Abstract
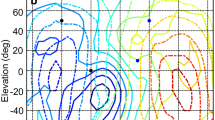
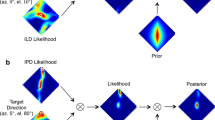
Two experiments investigated the ability and means by which two male Florida manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris) may determine the direction of a sound source. An eight-choice discrimination paradigm was used to determine the subjects’ sound localization abilities of five signal conditions covering a range of frequencies, durations, and levels. Subjects performed above the 12.5 % chance level for all broadband frequencies and were able to localize sounds over a large level range. Errors were typically located to either side of the signal source location when presented in the front 180° but were more dispersed when presented from locations behind the subject. Front-to-back confusions were few and accuracy was greater when signals originated from the front 180°. Head-related transfer functions were measured to determine if frequencies were filtered by the manatee body to create frequency-specific interaural level differences (ILDs). ILDs were found for all frequencies as a function of source location, although they were largest with frequencies above 18 kHz and when signals originated to either side of the subjects. Larger ILDs were found when the signals originated behind the subjects. A shadowing-effect produced by the body may explain the relatively low occurrence of front-back confusions in the localization study.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HRTF:
-
Head-related transfer functions
- ILD:
-
Interaural level difference
- MAR:
-
Minimum angle of resolution
References
Algazi VR, Avendano C, Duda RO (2001) Elevation localization and head-related transfer function analysis at low frequencies. J Acoust Soc Am 109:1110–1122
Algazi VR, Duda RO, Duraiswami R, Gumerov NA, Tang Z (2002) Approximating the head-related transfer function using simple geometric models of the head and torso. J Acoust Soc Am 112:2053–2064
Bauer GB, Colbert DE, Gaspard JC, Littlefield B, Fellner W (2003) Underwater visual acuity of Florida manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris). Int J Comp Psychol 16:130–142
Bauer GB, Gaspard JC III, Colbert DE, Leach JB, Stamper SA, Mann D, Reep R (2012) Tactile discrimination of textures by Florida manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris). Mar Mamm Sci. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2012.00565
Blauert J (1997) Spatial hearing: the psychophysics of human sound localization. Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, Massachusetts
Brown CH (1994) Sound localization. In: Fay RR, Popper AN (eds) Comparative hearing: mammals. Springer, New York, pp 57–97
Brown CH, May BJ (1990) Sound localization and binaural processes. In: Berkley MA, Stebbins WC (eds) Comparative perception, vol I. Wiley, New York, pp 247–284
Buckstaff KC (2004) Effects of watercraft noise on the acoustic behavior of bottlenose dolphins, Tursiops truncatus, in Sarasota Bay Florida. Mar Mamm Sci 20:709–725
Bullock TH, Domning DP, Best RC (1980) Evoked potentials demonstrate hearing in a manatee (Trichechus inunguis). J Mammal 61:130–133
Bullock TH, O’Shea TJ, McClune MC (1982) Auditory evoked potentials in the West Indian manatee (Sirenia: Trichechus manatus). J Comp Physiol 148:547–554
Casseday JH, Neff WD (1973) Localization of pure tones. J Acoust Soc Am 54:365–372
Chapla M, Nowacek D, Rommel S, Sadler V (2007) CT scans and 3D reconstructions of Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris) heads and ear bones. Hearing Res 228:123–135
Colbert DE, Fellner W, Bauer GB, Manire C, Rhinehart H (2001) Husbandry and research training of two Florida manatees, Trichechus manatus latirostris. Aquat Mamm 27:16–23
Colbert DE, Gaspard JC III, Reep R, Mann D, Bauer GB (2009) Four-choice sound localization abilities of two Florida manatees, Trichechus manatus latirostris. J Exp Biol 212(13):2105–2112
Gaspard JC, Bauer GB, Reep RL, Dziuk K, Mann DA (2012) Audiogram and auditory critical ratios of two Florida manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris). J Exp Biol 215:1442–1447
Gerstein E (1999) Psychoacoustic evaluations of the West Indian manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris). Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL
Gerstein E (2002) Manatees, bioacoustics and boats. Am Sci 90(2):154–163
Gerstein ER, Gerstein L, Forsythe SE, Blue JE (1999) The underwater audiogram of the West Indian manatee (Trichechus manatus). J Acoust Soc Am 105:3575–3583
Heffner RS (1997) Comparative study of sound localization and its anatomical correlates in mammals. Acta Otolaryngolog 532:46–53
Ketten DR, Odell DK, Domning DP (1992) Structure, function, and adaptation of the manatee ear. In: Thomas JA, Kastelein RA, Supin AY (eds) Marine mammal sensory systems. Plenum Press, New York, pp 77–79
