Abstract
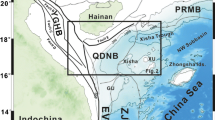
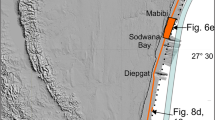
On the SE African shelf, a submerged shoreline at a depth of 60 m is examined and its attributes compared between two shelf sectors with different morphologies, yet similar energy regimes. The aim is to assess the controls of antecedent conditioning on shoreline development and later preservation from transgressive ravinement. Using a combination of multibeam bathymetry and single-channel seismic profiles, the stratigraphy and morphology of the shoreline is investigated. Low-gradient bedrock examples reveal several distinctive seismic facies, including onlapping chaotic reflector packages which are interpreted as calcarenite rubble fields. These palaeo-shorelines possess planform equilibrium morphologies, including parabolic dunes and blowout forms along with relict shore platforms. They are strongly associated with incised valleys of last glacial maximum age which underlie the shoreline locations; these provide wide, back-barrier accommodation space during transgression. In contrast, palaeo-shorelines on the steeper-gradient shelf have a simpler stratigraphic arrangement. They are not as well preserved, are generally covered by thick drapes of sediment, and lack the elaborate planform morphologies of their lower-shelf gradient equivalents. Isolated incised valleys and the steep bedrock gradient limit accommodation space. The comparison indicates that antecedent bedrock slope and available accommodation are amongst the dominant controls on overstepping, and thus potential preservation, of palaeo-shorelines on the shelf. Lower-gradient shelves not only promote rapid shoreline translation but, together with wide, sandy back-barrier accommodation, also foster larger barrier volumes. In suitable climates such as in the Mediterranean and other sub-tropical areas, the ensuing shoreline stability promotes rapid and effective cementation of the barrier. In comparison, steep bedrock profiles with limited back-barrier accommodation have much lower preservation potential. Transgressive ravinement is more focussed on steep slopes, effectively removing more material during the ravinement process. The more dynamic environment may also reduce the effectiveness of diagenesis. The potential of beachrock and aeolianite palaeo-shorelines as submerged sea-level indicators may be optimal in low-gradient settings in Mediterranean to subtropical environments.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams KD, Wesnousky SG (1998) Shoreline processes and the age of the Lake Lahontan highstand in the Jessup embayment, Nevada. GSA Bulletin 110:1318–1332
Alcántara-Carrió J, Albarracin S, Montoya Montes I, Flor-Blanco G, Bouzas ÁF, Salgado JR (2013) An indurated Pleistocene coastal barrier on the inner shelf of the Gulf of Valencia (western Mediterranean): evidence for a prolonged relative sea-level stillstand. Geo-Marine Letters 33:209–216. doi:10.1007/s00367-012-0316-9
Birch GF (1996) Unconsolidated sediments on the eastern margin of South Africa (Cape Padrone to Cape Vidal). Bull Geol Surv South Africa 118:55
Brenner OT, Moore LJ, Murray AB (2015) The complex influences of back-barrier deposition, substrate slope and underlying stratigraphy in barrier island response to sea level rise: insights from the Virginia Barrier Islands, mid-Atlantic bight, U.S.a. Geomorphology 246:334–350
Brooke B, Nichol S, Huang Z, Beaman RJ (2017) Palaeoshorelines on the Australian continental shelf: morphology, sea-level relationship and applications to environmental management and archaeology. Continental Shelf Research 134:26–38
Carter RWG (1988) Coastal environments: an introduction to the physical, ecological and cultural systems of coastlines. Elsevier, London
Cattaneo A, Steel RJ (2003) Transgressive deposits: a review of their variability. Earth Science Reviews 62:187–228
Cawthra HC, Neumann FH, Uken R, Smith AM, Guastella LA, Yates A (2012) Sedimentation on the narrow (8 km wide), oceanic current-influenced continental shelf off Durban, Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. Marine Geology 323-325:107–122
Cooper JAG (1991) Beachrock formation in low latitudes: implications for coastal evolutionary models. Marine Geology 98:145–154
