Abstract
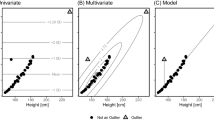
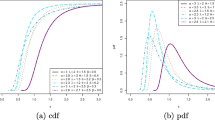
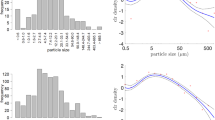
A set of k points that optimally summarize a distribution is called a set of k-principal points, which is a generalization of the mean from one point to multiple points and is useful especially for multivariate distributions. This paper discusses the estimation of principal points of multivariate distributions. First, an optimal estimator of principal points is derived for multivariate distributions of location-scale families. In particular, an optimal principal points estimator of a multivariate normal distribution is shown to be obtained by using principal points of a scaled multivariate t-distribution. We also study the case of multivariate location-scale-rotation families. Numerical examples are presented to compare the optimal estimators with maximum likelihood estimators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antle CE, Bain LJ (1969) A property of maximum likelihood estimators of location and scale parameters. SIAM Rev 11(2):251–253
Bali JL, Boente G (2009) Principal points and elliptical distributions from the multivariate setting to the functional case. Stat Probab Lett 79(17):1858–1865
Eaton ML (1983) Multivariate statistics: a vector space approach. Wiley, New York
Flury B (1990) Principal points. Biometrika 77(1):33–41
Flury B (1993) Estimation of principal points. J R Stat Soc 42(1):139–151
Gersho A, Gray RM (1992) Vector quantization and signal compression. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Graf L, Luschgy H (2000) Foundations of quantization for probability distributions. Springer, Berlin
Gu XN, Mathew T (2001) Some characterizations of symmetric two-principal points. J Stat Plann Inference 98(1–2):29–37
Hartigan JA, Wong MA (1979) A \({K}\)-means clustering algorithm. J R Stat Soc 28(1):100–108
Kurata H (2008) On principal points for location mixtures of spherically symmetric distributions. J Stat Plann Inference 138(11):3405–3418
Kurata H, Qiu D (2011) Linear subspace spanned by principal points of a mixture of spherically symmetric distributions. Commun Stat 40(15):2737–2750
Li L, Flury B (1995) Uniqueness of principal points for univariate distributions. Stat Probab Lett 25(4):323–327
Matsuura S, Kurata H (2010) A principal subspace theorem for 2-principal points of general location mixtures of spherically symmetric distributions. Stat Prob Lett 80(23–24):1863–1869
Matsuura S, Kurata H (2011) Principal points of a multivariate mixture distribution. J Multivar Anal 102(2):213–224
Matsuura S, Kurata H (2014) Principal points for an allometric extension model. Stat Pap 55(3):853–870
Matsuura S, Kurata H, Tarpey T (2015) Optimal estimators of principal points for minimizing expected mean squared distance. J Stat Plann Inference 167:102–122
Mease D, Nair VN (2006) Unique optimal partitions of distributions and connections to hazard rates and stochastic ordering. Stat Sin 16(4):1299–1312
Petkova E, Tarpey T (2009) Partitioning of functional data for understanding heterogeneity in psychiatric conditions. Stat Interface 2(4):413–424
Ruwet C, Haesbroeck G (2013) Classification performance resulting from a 2-means. J Stat Plann Inference 143(2):408–418
Shimizu N, Mizuta M (2007) Functional clustering and functional principal points. In: Apolloni B, Howlett RJ, Jain LC (eds) Knowledge-based intelligent information and engineering systems. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4693, pp 501–508
Stampfer E, Stadlober E (2002) Methods for estimating principal points. Commun Stat 31(2):261–277
Tarpey T (1995) Principal points and self-consistent points of symmetric multivariate distributions. J Multivar Anal 53(1):39–51
Tarpey T (1997) Estimating principal points of univariate distributions. J Appl Stat 24(5):499–512
Tarpey T (1998) Self-consistent patterns for symmetric multivariate distributions. J Classif 15(1):57–79
Tarpey T (2007) A parametric \(k\)-means algorithm. Comput Stat 22(1):71–89
Tarpey T, Kinateder K (2003) Clustering functional data. J Classif 20(1):93–114
Tarpey T, Li L, Flury B (1995) Principal points and self-consistent points of elliptical distributions. Ann Stat 23(1):103–112
Tarpey T, Loperfido N (2015) Self-consistency and a generalized principal subspace theorem. J Multivar Anal 133:27–37
Tarpey T, Petkova E (2010) Principal point classification: applications to differentiating drug and placebo responses in longitudinal studies. J Stat Plan Inference 140(2):539–550
Tarpey T, Petkova E, Lu Y, Govindarajulu U (2010) Optimal partitioning for linear mixed effects models: applications to identifying placebo responders. J Am Stat Assoc 105(491):968–977
Tarpey T, Petkova E, Ogden RT (2003) Profiling placebo responders by self-consistent partitions of functional data. J Am Stat Assoc 98(464):850–858
Trushkin A (1982) Sufficient conditions for uniqueness of a locally optimal quantizer for a class of convex error weighting functions. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 28(2):187–198
Yamamoto W, Shinozaki N (2000a) On uniqueness of two principal points for univariate location mixtures. Stat Probab Lett 46(1):33–42
Yamamoto W, Shinozaki N (2000b) Two principal points for multivariate location mixtures of spherically symmetric distributions. J Jpn Stat Soc 30(1):53–63
Yamashita H, Goto M (2017) The analysis based on principal matrix decomposition for 3-mode binary data. Asian J Manag Sci Appl 3(1):24–37
Yamashita H, Matsuura S, Suzuki H (2017) Estimation of principal points for a multivariate binary distribution using a log-linear model. Commun Stat 46(2):1136–1147
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Editors for considering our paper and to anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful and helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuura, S., Tarpey, T. Optimal principal points estimators of multivariate distributions of location-scale and location-scale-rotation families. Stat Papers 61, 1629–1643 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-018-0995-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-018-0995-z