini M, Takahashi Y, Rotter M, Sacher F, Rostock T, Hsu LF, Bordachar P, Reuter S, Roudaut R, Clémenty J, Jaïs P (2005) Catheter ablation of long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation: critical structures for termination. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 16:1125–1137
Matsuo S, Yamane T, Date T, Tokutake K, Hioki M, Narui R, Ito K, Tanigawa S, Yamashita S, Tokuda M, Inada K, Arase S, Yagi H, Sugimoto K, Yoshimura M (2012) Substrate modification by pulmonary vein isolation and left atrial linear ablation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation: its impact on complex-fractionated atrial electrograms. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 23:962–970
Handke M, Harloff A, Hetzel A, Olschewski M, Bode C, Geibel A (2005) Left atrial appendage flow velocity as a quantitative surrogate parameter for thromboembolic risk: determinants and relationship to spontaneous echocontrast and thrombus formation–a transesophageal echocardiographic study in 500 patients with cerebral ischemia. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1366–1372
Choi JI, Park SM, Park JS, Hong SJ, Pak HN, Lim do S, Kim YH, Shim WJ (2008) Changes in left atrial structure and function after catheter ablation and electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation. Circ J 72:2051–2057
Takahashi Y, O’Neill MD, Hocini M, Reant P, Jonsson A, Jaïs P, Sanders P, Rostock T, Rotter M, Sacher F, Laffite S, Roudaut R, Clémenty J, Haïssaguerre M (2007) Effects of stepwise ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation on atrial electrical and mechanical properties. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:1306–1314
Park MY, Shin SH, Oh WJ, Lim HE, Pak HN, Lim do S, Kim YH, Ro YM, Shim WJ (2008) Prognostic implication of the left atrial appendage mechanical reserve after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. Circ J 72:256–261
Jaber WA, Prior DL, Thamilarasan M, Grimm RA, Thomas JD, Klein AL, Asher CR (2000) Efficacy of anticoagulation in resolving left atrial and left atrial appendage thrombi: a transesophageal echocardiographic study. Am Heart J 140:150–156
Kim YY, Klein AL, Halliburton SS, Popovic ZB, Kuzmiak SA, Sola S, Garcia MJ, Schoenhagen P, Natale A, Desai MY (2007) Left atrial appendage filling defects identified by multidetector computed tomography in patients undergoing radiofrequency pulmonary vein antral isolation: a comparison with transesophageal echocardiography. Am Heart J 154:1199–1205
Feuchtner GM, Dichtl W, Bonatti JO, Jodocy D, Müller S, Hintringer F, Gradl J, Klauser A, Cury RC (2008) Diagnostic accuracy of cardiac 64-slice computed tomography in detecting atrial thrombi. Comparative study with transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac surgery. Invest Radiol 43:794–801
Hur J, Pak HN, Kim YJ, Lee HJ, Chang HJ, Hong YJ, Choi BW (2013) Dual-enhancement cardiac computed tomography for assessing left atrial thrombus and pulmonary veins before radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 112:238–244
Kapa S, Martinez MW, Williamson EE, Ommen SR, Syed IS, Feng D, Packer DL, Brady PA (2010) ECG-gated dual-source CT for detection of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients undergoing catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 29:75–81
Homsi R, Nath B, Luetkens JA, Schwab JO, Schild HH, Naehle CP (2015) Can contrast-enhanced multi-detector computed tomography replace transesophageal echocardiography for the detection of thrombogenic milieu and thrombi in the left atrial appendage: a prospective study with 124 patients. Rofo. doi:10.1055/s-0041-106067
Dorenkamp M, Sohns C, Vollmann D, Lüthje L, Seegers J, Wachter R, Puls M, Staab W, Lotz J, Zabel M (2013) Detection of left atrial thrombus during routine diagnostic work-up prior to pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation: role of transesophageal echocardiography and multidetector computed tomography. Int J Cardiol 163:26–33
Alkadhi H, Stolzmann P, Desbiolles L, Baumueller S, Goetti R, Plass A, Scheffel H, Feuchtner G, Falk V, Marincek B, Leschka S (2010) Low-dose, 128-slice, dual-source CT coronary angiography: accuracy and radiation dose of the high-pitch and the step-and-shoot mode. Heart 96:933–938
Thai WE, Wai B, Lin K, Cheng T, Heist EK, Hoffmann U, Singh JP, Truong QA (2012) Pulmonary venous anatomy imaging with low-dose, prospectively ECG-triggered, high-pitch 128-slice dual-source computed tomography. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 5:521–530
Lickfett L, Mahesh M, Vasamreddy C, Bradley D, Jayam V, Eldadah Z, Dickfeld T, Kearney D, Dalal D, Lüderitz B, Berger R, Calkins (2004) Radiation exposure during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 110:3003–3010
Macle L, Weerasooriya R, Jais P, Scavee C, Raybaud F, Choi KJ, Hocini M, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M (2003) Radiation exposure during radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 26:288–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in association with the present study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hioki, M., Matsuo, S., Tokutake, K. et al. Filling defects of the left atrial appendage on multidetector computed tomography: their disappearance following catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation and the detection of LAA thrombi by MDCT. Heart Vessels 31, 2014–2024 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0819-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0819-9