Cooper JAG, Green AN (2016) Geomorphology and preservation potential of coastal and submerged aeolianite: examples from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Geomorphology 271:1–12
Cooper JAG, Green AN, Meireles RP, Klein AHF, Souza J, Toldo EE Jr (2016) Sandy barrier overstepping, burial and preservation during rapid sea level rise: an example from southern Brazil. Marine Geology 382:80–91
Davies JL (1964) A morphogenic approach to world shorelines. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie 8:127–142
Davis RA, Clifton HE (1987) Sea-level change and the preservation potential of wave dominated and tide-dominated coastal sequences. In: Nummedal D, Pilkey OH, Howard JD (eds) Sea-level fluctuation and coastal evolution. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Spec Publ 41:167–178
De Falco G, Antonioli F, Fontolan G, Presti VL, Simeone S, Tonielli R (2015) Early cementation and accommodation space dictate the evolution of an overstepping barrier system during the Holocene. Marine Geology 369:52–66
Flemming BW (1978) Underwater sand dunes along the southeast African continental margin—observations and implications. Marine Geology 26:177–198
Flemming BW (1981) Factors controlling shelf sediment dispersal along the southeast African continental margin. Marine Geology 42:259–277
Flemming BW, Hay ER (1988) Sediment distribution and dynamics on the Natal continental shelf. In: Schumann EH (ed) Coastal ocean studies off Natal, South Africa. Lecture notes on coastal and estuarine studies, vol 26. Springer, New York, pp 47–80
Gardner JV, Dartnell P, Mayer LA, Hughes Clark JE, Calder BR, Duffy G (2005) Shelf-edge deltas and drowned barrier–island complexes on the northwest Florida outer continental shelf. Marine Geology 64:133–166
Goodlad SW (1986) Tectonic and sedimentary history of the mid-Natal Valley (SW Indian Ocean). Joint Geological Survey/University of Cape Town Marine Geoscience Unit, Bull 15:415
Green AN (2009a) Palaeo-drainage, incised valley fills and transgressive systems tract sedimentation of the northern KwaZulu-Natal continental shelf, South Africa, SW Indian Ocean. Marine Geology 263:46–63
Green AN (2009b) Sediment dynamics on the narrow, canyon-incised and current swept shelf of the northern KwaZulu-Natal continental shelf, South Africa. Geo-Marine Letters 29:201–219. doi:10.1007/s00367-009-0135-9
Green AN (2011) The late Cretaceous to Holocene sequence stratigraphy of a sheared passive upper continental margin, northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Marine Geology 289:17–28
Green AN, Cooper JAG, Leuci R, Thackeray Z (2013b) Formation and preservation of an overstepped segmented lagoon complex on a high-energy continental shelf. Sedimentology 60:1755–1768
Green AN, Cooper JAG, Salzmann L (2014) Geomorphic and stratigraphic signals of postglacial meltwater pulses on continental shelves. Geology 42:151–154
Green AN, Dladla N, Garlick GL (2013a) Spatial and temporal variations in incised valley systems from the Durban continental shelf, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Marine Geology 335:148–161
Green AN, Garlick GL (2011) A sequence stratigraphic framework for a narrow, current-swept continental shelf: the Durban bight, central KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Journal of African Earth Sciences 60:303–314
Hayes MO (1979) Barrier island morphology as a function of tidal and wave regime. In: Leatherman SP (ed) Barrier islands. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–27
Jackson DWT, Cooper JAG, Green AN (2014) Preliminary classification of coastal dunes of KwaZulu-Natal. Journal of Coastal Research, SI 74:718–722
Jarret BD, Hine AC, Halley RB, Naar DF, Locker SD, Neumann AC, Twichell D, Hu C, Donahue BT, Jaap WC, Palandro D, Ciembronowicz K (2005) Strange bedfellows—a deep-water hermatypic coral reef superimposed on a drowned barrier island; southern pulley ridge, SW Florida platform margin. Marine Geology 214:295–307
Liu JP, Milliman JD (2004) Reconsidering melt-water pulses 1-A and 1-B: global impacts of rapid sea-level rise. Journal of Ocean University of China 3:183–190
Lobo FJ, García M, Luján M, Mendes I, Reguera MI, Van Rooij D (2017) Morphology of the last subaerial unconformity on a shelf: insights into transgressive ravinement and incised valley occurrence in the Gulf of Cádiz. Geo-Mar Lett. doi:10.1007/s00367-017-0511-9
