Abstract
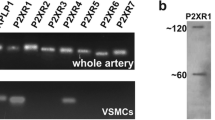
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of GABAB receptors, a subclass of receptors to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAB), in human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs), and to explore if altering receptor activation modified intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) of HASMCs. Real-time PCR, western blots and immunofluorescence were used to determine the expression of GABABR1 and GABABR2 in cultured HASMCs. Immunohistochemistry was used to localize the two subunits in human left anterior descending artery (LAD). The effects of the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen on [Ca2+]i in cultured HASMCs were demonstrated using fluo-3. Both GABABR1 and GABABR2 mRNA and protein were identified in cultured HASMCs and antibody staining was also localized to smooth muscle cells of human LAD. 100 μM baclofen caused a transient increase of [Ca2+]i in cultured HASMCs regardless of whether Ca2+ was added to the medium, and the effects were inhibited by pre-treatment with CGP46381 (selective GABAB receptor antagonist), pertussis toxin (a Gi/o protein inhibitor), and U73122 (a phospholipase C blocker). GABAB receptors are expressed in HASMCs and regulate the [Ca2+]i via a Gi/o-coupled receptor pathway and a phospholipase C activation pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- GABABR1 :
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit one
- GABABR2 :
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit two
- HASMCs:
-
Human aortic smooth muscle cells
- VSMCs:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- G proteins:
-
Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins
- [Ca2+]i:
-
Intracellular Ca2+ concentration
- SMCM:
-
Smooth muscle cell medium
- LAD:
-
Left anterior descending artery
References
White JH, Wise A, Main MJ, Green A, Fraser NJ, Disney GH, Barnes AA, Emson P, Foord SM, Marshall FH (1998) Heterodimerization is required for the formation of a functional GABA(B) receptor. Nature 396:679–682
White JH, Wise A, Marshall FH (2002) Heterodimerization of gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor subunits as revealed by the yeast two-hybrid system. Methods 27:301–310
Jones KA, Borowsky B, Tamm JA, Craig DA, Durkin MM, Dai M, Yao WJ, Johnson M, Gunwaldsen C, Huang LY, Tang C, Shen Q, Salon JA, Morse K, Laz T, Smith KE, Nagarathnam D, Noble SA, Branchek TA, Gerald C (1998) GABA(B) receptors function as a heteromeric assembly of the subunits GABA(B)R1 and GABA(B)R2. Nature 396:674–679
Kaupmann K, Malitschek B, Schuler V, Heid J, Froestl W, Beck P, Mosbacher J, Bischoff S, Kulik A, Shigemoto R, Karschin A, Bettler B (1998) GABA(B)-receptor subtypes assemble into functional heteromeric complexes. Nature 396:683–687
Gassmann M, Bettler B (2012) Regulation of neuronal GABA(B) receptor functions by subunit composition. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:380–394
Ong J, Kerr DI (2000) Recent advances in GABAB receptors: from pharmacology to molecular biology. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21:111–123
Isomoto S, Kaibara M, Sakurai-Yamashita Y, Nagayama Y, Uezono Y, Yano K, Taniyama K (1998) Cloning and tissue distribution of novel splice variants of the rat GABAB receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 253:10–15
Schwarz DA, Barry G, Eliasof SD, Petroski RE, Conlon PJ, Maki RA (2000) Characterization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor GABAB(1e), a GABAB(1) splice variant encoding a truncated receptor. J Biol Chem 275:32174–32181
Marshall FH, Jones KA, Kaupmann K, Bettler B (1999) GABAB receptors—the first 7TM heterodimers. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:396–399
Tabata T, Kano M (2010) GABAB receptor-mediated modulation of metabotropic glutamate signaling and synaptic plasticity in central neurons. Adv Pharmacol 58:149–173
Yang XL (2004) Characterization of receptors for glutamate and GABA in retinal neurons. Prog Neurobiol 73:127–150
