Abstract
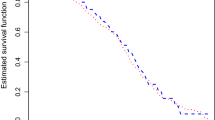
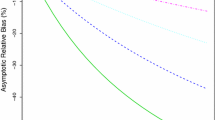
We use the general additive–multiplicative hazard model to analyze the length biased data with right censorship and use the estimating equation method that incorporates the information about length-biased sampling scheme to do the inference. In addition, some graphical and numerical methods are developed for assessing the adequacy of the general additive–multiplicative hazard model. The procedures are derived from cumulative sums of martingale-based residuals over follow-up time and covariate values. The simulations are conducted to insure the good performance of this method. An application to the Oscar data is also illustrated.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addona V, Wolfson DB (2006) A formal test for the stationarity of the incidence rate using data from a prevalent cohort study with follow-up. Lifetime Data Anal 12:267–284
Andersen PK (1993) Statistical models based on counting processes. Springer, New York
Andersen PK, Gill RD (1982) Cox’s regression model for counting processes: a large sample study. Ann Stat 10:1100–1120
Asgharian M, M’Lan CM, Wolfson DB (2002) Length-biased sampling with right censoring: an unconditional approach. J Am Stat Assoc 97:201–209
Asgharian M, Wolfson DB, Zhang X (2006) Checking stationarity of the incidence rate using prevalent cohort survival data. Statistics Med 25(10):1751–1767
Chen XP, Shi JH, Zhou Y (2015) Monotone rank estimation of transformation models with length-biased and right-censored data. Sci China Math 58(10):2055–2068
Cheng YJ, Huang CY (2014) Combined estimating equation approaches for semiparametric transformation models with length-biased survival data. Biometrics 70(3):608–618
Dai JJ, Sun LQ, Yang ZH (2009) A general additive-multiplicative rates model for recurrent event data. Sci China Ser A 52(10):2257–2265
Foutz RV (1977) On the unique consistent solution to the likelihood equations. J Am Stat Assoc 72(357):147–148
He SY, Yang GL (2003) Estimation of regression parameters with left truncated data. J Stat Plan Inference 117(1):99–122
Huang CY, Qin J (2011) Nonparametric estimation for length-biased and right-censored data. Biometrika 98(1):177–186
Huang CY, Qin J (2012) Composite partial likelihood estimation under length-biased sampling, with application to a prevalent cohort study of dementia. J Am Stat Assoc 107(499):946–857
Jacobo DU (2004) Nonparametric estimation under length-biased sampling and type I censoring: a moment based approach. Ann Inst Stat Math 56:667–681
Liang HY, Baek JI (2016) Asymptotic normality of conditional density estimation with left-truncated and dependent data. Stat Pap 57(1):1–20
Lin DY (2000) On fitting Cox’s proportional hazards models to survey data. Biometrika 87(1):37–47
Lin DY, Ying ZL (1994) Semiparametric analysis of the additive risk model. Biometrika 81(1):61–71
Lin DY, Ying ZL (1995) Semiparametric analysis of general additive-multiplicative hazard models for counting processes. Ann Stat 23(1):1712–1734
Lin CJ, Zhou Y (2014) Analyzing right-censored and length-biased data with varying-coefficient transformation model. J Multivar Anal 130:45–63
Lin DY, Wei LJ, Ying Z (1993) Checking the Cox model with cumulative sums of martingale-based residuals. Biometrika 80:557–572
Lin CJ, Zhang L, Zhou Y (2015) Conditional quantile residual lifetime models for right censored data. Lifetime Data Anal 21(1):75–96
Liu YY, Wu YS, Cai JW, Zhou HB (2010) Additive-multiplicative rates model for recurrent events. Lifetime Data Anal 16(3):353–373
Luo XD, Wei YT (2009) Nonparametric estimation for right-censored length-biased data: a pseudo-partial likelihood approach. Biometrika 96(4):873–886
Ma HJ, Fan CY, Zhou Y (2015a) Estimating equation methods for quantile regression with length-biased and right censored data. Sci China Math 45:1981–2000 (in Chinese)
Ma HJ, Zhang FP, Zhou Y (2015b) Composite estimating equation approach for additive risk model with length-biased and right-censored data. Stat Probab Lett 96:45–53
Mohamed L, Elias OS, Abdelkader T (2017) Nonparametric robust regression estimation for censored data. Stat Pap 58(2):505–525
Qin J, Shen Y (2010) Statistical methods for analyzing right-censored length-biased data under cox model. Biometrics 66(2):382–392
Redelmeier DA, Singh SM (2001) Survival in academy award-winning actors and actresses. Ann Intern Med 134:955–962
Shen Y, Ning J, Qin J (2009) Analyzing length-biased data with semiparametric transformation and accelerated failure time models. J Am Stat Assoc 104(487):1192–1202
Shen PS, Liu Y (2017) Pseudo maximum likelihood estimation for the Cox model with doubly truncated data. Stat Pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-016-0870-8
Sylvestre MP, Huszti E, Hanley JA (2006) Do Oscar winners live longer than less successful peers? A reanalysis of the evidence. Ann Intern Med 145(5):361–363
Tsai WY (2009) Pseudo-partial likelihood for proportional hazards models with biased-sampling data. Biometrika 96(3):601–615
Tsai WY, Nicholas PJ, Wang MC (1989) A note on the product-limit estimator under right censoring and left truncation. Biometrika 74(4):883–886
Van der Vaart A (2000) Asymptotic statistics. Cambridge Series in Statistical and Probabilistic Mathematics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Van der Vaart A, Wellner J (1996) Weak convergence and empirical processes. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, New York
Xu HX, Chen ZL, Wang JF, Fan GL (2017) Quantile regression and variable selection for partially linear model with randomly truncated data. Stat Pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-016-0867-3
Wang MC (1991) Nonparametric estimation from cross-sectional survival data. J Am Stat Assoc 86:130–43
Wang YX, Liu P, Zhou Y (2015) Quantile residual lifetime for left-truncated and right-censored data. Sci China Math 58(6):1217–1234
Woodroofe W (1985) Estimating a distribution function with truncated data. Ann Stat 13(1):163–177
Zhou Y (1996) A note on the TJW product-limit estimator for truncated and censored data. Stat Probab Lett 26(4):381–387
Zhou Y, Yip PSF (1999) A strong representation of the product-limit estimator for left truncated and right censored data. J Multivar Anal 69(2):261–280
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Editor, an Associate Editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions, which have helped greatly improve our paper. Zhou’s work is supported by the State Key Program in the Major Research Plan of National Natural Science Foundation of China (91546202), the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (71331006). Li’s research is partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants (NO. 11601307).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Zhou, Y. The estimation for the general additive–multiplicative hazard model using the length-biased survival data. Stat Papers 62, 53–74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-018-01079-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-018-01079-3