Locker SD, Hine AC, Tedesco LP, Shinn EA (1996) Magnitude and timing of episodic sea-level rise during the last deglaciation. Geology 24:827–830
Lutjeharms JRE (2006) The ocean environment off south-eastern Africa: a review. South African Journal of Science 102:419–425
Martin AK, Flemming BW (1986) The Holocene shelf sediment wedge off the south and east coast of South Africa. Memoir. Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists 2:27–44
Martin AK, Flemming BW (1987) Aeolianites of the south African coastal zone and continental shelf as sea-level indicators. South African Journal of Science 83:597–598
Martin AK, Flemming BW (1988) Physiography, structure and geological evolution of the Natal continental shelf. In: Schumann EH (ed) Coastal ocean studies off Natal, South Africa. Lecture notes on coastal and estuarine studies, vol 26. Springer, New York, pp 11–46
Mellett CL, Hodgson DM, Lang A, Mauz B, Selby I, Plater AJ (2012) Preservation of a drowned gravel barrier complex: a landscape evolution study from the north-eastern English Channel. Marine Geology 315:115–131
Otvos EG (2000) Beach ridges – definitions and significance. Geomorphology 32:83–108
Pretorius L, Green AN, Cooper JAG (2016) Submerged shoreline preservation and ravinement during rapid sea level rise and subsequent slowstand. GSA Bulletin 128:1059–1069
Pretorius L, Green AN, Cooper JA (2017) Submerged beachrock preservation in the context of wave ravinement. Geo-Mar Lett. doi:10.1007/s00367-017-0503-9
Ramsay PJ (1994) Marine geology of the Sodwana Bay shelf, southeast Africa. Marine Geology 120:225–247
Ramsay PJ, Cooper JAG (2002) Late Quaternary sea-level change in South Africa. Quaternary Research 57:82–90
Salzmann L, Green AN (2012) Boulder emplacement on a tectonically stable, wave dominated coastline, mission rocks, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Marine Geology 323-325:95–106
Salzmann L, Green AN, Cooper JAG (2013) Submerged barrier shoreline sequences on a high energy, steep and narrow shelf. Marine Geology 346:366–374
Smith AM, Mather AA, Bundy SC, Cooper JA, Guastella LA, Ramsay PJ, Theron A (2010) Contrasting styles of swell-driven coastal erosion: examples from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Geological Magazine 147:940–953
Storms JE, Weltje GJ, Terra GJ, Cattaneo A, Trincardi F (2008) Coastal dynamics under conditions of rapid sea-level rise: late Pleistocene to early Holocene evolution of barrier–lagoon systems on the northern Adriatic shelf (Italy). Quaternary Science Reviews 27:1107–1123
Vital H, Stattegger K, Amaro VE, Schwarzer K, Frazão EP, Tabosa WF, Silveira IM (2008) A modern high-energy siliciclastic-carbonate platform: continental shelf adjacent to northern Rio Grande do Norte state, northeastern Brazil. In: Hampson G, Steel R, Burguess P, Dalrymple RW (eds) Recent advances in models of siliciclastic shallow-marine stratigraphy. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Spec Publ 90:175–188
Vousdoukas MI, Velegrakis AF, Plomaritis TA (2007) Beachrock occurrence, characteristics, formation mechanisms and impacts. Earth Science Reviews 85:23–46
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge funding from the University of KwaZulu-Natal and the National Research Foundation (NRF) via the African Coelacanth Ecosystem Programme (ACEP; grant number 97968). We further acknowledge the National Ports Authority who gave their kind permission to publish the datasets collected from the south of Durban. In this regard, we thank SUBTECH’s surveying department. Errol Wiles, Enviromap and KZN Boat Hire assisted us in the collection of the WASSP and seismic datasets from Durban, and are acknowledged accordingly. Ryan Palmer of ACEP is thanked for the ROV imagery from the Umdloti shoreline. Prof. B.W. Flemming, Dr. M.T. Delafontaine and two anonymous reviewers are thanked for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with third parties.
Additional information
Responsible editor: B.W. Flemming
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Green, A.N., Cooper, J.A.G. & Salzmann, L. The role of shelf morphology and antecedent setting in the preservation of palaeo-shoreline (beachrock and aeolianite) sequences: the SE African shelf. Geo-Mar Lett 38, 5–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-017-0512-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-017-0512-8