Mizuta K, Osawa Y, Mizuta F, Xu D, Emala CW (2008) Functional expression of GABAB receptors in airway epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 39:296–304
Zhou Z, Sun H, Li X, Li Y, Zhao S, Zhang D, Yao Z, Li J (2010) A local GABAergic system is functionally expressed in human fallopian tube. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398:237–241
Osawa Y, Xu D, Sternberg D, Sonett JR, D’Armiento J, Panettieri RA, Emala CW (2006) Functional expression of the GABAB receptor in human airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291:L923–L931
Parramon M, Gonzalez MP, Herrero MT, Oset-Gasque MJ (1995) GABAB receptors increase intracellular calcium concentrations in chromaffin cells through two different pathways: their role in catecholamine secretion. J Neurosci Res 41:65–72
Guatteo E, Bengtson CP, Bernardi G, Mercuri NB (2004) Voltage-gated calcium channels mediate intracellular calcium increase in weaver dopaminergic neurons during stimulation of D2 and GABAB receptors. J Neurophysiol 92:3368–3374
New DC, An H, Ip NY, Wong YH (2006) GABAB heterodimeric receptors promote Ca2+ influx via store-operated channels in rat cortical neurons and transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. Neuroscience 137:1347–1358
Harvey RD (2012) Muscarinic receptor agonists and antagonists: effects on cardiovascular function. Handb Exp Pharmacol 208:299–316
Cucina A, Fuso A, Coluccia P, Cavallaro A (2008) Nicotine inhibits apoptosis and stimulates proliferation in aortic smooth muscle cells through a functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Surg Res 150:227–235
Li S, Zhao T, Xin H, Ye LH, Zhang X, Tanaka H, Nakamura A, Kohama K (2004) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit mediates migration of vascular smooth muscle cells toward nicotine. J Pharmacol Sci 94:334–338
Gu Z, Fonseca V, Hai CM (2013) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor mediates nicotine-induced actin cytoskeletal remodeling and extracellular matrix degradation by vascular smooth muscle cells. Vasc Pharmacol 58:87–97
Garcia-Cazarin ML, Smith JL, Olszewski KA, McCune DF, Simmerman LA, Hadley RW, Kraner SD, Piascik MT (2008) The alpha1D-adrenergic receptor is expressed intracellularly and coupled to increases in intracellular calcium and reactive oxygen species in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J Mol Signal 3:6
Chotani MA, Mitra S, Su BY, Flavahan S, Eid AH, Clark KR, Montague CR, Paris H, Handy DE, Flavahan NA (2004) Regulation of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H59–H67
Johnson R, Webb JG, Newman WH, Wang Z (2006) Regulation of human vascular smooth muscle cell migration by beta-adrenergic receptors. Am Surg 72:51–54
Feletou M, Dellazuana O, Duhault J (1994) Serotoninergic receptor subtype in coronary artery smooth muscle from young and atherosclerotic rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:124–132
Watanabe T, Pakala R, Koba S, Katagiri T, Benedict CR (2001) Lysophosphatidylcholine and reactive oxygen species mediate the synergistic effect of mildly oxidized LDL with serotonin on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation 103:1440–1445
Vanhoutte PM (1991) Serotonin, hypertension and vascular disease. Neth J Med 38:35–42
Igarashi A, Zadzilka N, Shirahata M (2009) Benzodiazepines and GABA-GABAA receptor system in the cat carotid body. Adv Exp Med Biol 648:169–175
Mizuta K, Mizuta F, Xu D, Masaki E, Panettieri RA Jr, Emala CW (2011) Gi-coupled gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptors cross-regulate phospholipase C and calcium in airway smooth muscle. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45:1232–1238
Chen X, Liu H, Pan Z, Miao Q, Zhang Y (2012) The inhibitory effects of m-nisoldipine on the 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells via Ca2+ antagonism and antioxidant mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 686:32–40