Kirkpatrick B, Colbert DE, Dalpra D, Newton EAC, Gaspard J, Littlefield B, Manire CA (2002) Florida red tides, manatee brevetoxicosis, and lung models. In: Steidinger KA, Landsberg JH, Tomas CR, Vargo GA (eds) Sixth International conference on harmful algae. Florida fish and wildlife conservation commission and intergovernmental oceanographic commission of UNESCO
Klishen VO, Diaz RP, Popov VV, Supin AY (1990) Some characteristics of hearing of the Brazilian manatee, Trichechus inunguis. Aquat Mamm 16:139–144
Kuhn GF (1987) Physical acoustics and measurements pertaining to directional hearing. In: Yost WA, Gourevitch G (eds) Directional hearing. Springer, New York, pp 3–25
Kuhn GF, Guernsey RM (1983) Sound pressure distribution about the human head and torso. J Acoust Soc Am 73:95–105
Manire CA, Walsh CJ, Rhinehart HL, Colbert DE, Noyes DR, Luer CA (2003) Alterations in blood and urine parameters in two Florida manatees, Trichechus manatus latirostris, from simulated conditions of release following rehabilitation. Zoo Biol 22:103–120
Mann D, Colbert DE, Gaspard JC III, Casper B, Cook MLH, Reep RL, Bauer GB (2005a) Temporal resolution of the Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris) auditory system. J Comp Physiol A 191:903–908
Mann D, Colbert DE, Gaspard JC III, Casper B, Cook MLH, Reep RL, Bauer GB (2005b) Temporal resolution of the Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris) auditory system. J Comp Physiol A 191:903–908
Marler P (1955) Some characteristics of animals calls. Nature 176:6–8
Masterson B, Heffner H, Ravizza R (1969) The evolution of human hearing. J Acoust Soc Am 45:966–985
Medwin H, Clay CS (1998) Fundamentals of acoustical oceanography. Academic Press, New York
Middlebrooks JC, Green DM (1991) Sound localization by human listeners. Ann Rev Psychol 42:135–159
Middlebrooks JC, Makous JC, Green M (1989) Directional sensitivity of sound-pressure intensity levels in the human ear canal. J Acoust Soc Am 86:89–108
Miksis-Olds JL (2006) Manatee response to environmental noise. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. University of Rhode Island, Narragansett, Rhode Island
Nowacek DP, Casper BM, Wells RW, Nowacek SM, Mann DA (2003) Intraspecific and geographic variation of West Indian manatee (Trichechus manatus spp) vocalizations. J Acoust Soc Am 114:66–69
Nowacek SM, Wells RS, Owen ECG, Speakman TR, Flam RO, Nowacek DP (2004) Florida manatees, Trichechus manatus latirostris, respond to approaching vessels. Biol Conserv 119:517–523
Popov VV, Supin AY (1990) Electrophysiological studies on hearing in some cetaceans and a manatee. In: Thomas JA, Kastelein RA (eds) Sensory abilities of cetaceans: laboratory and field evidence. Plenum Press, New York
Richardson W, Greene C, Malme C, Thompson D (1995) Marine mammals and noise. Academic Press, San Diego
Samuelson D, McGee J, Ben-Shlomo G, Bauer G, Murphy C, Howland H, Lewis P (2012) An overview of the visual system of the Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris). Florida Marine Mammal Health Conference IV, Mote Marine Laboratory, 24–27 April 2012
Searle CL, Braida LD, Cuddy DR, Davis MF (1975) Binaural pinna disparity: another auditory localization cue. J Acoust Soc Am 57:448–455
Stevens SS, Newman EB (1936) The localization of actual sources of sound. Am J Psychol 48:297–306
Urick RJ (1996) The principles of underwater sound, 3rd edn. Peninsula Publications, Newport Beach
US Fish and Wildlife Service (2001) Florida manatee recovery plan (Trichechus manatus latirostris), Third Revision. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Atlanta
Wightman FL, Kistler DJ (1997) Factors effecting the relative salience of sound localization cues. In: Gilkey RH, Anderson TR (eds) Binaural and spatial hearing in real and virtual environments. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ, pp 1–23
Yost WA (2000) Sound localization and binaural hearing. Fundamentals of hearing: An introduction. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 179–192
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the US Fish and Wildlife Service (Permit MA837923-6); the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission; Mote Marine Laboratory staff Jay Sprinkel, volunteer trainer Jann Warfield; Ronnie and John Enander; the Thurell family; and the Manatee Care Team Interns and New College Student trainers. Special gratitude is also given to Toru Shimizu, PhD, Stephen Stark, PhD and Theresa Chisolm, PhD. The experiments comply with the ‘Principles of animal care’, publication No. 86-23, revised 1985, of the National Institute of Health, and also with the current laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colbert-Luke, D.E., Gaspard, J.C., Reep, R.L. et al. Eight-choice sound localization by manatees: performance abilities and head related transfer functions. J Comp Physiol A 201, 249–259 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-014-0973-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-014-0973-4