Scott JA, Xie L, Li H, Li W, He JB, Sanders PN, Carter AB, Backs J, Anderson ME, Grumbach IM (2012) The multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II regulates vascular smooth muscle migration through matrix metalloproteinase 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H1953–H1964
Pande J, Dimmers G, Akolkar G, Skelley L, Samson SE, Grover AK (2012) Store operated Ca2+ entry dependent contraction of coronary artery smooth muscle: inhibition by peroxide pretreatment. Cell Calcium 51:149–154
Linde CI, Karashima E, Raina H, Zulian A, Wier WG, Hamlyn JM, Ferrari P, Blaustein MP, Golovina VA (2012) Increased arterial smooth muscle Ca2+ signaling, vasoconstriction, and myogenic reactivity in Milan hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H611–H620
Sharma RV, Bhalla RC (1988) Calcium and abnormal reactivity of vascular smooth muscle in hypertension. Cell Calcium 9:267–274
Aritomi S, Konda T, Yoshimura M (2012) L/N-type calcium channel blocker suppresses reflex aldosterone production induced by antihypertensive action. Heart Vessels 27:419–423
Wiecha J, Schlager B, Voisard R, Hannekum A, Mattfeldt T, Hombach V (1997) Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in human smooth muscle cells of coronary atherosclerotic plaques and coronary media segments. Basic Res Cardiol 92:233–239
Li Z, Zhang Q, Zhao S, Wei M, Shenghui Z, Cong H, Ouda H, Odajima K, Takemura H (1997) Responsiveness of cytosolic free calcium concentration in cultured rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: confocal microscopic measurement. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 97:47–52
Miyagawa K, Vidgoff J, Hermsmeyer K (1997) Ca2+ release mechanism of primate drug-induced coronary vasospasm. Am J Physiol 272:H2645–H2654
Xi Q, Umstot E, Zhao G, Narayanan D, Leffler CW, Jaggar JH (2010) Glutamate regulates Ca2+ signals in smooth muscle cells of newborn piglet brain slice arterioles through astrocyte- and heme oxygenase-dependent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298:H562–H569
Padgett CL, Slesinger PA (2010) GABAB receptor coupling to G-proteins and ion channels. Adv Pharmacol 58:123–147
Wang XP, Chen YG, Qin WD, Zhang W, Wei SJ, Wang J, Liu FQ, Gong L, An FS, Zhang Y, Chen ZY, Zhang MX (2011) Arginase I attenuates inflammatory cytokine secretion induced by lipopolysaccharide in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:1853–1860
Cheng ZY, Chebib M, Schmid KL (2012) Identification of GABA receptors in chick cornea. Mol Vis 18:1107–1114
Ryan JS, Baldridge WH, Kelly ME (1999) Purinergic regulation of cation conductances and intracellular Ca2+ in cultured rat retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Physiol 520(Pt 3):745–759
Uehara Y, Azuma Y, Minai K, Yoshida H, Yoshimura M, Shimizu M (2012) Endothelin-1 prolongs intracellular calcium transient decay in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Heart Vessels 27:98–105
Xiao H, Wang M, Du Y, Yuan J, Zhao G, Tu D, Liao YH (2012) Agonist-like autoantibodies against calcium channel in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart Vessels 27:486–492
Kobayashi Y, Fukuda T, Tanaka M, Matsui T (2012) The anti-atherosclerotic di-peptide, Trp-His, inhibits the phosphorylation of voltage-dependent L-type Ca(2+) channels in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Open Bio 2:83–88
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81271038), grant from the Department of Science and Technology of Shandong Province of China (No. ZR2012HM022) to ZYC, grant from National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 80200212) and grant from the Department of Science and Technology of Shandong Province of China (No. ZR2012HQ029) to XPW.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
X.-P. Wang, Z.-Y. Cheng made the same contribution to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XP., Cheng, ZY. & Schmid, K.L. GABAB receptors are expressed in human aortic smooth muscle cells and regulate the intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Heart Vessels 30, 249–257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-014-0499-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-014-0499-2